SBI3U - Genetics
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/52
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
1
New cards
Non-disjunction
* The failure of homologous chromosomes to move to opposite poles of the cell during meiosis;
* results in an abnormal number of chromosomes in the daughter cells
* Trisomy (24)
* Monosomy (23)
* results in an abnormal number of chromosomes in the daughter cells
* Trisomy (24)
* Monosomy (23)
2
New cards
Autosomes
Chromosome pair #1-22
3
New cards
Sex Chromosomes
* Chromosome pair 23
* determines gender
* female (XX)
* Male (XY)
* determines gender
* female (XX)
* Male (XY)
4
New cards
karyotype
The chromosomes of an individual that have been sorted and arranged according to size and shape
5
New cards
XO (Female)
Turner Syndrome
* Sterile, short/stockier build
* Most XO fetuses usually die.
* **Disorders of Sex Chromosome Non-disjunction**
* Sterile, short/stockier build
* Most XO fetuses usually die.
* **Disorders of Sex Chromosome Non-disjunction**
6
New cards
Triple X Syndrome
XXX
(Female)
* 1/1000 female births
* poorly diagnosed
(Female)
* 1/1000 female births
* poorly diagnosed
7
New cards
XXY (Male)
Klinefelter Syndrome
* Can exhibit female characteristics,
* **Disorders of Sex Chromosome Non-disjunction**
* Can exhibit female characteristics,
* **Disorders of Sex Chromosome Non-disjunction**
8
New cards
Trisomy 21
\
Down syndrome
* round face, short height
* range of intellectual abilities
* **Disorders of Autosomal Non-disjunction**
Down syndrome
* round face, short height
* range of intellectual abilities
* **Disorders of Autosomal Non-disjunction**
9
New cards
Trisomy 13
Patau Syndrome
* serious developmental problems
* live several months (sometimes yrs)
* **Disorders of Autosomal Non-disjunction**
* serious developmental problems
* live several months (sometimes yrs)
* **Disorders of Autosomal Non-disjunction**
10
New cards
Trisomy 18
Edwards Syndrome
* many organ system failures
* most die before birth
* **Disorders of Autosomal Non-disjunction**
* many organ system failures
* most die before birth
* **Disorders of Autosomal Non-disjunction**
11
New cards
Why does primary nondisjunction occurs more often in women than men?
* because all the eggs a woman will produce have begun their development (to Prophase I) by the time she is born.
* Therefore, a much greater chance exists for problems to occur in the gametes of women than men.
* Therefore, a much greater chance exists for problems to occur in the gametes of women than men.
12
New cards
Mendel’s Law of Segregation
* Gametes only carry one allele for a gene
13
New cards
Law of Independent Assortment
* Different characteristics are inherited independently from one another
14
New cards
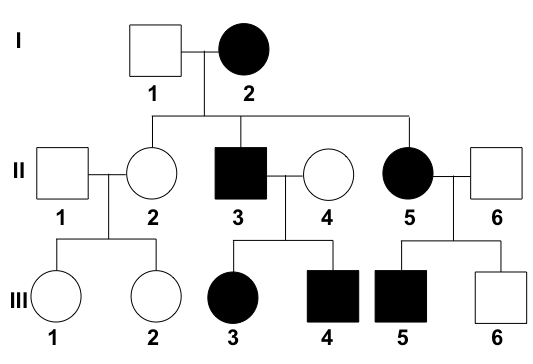
Pedigree
* a diagram of of an individual's ancestors used in human genetics
* to analyze the Mendelian inheritance of a certain trait;
* also used for selective breeding of plants and animals.
* to analyze the Mendelian inheritance of a certain trait;
* also used for selective breeding of plants and animals.
15
New cards
GAMETOGENESIS
* The formation of sex cells in meiosis
16
New cards
Describe OOGENESIS
\
* Egg cell formation
* The CYTOPLASM does NOT divide equally
* Daughter cells with less cytoplasm called POLAR BODIES
* Polar bodies will DIE therefore final product is A SINGLE OVUM (EGG CELL)
* Egg cell formation
* The CYTOPLASM does NOT divide equally
* Daughter cells with less cytoplasm called POLAR BODIES
* Polar bodies will DIE therefore final product is A SINGLE OVUM (EGG CELL)
17
New cards
Describe SPERMATOGENESIS
* Sperm cell formation is called
* Cytoplasm is divided equally
* Forms FOUR equal sized SPERM CELLS
* Each sperm cell is SMALL AND STREAMLINED in size
* Cytoplasm is divided equally
* Forms FOUR equal sized SPERM CELLS
* Each sperm cell is SMALL AND STREAMLINED in size
18
New cards
**Incomplete Dominance**
Occurs when two different alleles control a characteristic, but neither is dominant so both are expressed or blended in the phenotype.
\
\
19
New cards
**Codominance**
both allele products appear in the offspring at the same time.
20
New cards
Sex linked inherited traits
Hemophilia, color blindness, male pattern balding,, muscular dystrophy
hemophilia:
* bleeding disorder in which the blood does not clot properly.
* This can lead to spontaneous bleeding as well as bleeding following injuries or surgery.
Muscular dystrophy:
* Over time, muscle weakness decreases mobility, making everyday tasks difficult.
hemophilia:
* bleeding disorder in which the blood does not clot properly.
* This can lead to spontaneous bleeding as well as bleeding following injuries or surgery.
Muscular dystrophy:
* Over time, muscle weakness decreases mobility, making everyday tasks difficult.
21
New cards
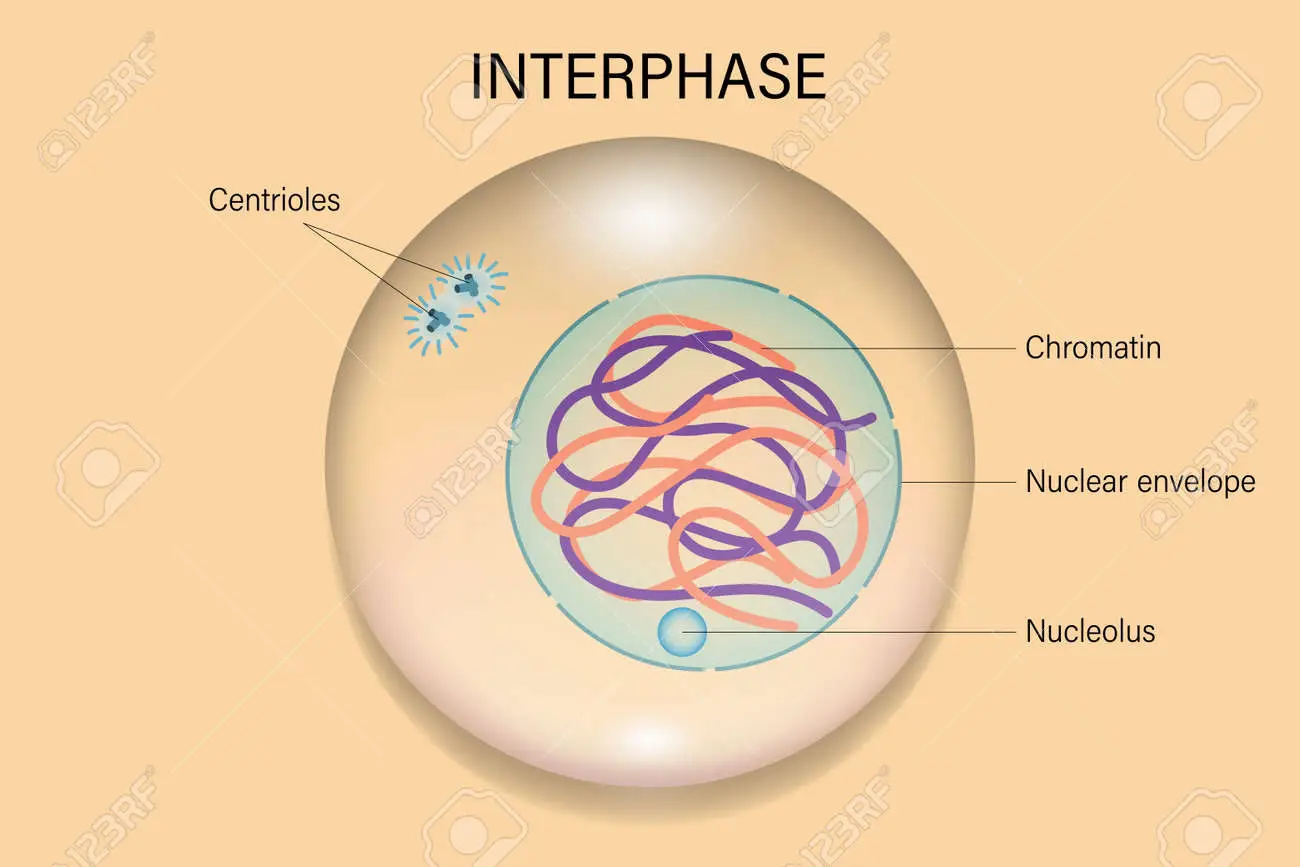
Interphase (Mitosis)
* grows
* DNA replicates
* The cell performs its daily functions
* DNA replicates
* The cell performs its daily functions
22
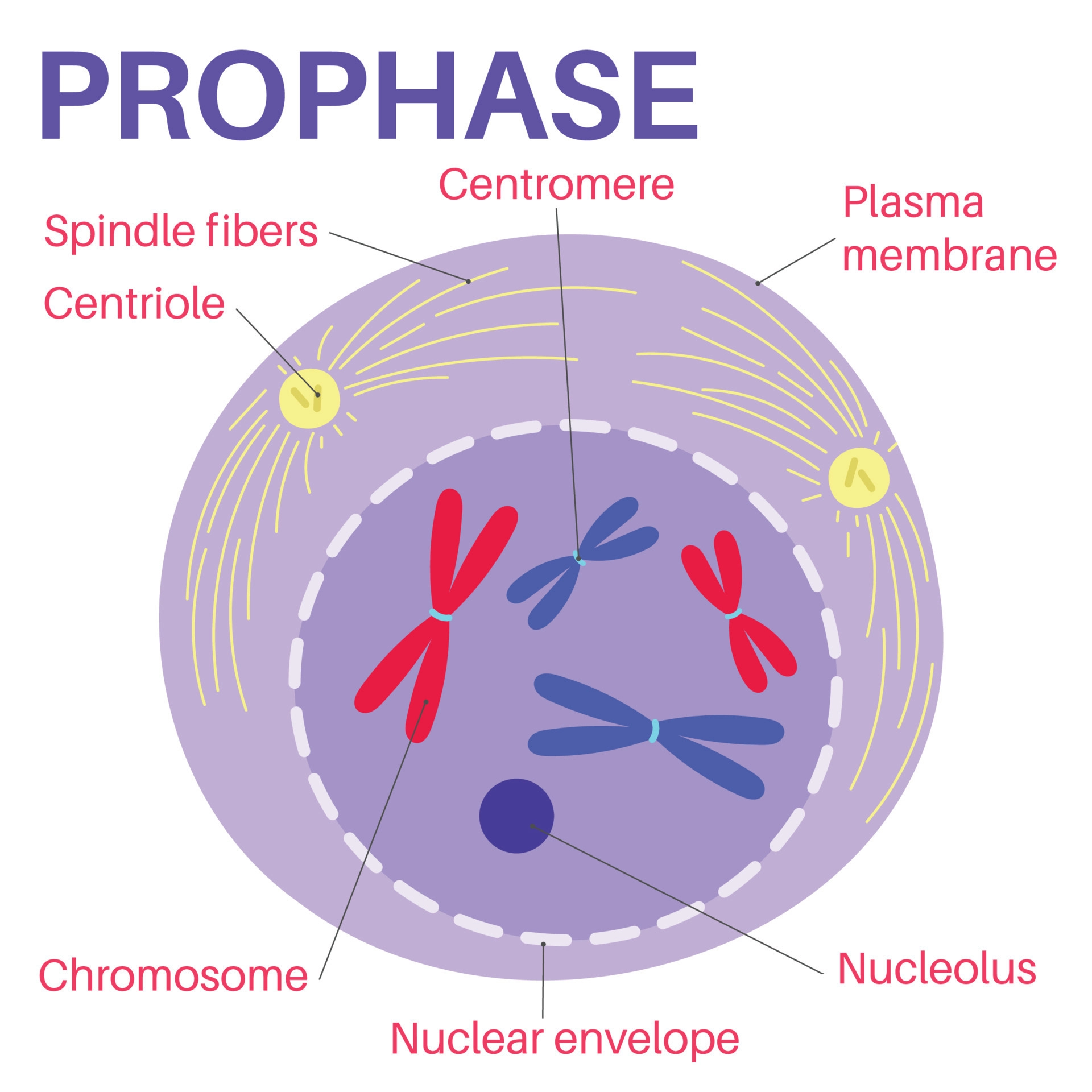
New cards
Prophase (Mitosis)
* Spindle fibers form
* Nuclear membrane begins to dissolve
* Centrioles begin to move to opposite sides
* Nuclear membrane begins to dissolve
* Centrioles begin to move to opposite sides
23
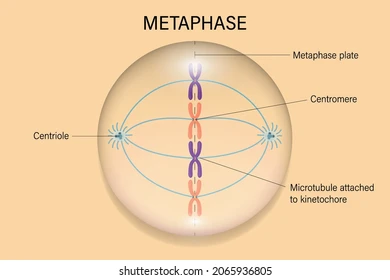
New cards
Metaphase (Mitosis)
* The spindle fibbers move the chromosomes to the equator
24
New cards
Anaphase (Mitosis)
* spindle fibbers shorten and contract pulling apart chromosomes and pulling each sister chromatid
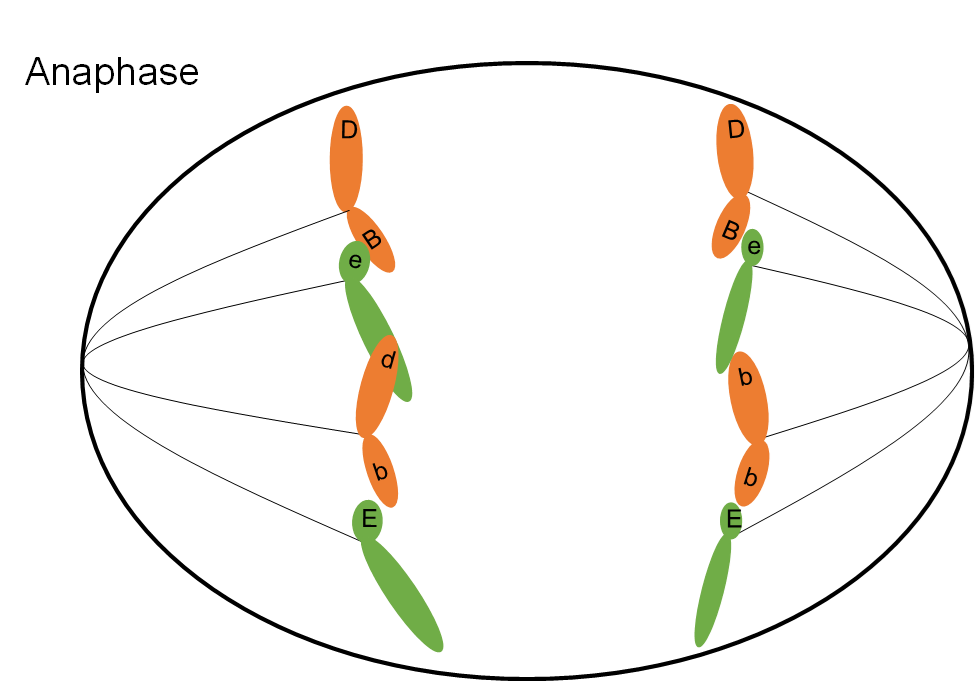
25
New cards
telophase/cytokinesis (Mitosis)
telophase:
* spindle fibre’s disappear
* nuclear membrane begins to reform
* the cell begins to divide
cytokinesis:
* the cell separates into two identical *daughter* cells
* the cytoplasm seperate’s
* spindle fibre’s disappear
* nuclear membrane begins to reform
* the cell begins to divide
cytokinesis:
* the cell separates into two identical *daughter* cells
* the cytoplasm seperate’s
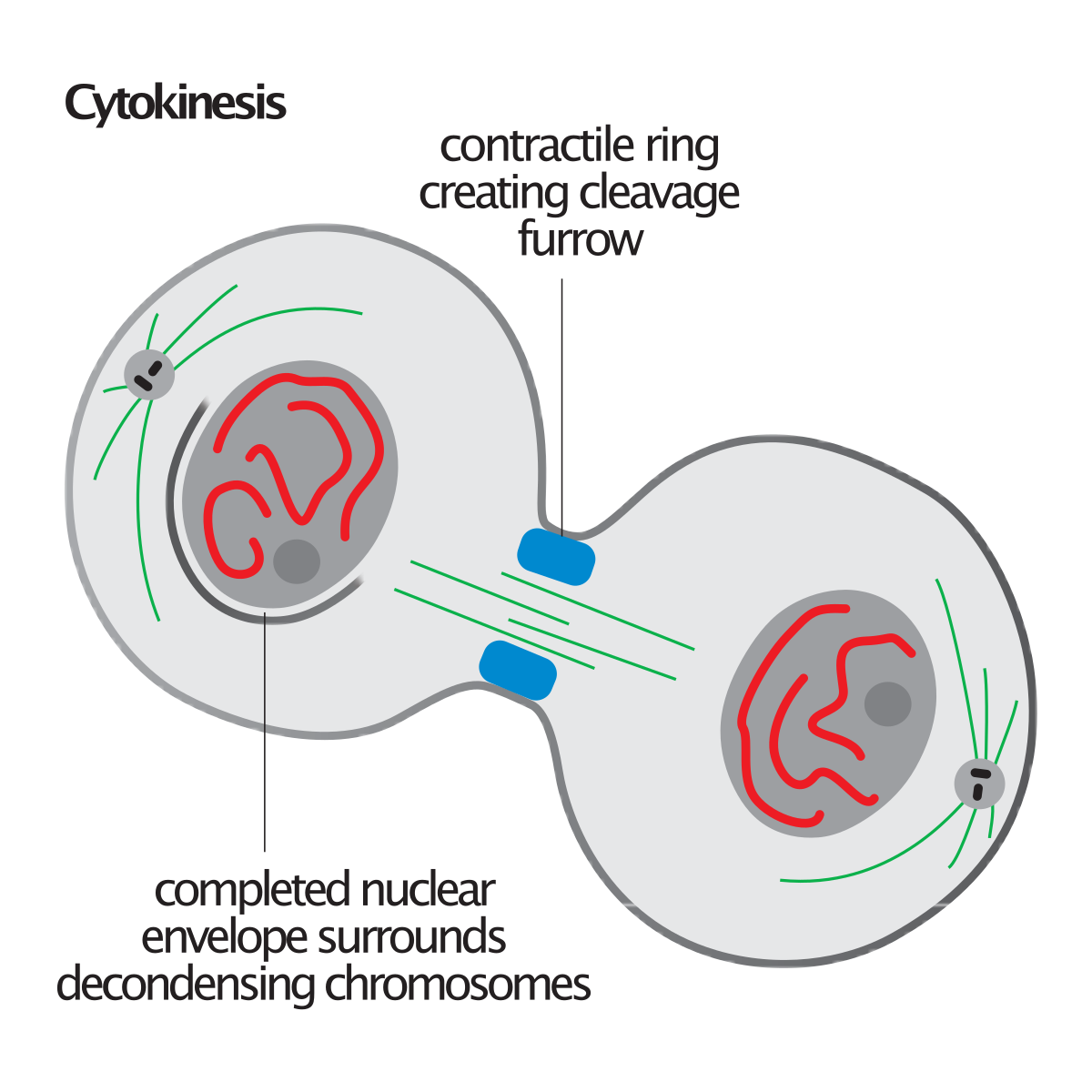
26
New cards
Prophase 1 (Meiosis)
* in a process called synapsis, chromosomes pair up & bind to form homologous chromosomes forming a tetrad
* In a process called crossing over chromatids from homologous homologous chromosomes exchange allies to create genetic verity
* nuclear membrane dissolves
* spindle fibers form
* In a process called crossing over chromatids from homologous homologous chromosomes exchange allies to create genetic verity
* nuclear membrane dissolves
* spindle fibers form
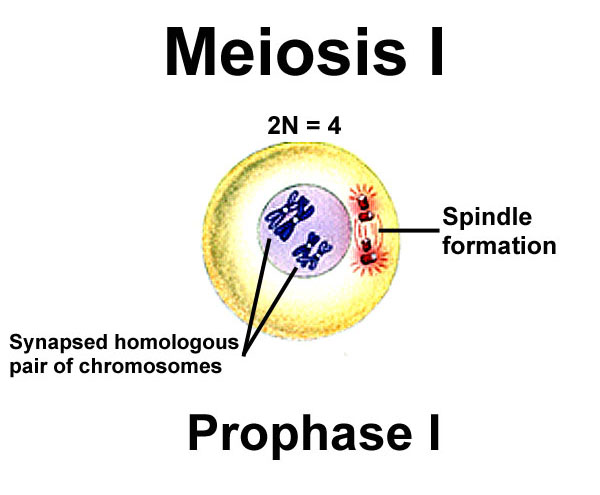
27
New cards
Metaphase 1 (meiosis)
* tetrads line up at the equator attached to the spindle fibers
* random assortment is when homologous pairs are randomly orientated to face opposite poles
* random assortment is when homologous pairs are randomly orientated to face opposite poles
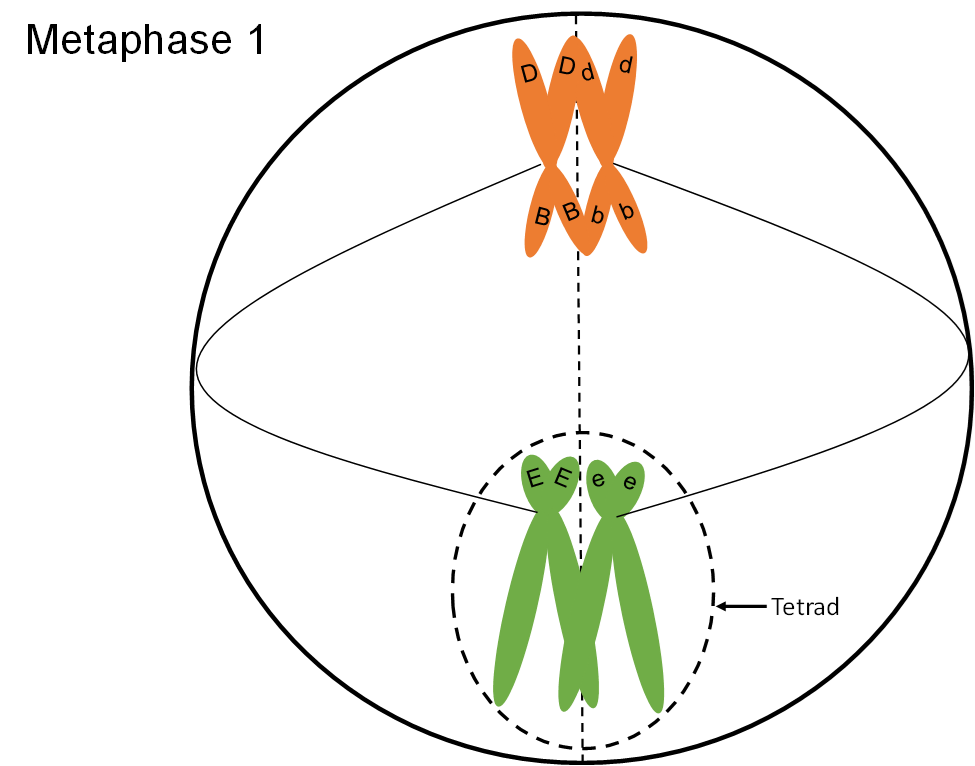
28
New cards
Describe this photo Meiosis
\
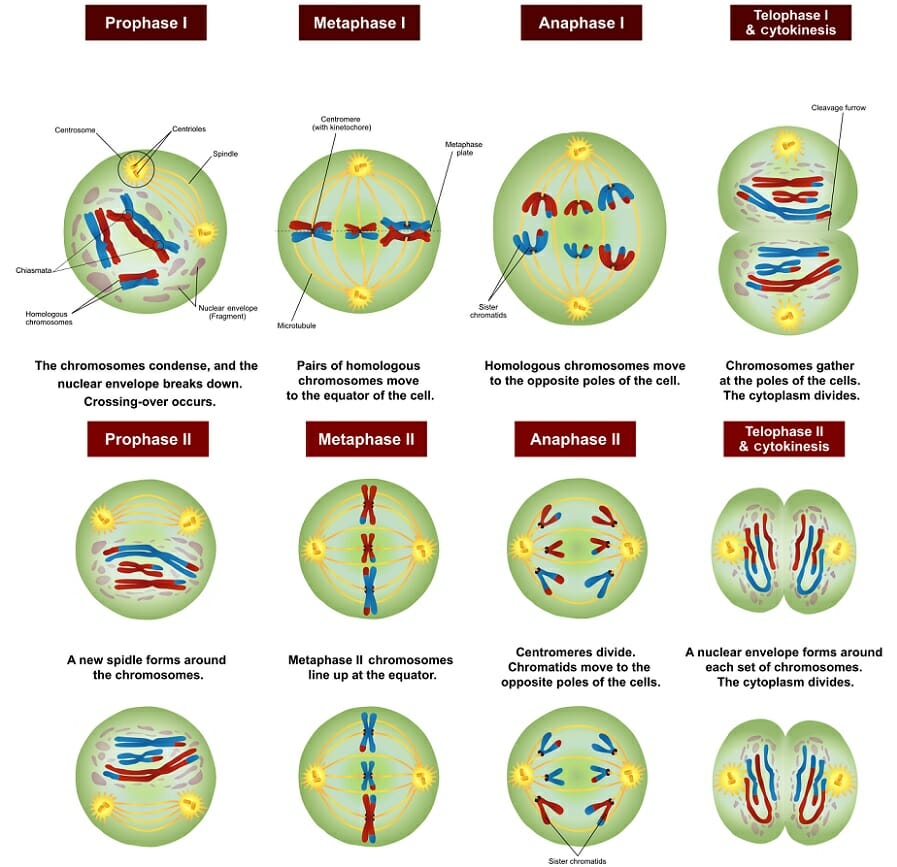
29
New cards
Describe Alkaptonuria
* the accumulation of alkapton in the body
* kidney stones cause damage to cartilage
* recessive allele
* kidney stones cause damage to cartilage
* recessive allele
30
New cards
Describe (cystic fibrosis)
* body creates thick sticky mucus that clogs the lungs
* blocks the release of enzymes from the pancreas
* recessive allele
* blocks the release of enzymes from the pancreas
* recessive allele
31
New cards
Describe PKU (Phenylketonuria)
* Accumulation of phenylalanine
* poor mental development and growth
* weak tooth enamel
* recessive allele
* poor mental development and growth
* weak tooth enamel
* recessive allele
32
New cards
Tay Sachs Disease.
* nerve cells in the brain are effected
* deuteriation of muscles and physical abilities
* deuteriation of muscles and physical abilities
33
New cards
Name all recessive autosomal diseases (5)
* Tay Sachs Disease
* PKU (Phenylketonuria)
* Describe (cystic fibrosis)
* Alkaptonuria
* Albinism
* PKU (Phenylketonuria)
* Describe (cystic fibrosis)
* Alkaptonuria
* Albinism
34
New cards
Progeria
* genetic disorder that causes accelerated aging in children. It is caused by a mutation
* dominate allele
* dominate allele
35
New cards
Huntington’s
* degeneration of nervous system that causes loss in muscular control and cognitive abilities
* dominate allele
* dominate allele
36
New cards
Hypercholesterolemia
* high levels of cholesterol accumulation in the blood
* dominate allele
* dominate allele
37
New cards
Name all dominate autosomal diseases (3)
* Progeria
* Huntington’s
* Hypercholesterolemia
* Huntington’s
* Hypercholesterolemia
38
New cards
What does DNA stand for
Deoxyribo==nucleic== %%acid%%
39
New cards
Who is Hammering and what did he figure out?
* In 1930 Hammering found out that genetic information is found in the nucleus
* Before that scientist had no idea DNA held genetic information
* Before that scientist had no idea DNA held genetic information
40
New cards
What happened in 1952
* Hershey and chase experiment confirmed that DNA carried genetic information
41
New cards
What is the basic unit of Dna
* Nucleotide
42
New cards
What are nucleotides made up of
* Sugar (deoxyribose)
* nitrogenous base
* Phosphate
* nitrogenous base
* Phosphate
43
New cards
What are the 4 different types of bases
* Adenine (A)
* Thymine (T)
* Cytosine (C)
* Guanine (G)
A+T (%%**A**%%pple grow on %%**T**%%rees)
C+G (%%**C**%%ars go in %%**G**%%rudges)
* Thymine (T)
* Cytosine (C)
* Guanine (G)
A+T (%%**A**%%pple grow on %%**T**%%rees)
C+G (%%**C**%%ars go in %%**G**%%rudges)
44
New cards
Describe this photo
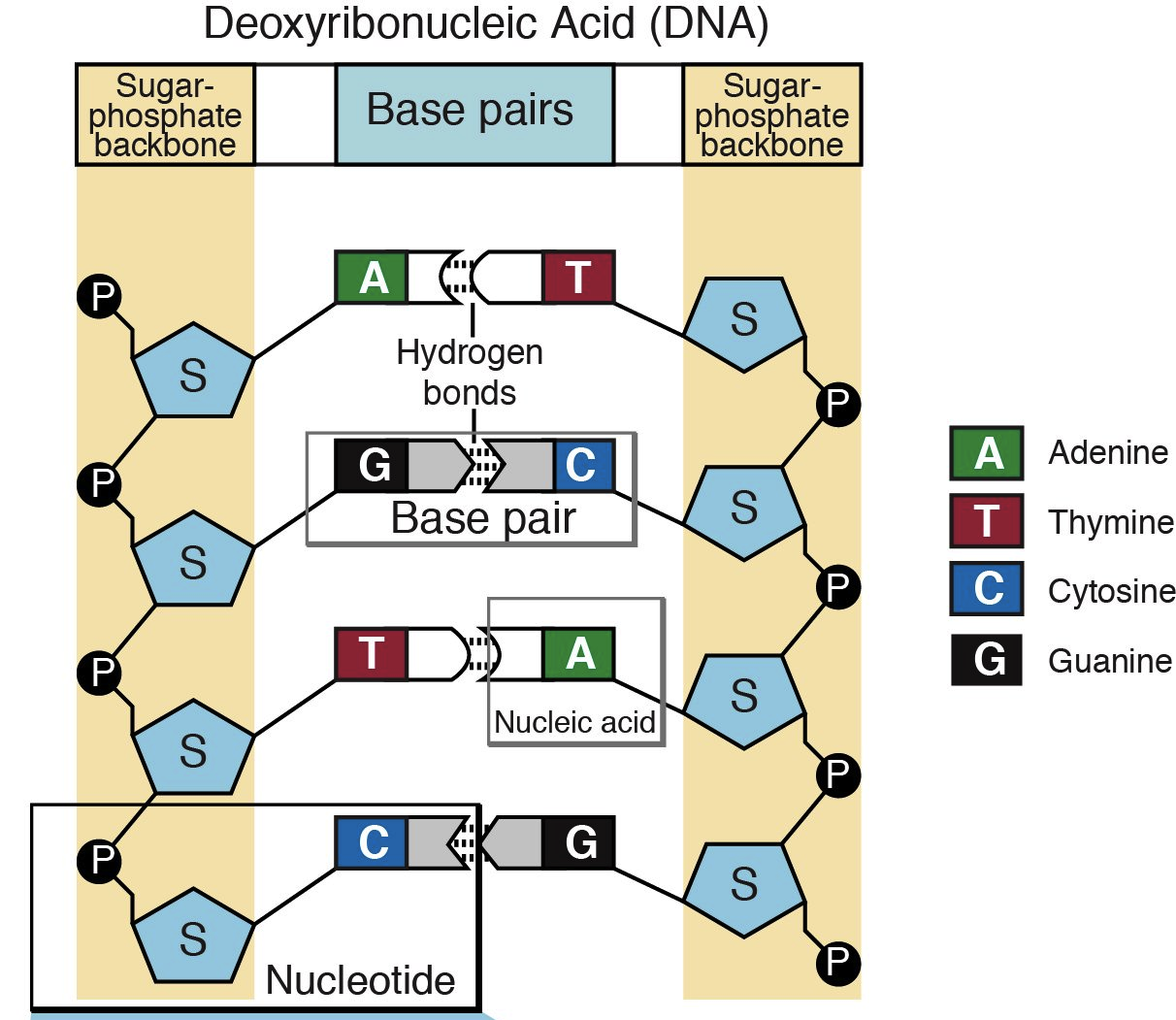
45
New cards
What are mutations?
* Changes to the gene or even chromosome.
* Can be helpful, harmful or have no impact depending on the location of the mutation and the impacts it could have
* Can be helpful, harmful or have no impact depending on the location of the mutation and the impacts it could have
46
New cards
Describe the three types of point mutations.
* %%substitution%% - one nucleotide is substituted for another
* %%insertion%% - an extra nucleotide(s) is inserted into a sequence of nucleotides
* %%deletion%% - a nucleotide(s) is removed from a sequence of nucleotides
* %%insertion%% - an extra nucleotide(s) is inserted into a sequence of nucleotides
* %%deletion%% - a nucleotide(s) is removed from a sequence of nucleotides
47
New cards
How does DNA make a protein
* the information in the sequence of DNA nucleotides is read by ribosomes that make proteins.
48
New cards
Which do you think is more devastating, a point mutation or a chromosomal mutation?
* chromosomal mutation because it impacts 100s or 1000s of genes whereas a point mutation is an error in one gene.
49
New cards
Compare animal mitosis and plant mitosis
Animal:
* have centrioles to organize spindle fibers
* forms a cleavage furrow when becoming two daughter cells
Plant:
* no centrioles so microtubles organize the spindle fibers
* forms a cell plate when separating into two daughters cells
* have centrioles to organize spindle fibers
* forms a cleavage furrow when becoming two daughter cells
Plant:
* no centrioles so microtubles organize the spindle fibers
* forms a cell plate when separating into two daughters cells
50
New cards
mitosis
* body cells dividing to two identical daughter cells
51
New cards
meiosis
* production of gametes (sex cells) that are genetically unique
52
New cards
gamets
* haploid
* haploid
reproductive cells (sperm/egg)
* haploid 1n (one set of chromosomes)
* haploid 1n (one set of chromosomes)
53
New cards
diploid
carries 2 sets of chromosomes (parents)
* 2n
* 2n