MARKETS /. Segmentation, targeting and positioning
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
market share
A firm’s share of the total value of sales within an industry →
market leadership
The position at which a business has the largest market share in a market
Market growth
The rate at which the size of the market is increasing
Market concentration
The degree of competitiveness within a given market. High concentration means a few companies control most of the market share, indicating less competition, while low concentration means many companies share the market, suggesting a more competitive landscape.
Benefits of being a market leader
economies of scales
premium pricing
Greater publicity and brand exposure
Easier to attract and recruit qualified stakeholders
disadvantages of being a market leader
diseconomies of scales
higher standards —> be stricter
increased competition
Marketing Plan
A marketing plan outlines a firm's marketing objectives and the marketing strategies used to achieve these objectives:
Marketing budget
anticipated difficulties and potential solutions
Marketing mix
Strengths and weaknesses of competitors
SMART marketing objectives
Methods of market research
Marketing process
Marketing audit
Set marketing objectives
Plan marketing strategies
Monitor and review performance
Evaluation
Marketing audit
An examination of the current climate in which the business operates
Marketing objectives
Marketing audit allows companies to set informed marketing goals, whether that be long-term or short-term
Monitor and review performance
Checking and monitoring progress
Evaluation
Evaluation and determine if the business has met their goals
Target market
A market for a particular good or service consists of different types of customers, subdivided into market segments.
Market segment
A distinct group of customers with similar characteristics (such as age and gender), similar needs and wants.
Consumer profile
records held about individual customers, used as a guide for determining whom to target with certain products
Consumer profile characteristics
demographic
geographic
psychographic
Demographic factors
Demography is the study of the characteristics of the human population within a certain area, country or region. The range of demographic variables include:
Age
Gender
race and ethnicity
Religion
income and soci-economic class
Geographic factors
Geographic location impacts the needs and wants of customers. This falls into two broad categories: location and climate
psychographic factors
Those that consider the emotions and lifestyles (hobbies) of customers. These factors include:
hobbies and interests
values
religion
Status
culture
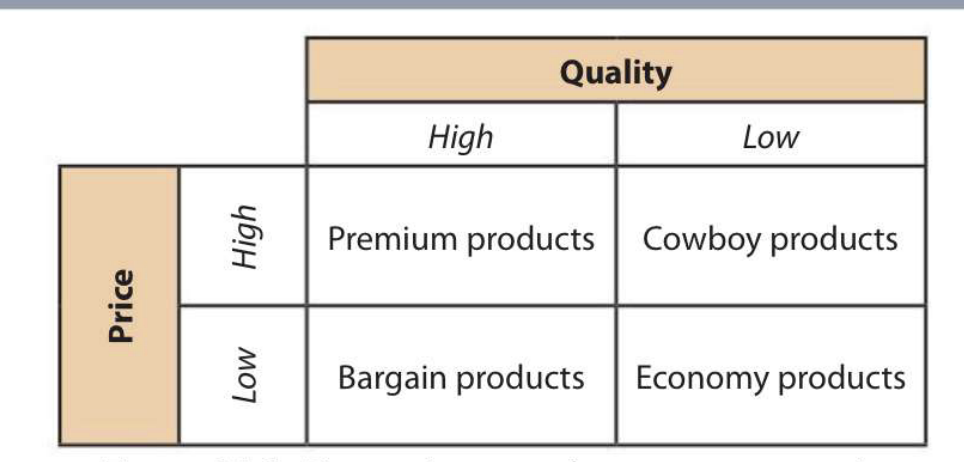
Product position map
a visual tool. that reveals customer perceptions of a product compared to others in the market
Prenium products
goods and services of high quality and high prices
Bargain products
goods and services of high quality but with low prices
Economy products
low prices and low quality
Cowboy products
poor quality, but highly priced used to deceive customers and used short-term tactic to gain sales
niche marketing
targeting a specific and well-defined market segment
advantages of niche marketing
there is a better focus whilst mass marketing has no real focus,
less competition —> businesses can charge higher prices for their unique and exclusive products --> higher profit margins on its products
Businesses become highly specialized in meeting the need and wants of their niche target market
disadvantages of niche marketing
Limits number of potential customers due to small market size
Fewer opportunities to exploit economies of scale --> average costs tend to be higher
The threat of larger firms entering the market might endanger the survival of businesses operating in niche markets
Mass marketing
undifferentiated marketing --> ignores targeting individual market segments
adv of mass marketing
gain from huge potential economies of scale by suppling products in mass markets, thereby helping them to cut unit costs and raise profit margins
No need to modify marketing strategies for different market segments --> saves both time and resources
Catering for larger markets --> establish larger customer base
disadv. of mass marketing
not suitable for all businesses due to the high barriers to entry required for mass production
lots of competition
lack of focus --> can be wasteful
Unique selling point / proposition
any aspect of a business, product or brand that makes it stand out from those offered by competitors
Common ways for differentiation (marketing mix)
product
place
price
promotion
people
processes
physical environment (the physical location can make it easier for customers)
packaging
First mover
an advantage gained by a company that first introduces a product or service to the market
Targeting
each distinctive market segment having its own specific marketing mix, depending on whether the business operates in niche or mass markets
mass market
undifferentiated market, large group of different market segments. These segments consist of people in different demographics and geographics. Also, their wants and needs may be different