chapter 2- medical terminology notes
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
1
New cards
dermatology
medical specialty that studies the anatomy and physiology of the integumentary system.
2
New cards
Integumentary System
covers most of the surface of the body. It consists of the skin, the nails, and the subcutaneous tissue. The functions of the integumentary system include protection, repair, sensation, synthesis of vitamin D, and thermoregulation.
3
New cards
Integumentary/Cutaneous
pertaining to the skin
4
New cards
epidermis
thin, outermost layer of the skin made up of epithelial tissues. It contains dead protective cells on its surface that are actively dividing on the base
5
New cards
dermis
thick, inner layer of the skin that lies below the epidermis made up of connective tissue. It contains sebaceous glands, sudoriferous glands and hair follicles
6
New cards
subcutaneous tissue
type of connective tissue that lies beneath the dermis composed of adipose tissue that insulates the body
7
New cards
dermatome
a specific area on the skin that sends sensory information to the spinal cord
8
New cards
Dermatitis
Any infection or inflammation of the skin.
9
New cards
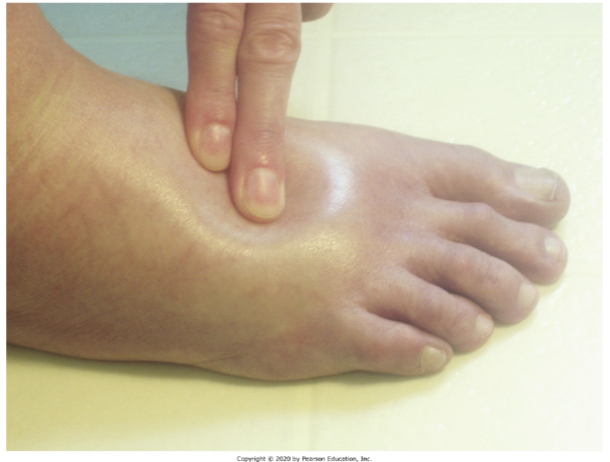
Edema
Swelling from excessive amounts of fluid that move from the blood into the dermis or subQ.
10
New cards
Hemorrhage
\n Injury to the blood vessels that releases blood into the skin.
11
New cards
Lesion
Any area of visible damage on the skin or a variation from normal skin.
12
New cards
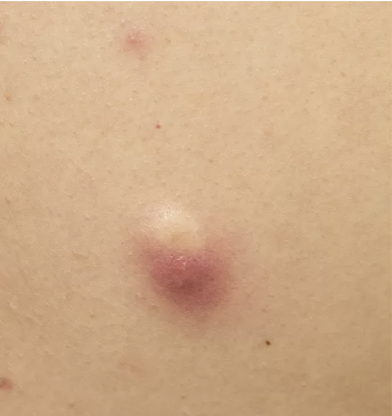
skin lesion: cyst
elevated circular mound; acne
13
New cards
skin lesion: Fissure
small, crack crevice; chapped lips
14
New cards
Skin Lesion: Macule
flat pigmented brown circle; freckle
15
New cards
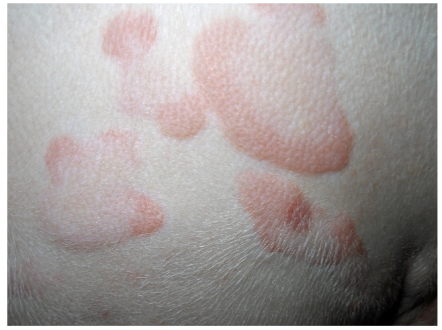
skin lesion: wheal
elevated red spots filled with fluid; insect bites
16
New cards
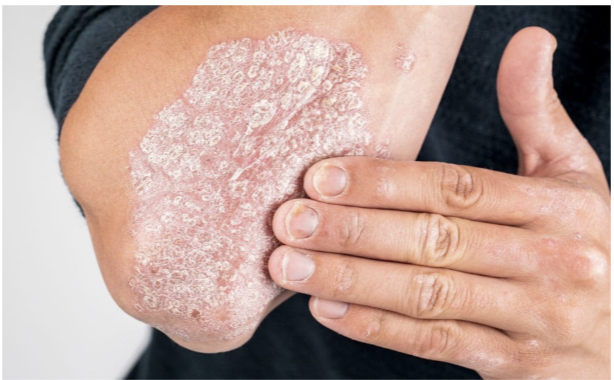
skin lesion: scale
flat think white flakes; dandruff or psoriasis
17
New cards
neoplasm
New growth on the skin, benign or malignant.

18
New cards
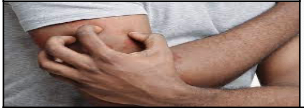
Pruritus
The condition of itching; may be associated with \n many diseases, especially allergic reactions on \n the skin.
19
New cards
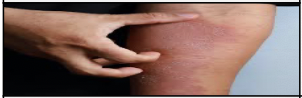
rash
A red or pink skin lesion that is flat or raised, itchy or not itchy.
20
New cards
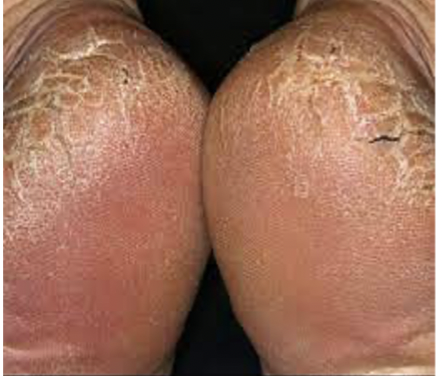
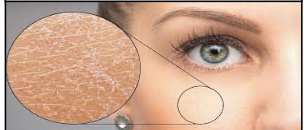
Xeroderma
Excessively dry skin.
21
New cards
melanocytes
cells in the epidermis that produce the pigment melanin that absorbs the sun’s UV light. Sunburn occurs when melanocytes can’t \n absorb all UV light.
22
New cards
skin color condition: albinism
\n Genetic mutation in which melanocytes do not produce melanin; results in a lack of coloration of the skin, hair, and eye.

23
New cards
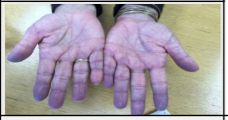
skin color condition: cyanosis
\n A bluish-purple discoloration of the skin and nails.
24
New cards
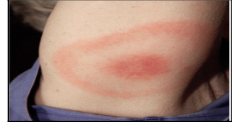
skin color condition: erythema
Red discoloration of the skin; may be local or over large areas of skin.
25
New cards
skin color condition: Jaundice
Yellowish discoloration of the skin, mucous membranes, and sclera due to inability of the liver to process bilirubin.

26
New cards
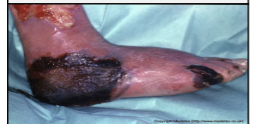
skin color condition:
Necrosis
Necrosis
Gray-to-black discoloration of skin due to skin death from a burn, ulcer, wound, or poor blood supply.
27
New cards
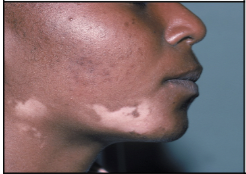
skin color condition:
Vitiligo
Vitiligo
Autoimmune disease in which melanocytes are slowly destroyed and patches of depigmentation appear.
28
New cards
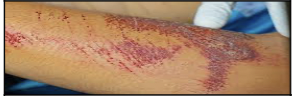
skin injury: Abrasion
\n Sliding or scraping injury that mechanically removes the epidermis.
29
New cards
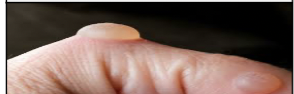
skin injury: Blister
Fluid-filled sac with a thin, transparent covering of epidermal cells; caused by repetitive rubbing \n injury.
30
New cards
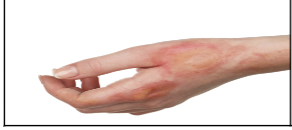
skin injury: Burns
Caused by heat, hot objects, steam, boiling water, electricity, chemicals, and radiation. \n • Superficial \n • Partial-thickness \n • Full-thickness
31
New cards
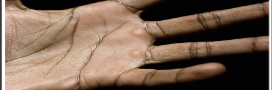
skin injury: Callus
Thickened, elevated pad on the dermis caused by repetitive rubbing.
32
New cards
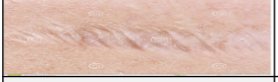
skin injury: Cicatrix
Collagen that forms as an injury heals; a scar.
33
New cards
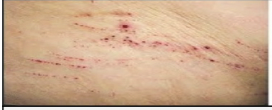
skin injury: Excoriation
\n Superficial injury with a sharp object that creates a linear scratch on the skin.
34
New cards
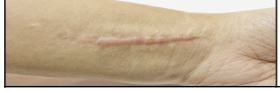
skin injury: Keloid
Firm abnormally large scar that grows larger than the original injury due to overproduction of collagen.
35
New cards
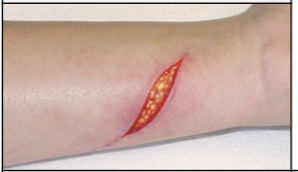
skin injury:Laceration
Linear penetrating wound; may have clean-cut edges or torn, ragged edges.
36
New cards
skin injury: Decubitus ulcer
Ulcer in the skin caused by epidermal and dermal breakdown; associated with constant pressure on the skin that decreases blood flow \n over bony areas.
37
New cards
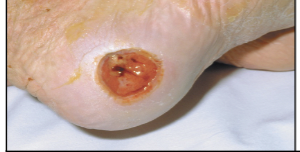
skin infection: abscess
Localized pus-containing pocket under the skin caused by a bacterial infection.
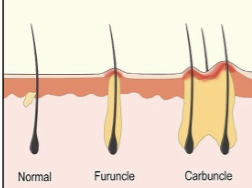
38
New cards
skin infection: cellulitis
\n Infection and inflammation of the connective tissues of the skin
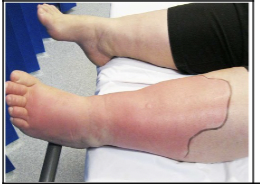
39
New cards
skin infection: shingles
Infection with the virus herpes; involves vesicles, erythema, edema, and pain.Shingles is from herpes varicella-zoster. The lesions occur along a dermatome (an area of skin \n associated with a specific spinal nerve that goes to the spinal cord).
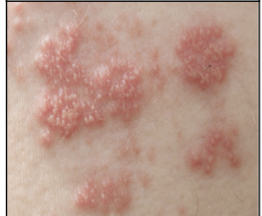
40
New cards
skin infections: Verruca
Rough, irregular skin lesion caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV); occurs on hands, fingers, or soles of the feet. also known as a wart
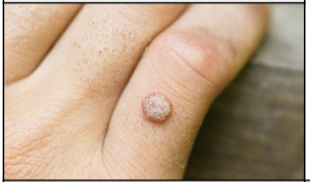
41
New cards
skin infections: Tinea (worm)
Fungal infection of the skin (ringworm); severe itching and burning with red, scaly lesions. \n • Tinea capitis (head) \n • Tinea corporis (body) \n • Tinea cruris (groin) –“jock itch” \n • Tinea pedis (feet)
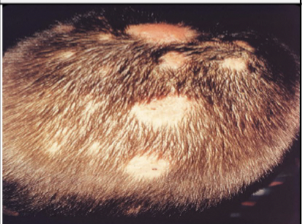
42
New cards
skin infestations: pediculosis
Infestation of lice and their eggs (nits); can occur in the scalp, hair, eyelashes, and genital area.
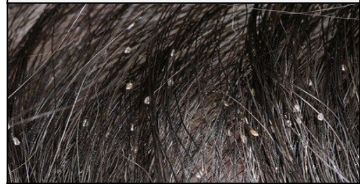
43
New cards
skin infestations: scabies
Infestation of parasitic mites that tunnel under the skin and produce itchy vesicles; caused by the same parasite that causes mange in dogs.
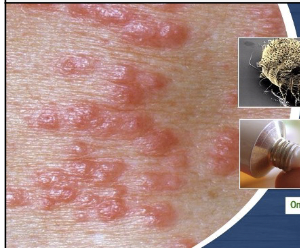
44
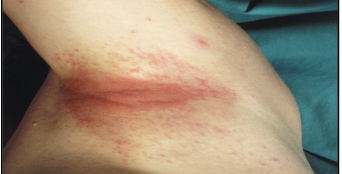
New cards
allergic skin conditions: contact dermatitis
Dermatitis caused by physical contact with an allergen or irritant like deodorant, soap, makeup, or urine.
45
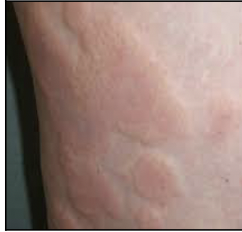
New cards
Allergic skin conditions: Urticaria
Local allergic reaction to food, plants, animals, insect bites, or drugs; caused by release of histamines and involves raised areas of redness \n and edema that occur suddenly \n (rash)
46
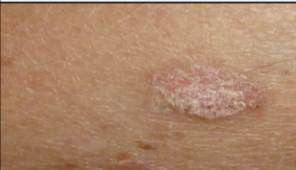
New cards
benign skin neoplasm: Actinic keratosis
Raised, rough areas due to chronic sun exposure.
47
New cards
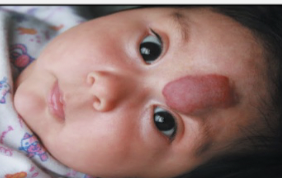
benign skin neoplasm: Hemangioma
Mass of superficial, dilated blood vessels present at birth; usually disappears without treatment.
48
New cards
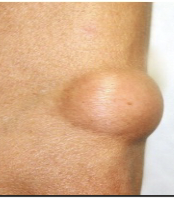
benign skin neoplasms: Lipoma
Rounded growth of adipose tissue (fat) in the skin.
49
New cards
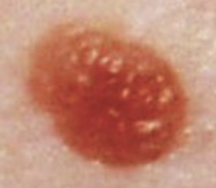
benign skin neoplasms: Nevus
Lesion that comes in a variety of shapes and colors; present at birth.
(Ex. mole, birthmark, port-wine stain)
(Ex. mole, birthmark, port-wine stain)
50
New cards
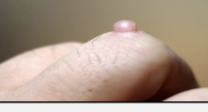
benign skin neoplasms: Papilloma
Soft, flesh-colored growth that protrudes from the skin; grows as a flap or polyp on a stalk (skin tag)
51
New cards
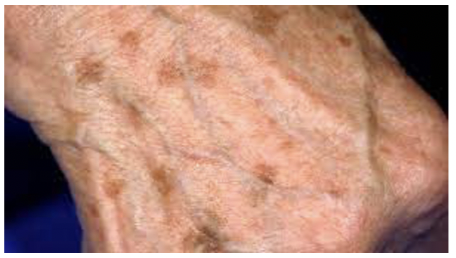
benign skin neoplasms: Senile lentigo
\n Light-to-dark brown, flat macules on the skin in areas exposed to the sun; also called age spots or liver spots.

52
New cards
benign skin neoplasms: Syndactyly
Condition in which the skin and tissues between the toes or fingers are joined.
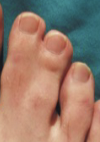
53
New cards
malignant skin neoplasms: Basal cell carcinoma
Begins in the basal epidermis; slow-growing cancer that appears as a raised, pearly bump.
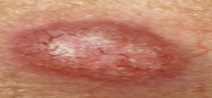
54
New cards
malignant skin neoplasms: Malignant melanoma
Begins in melanocytes; fast-growing and spreading cancer.
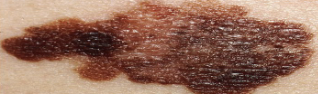
55
New cards
malignant skin neoplasms: Squamous cell \n carcinoma
Begins in the squamous epidermis; slow-growing red bump or ulcer.
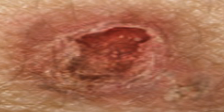
56
New cards
determining malignant neoplasms on the skin
A- ASYMMETRY
B- irregular BORDER
C-varied COLORING
D- large DIAMETER
E-EVOLVING size increase
B- irregular BORDER
C-varied COLORING
D- large DIAMETER
E-EVOLVING size increase
57
New cards
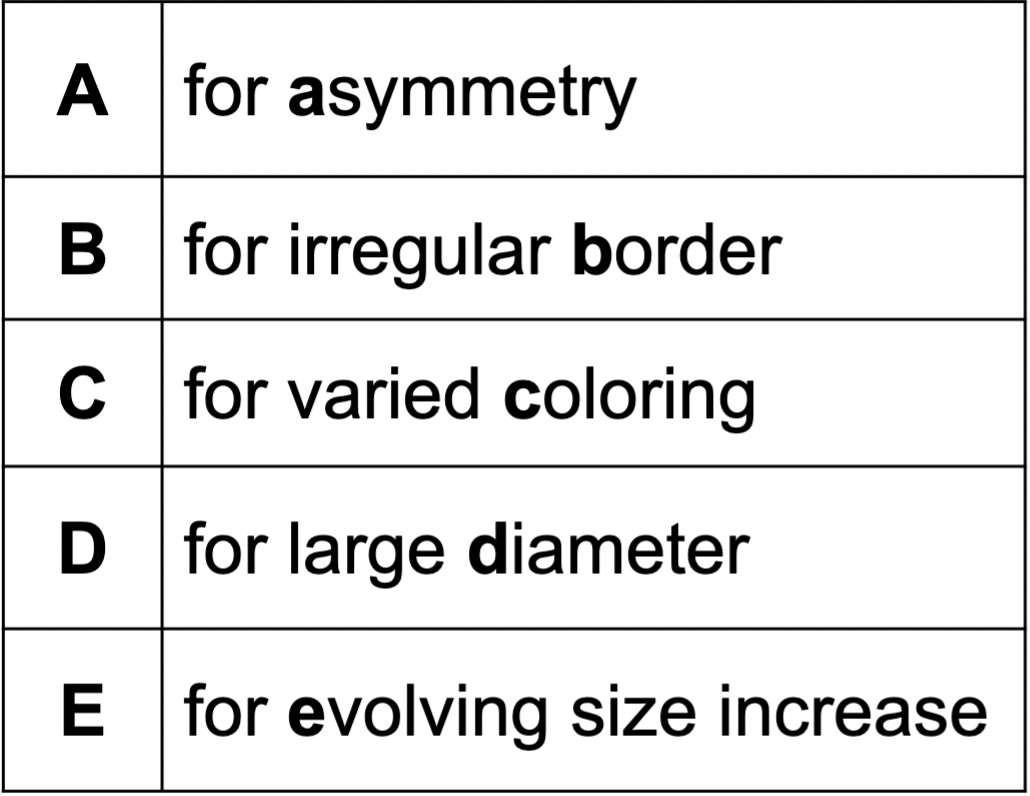
autoimmune disorders: psoriasis
Autoimmune disorder in which too many abnormal epidermal cells are produced; produces itch, silvery scales, and plaques.
58
New cards
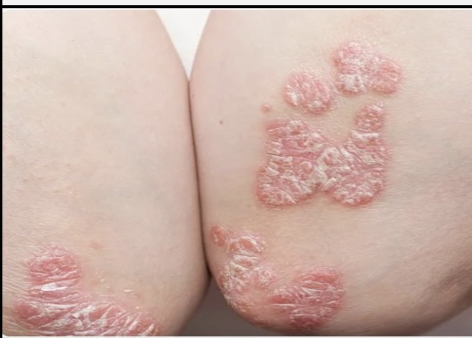
autoimmune disorders: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
Autoimmune disorder in which collagen in the \n skin and connective tissues deteriorates; characterized by butterfly rash on nose and cheeks.
59
New cards
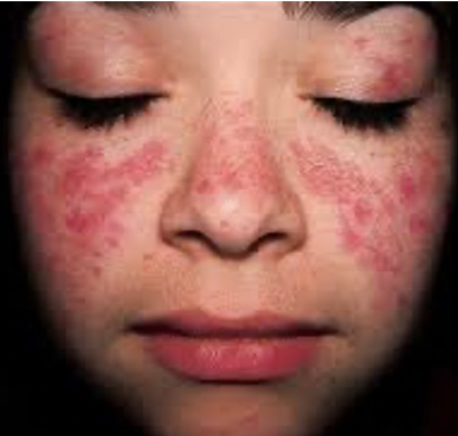
sebaceous glands
exocrine glands that produce a type of oil called sebum. \n –Sebum travels through a duct to a hair follicle. \n –Sebum coats the hair shaft and moisturizes \n the skin’s surface.
60
New cards
Sebaceous Gland disease: acne
Chronic skin condition of adolescence. Sebum hardens and blocks hair follicles, producing comedos (black and white headed pimples).
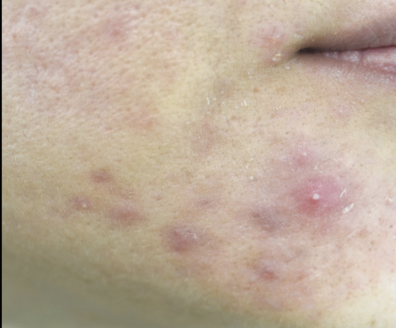
61
New cards
Sebaceous Gland disease: Rosacea
Chronic skin condition of middle age. Skin has blotchy erythema and dilated blood vessels (= rose colored).
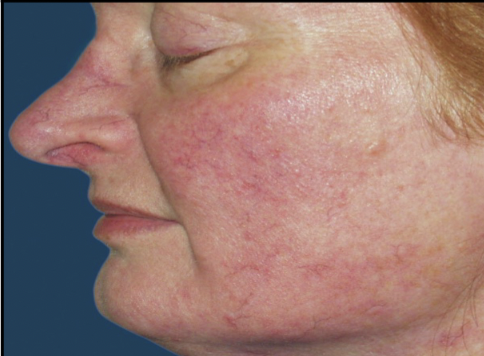
62
New cards
Sudoriferous (sweat) glands
Exocrine glands that secrete sweat through a duct that opens into a pore in the skin. \n –Sweat contains water, sodium, and small amounts of body waste. \n –Sweat is odorless, but takes on an odor when it contacts bacteria on the skin’s surface.
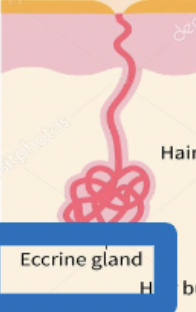
63
New cards
sweat gland disease: Anhidrosis
Congenital absence of sweat glands. No sweat is produced and heat is intolerable.

64
New cards
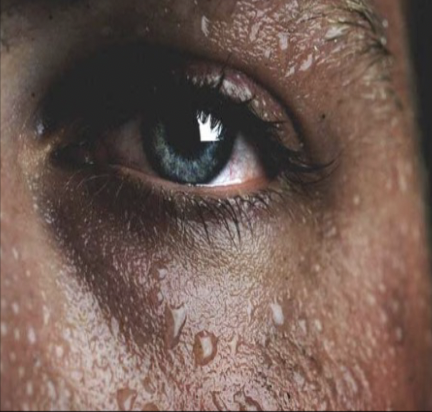
sweat gland disease: Diaphoresis
Profuse sweating; may indicate a serious underlying condition like myocardial infarction, hyperthyroidism, or drug withdrawal.

65
New cards
Piloerection
A tiny muscle at the base of the hair follicle contracts, which makes the hair stands up and causes a “goosebump” when the skin gets cold.
66
New cards
Hair disease: Alopecia
Loss of hair from the scalp due to disease, medication, or changes in hormone levels.
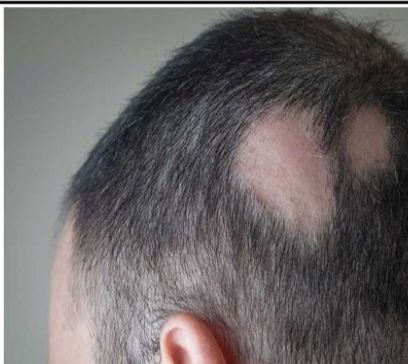
67
New cards
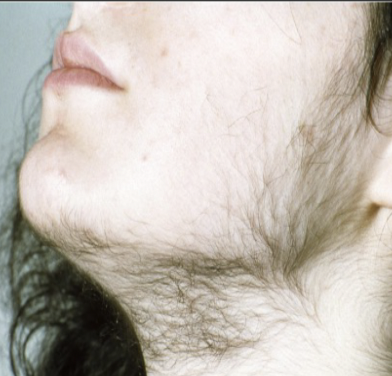
Hair disease: Hirsutism
Presence of excessive, dark hair on the forearms and upper lip of women; caused by hormone changes associated with a tumor of the adrenal cortex.
68
New cards
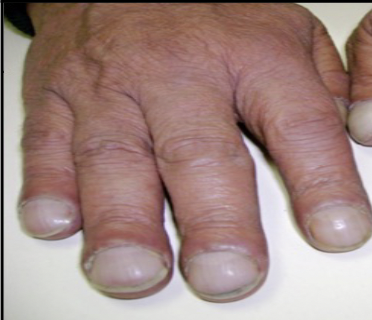
Nail disease: Clubbing and \n cyanosis
abnormal downward curve and bluish coloration of the fingernails accompanied by stunted growth of the fingers. Associated with lack of oxygen in cystic fibrosis.
69
New cards
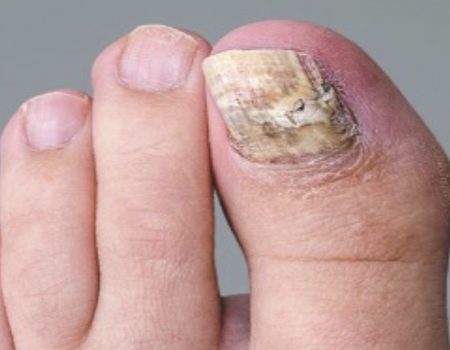
Nail disease: Onychomycosis
Fungal infection of the nail; nail root is infected and the nail is deformed as it grows.
70
New cards
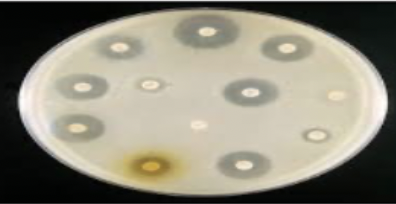
lab procedures: Culture and sensitivity
Growth of bacteria taken from a wound or lesion in a lab; colonies are used to make a diagnosis and to determine the correct antibiotic treatment.
71
New cards
lab procedure: allergy testing
Intradermal injection or scratch of liquid \n allergen; formation of a wheal in response to the allergen is indicative of allergy.
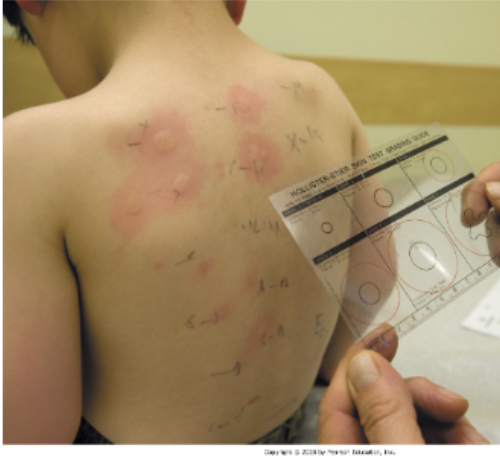
72
New cards
lab procedure: skin scraping
Scraping of cells from a lesion done with the edge of a scalpel; cells are examined under a microscope to diagnose tinea.
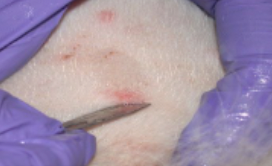
73
New cards
lab procedure: Tzanck test
Scraping of fluid from a vesicle to produce a slide for microscopic inspection; used to diagnose herpes virus \n and shingles.
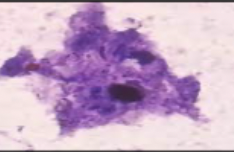
74
New cards
lab procedure: Wood lamp or \n light
Ultraviolet light used to highlight areas of abnormal skin; light makes vitiligo appear bright white and tinea \n capitis appear blue-green.

75
New cards
medical procedures: botox injections
Treatment for deep wrinkles; Botox is injected into muscle; releases wrinkle lines and prevents the muscle from contracting (also used as a treatment \n for migraines)
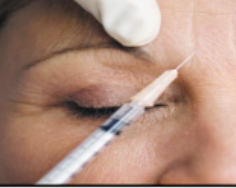
76
New cards
medical procedures: Collagen injections
Treatment for wrinkles or acne scars; liquid collagen solution plumps up skin to decrease the depth of the wrinkle or scar.
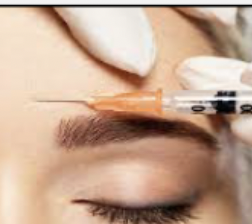
77
New cards
medical procedures: Cryolipolysis
Treatment for unwanted fat deposits; cold device applied to the skin freezes fat cells and causes them to crystalize and die.
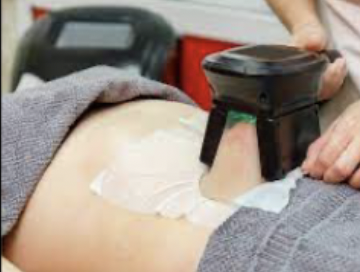
78
New cards
medical procedures: Cryosurgery
Treatment for benign or small malignant lesions; liquid nitrogen is applied to the lesion to freeze / destroy it
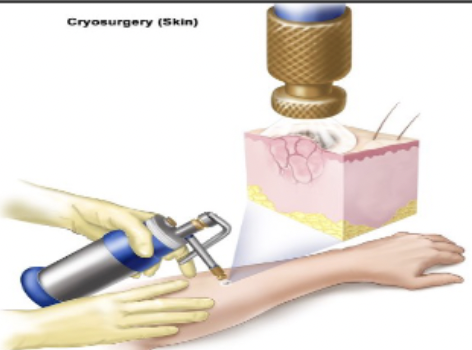
79
New cards
medical procedures: Debridement
Treatment for necrotic tissue removal; prevents infection and creates a clean, raw surface for healing or grafting.
(= remove the bridle from (French))
(= remove the bridle from (French))
80
New cards
medical procedures: Electrosurgery
Treatment for benign or small malignant \n lesions; electricity evaporates cellular \n contents and kills cells.
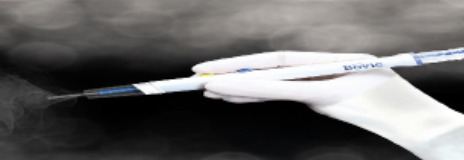
81
New cards
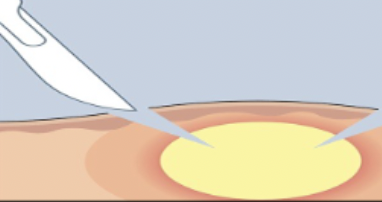
medical procedures: Incision and drainage (I&D)
Treatment to drain fluid; an incision is made and fluid is expressed or drained.
82
New cards
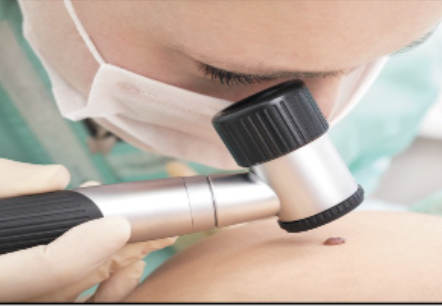
medical procedures: Skin examination
Inspection of the skin during dermatologist visit; may involve all of the skin or a specific rash or lesion.
83
New cards
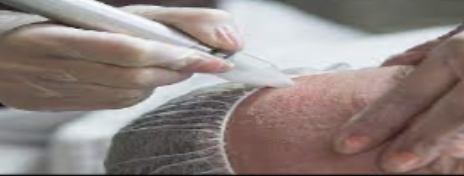
medical procedures: Skin resurfacing
Treatment to improve skin appearance; \n involves removal of part of the epidermis.
84
New cards
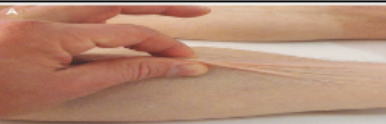
medical procedures: Skin turgor assessment
Assessment of hydration level; skin fold is pulled up and time to flatten is noted.
85
New cards
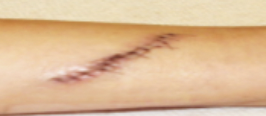
medical procedures: Suturing
Treatment to bring edges of skin together after laceration in injury; sewing skin and tissue together.
86
New cards
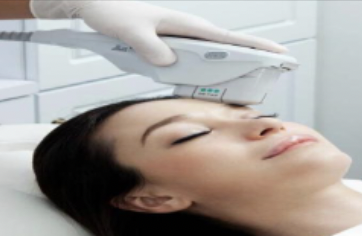
medical procedures: Ultherapy
Treatment for wrinkles on the face and neck; ultrasound waves stimulate production of new collagen.
87
New cards
Anesthetic \n drugs
Provide temporary numbness of the skin during procedures that involve cutting or suturing.
88
New cards
Antibiotic drugs
Treat bacterial infections or acne vulgaris; may be topical or oral.
89
New cards
Antifungal drugs
Treat fungal infections; may be topical or oral depending upon the fungus involved.
90
New cards
Antipruritic drugs
Treat itching associated with skin diseases; may be topical or oral.
91
New cards
Antiviral drugs
Treat viral infections; may be topical or oral.
92
New cards
Coal tar drugs
Treat psoriasis by slowing multiplication of epidermal cells; applied topically.
93
New cards
Corticosteroid drugs
Treat inflammation by suppressing \n the immune response; may be topical \n or oral.
94
New cards
Alopecia drugs
Improve blood flow to the scalp to \n increase hair growth
95
New cards
Drugs for infestations
Treats scabies (mites) and pediculosis (lice); applied topically as a lotion and shampoo.
96
New cards
Vitamin A-type drugs
Treat acne vulgaris and severe cystic \n acne; may be topical or oral.
97
New cards
Topical drugs
Applied directly to the skin; has a local effect.
98
New cards
Transdermal drugs
Patches that are placed on the skin; drug is absorbed through the skin and transported through the blood to exert a systemic effect.
99
New cards
Intradermal drugs
Needle inserted just under the epidermis; used for tuberculosis and allergy testing.
100
New cards
Hypodermic drugs
Needle inserted all the way into the hypodermis; Also referred to as subcutaneous (SQ, subcu, subQ) injection