A&P 2 - Unit 1
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
151 Terms
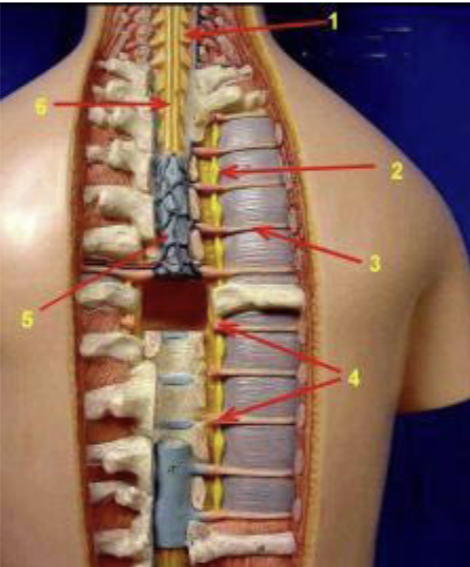
ID the structure indicated by 1
Spinal nerve
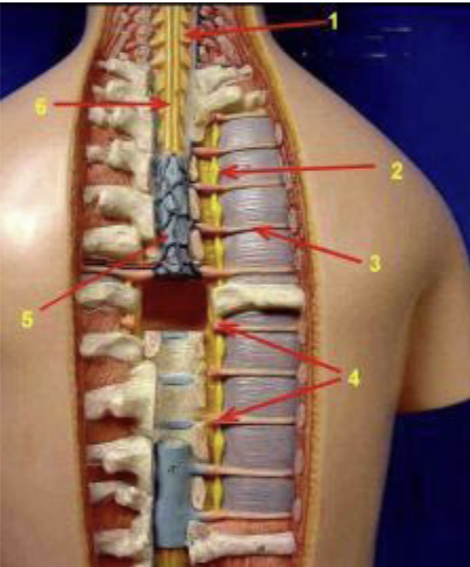
ID the structure indicated by 6
Spinal cord
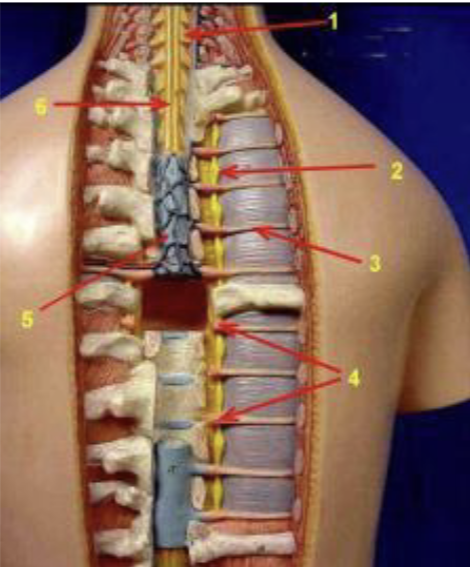
ID the entire region in the image
thoracolumbar region
Cells that have specific receptors for a hormone are called __________.
target cells
The nervous system affects target organs through the release of chemicals called _____________.
neurotransmitters
Regulating ______ composition is a function of the endocrine system.
blood
Controlling ________ is a function of the endocrine system.
metabolism
Overseeing __________ functions is a function of the endocrine system.
reproductive
The endocrine system releases chemical messengers called ________ into the bloodstream
hormones
Testosterone is a ________ hormone.
steroid
Prostaglandins are local, autocrine, or _________ hormones.
localized
Most hormones are transported in the ________ to their target.
bloodstream
Hormones can be released as a direct response to ________, humoral, and hormonal simuli.
neural
Steroid hormones are a type of lipid derived from ___________.
cholesterol
Lipid-soluble hormones travel in the blood joined to a protein carrier and thus are called ______ hormones.
bound
Hormones that are transported in the blood are released from _________ _______.
endocrine glands
___________ and ___________ are the two factors that affect the concentration of a circulating hormone.
Synthesis; elimination
To eliminate them from the bloodstream, hormones have to be _________ by the kidneys or _______ by enzymes.
excreted; degraded
Because of their structure, lipid-soluble hormones bind to the receptors of target cells ______ the cell.
inside
The more receptors a cell has for a hormone, the _____ sensitive it is to that hormone
more
Because of their structure, water-soluble hormones bind a receptor on the cell membrane initiating a series of biochemical events across the membrane known as a _______ transduction pathway.
signal
The gland that is also known as the hyophysis is the ________ gland.
pituitary
The pituitary gland is connected to the hypothalamus through a thin stalk called the _____________.
infundinulum
A hormone secreted by the hypothalamus is _____________-_______ ______.
corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
The parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland synthesize and release __________.
calcitonin
The full name of the hormone T4 is __________.
thyroxine
__________ lowers blood calcium leverls.
Calcitonin.
The outer region of the adrenal gland is the cortex, within which lies the inner region called the adrenal ________.
medulla
Hormone that directly stimulates the adrenal cortex to release cortisol.
ACTH.
The pineal gland releases this hormone.
Melatonin.
A hormone that helps set the internal biological clock.
Melatonin.
The thymus is located in the _________ cavity.
thoracic
In T3 the 3 refers to the number of ______ molecules in the hormone.
iodine
Secretin is released by enteroendocrine cells in response to changes in pH. How would
you classify the mechanism of release?
Humoral stimulus
Growth hormone releasing hormone is released by the hypothalamus and stimulates
target cells in the anterior pituitary to release growth hormone. How would you classify
the mechanism of release?
Hormonal stimulus.
Preganglionic cells of the sympathetic nervous system trigger the release of epinephrine
from Chromaffin cells in the adrenal medulla. How would you classify the mechanism of
release?
Neural stimulus.
Tropic hormone.
A hormone that triggers the release of another hormone.
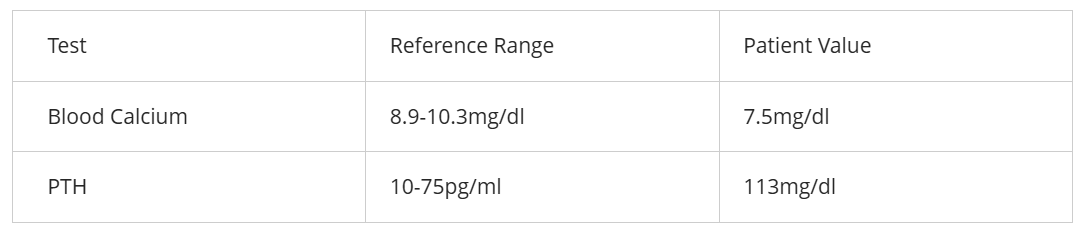
Based on the lab values above, we are likely looking at a _________________, and it would be considered a disease of ______________________
secondary disease; hyposecretion.
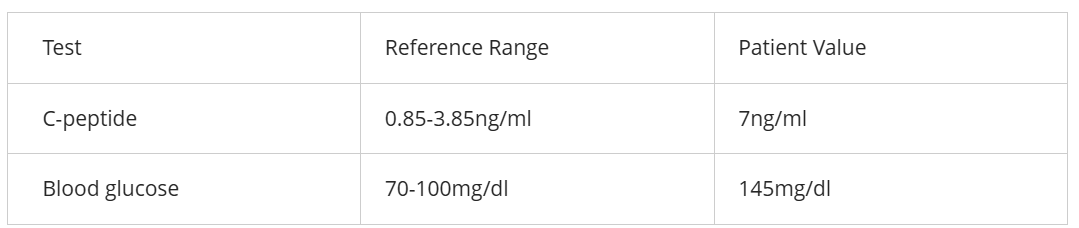
This patient is suffering from type ____ diabetes and _____ and _________ would be valuable in their treatment
II; diet and exercise.
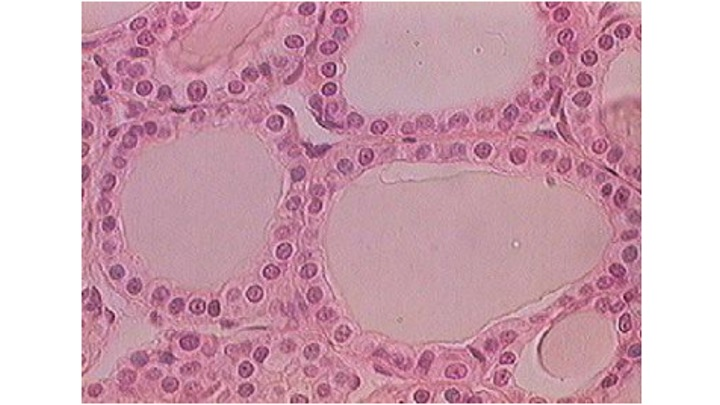
This tissue being destroyed by an autoimmune disease would cause the patient to…
suffer from a drop in metabolism, feel fatigued, and gain weight (thyroid tissue).
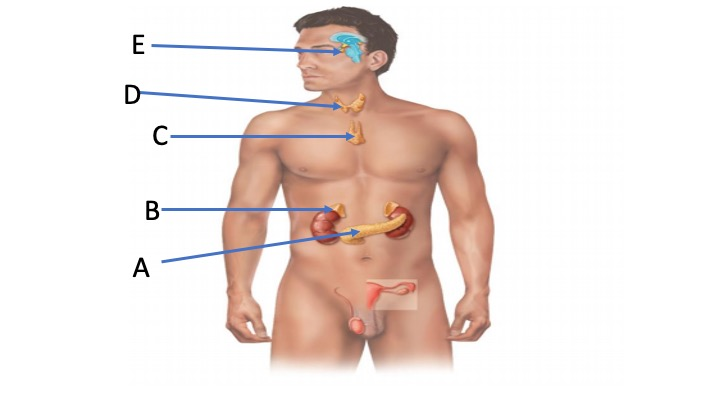
ID the gland indicated by A
Pancreas
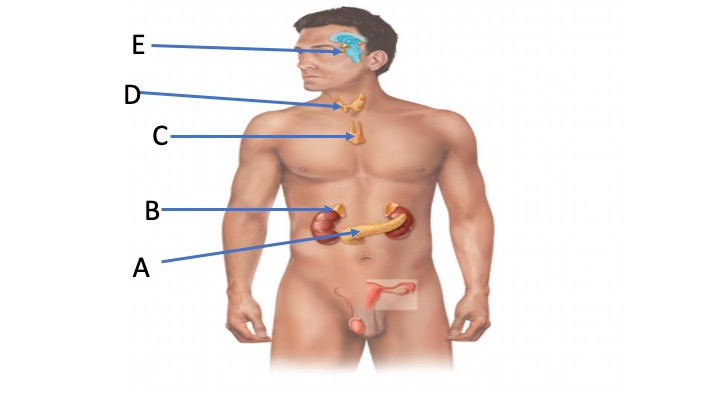
ID the gland indicated by B
Adrenal gland
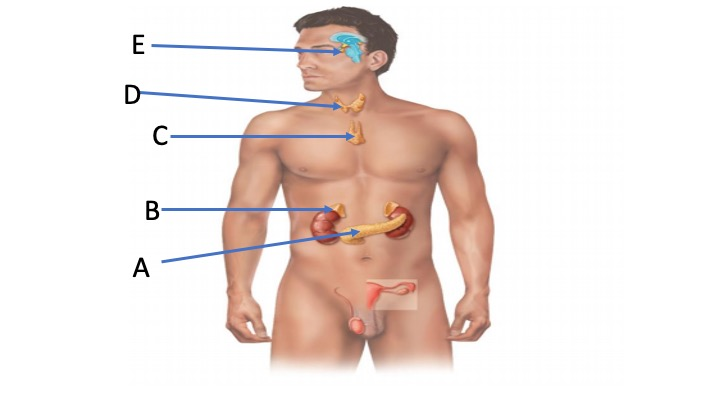
ID the gland indicated by C
Thymus
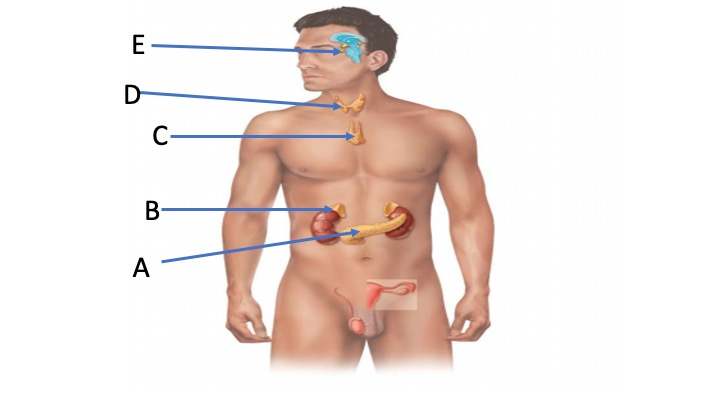
ID the gland indicated by D
Thyroid
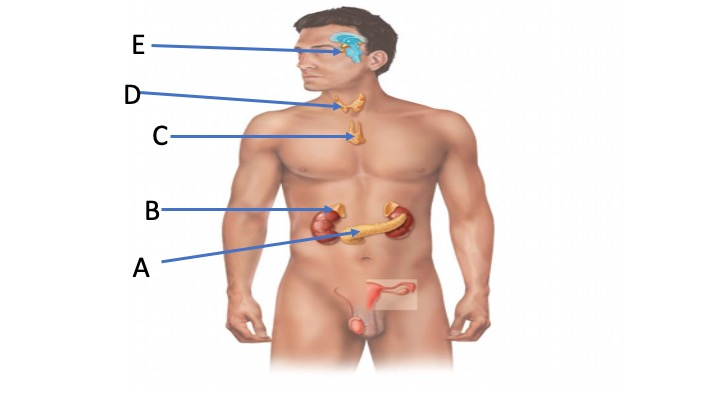
ID the gland indicated by E
Pituitary gland
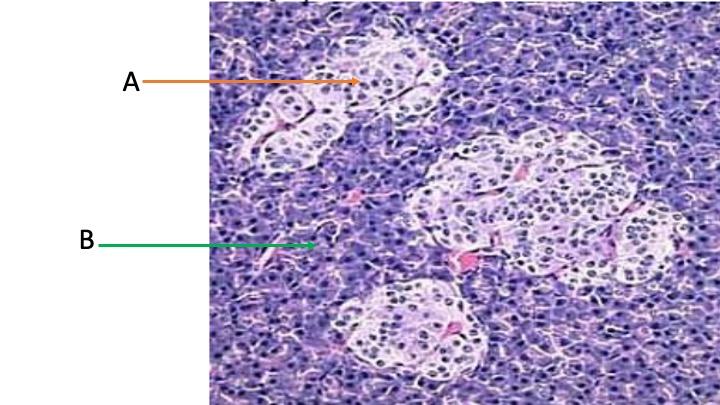
If tissue A was destroyed by a toxin…
Islets of Langerhans would be destroyed, including alpha and beta pancreatic cells.
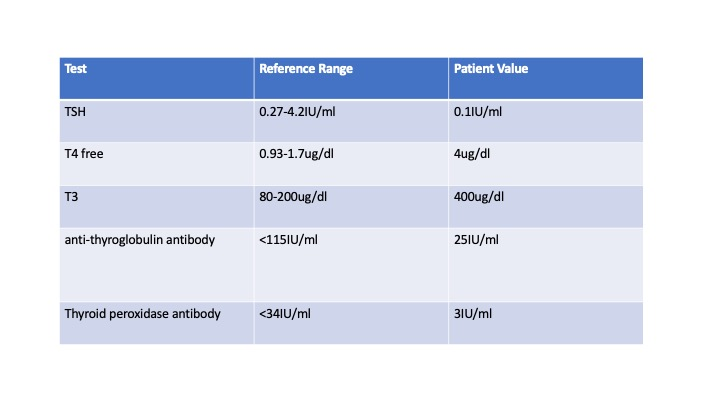
This patient would be suffering from…
A primary endocrine disease of hypersecretion. Patient would be agitated, losing weight, indicative of Graves disease.
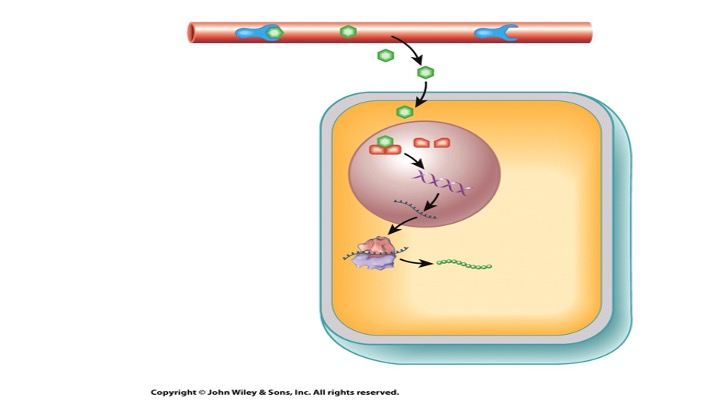
The hormone in the image would be…
lipid soluble, potentially a steroid, such as testosterone.
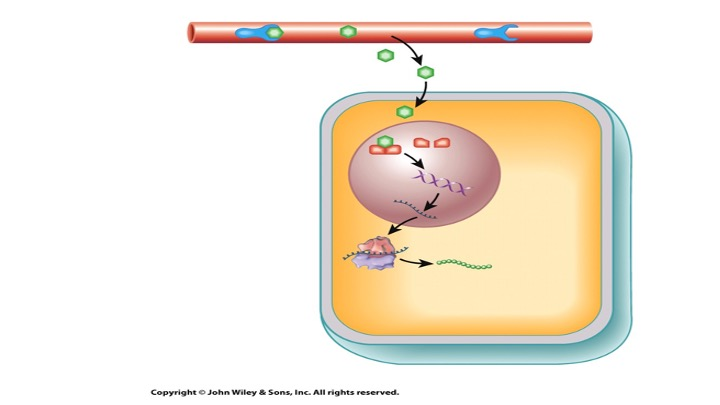
The receptor above would be…
intracellular.
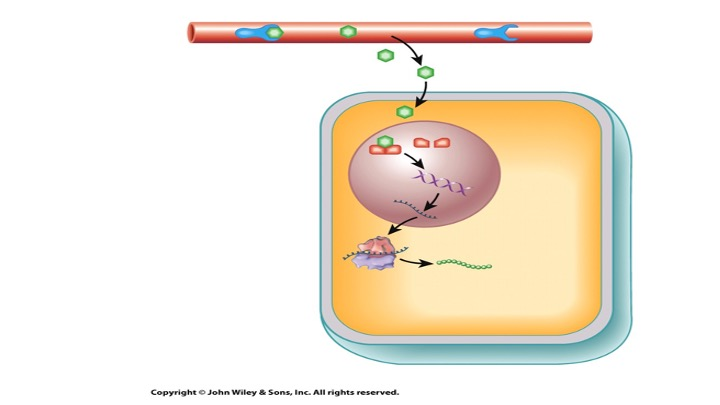
The depicted pathway would happen…
slowly, as it influences gene expression.
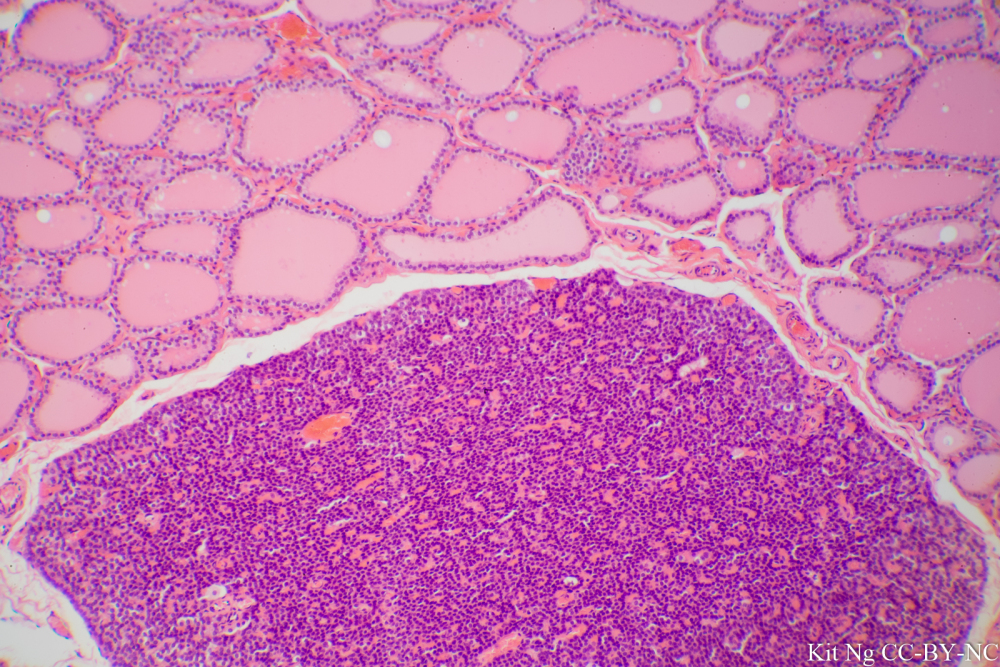
Three cell types in the image include:
Parafollicular cells, follicular cells, and chief cells.
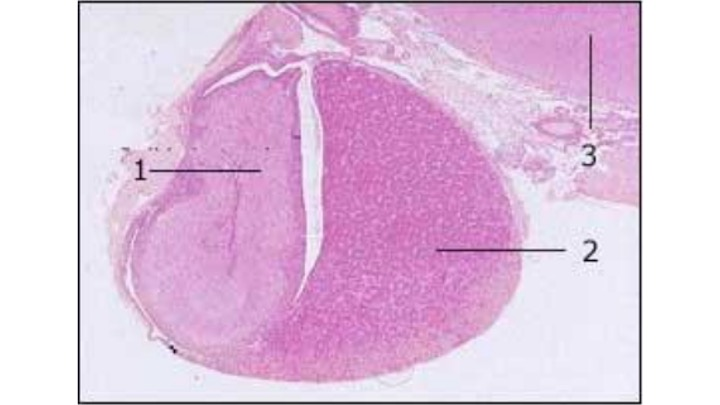
The structure indicated by 1 is the…
Neurohypophysis/Posterior pituitary gland. Releases oxytocin.
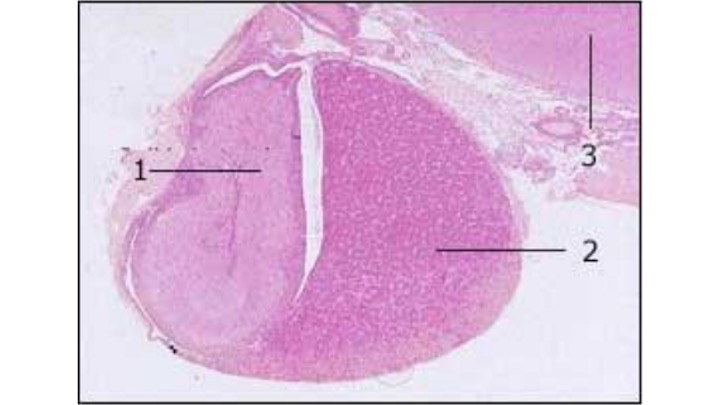
The structure indicated by 2 is the…
Adenohypophysis/anterior pituitary gland. It monitors metabolic levels and releases growth hormone.
A blood clot in the hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system would...
prevent communication with the adenohypophysis.
Question 11
A tumor that compressed and inhibited the function of the paraventricular nuclei....
would interfere with ADH (anti diuretic hormone) release.
A voltage gated Ca2+ channel blocker that targeted beta pancreatic cells would likely......
decrease insulin release.
As we age, our immune function tends to decrease. This is because a key gland begins to atrophy (get smaller). What gland might that be?
The thymus; it plays a critical role in the development of our immune system.
Billy bob has a fasting blood glucose of 107mg/dl. Based on this, Billy would be considered….
prediabetic (range is 100-125mg/dl).
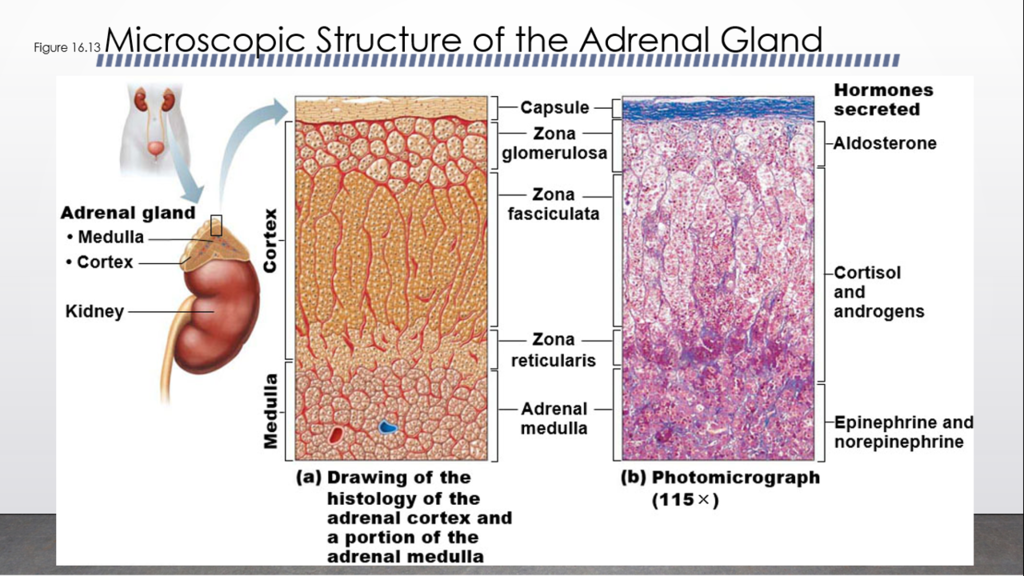
Question 17
Damage to this structure would dramatically lower cortisol levels in the blood.
Zona fasciculata.
Hormones released by the hypothalamus are considered ___________________ and often end with__________________________.
tropic hormone; releasing hormone.
In a healthy person, 30 mins after eating ice cream you would expect insulin levels to be _____ and glucagon to be _____.
low; high.
In a metabolically healthy person, a glucose spike would cause insulin to be released resulting in the insertion of _________ transporters into ___________ _______ __________ and ________ __________.
GLUT4; skeletal muscle tissue; adipose tissue.
Question 22
Intravenous (IV) glucose administration would produce and insulin response that is _________ to that of oral glucose administration.
lower; IV administration bypasses the gut, where incretins tell the body to produce significantly more insulin.
Once glucose enters into any cell in the body it is.....
burned in the presence of oxygen to create ATP (cellular respiration).
Question 24
The most insulin will be released in response to a…
humoral stimulus (blood glucose).
The primary role of melatonin is to promote…
sleep.!
The primary target of glucagon is…
the liver (breaks glycogen into glucose).
The process in which DNA is used to make mRNA is called _____________________ and takes place in the ________________________.
transcription; nucleus.
The stimulus for the release of PTH (parathyroid hormone)
Low blood Ca2+.
Question 29
The stimulus for the release of thyroid hormone (T3 and T4)
A decrease in thyroid hormone concentrations.
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Released by anterior pituitary gland in response to TRH; tropic hormone; triggers release of T3 and T4
When dehydrated, blood concentration…
increases.
When dehydrated, blood becomes ____________ to neurons.
hypertonic
When dehydrated, Na+ channels on osmoreceptors are…
open.
When dehydrated ______ hormone is released.
ADH
When a developing fetus gets large enough, it will produce stretch on the cervix…
which releases oxytocin; positive feedback pathway takes place.
When growth hormone binds to cells in the liver it....
triggers release of insulin like growth factor (ILGF of IGF-1).
____________ is necessary for Thyroid hormone synthesis.
Iodide
A ___________ _________ could influence prolactin release.
dopamine agonist
A patient who is ________ has trouble regulating melatonin release.
blind; they cannot retrieve stimulus from light cues to regulate sleep cycle properly.
Type 2 diabetes is classified as a disease of…
insensitivity.C
Chronic stress may elevate…
cortisol levels.
Neurons in the hypothalamus do/don’t come into contact with the blood.
do
-cyte
Suffix for medical terminology of cell.
Blood
Delivers nutrients and oxygen to and around your body. Consists of formed elements and plasma.
Blood plasma and interstital fluid have similar concentrations of…
electrolytes, waste products, and nutrients
Erythrocyte
Medical term for RBC. Transports oxygen and carbon dioxide; myeloid
Albumins
Proteins that exert the greatest colloid osmotic pressure to maintain blood volume, blood pressure, and especially fluid balance in the cardiovascular system
The only formed elements that are nucleated when mature are
leukocytes.
The temperature of the blood is about ________ than body temp. when measured.
1 degree Celsius higher
Hemocytoblasts
Cells in the bone marrow that all formed elements are derived from
Erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets
The general classes of the cell components of whole blood
Protein
The plasma component least likely to be present in the same amount in interstitial fluid
Formed elements
what platelets and erythrocytes are more correctly called rather than cells, as platelets are cell fragments and erythrocytes aren’t nucleated.
Bright red blood
Oxygenated blood, scarlet red.
Dark red blood
Hypo-oxygenated blood, deep red.
Multipotent stem cell
bone marrow cell from which all formed elements are derived because it can differentiate into many different kinds of cells.
Blood’s bright red color is because…
oxygen bound to hemoglobin gives it that color
Alpha chains/Beta chains
Two of each polypeptide chain (globins) comprises a hemoglobin molecule
Blood plasma
Transports electrolytes, waste products, nutrients; dissolved ions; hormones; alpha and beta globulins