Electricity and circuits
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What does electricity pass through?
Conductors.
What doesn’t electricity pass through?
Insulators.
What are some examples of insulators?
Plastic and air.
What do ammeters measure?
Current.
What causes an electric current?
Electrons.
What is a battery made of?
Cells connected together in series.
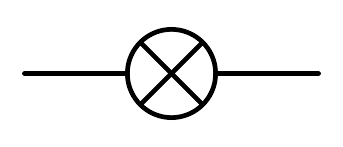
What is this circuit symbol and what does it do?
Lamp, lights up.
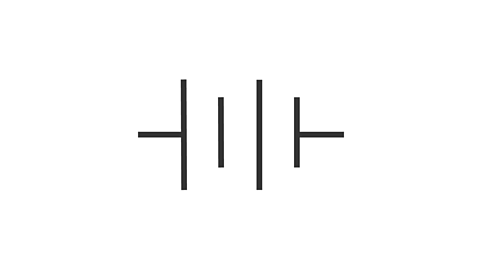
What is this circuit symbol and what does it do?
Battery, provides the energy for an electrical charge to flow.
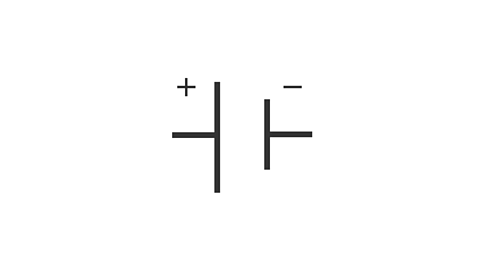
What is this circuit symbol and what does it do?
Cell, provides power to a circuit.
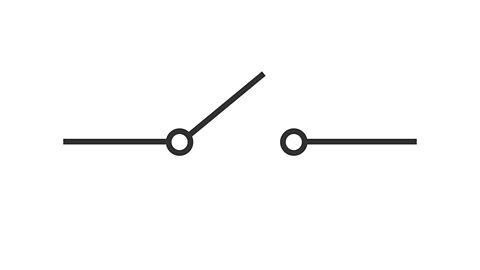
What is this circuit symbol and what does it do?
Switch, controls the flow of the electric current by opening and closing.
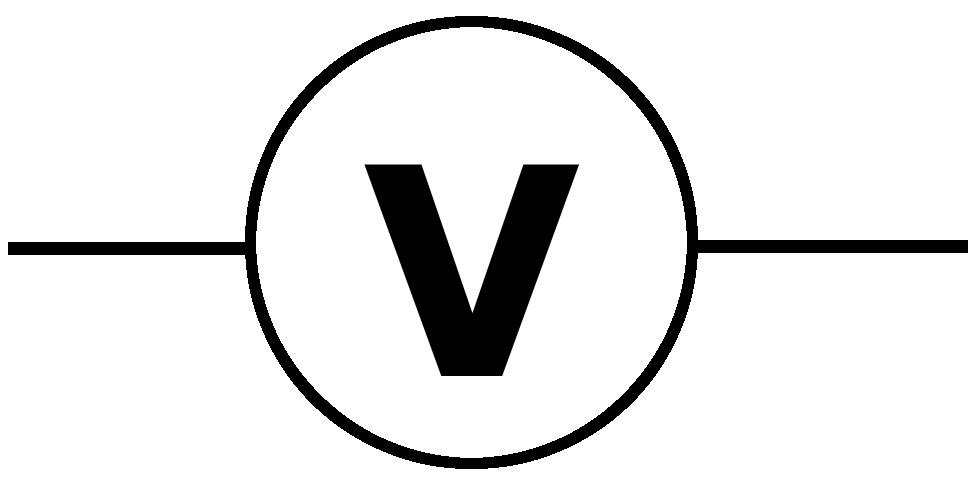
What is this circuit symbol and what does it do?
Voltmeter, measures voltage.
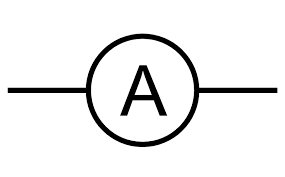
What is this circuit symbol and what does it do?
Ammeter, measures the electric current flowing through a circuit.

What circuit symbol is this?
Fixed resistor, limits the flow of electric charge.

What is this circuit symbol?
Motor.
What is a series circuit?
A circuit where the current can only take one route.
What is a parallel circuit?
A circuit where there are junctions, allowing the current to take different routes.
What is a current?
The flow of electrons around the circuit.
What is the unit of electric current?
Amperes (amps).
What reading will ammeters have in a series circuit?
They will all have the same reading as the current is the same all through the circuit.
What is another word for potential difference?
Voltage.
What is potential difference?
Potential difference is what’s needed to push current around a circuit. Electrons will flow when potential difference is applied across a component.
What two things are needed for a current to flow?
A closed circuit, and a source of potential difference (cell or battery).
How do voltmeters go into a circuit?
In parallel with the component they’re reading.
What forms an electric current?
Moving charged particles.
What is the unit of an electric current?
Coulombs.
How does charge behave through parts of a circuit?
It begins as energy in a cell, and is then transferred to the electrical charge itself. The charge has potential energy to transfer to the components it comes across and this energy is transferred from the charge to the components as it moves through it.
What is the relationship between resistance and current?
As the resistance increases, the current decreases.
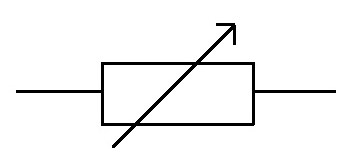
What is this circuit symbol?
Variable resistor.
What is electrical resistance?
The opposition to the flow of charge in a circuit.
What is electrical resistance measured in?
Ohms.
Where does an ammeter fit into a circuit?
Always in series with the component it’s reading.
What happens when two resistors are in series?
The total resistance increases.
What happens when two resistors are in parallel?
The total resistance decreases.
What is the total resistance of two resistors in series?
Both resistances added together.
What happens when the potential difference across a fixed resistor is doubled?
The current doubles.
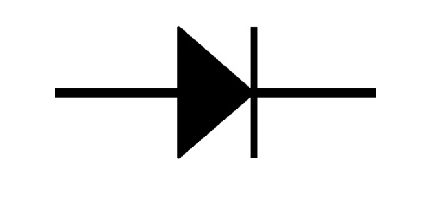
What is this circuit symbol and what does it do?
Diode, only allows current to flow in one direction.
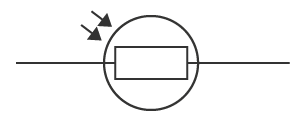
What is this circuit symbol and what does it do?
Light dependent resistor (LDR), a device that can detect light; the resistance is high in the dark but decreases as the surroundings get lighter.
What is this circuit symbol and what does it do?
Thermistor, detects temperature; has a high resistance at low temperatures but it decreases as the temperature rises.
How can the resistance in wires be reduced?
By thickening them.
What does dissipated mean?
Spread out into the surroundings.
How does resistance work?
The electrons move through the lattice of metal ions and collide with it, causing the ions to vibrate so it’s harder for the electrons to get through.
When is the heating effect of a current useful?
Electric radiators, hobs and ovens, and toasters.
When is the heating effect of a current not useful?
In computers.
How can resistance in circuits be decreased?
Using wires made from metals with low resistance.
Thickening wires.
Cooling metals so the lattice ions don’t vibrate as much.
What is the live wire and how many volts does it contain?
The brown wire in a plug that connects the appliance to the power station generators, containing 230V.
What are the three wires in a plug?
Live wire, neutral wire, Earth wire.
What is the neutral wire and how many volts does it contain?
The blue wire in a plug that acts as a return path to the power station, containing 0V.
What is the earth wire and how many volts does it contain?
The green and yellow wire in a plug that connects the metal parts to the ground for safety, containing 0V.
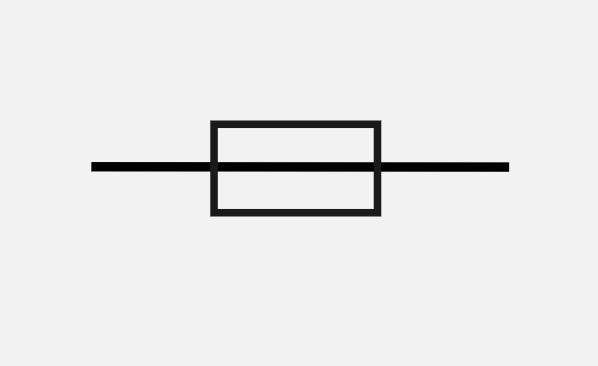
What is this circuit symbol and what does it do?
Fuse, a tube with a thin wire inside that will break if the current exceeds a certain value, breaking the circuit and stopping it.
How is mains electricity produced?
Using rotating generators, causing the direction of the current to keep changing. The voltage also changes, increasing to its peak before decreasing to 0 and repeating in the opposite direction.
What is the mains voltage in the UK?
230V.
What is the frequency of A/C voltage?
50Hz.
Where is chemical energy stored?
Food, fuel and batteries.
Where is elastic potential energy stored?
In stretched, squashed or twisted objects.
Where is nuclear energy stored?
Inside atoms.