Fields
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What is Kepler’s 1st Law?
The orbit of a planet is an ellipse, with the Sun at one of the two foci.
What is Kepler’s 2nd Law?
A line segment joining the Sun to a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal time intervals
What is Kepler’s 3rd Law?
Kepler's Third Law states that the square of the orbital period of a planet (P) is proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis (a) of its orbit
P² ∝ a³
When can bodies be treated as point masses?
A uniform sphere (mass distributed equally) covers a very large distance compared to its size, so, to study its motion, its size or dimensions can be neglected.
What is Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation?
F = Gm1m2/r² where;
r is the distance between the 2 masses.
The gravitational field strength at a point (g) formulae?
F/m = GM/r²
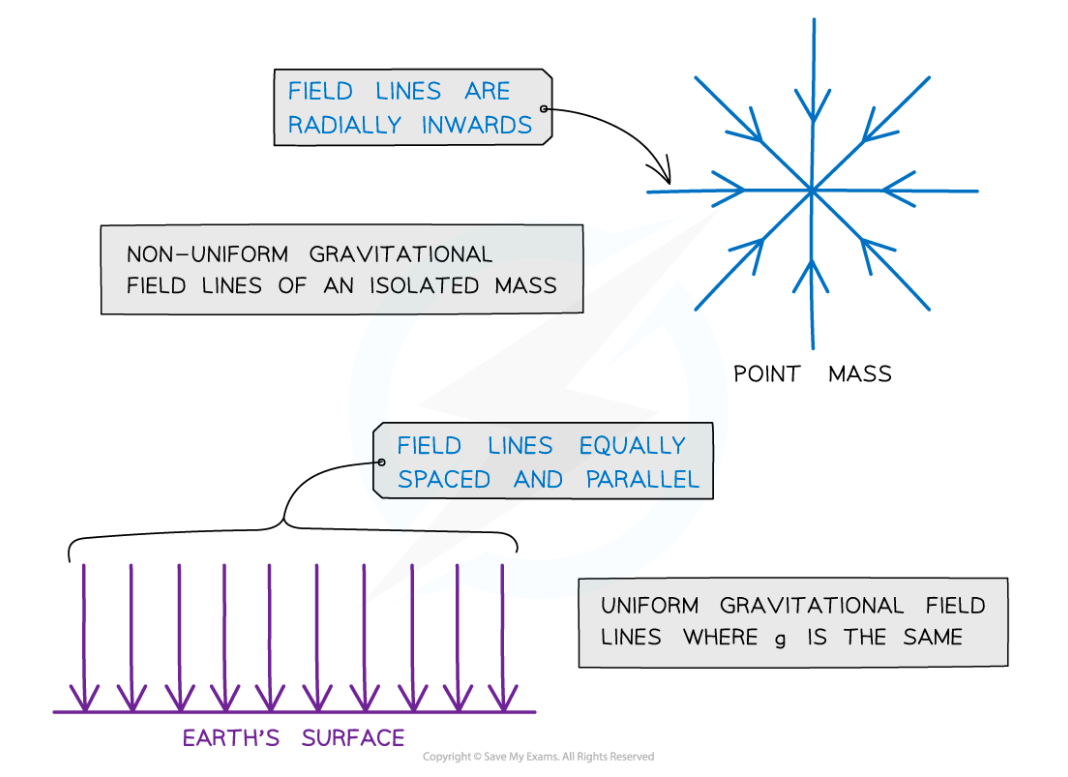
What do radial and uniform field lines look like?
What is the definition and formula of gravitational potential energy of a system?
The work done to assemble the system frominfinite separation of the components of the system
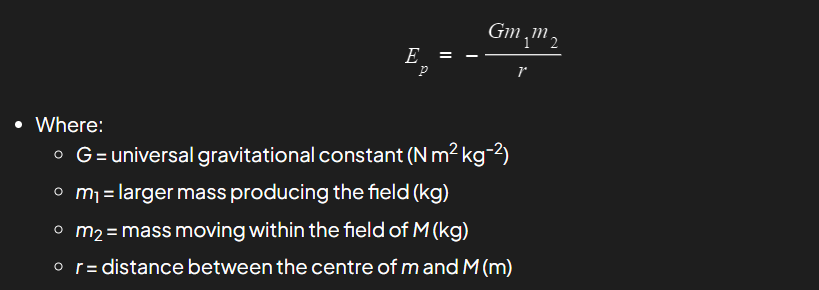
What is the definition and formula of gravitational potential of an object?
The gravitational potential Vg at a point is the work done per unit mass in bringing a mass from infinity to that point.
Vg = –GM/r where;
M - Mass of the object creating the field.
r - distance between bodies
G - Gravitational constant
How does gravitational potential change with radius?
When a mass is closer to a planet, its gravitational potential becomes smaller (more negative)
As a mass moves away from a planet, its gravitational potential becomes larger (less negative) until it reaches 0 at infinity
Work done on a mass in terms of Vg
W = mΔVg
What is the the gravitational field strength g as the gravitational potential gradient?
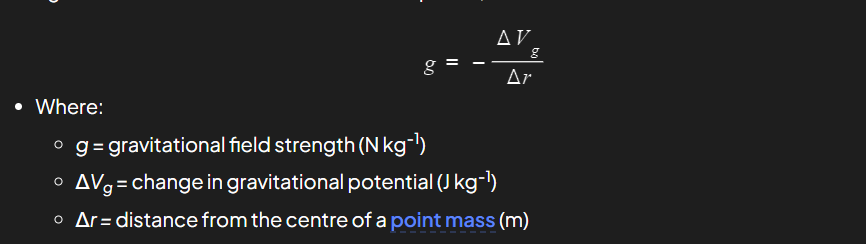
How are equipotential lines drawn and when is work done considering them?
In dotted lines - Perpendicular to the gravitational field lines in both radial and uniform fields with no arrows.
No work is done moving along them - but work is done moving between them.
What is the escape speed and its fomula?
The minimum speed that will allow an object to escape a gravitational field with no further energy input
vesc = √(2GM/r) where;
M is the mass of the body creating the field.
What is formula for orbital speed?
vorbital = √(GM/r)
Effect of drag due to atmosphere on orbital speed and radius of an orbit?
When a satellite loses energy, its orbital radius decreases slowly.
However, as the satellite's orbit becomes lower, some of its potential energy is transferred to kinetic energy - increaisng its speed.
What is the direction of forces between two types of electric charges?
Like charges repel each other, and unlike charges attract each other.
How can electric charge be transferred between bodies?
Through:
Friction - one becomes negative and the other becomes positive.
Electrostatic induction and contact
Role of grounding (earthing)- low resistance path for excess current.
What did Millikan’s experiment demonstrate?
It quantized the value of fundamental or elementary charge.
What creates an electric field and how do you calculate its field strength?
Potential difference.
E = F/q where;
F- electrostatic force on charge
q- charge (C)
It is important to use a positive test charge in this definition, as this determines the direction of the electric field.
What is Coulomb’s Law for point charges?
F = kq1q2/r²
where k is Coulumb’s constant
What are point charges in a system?
Size is negligible compared to the distance between them.
How do electric field lines move and what does their density and direction represent?
From positive to negative.
Their density represents the field strength.
Radial field lines - non-uniform
Evenly spaced and perpendicular to plates - uniform
What is coulumbs constant and what is permittivity?
How is relative permittivity expressed mathematically
k = 1 4πε0 where
ε0 - permittivity -the lower the permittivity the better the insulator.
εr=ε/ε0
How is the uniform electric field strength (E) between parallel plates calculated?
If a plate is earthed what is the pd at that point?
E = V/d where;
d - separation between plates
Electric potential =energy definition and formula inlcuding sign conventions
The work done per unit positive charge in bringing a small test charge from infinity to a defined point
Positive when near an isolated positive charge
Negative when near isolated negative charges
Zero at infinity
Ve = kQ/r

What is the gradient of a potential distance graph show?
-Electric field strength
E = – ΔVe/Δr
What happens when a mass with charge moves through an electric field?
What us the formula relevant?
W = qΔVe
What is electric potential energy and its formula?
Work done to assemble the system from infinite separation.
Ep = kq1q2/r
What does distance between equipotential lines indicate?
Strength of electric potential - stronger as they are closer.
How does a magnetic field move?
North to south
What is the electric field in a spherical shell?
The free charges within the conductor move to the surface and redistribute in such a way that they cancel out any internal electric field, resulting in a net electric field of zero inside.
What does the right hand grip rule represent?
Wire - Thumb gives current and fingers give magnetic field.
Solenoid - Thumb gives magnetic field and fingers give current.
What does deflection of a charged and uncharged particle depend upon in an electric field?
Uncharged - 0
Charged:
Mass - greater mass - smaller deflection
Charge - greater charge - greater deflection
Speed - greater speed - smaller deflection
How does a charged particle travelling perpendicular to a magnetic field behave and what is the formula for the force it experiences?
It travels in a circular path until it exits the field.
F = qvBsin θ where;
F = force on the charge (N)
B = magnetic flux density (T)
Q = charge of the particle (C)
v = speed of the charge (m s-1)
θ = angle between charge’s velocity and magnetic field (degrees)
(can be equated to centripetal force in a perp field)
Formula for the magnitude and direction of the force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field
F = BIL sinθ where;
F = force on a current carrying conductor in a magnetic field (N)
B = magnetic flux density of external magnetic field (T)
I = current in the conductor (A)
L = length of the conductor (m)
θ = angle between the conductor and external magnetic field (degrees)
What is flemmings left hand rule?
Thumb - father- force experienced by charge
First finger - mother - Magnetic field
Middle finger - child - current (flow of POSITIVE charge)
When no force is experienced by a charge in a combined field what is the euqation used?
Equate equations for electric and magnetic field
Eq=Bvq
v=E/B
Formula for the force per unit length between parallel wires.
F/L = μ0I1I2/2πr where;
r is the distance between the 2 wires
What is emf?
Terminal potential difference when no current is flowing between the terminals of the cell.
What is electromagnetic induction?
Occurs when an emf is induced when a conductor moves through a magnetic field. As a conductor cuts through magnetic field lines there is a change in magnetic flux which causes work to be done. The work is then transformed into electrical energy.
If it is attached to a complete circuit, a current would be induced.
Formula and definition for magnetic flux (Φ)
Number of magnetic field lines passing through a surface
Φ = BA cos θ
Where;
B - Magnetic field strength
A - Area of surface
Formula for emf induced in a straight conductor moving perpendicularly to a uniform magnetic field.
ε = BvL
where L is the length of the conductor in the field.
Magnetic flux linkage formula?

Faraday’s law of induction
ε = − N (ΔΦ)/ Δt
The minus sign is to remind us that the emf always acts to oppose the change in magnetic flux which generates the emf.
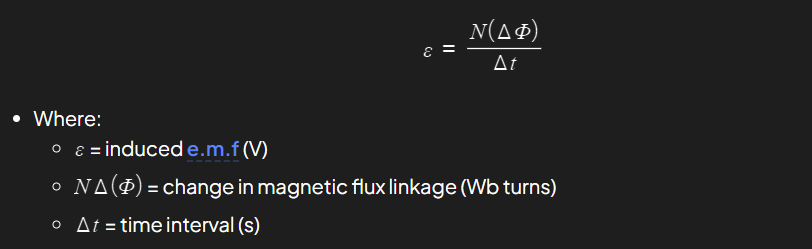
What is Lenz’s law?
The induced e.m.f is such that it will oppose the change causing it
What is the generator effect?
If a coil of wire is rotated inside a magnetic field by an external force, an emf will be generated in the wire which causes current to flow within the coil.
What is self-induction?
Self-induction is the property of a conductor whereby a change in the current flowing through it induces an electromotive force (EMF) within the same coil.
Describe the field and voltage in a uniform conduction within and on the surface of a sphere.
Within - The field is 0 and the potential difference stays constant.
Outisde - Charge is evenly spread on the surface.
What does deflection of a charged and uncharged particle depend upon in a magnetic field?
Stronger charge - Shorter deflection
More mass - Larger deflection
From Coulomb's law, the electric field 𝐸E created by a point charge 𝑞q at a distance 𝑟r from the charge is given by?
E=kq/r²