Ap Macroeconomics Unit 4 Study Guide
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
what is the relationship between interest rate and interest sensitive spending
inverse relationship
liquidity
the ease with which an asset can be converted to a medium of exchange
bonds
loans or IOUs that represent debt that the govt., business, or individual must repay to the lender
stocks
represent ownership of a corporation and the stockholder is often entitled to a portion of the profit paid out as dividends
what is the relationship between bond prices and interest rate
inversely related
formula for real interest rates
real ir = nominal ir- expected inflation
formula for nominal interest rates
nominal ir= real ir - expected inflation
commodity money
something that preforms the function of money and has intrinsic value
fiat money
something that serves as money but has no other value/uses
what are the 3 functions of money
medium of exchange
measure of value
store of value
M0 money (monetary base)
currency in circulation
bank reserves
M1 money
currency in circulation
demand deposits in the bank (checking account and savings account)
M2 money
M1 money
certificates of deposit
money market funds
fractional reserve banking
when the bank holds a portion of deposits to cover potential withdraws and then loans the rest out
formula for money multiplier
1/reserve requirement
when the FED gives money to commercial banks do they have to keep required reserves
no, they do not have to keep any reserves they can loan it all out
relationship between interest rate and quantity of money demanded
inverse relationship
money market graph
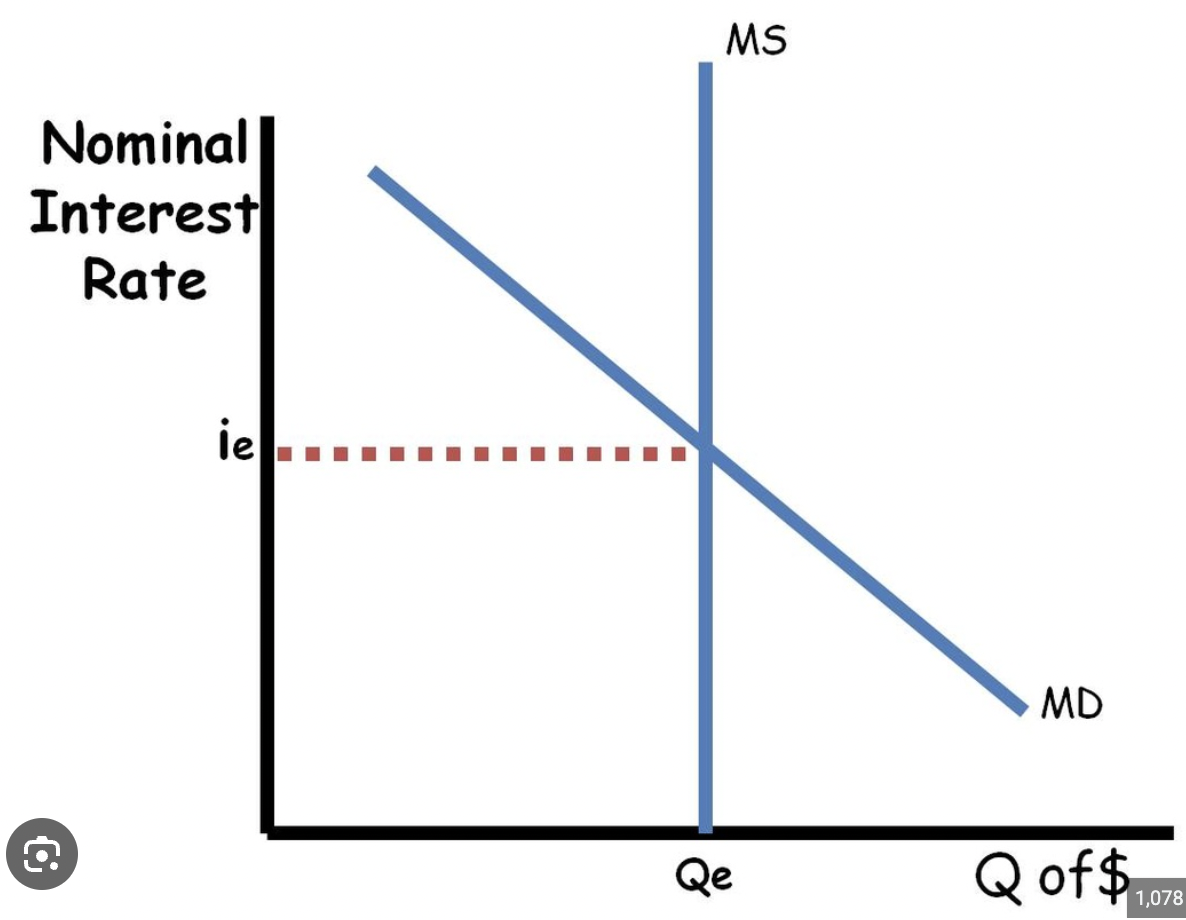
money demand shifters
changes in price level
change in income
change in technology
what monetary policy does the FED use to adjust money supply in limited reserves
reserve requirement ratio
amount commercial banks need to keep in reserves
discount rate
interest rate the FED charges commercial bank
inverse relationship between MS and DR
open market operations
buying and selling bonds
buy big, sell small
federal funds rate
the interest rate that banks charge one another for one day loans of reserve
monetary policy the FED uses to adjust monetary supply in ample reserves
Administered rates like interest on reserves
the interest rate that the FED pays commercial banks to hold reserves
IOR and MS have an inverse relationship
increase IOR to slow economy
decrease IOR to boost economy
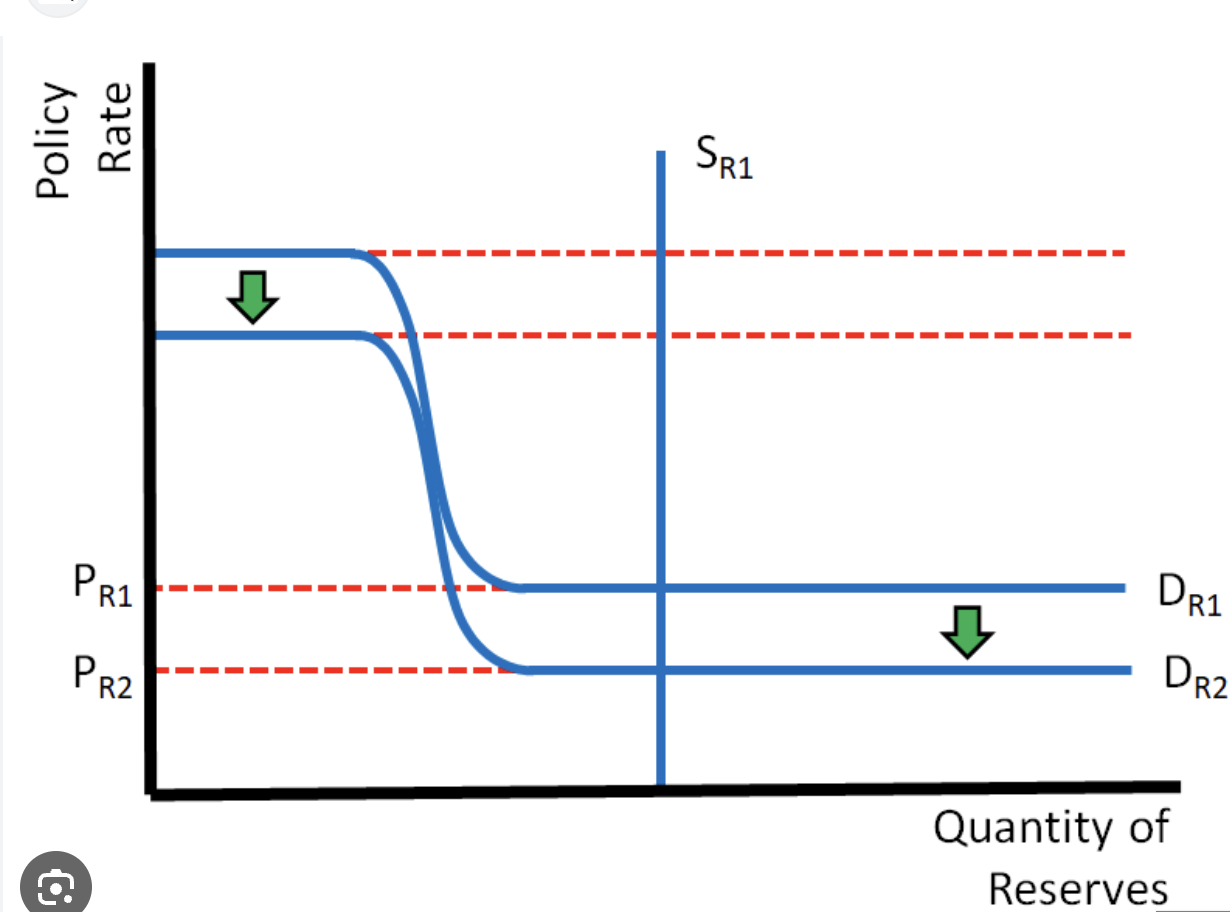
reserve market model
top line
represents the discount rate
bottom line
represents IOR
middle section
represents federal funds rate
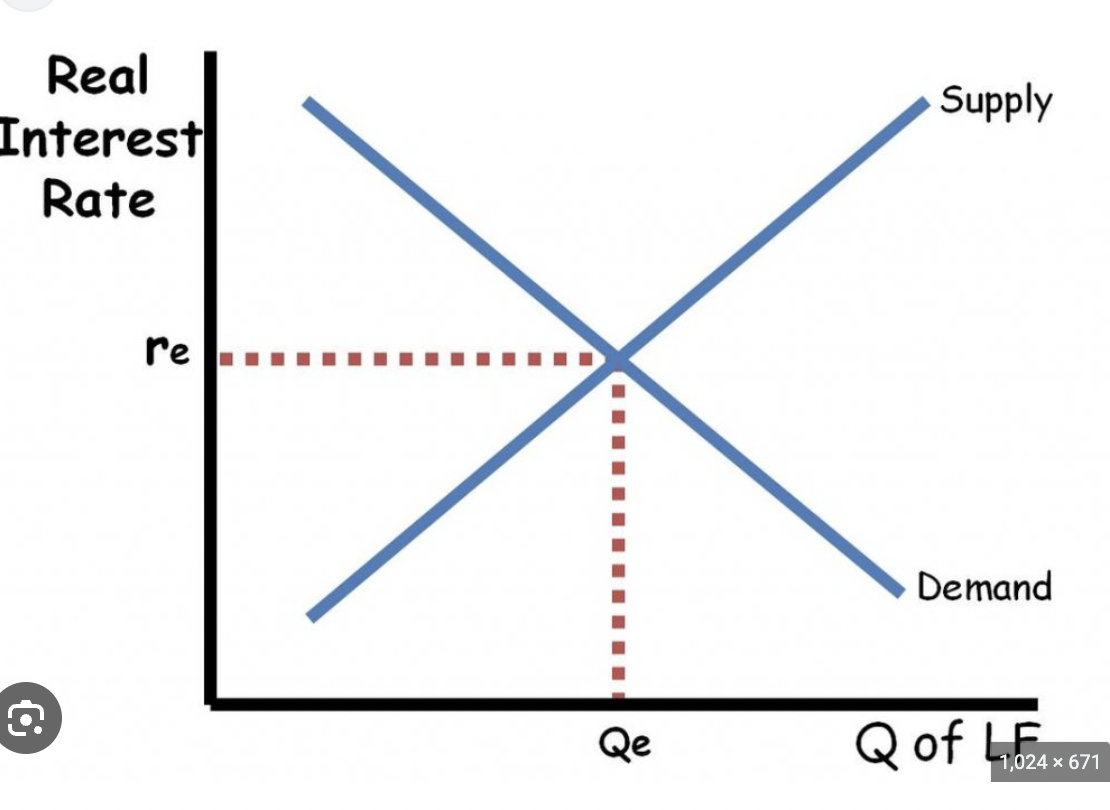
loanable funds market
supply (lenders)
shifts by change in inflow/outflow
demand (borrows)
shifts by change in borrowing