GI Autonomic Nervous System
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
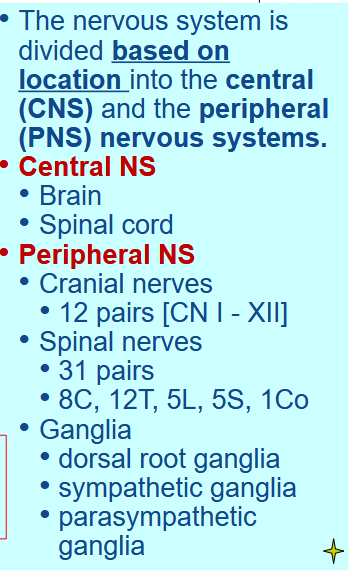
[REVIEW] CNS and PNS
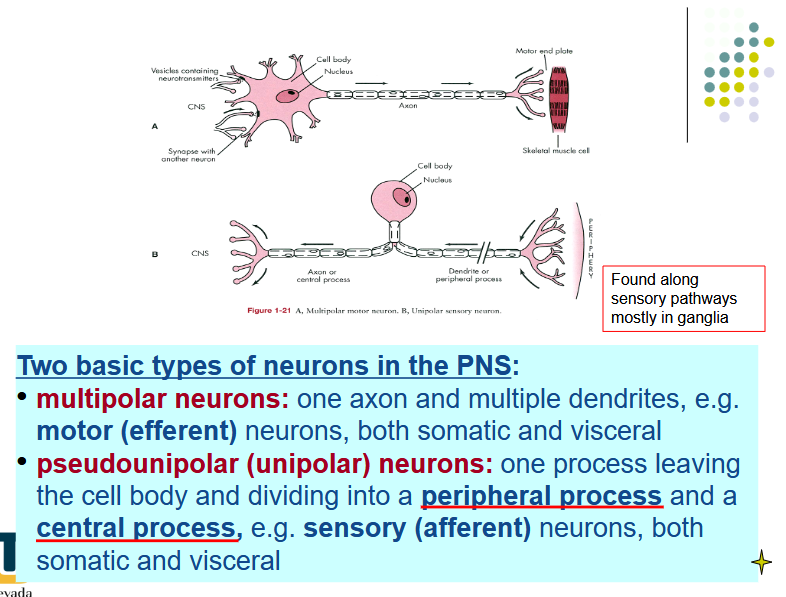
[REVIEW] Multi vs pseudounipolar neurons
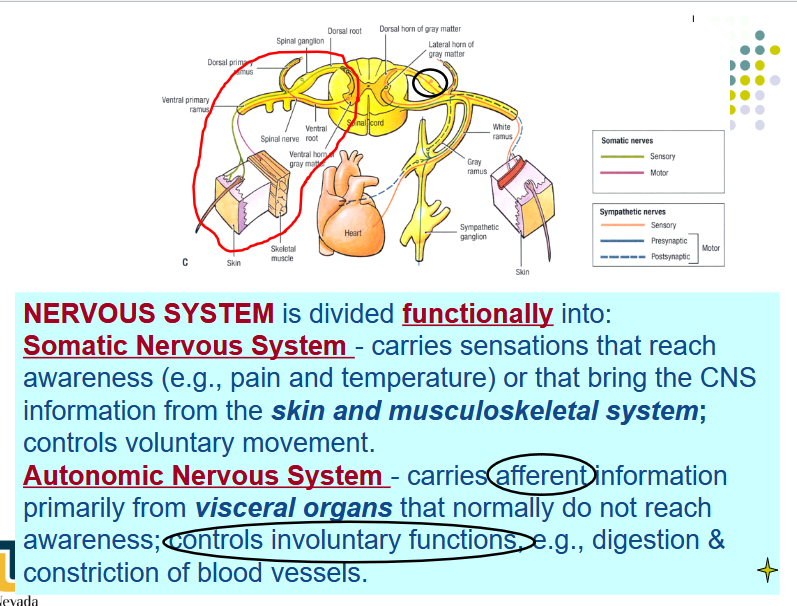
[REVIEW] Somatic vs Autonomic Nervous System
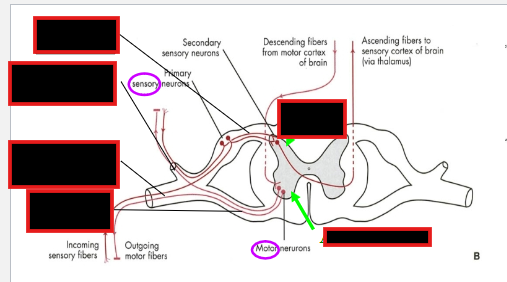
Describe the location of these neurons’ cell bodies in the somatic system:
Pseudounipolar
multipolar
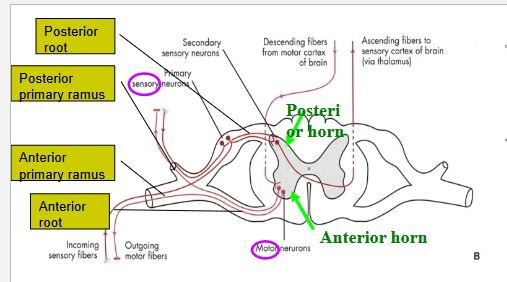
Differentiate between the posterior and anterior primary ramus
Pseudounipolar neurons:
dorsal root ganglion with the central process in the dorsal
root and the peripheral process in the spinal nerve
Multipolar neurons:
anterior/ventral horn with their axons contributing to
the spinal nerve and the ventral or dorsal rami.
Dorsal vs Ventral Primary Ramus:
posterior (dorsal) primary ramus: back
anterior (ventral) primary ramus: anterolateral body wall and the extremities.
[REVIEW] Sympathetic vs Parasympathetic
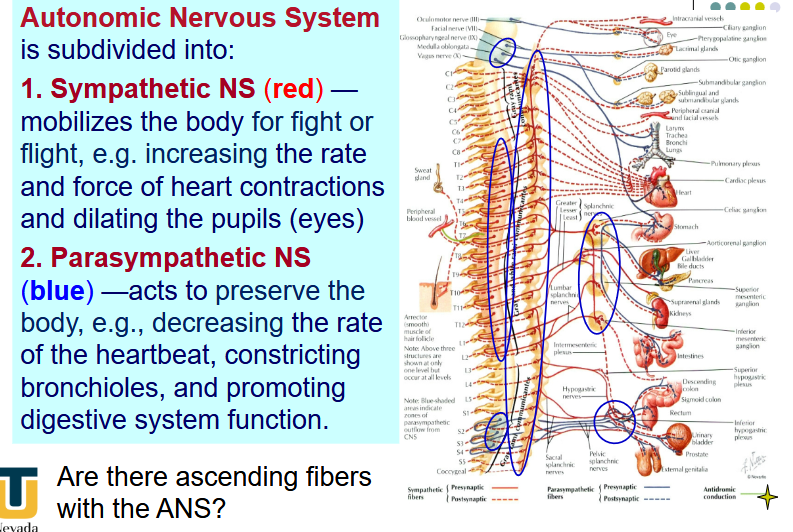
Where are the preganglionic neuronal cell bodies of the parasympathetic division?
Where are these fibers never found in?
PNS:
Cell bodies in brainstem nuclei and S2-S4
parasympathetic fibers are never found in the body wall and limbs.
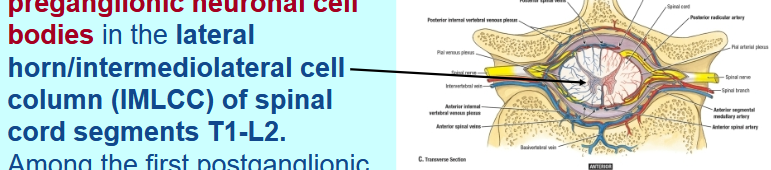
Where are the preganglionic neuronal cell bodies of the Sympathetic division?
What is the first postganglionic target?
Lateral horn/intermediolateral cell column (IMLCC) of spinal cord segments T1-L2.
Among the first postganglionic targets are series of interconnected ganglia on each side of the vertebral column - paravertebral sympathetic trunk
[REVIEW] Describe the path of the Visceral Efferent Fibers (sympathetic)
General path
Path towards skin and blood vessels
Thoracic Cavity
Abdominapelvic Cavity
Describe the path of Visceral Afferent Fibers
Visceral efferent fibers:
Cell bodies @ IMLCC → Ventral Root → Spinal N → Ventral Rami → White Rami communicates → sympathetic ganglia (can synapse or pass through)
To Glands of Skin and SM of blood vessels: From sympathetic trunk → Gray Rami → ventral rami
Thoracic Cavity: Synapse @ Sympathetic paravertebral ganglia
Abdominaopelvic Cavity: No Synpase @ Sympathetic Trunk → Pass through Sympathetic Trunk as abdominolpelvic splanchnic nerves( preganglionic fibers) → Synpase @ prevertebral ganglia around aorta branches
Visceral Afferent Fibers:
accompany visceral efferent fibers from the visceral organs to the spinal nerve; their cell bodies are found in the posterior/dorsal root ganglia.
Describe the generalization explaining the NS of the Digestive System
The digestive system and other abdominal organs are innervated by autonomic nerve fibers from both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems
Nerve fibers travel along blood vessels to reach their target organs
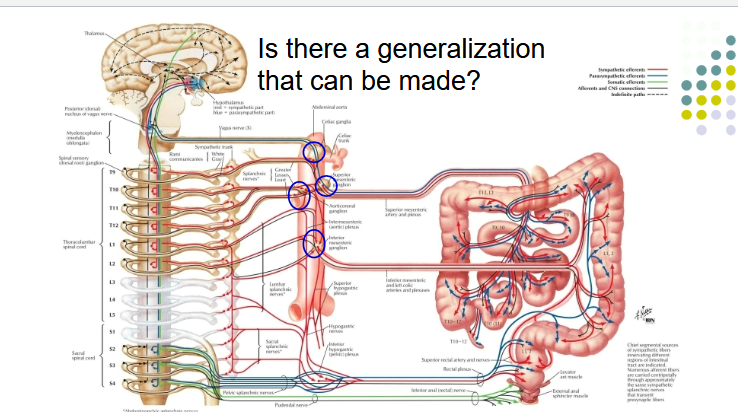


LIst out the prevertebral ganglia for the sympathetic NS
Celiac trunk – celiac ganglia
Superior mesenteric artery – superior mesenteric ganglion
Inferior mesenteric artery – inferior mesenteric ganglio
Describe the pathway of the Parasympathetic NS
Vagus N.: Brain/Spinal Cord → Vagus N. carries Afferent/Efferent (from the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus in the medulla oblongata) → enters abdomen through esophageal hiatus
Pelvic Splanchnic N.:
arise from cell bodies in the spinal cord at S2-S4 in the same area as IMLCC but do not form a discreet structure.
Preganglionic fibers reach the wall of the viscera via mesenteries and synapse with short postganglionic neurons with cell bodies in the wall of the viscera:
Myenteric (Auerbach’s) plexus
Submucous (Meissner’s) plexus
In regards to Hirschsprung disease:
What gene is involved
Why is there dilation?
mutations in the RET gene,
tyrosine kinase receptor involved in neural crest migration
dilation is due to failure of peristalsis in the aganglionic segment
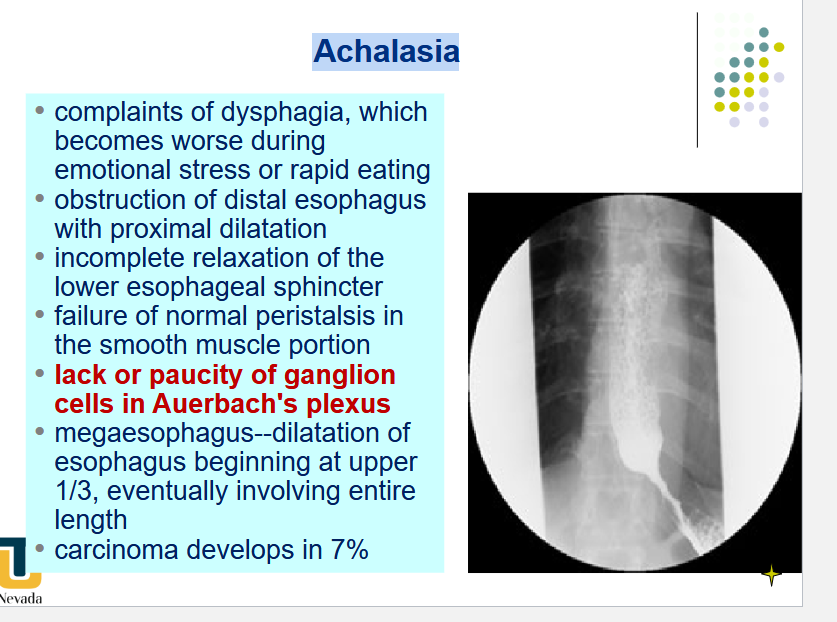
[REVIEW] Achalasia
[REVIEW] Referred Pain
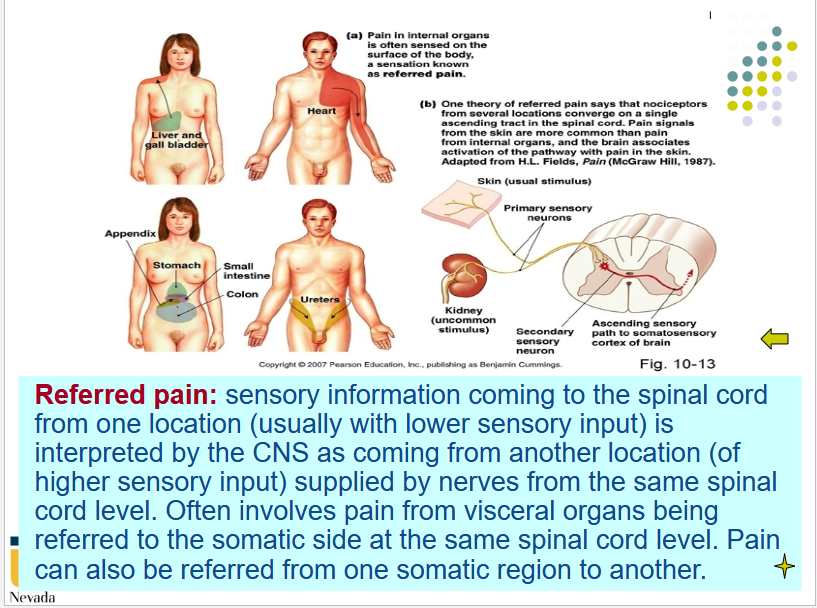
Describe why the pain changes in appendicitis
