3.5.1.6 Electromotive force and Internal resistance
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/8
Last updated 5:29 PM on 2/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
1
New cards
Define electromotive force (e.m.f).
The electromotive force is the amount of chemical energy converted to electrical energy per coulomb of charge (C) when passing through a power supply.
2
New cards
What is e.m.f equal to when no current is flowing?
E.m.f is equal to the potential difference of the cell when no current is flowing.
3
New cards
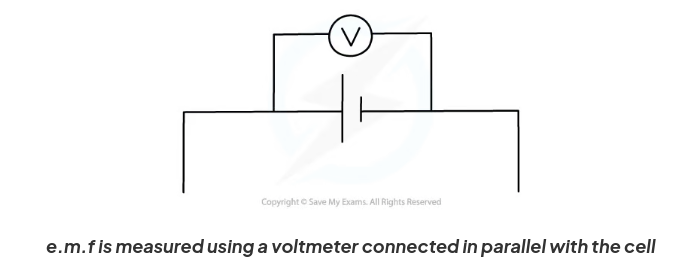
Describe a circuit that can be used to measure e.m.f.
E.m.f can be measured by connecting a high-resistance voltmeter around the terminals of a cell in an open circuit.
4
New cards
What is the terminal potential difference?
The terminal p.d is the potential difference across the terminals of a cell.
5
New cards
Why is the cells terminal p.d always lower than the e.m.f?
A cell’s terminal p.d is always lower than the emf as a cell has internal resistance.
6
New cards
What would the terminal p.d be equal to if there was no internal resistance?
The terminal p.d would be equal to the e.m.f if there was no internal resistance.
7
New cards
Define lost volts.
Lost volts is the work done per unit charge to overcome the internal resistance inside a battery. (The voltage lost in the cell due to internal resistance.)
8
New cards
Define internal resistance.
Internal resistance is the resistance of the materials within the battery.
9
New cards
Why does a cell become warm after a certain period of time?
The internal resistance causes the charge that is circulating to dissipate some electrical energy from the power supply itself hence the cell becomes warm after a period of time.