Kinesiology - Intro to Anatomy, Osteology, Joints
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Kinesiology
human movement across all dimensions
Kinematics
examines space and time of movement without regards to involved forces
Kinetics
examines forces involved
Linear Motion
translational; all points move the same distance at the same time
Angular Motion
rotational motion; all points move about the same angle
Statics
systems not moving or at a constant speed
Dynamics
systems thar are moving/accelerating
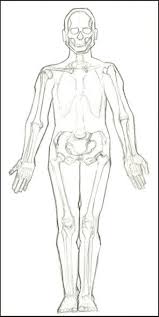
Anatomical Position - body erect, head forward, arms hanging down
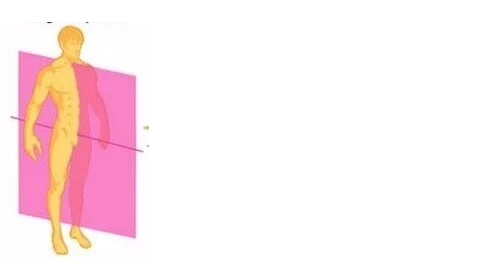
Saggital
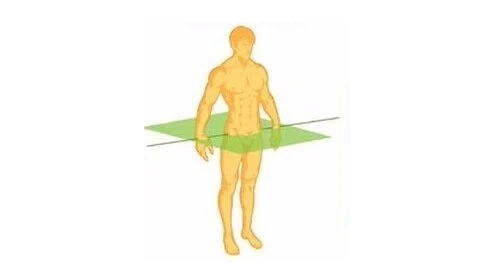
Transverse

Frontal
What axis of rotation is perpendicular to Transverse Plane?
Longitudinal Axis
What axis of rotation is perpendicular to Sagittal Plane?
Mediolateral Axis
What axis of rotation is perpendicular to Frontal Plane?
Anteroposterior Axis
Flexion
decreasing joint angle
Extension
increasing joint angle
Abduction
moving away from the midline
Adduction
moving toward the midline
Lateral flexion
aka side bending; head and trunk only
Circumduction
multiplanar movement
Functions of Skeletal System
Structure, movement, protection, mineral storehouse, blood cell production
Example of long bone
tibia
Example of short bone
carpals
Example of flat bone
sternum
Example of irregular bone
sacrum
Example of sesamoid bone
patella
Bone composition (water)
25-30%
Bone composition (minerals)
60-70%
What minerals are in bone?
calcium phosphate and collagen
What does calcium phosphate help in?
density
What does collagen help in?
tension resistance, bending, twisting
Function of osteoblasts?
build bone
Function of osteoclasts?
carve/breaks down bone
Function of osteocytes?
maintains bones
What are the bone tissues?
Cortical and Travecular
Function of Cortical tissue?
compact; very dense; high bone mass; outer shell of long bones
Function of Trabecular bones?
cancellous; porous and spongy; end of long bones; not very dense
Internal factors bone can adapt to?
hormone levels, calcium concentrations
External factors bones can adapt to?
mechanical loads
Bone remodeling
resorption and replacement of bone
Woff’s Law
bone can structurally adapt to repaired imposed focus placed upon it
Stress
force per unit area
Strain
resulting deformation
Elastic response?
returns to original shape after load is removed
Plastic loading?
loading past yield point
What happens after continued loading?
Fracture
What happens after the load is removed
permanent deformation
Viscoelastic
stretch, spring back, resist motion, absorb energy
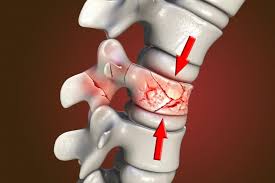
Compression
ends of bones are pressed
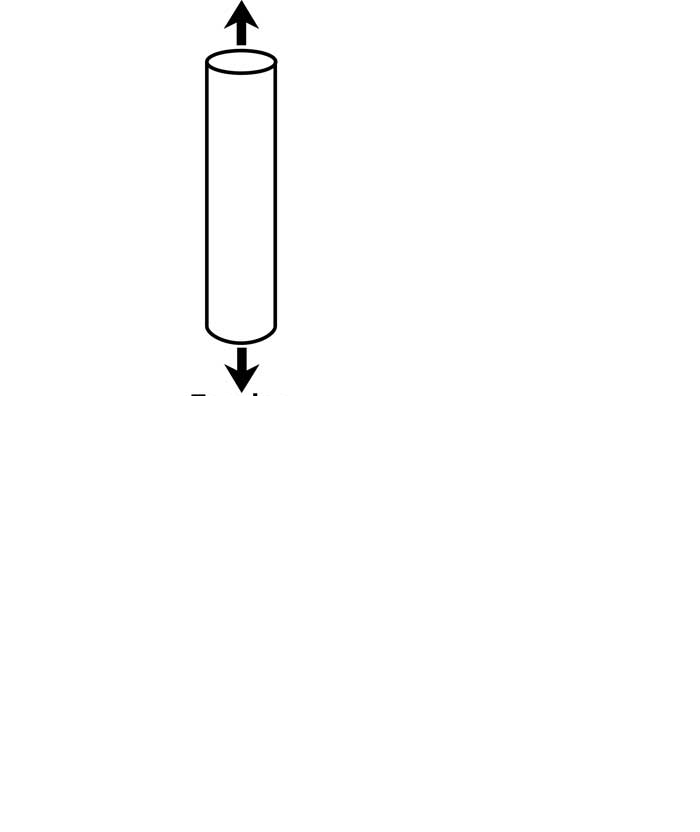
Tension
ends are stretched
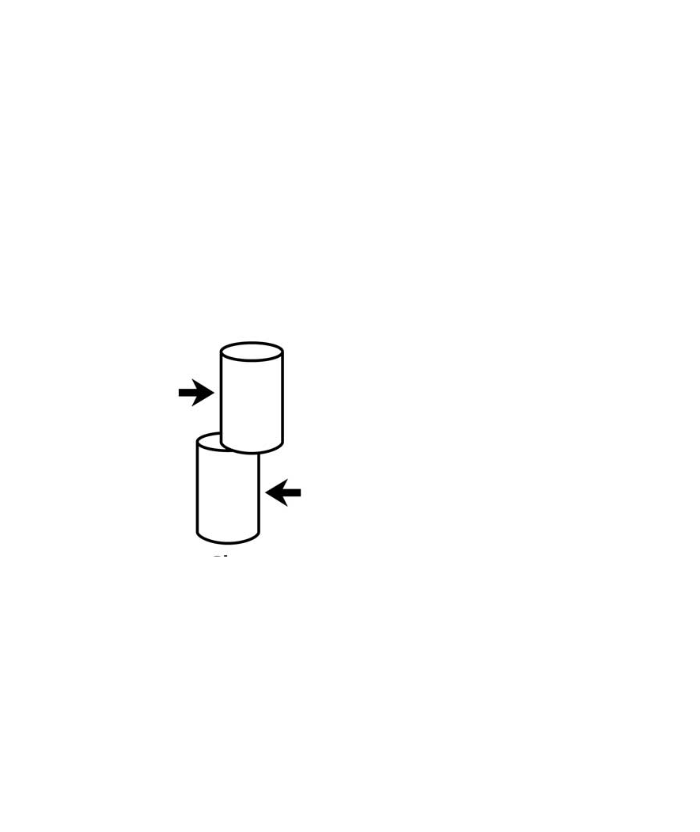
Shear
parallel
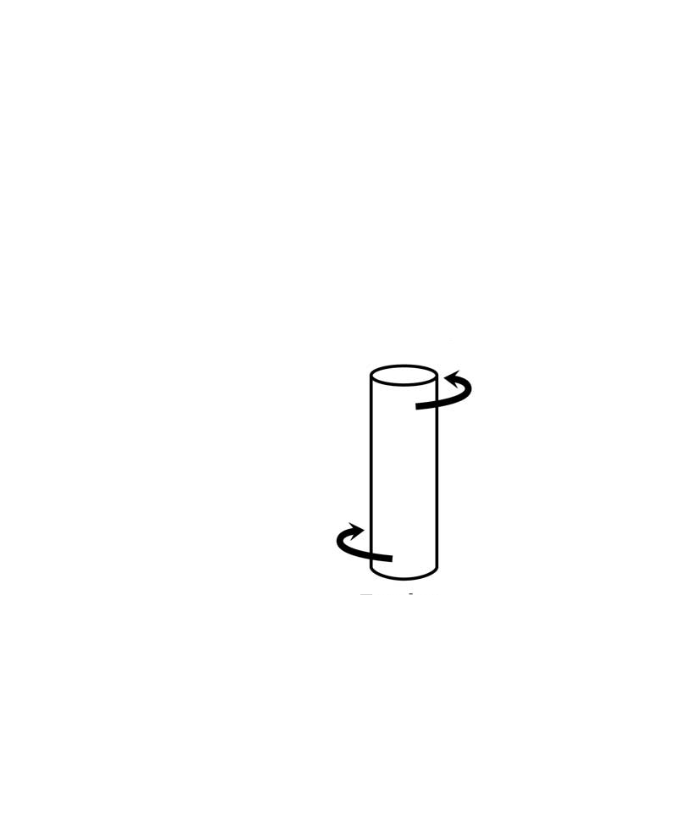
Torsion
twisting face

Bending
no direct support
What does high rate of loading do?
higher risk of injury
What do bones need to grow and strengthen?
Mechanical stress
Where do stress fractures come from?
repetitive muscles forces pulling on the bone; muscle fatigue
Effect of little exercise on bone health?
loss of bone mass
Proper diet to maintain bone health?
calcium, vitamin D/C, low sugar/fat intake, dietary protein
Osteopenia
mild bone loss (lower bone density)
Osteoporosis
severe bone loss
What demographic is the increased risk of osteoporosis?
post-menopausal women
Tendon
connective tissue that connects muscle to bone; parallel arranged; transmits muscle force to bone to produce movement; stronger
Ligament
connective tissue that connects bones to bones; irregularly arranged; resists tensile forces; loading it makes it stronger and stiffer
Joint stability:
reisstance to dislocation
Joint mobility:
range of motion
Synarthroses
no joint movement
Amphiarthroses
limited movement
Diarthroses
free movements
Fibrous
bound by collagen fibers; little/no movement
Cartilaginous
bound by cartilage; no joint cavity
Synovial
most common; in the hip, knee, ankle, hip, ankle, shoulder, elbow, wrist
Cartilage
firm, flexible tissue; nourished by synovial fluid
What happens due to cartilage having no blood supply?
harder for recovery
Articular/Hyaline cartilage
covers joint ends at articulations; 60-80% water, collagen, and proteoglycan
Fibrocartilage
at the meniscus and labrum; synovial fluid and blood vessels in the outer region; reduce friction at the body’s stress point
Joint movements
gliding, angular and rotational movements
Gliding Joint
opposing flat or slightly curved surfaces; on one another; no axis of rotation
Hinge Joint
angular motion about a fixed axis
Pivot Joint
uniaxial; axis runs longitudinally along a bone
Ellipsoidal Joint
unstable joints formed by articulation of a shallow convex surface of one bone with concave surface of another
Saddle Joint
one bone sits on another
Ball and Socket Joint
rounded end housed in a depression
Arthritis
inflammation of a joint
Osteoarthritis
hyaline articular cartilage breakdown —> degenerative
Rheumatoid Arthritis
autoimmune condition; inflammation of the synovium
Effect of close packed position of joint
max stability
Effect of loose packed position of joint
articular surfaces are in minimal contact