ryanef123 RPD - Biomechanics in RPD (Quiz 3)
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Define the following:
Study of physical bodies subjected to forces (movements, directions, speed)
mechanics
Define the following:
- The application of mechanical laws to living structures, specifically the locomotor system of the body
- The study of biology from the functional viewpoint
- An application of the principles of engineering design as implemented in living organisms
biomechanics
What are the goals of biomechanics?
- To understand the possible movements of a RPD in response to function (mastication, speech, swallowing).
- To be able to logically design a RPD so that forces resulting from function can be properly distributed between the teeth and the residual ridges.
- Failing to distribute these forces usually lead to complications; either mechanical (fracture of a component of the denture) or biological (bone loss, fracture of a tooth…)
In intact dentition, teeth are subjected primarily to which type of loading?
Axial loading
Support is gained entirely from the ___________ of individual teeth. As might be expected, a similar situation occurs with a properly constructed fixed partial denture
Periodontal ligaments
The mandible is most like what class lever system?
Class III
Which Kennedy Classification is the only one that requires an RPD that is entirely tooth-supported?
Class III (off-axis loading in class III applications is extremely limited)
Why is off-axis loading in Class III RPDs considered extremely limited?
Because forces are directed primarily within the long axes of abutments
What is the key difference between a fixed prosthesis and a removable prosthesis in terms of abutment connection?
Fixed prostheses connect abutments more rigidly
Which Kennedy Classification is a combination tooth-tissue supported prostheses?
classes I, II, and IV
Why do Classes I, II, and IV RPDs introduce an important variable in support?
They are not completely tooth supported but they derive varying support from the residual ridge tissues
In combined tooth-tissue supported prostheses, what type of loading often results?
Non-axial loading
On which abutment does the prosthesis typically pivot in combined support cases?
The abutment closest to the extension base
What is a possible consequence of not accounting for force distribution in the design of a removable partial denture?
- Tooth mobility
- Restoration failure
How can you describe the movements of an RPD under function?
It can be describes as a lever system
What four things does a lever consist of?
- A rigid bar
- A fulcrum
- An object to be moved
- An applied force
What does the efficiency of a lever system depend on?
- The arrangement of the fulcrum
- The object
- The force in arrangement of the bar
Which three fundamental components define all types of levers in biomechanics?
- Load
- Fulcrum
- Effort
what is a class I lever?
Force and resistance on opposite sides of fulcrum
What is an example of a Class I lever?
Scissors
What is an example of a Class II lever?
Wheelbarrow
What is an example of a Class III lever?
Shovel
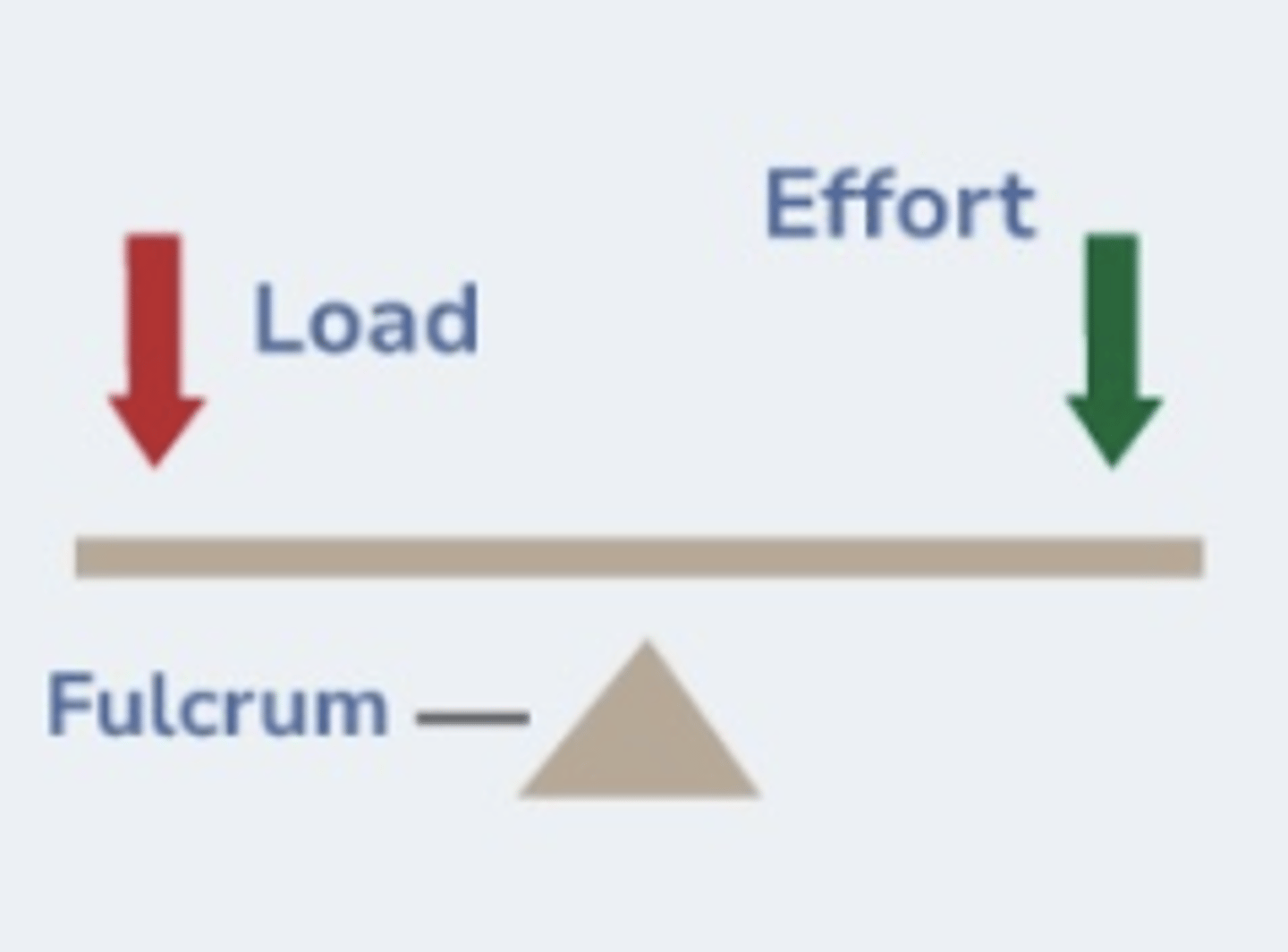
ID the lever class:
Class I
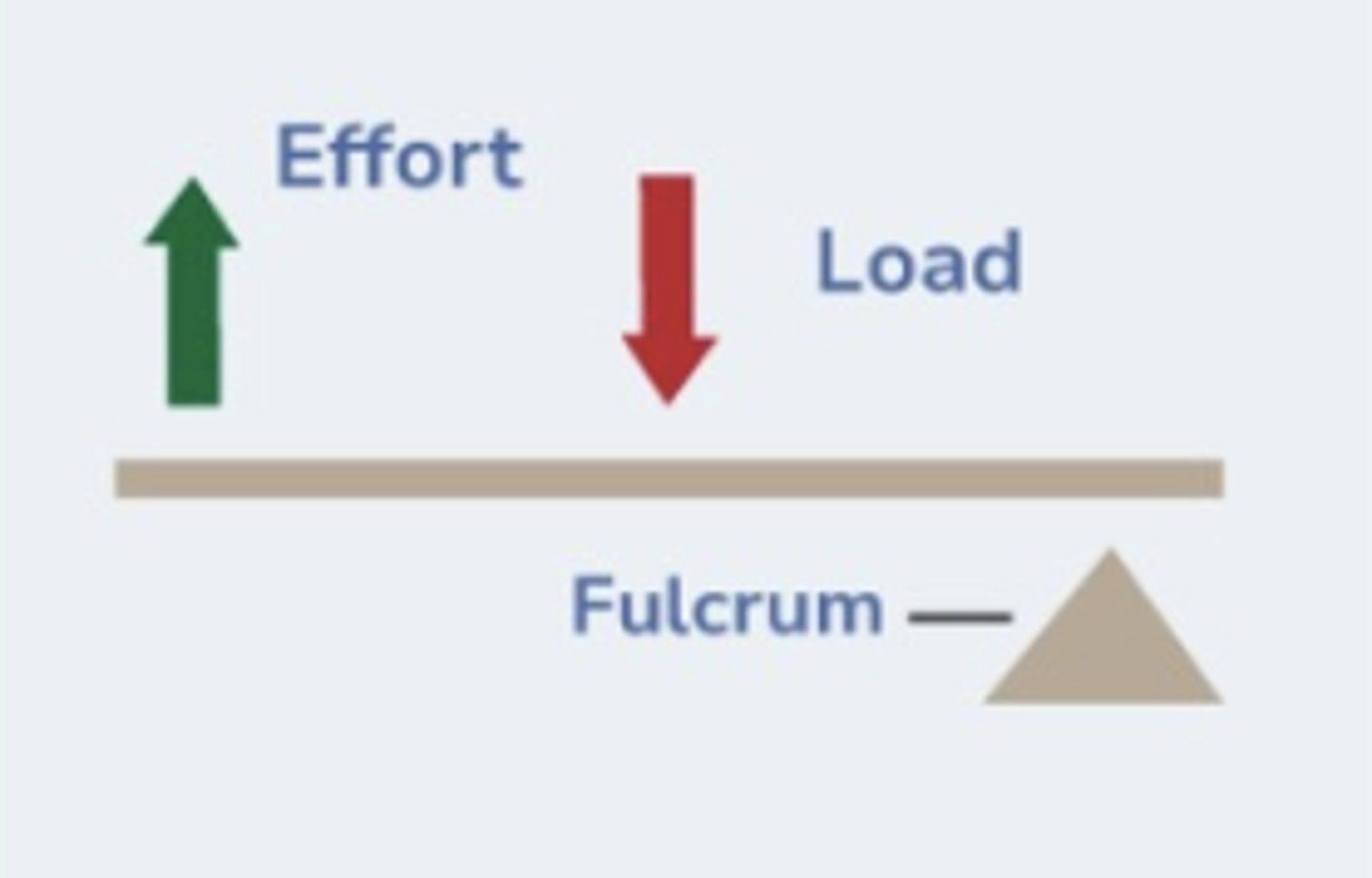
ID the lever class:
Class II
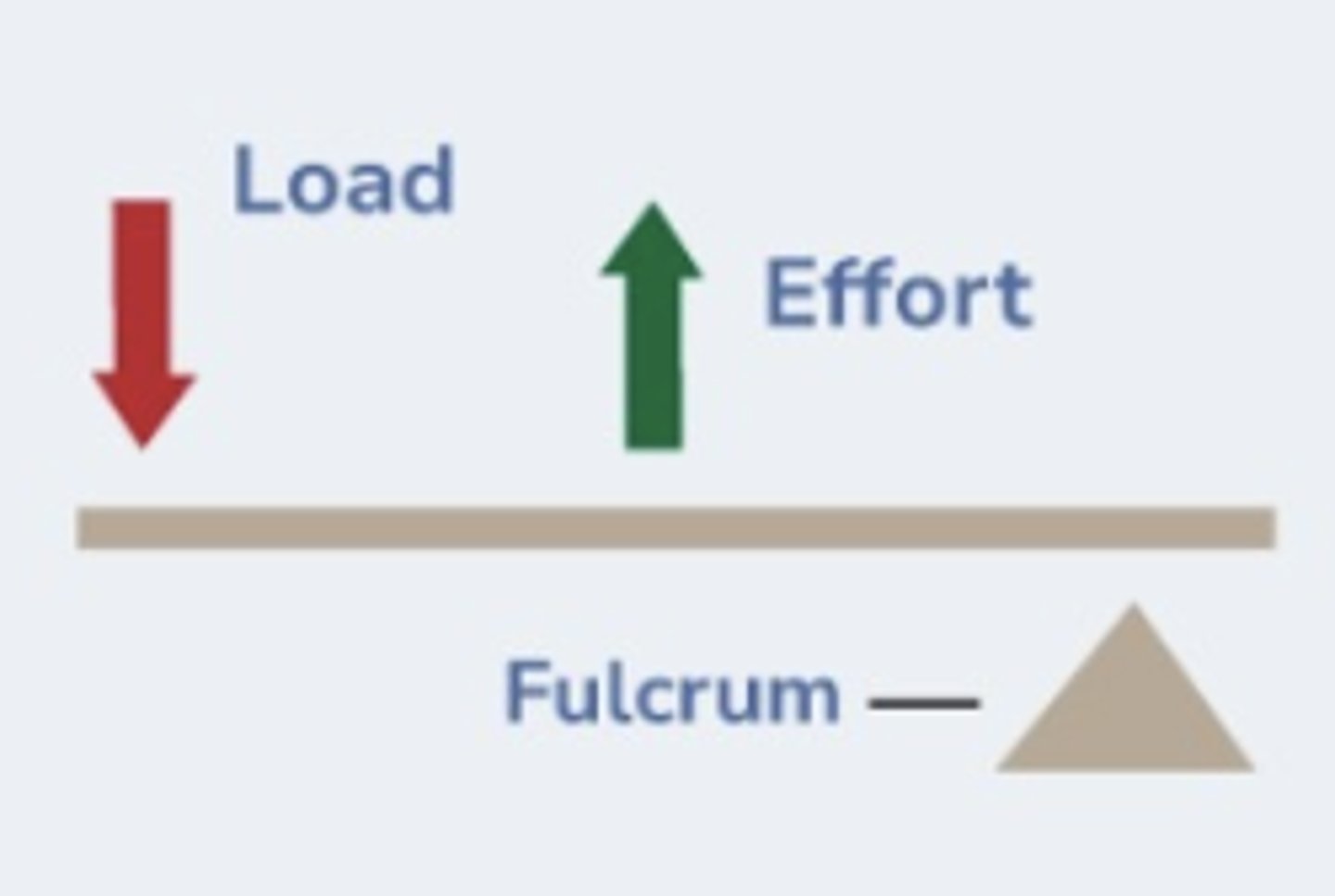
ID the lever class:
Class III
Which lever class is considered the most efficient in biomechanics?
Class I
Arrange the lever classes (1 through 3) in increasing order of efficiency:
Class III < Class II < Class I
A Kennedy Class I and Class II partial dentures (distal extension) may create what type of lever?
Type I lever
A Class IV removable partial denture can function in a similar manner as a type I lever, but it fulcrums about a _________ abutment.
Mesial
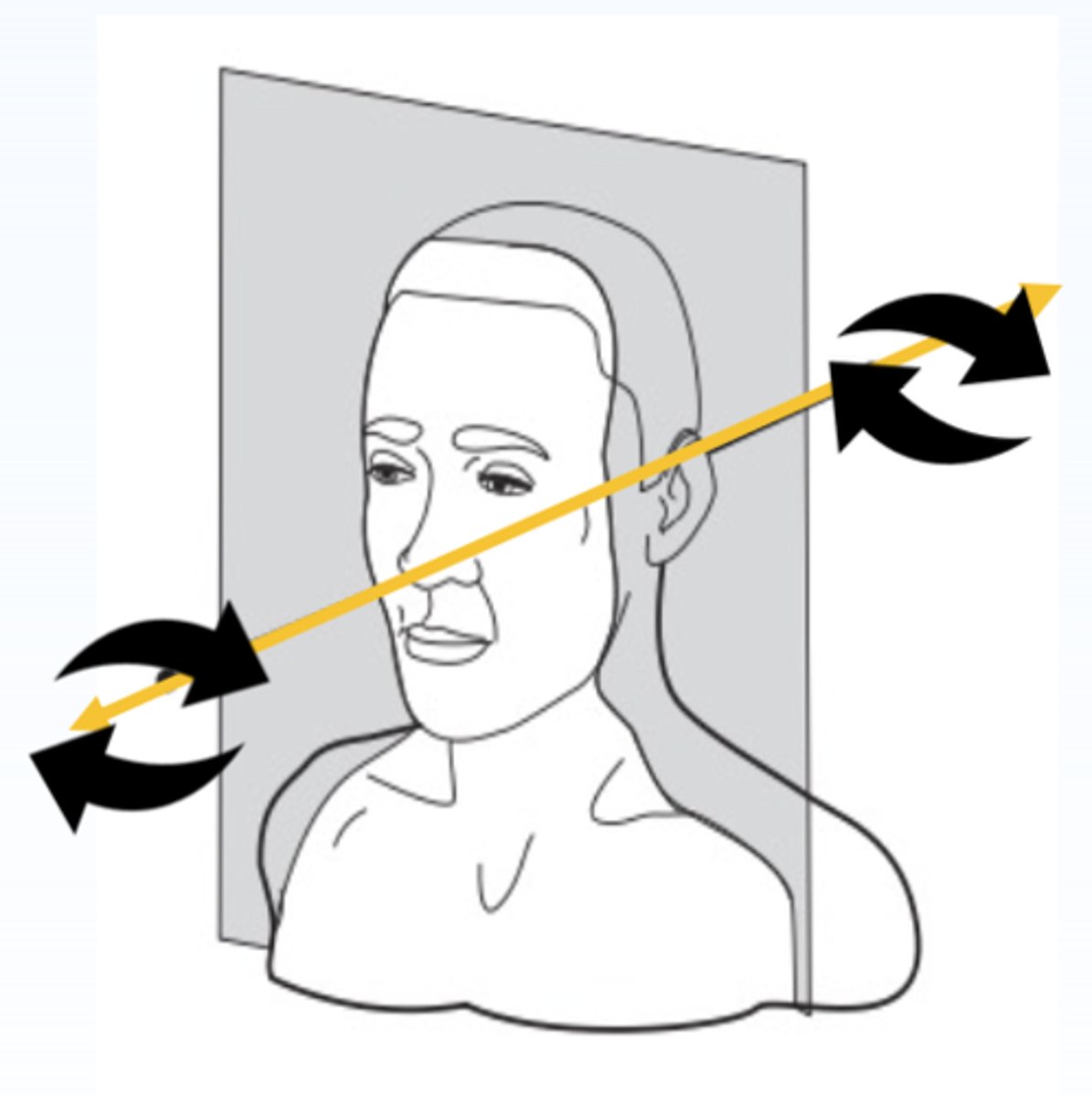
Movement of a partial denture can occur in what three fundamental planes?
- Sagittal
- Frontal
- Horizontal
The sagittal, frontal and horizontal planes are mutually perpendicular and therefore intersect one another at right angles. The intersection of any two planes forms a ____________
Linear axis
Because there are three planes, there are also three axes. What are they?
- Horizontal (transverse/fulcrum) axis
- Longitudinal axis
- Vertical axis
Rotational movement around any one of the three axes can only occur within the plane that runs exactly __________ to that axis
Perpendicular
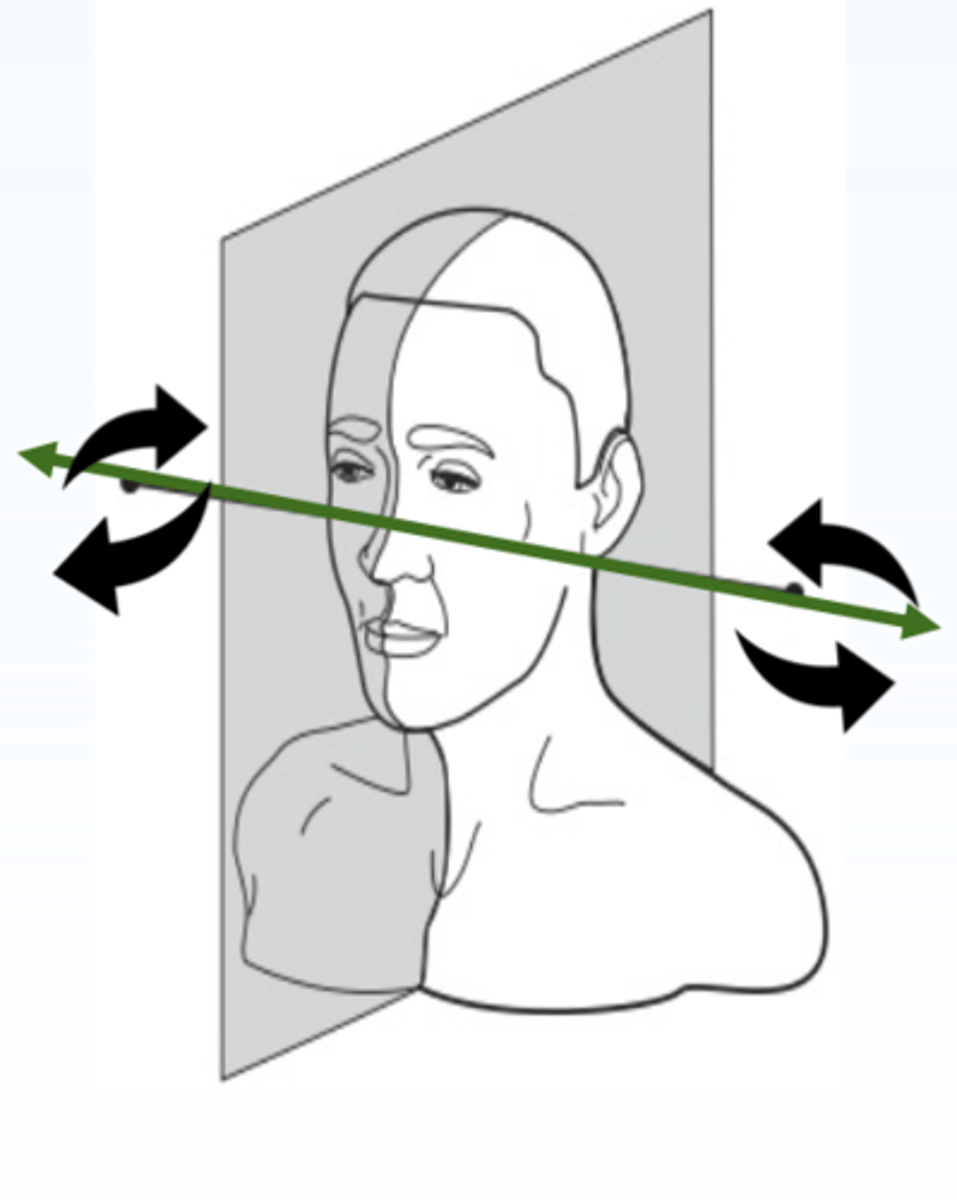
ID the plane:
Sagittal plane
ID the plane:
Frontal plane
ID the plane:
Horizontal plane
ID the plane:
Movement around the fulcrum/horizontal axis
Sagittal plane
ID the plane:
Movement around the longitudinal axis
Frontal plane
ID the plane:
Movement around the vertical axis
Horizontal plane
The first movement of a partial denture occurs in which plane?
Sagittal plane
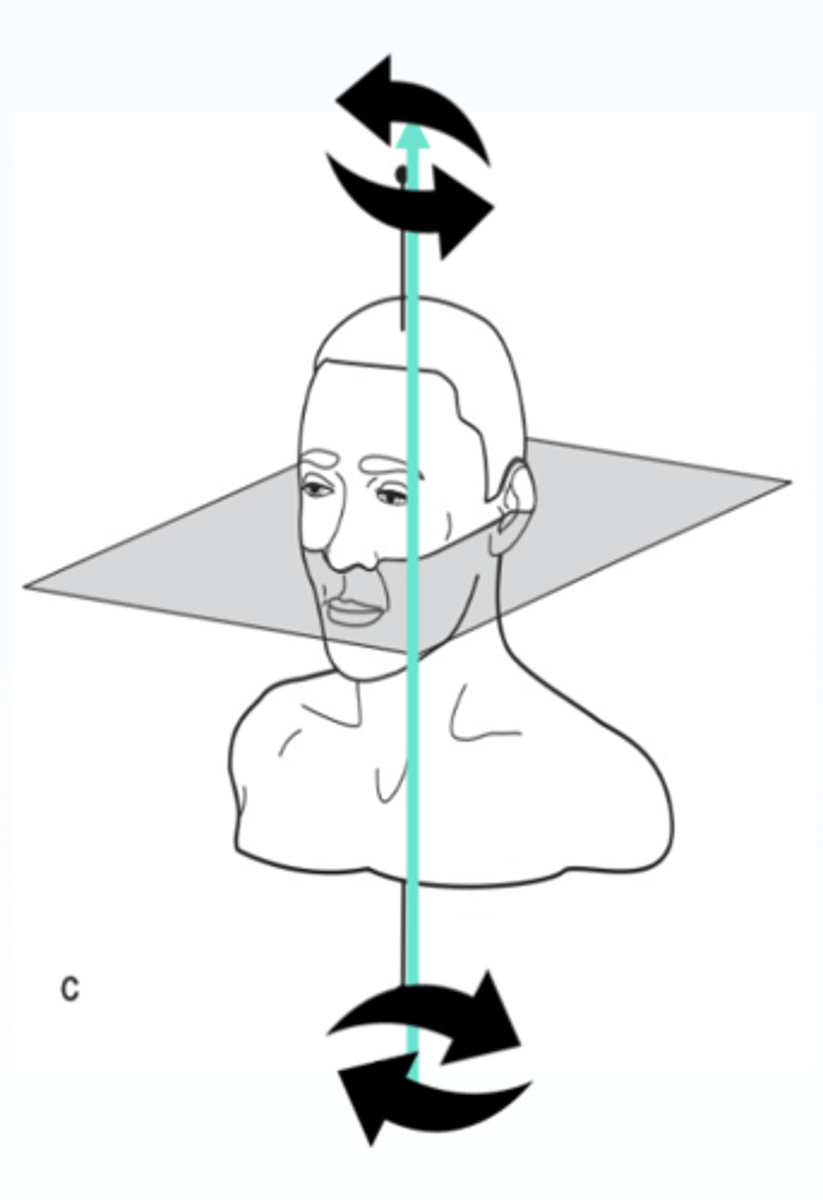
What has the following characteristics?
- A line connecting the most posterior abutment teeth or principal abutments.
- Rotational movement of the denture can occur around the _________ in the sagittal plane.
- Vertical movements by vertical seating and dislodging forces. (i.e. chewing sticky food)
Fulcrum or horizontal axis
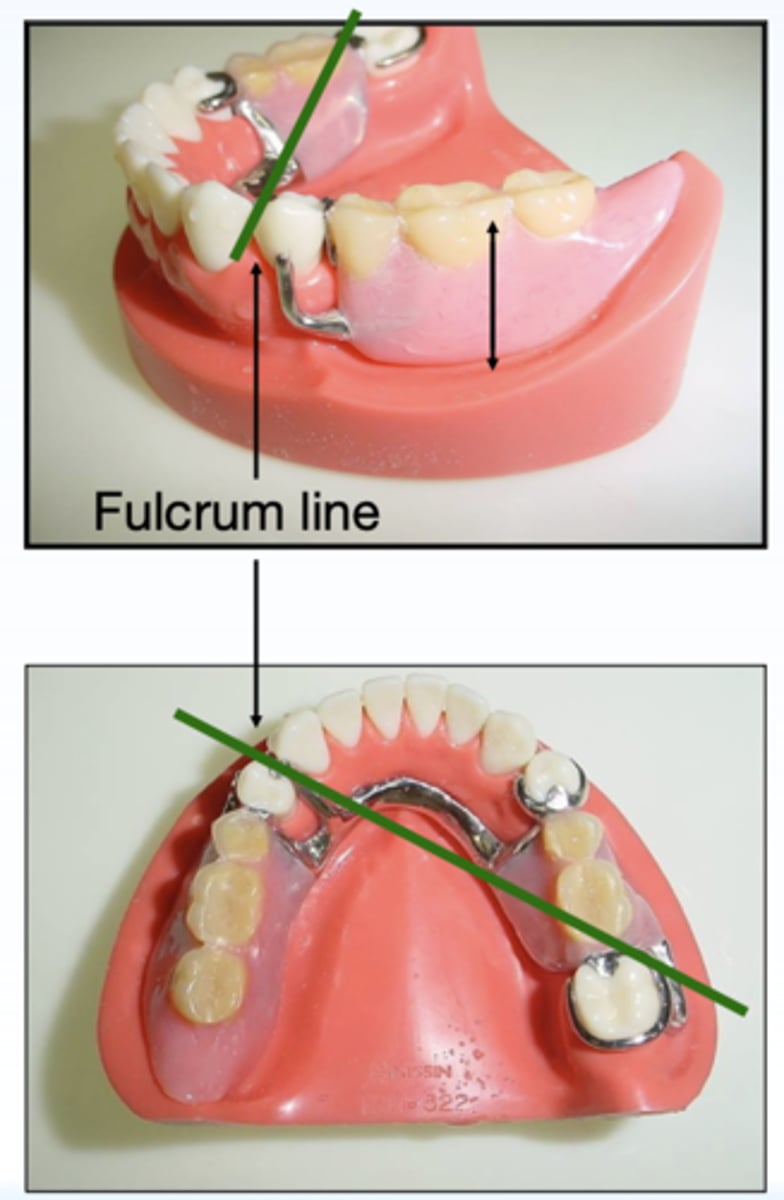
ID the type of axis in green:
Fulcrum or horizontal axis
what does the fulcrum line connect?
posterior abutment teeth of each side
The second movement of a partial denture occurs in which plane?
Frontal plane
What has the following characteristics?
- An imaginary line formed by the crest of the residual ridge.
- Rotational movement of the denture can occur around the _________ in the frontal plane.
- Dislodging of the base on the opposite side at unilateral loading.
Longitudinal axis
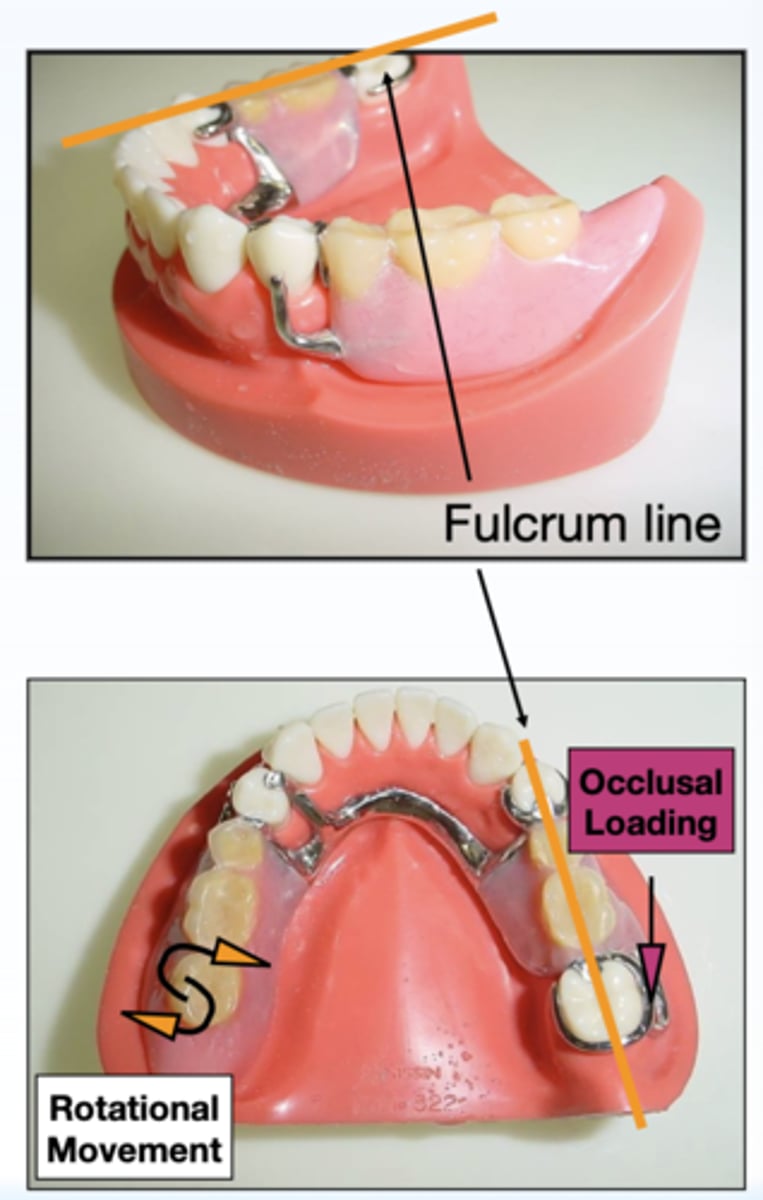
ID the type of axis in orange:
Longitudinal axis
what line of the RPD delineates the longitudinal axis?
crest of residual ridge
The third movement of a partial denture occurs in which plane?
Horizontal plane
What has the following characteristics?
- Imaginary vertical line located close to the center of the arch.
- Rotational movement of the denture can occur around the fulcrum line in the horizontal plane.
- Bucco-lingual movements of the RPD due to masticatory forces.
Vertical axis
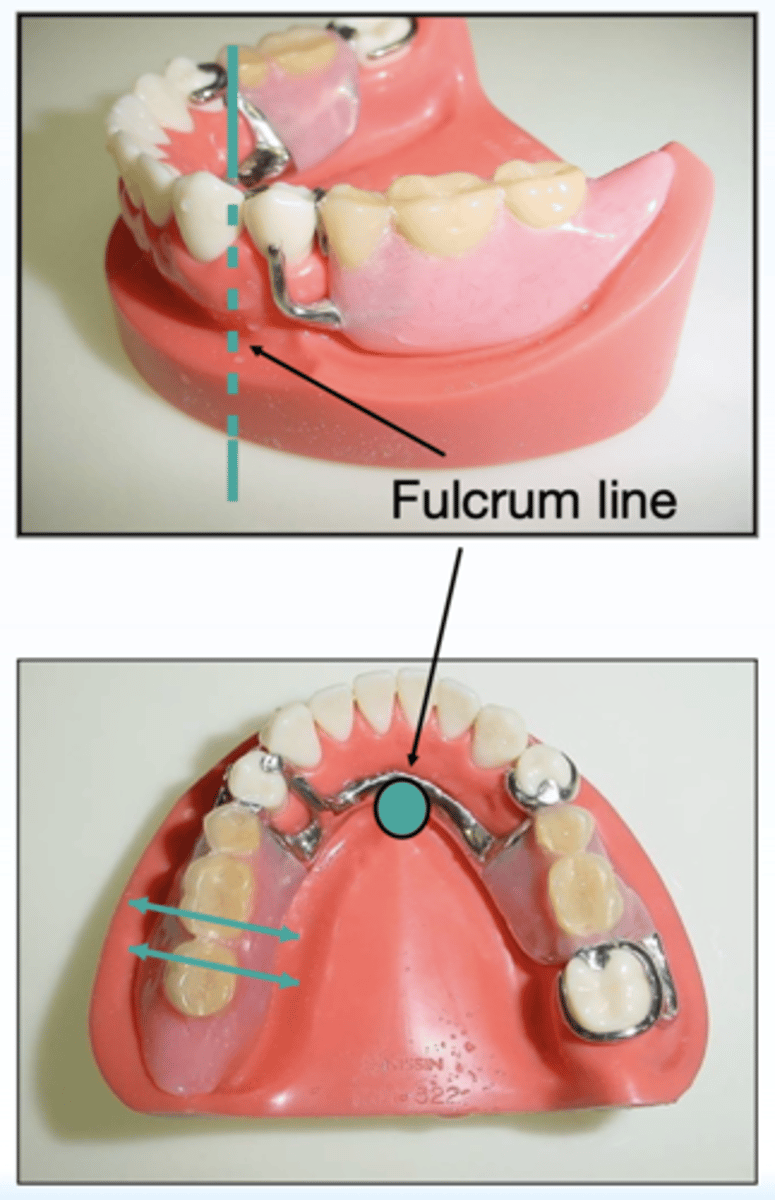
ID the type of axis in teal:
Vertical axis
what line of the RPD delineates the vertical axis?
vertical line close to the center of the arch
Why does the third movement of a removable partial denture (in the horizontal plane) require special design consideration?
Because the forces generated are almost entirely horizontal, which can be extremely damaging.
Define the following:
Resistance to vertical components of mastication and occlusal forces applied in the direction of the basal seat
support
Define the following:
Resistance to removal in a direction opposite that of its insertion. Resistance to movement away from the tissue
retention
Define the following:
Quality of a denture to be firm, steady and constant in position when forces are applied to it
stability
what is support of a partial denture supplied by? (3)
- Rests
- Maxillary major connectors
- Denture bases
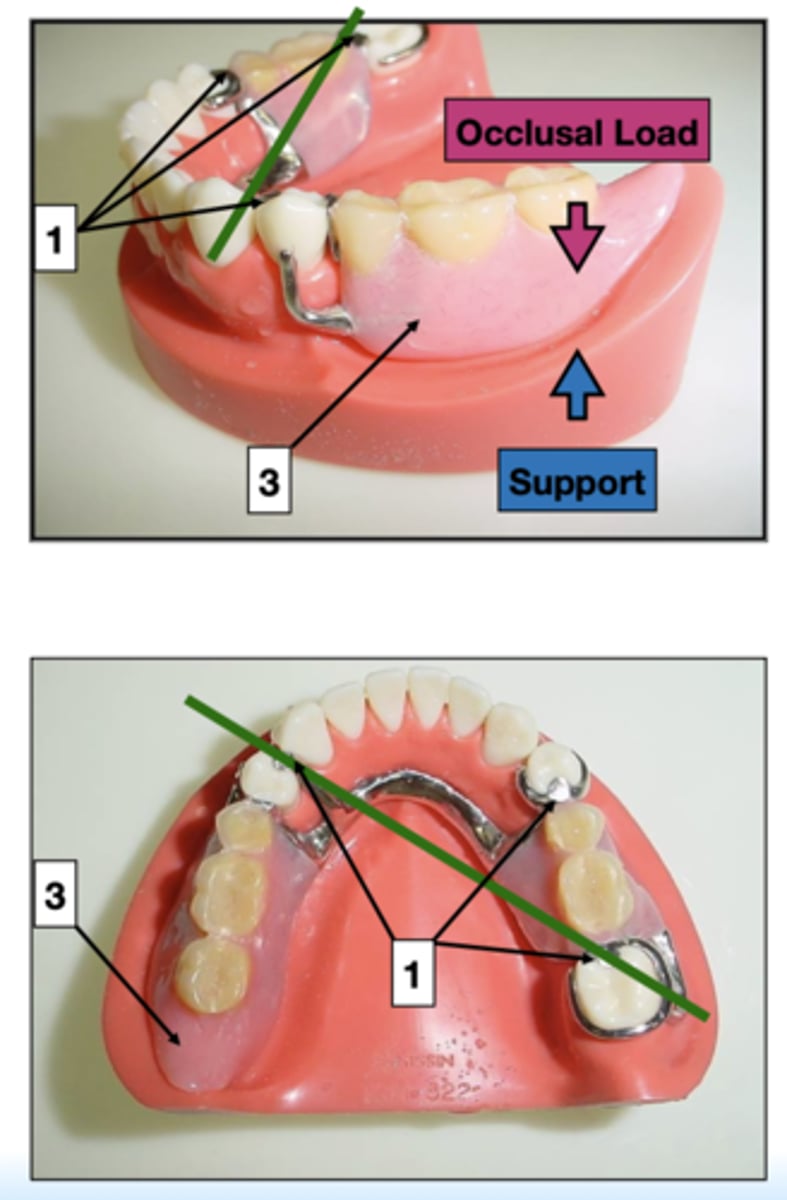
ID 1:
Rests
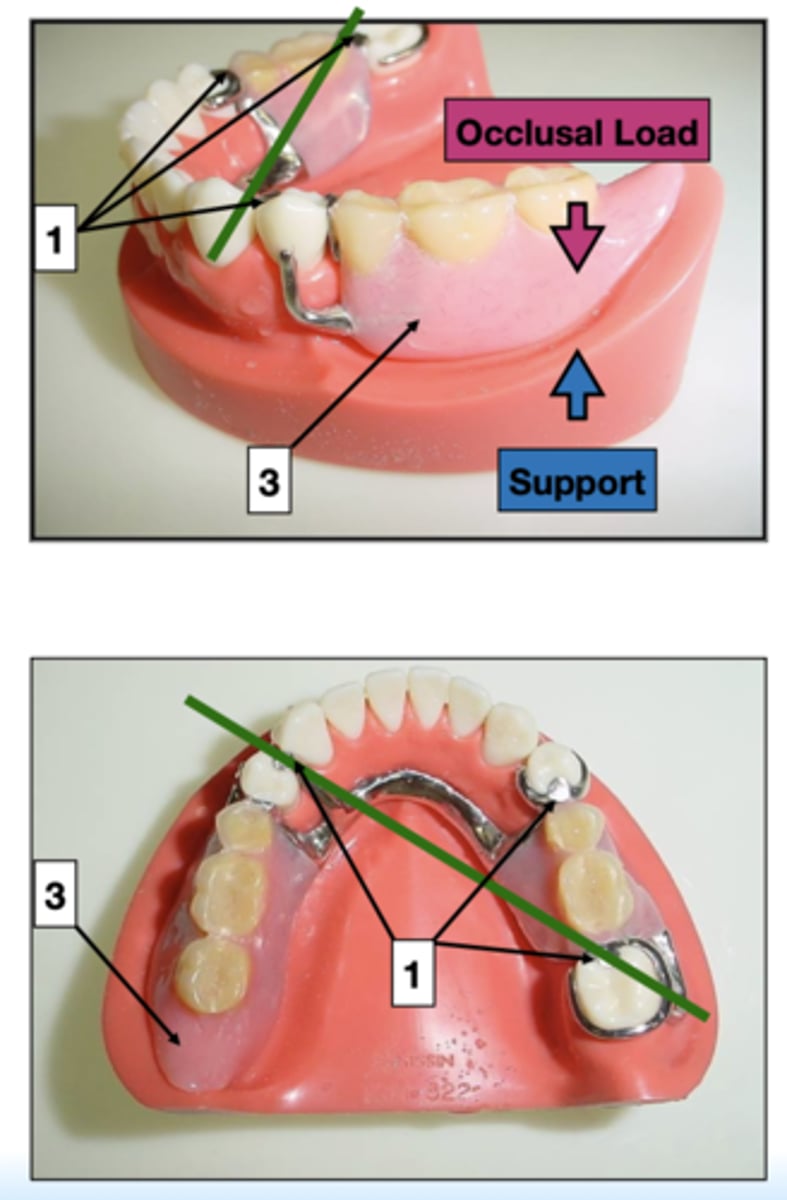
ID 3:
Denture base
what is retention of a partial denture supplied by? (5)
- Direct retainer (retentive arm of clasp)
- Indirect retainers
- Guiding planes
- Minor connectors
- Gravity (mandible)
Stability can be defined as resistance to dislodging on the opposite side of the occlusal load and it prevents rotation around longitudinal axis. What is this type of stability of a partial denture supplied by?
- Minor connector
- Clasp assembly
- Major connector
- Rests (e,g, internal rest)
- Denture base in long span distal extension
- Artificial tooth replacement
Stability can be defined as resistance to bucco-lingual
movement and rotation around vertical axis. What is this type of stability of a partial denture supplied by?
- Denture base
- Maxillary major connector
- Minor connector
- Reciprocal arm of clasp
The foundation for dentures is made up of __________ and covering __________
bone, soft tissues
The denture rest on the _________ that serves as a cushion between the denture base and the supporting bone.
Mucosa
Why are primary stress-bearing areas more resistant to resorption?
Because they have thicker mucosa and/or underlying cortical bone
what features gives bearing areas best stability?
parallel with plane of occlusion or perpendicular to forces of mastication
what is the primary bearing area of the maxilla?
horizontal hard palate
The ultimate support for the maxillary denture is the bone of the two maxillae and palatine bone. A cross-section of the hard palate shows that the palate is covered by soft tissues of varying thickness even though the epithelium is _________ throughout
Keratinized
what is the secondary bearing area of the maxilla?
residual ridge
why is the residual ridge considered a secondary bearing area?
the bone is prone to resorption
T/F: In the area of the rugae, the palate is set at an angle to the residual ridge and is rather thinly covered by soft tissue
True
When the submucosa is thin, the soft tissue is less resilient, and the mucous membrane is easily traumatized. What is the recommended management?
Provide some relief in the denture
When the submucosa is loosely attached to the periosteum, inflamed, or edematous, the tissue is easily displaceable. What is the recommended management?
Pre-prosthetic surgery
what areas of the maxilla require relief?
- Medial palatal suture
- Incisive papilla
- Torus
T/F: In the region of the medial palatal suture, the submucosa is extremely thin, with the result that the submucosa is practically in contact with the bone. For this reason, the soft tissue covering the mid palatal suture is non-resilient and may need to be relieved to avoid trauma from the denture base.
True
The ____________ is located in the palate on the median line and comes nearer to the crest of the ridge as resorption progresses. The incisive foramen should be relieved routinely to prevent impingement on the has-palatine nerves and blood vessels as they pass through the incisive foramen.
Incisive papilla
Torus palatinus is found in what percent of the population?
20%
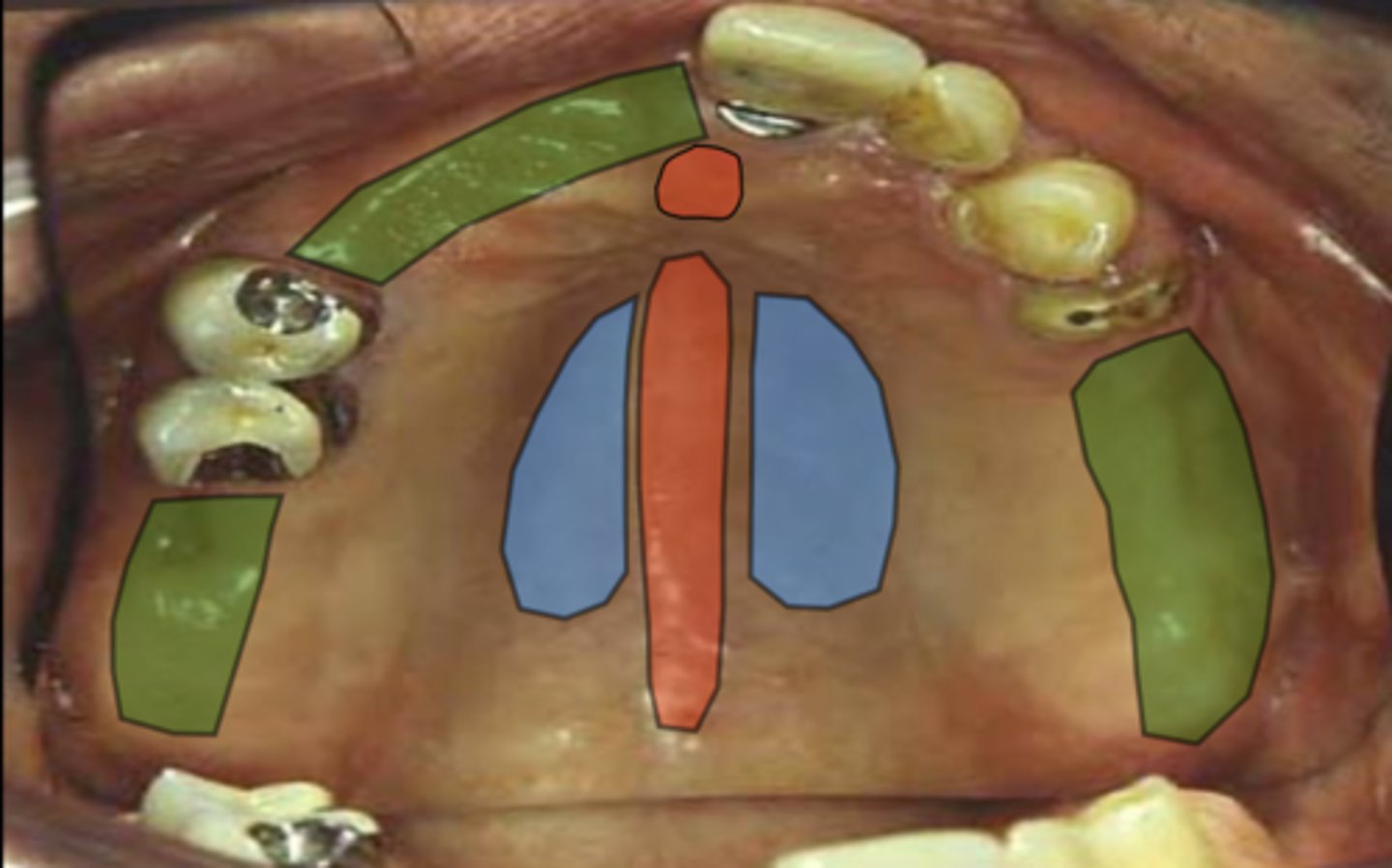
What does the area in blue represent in terms of stress-bearing areas?
Hard palate - primary bearing area
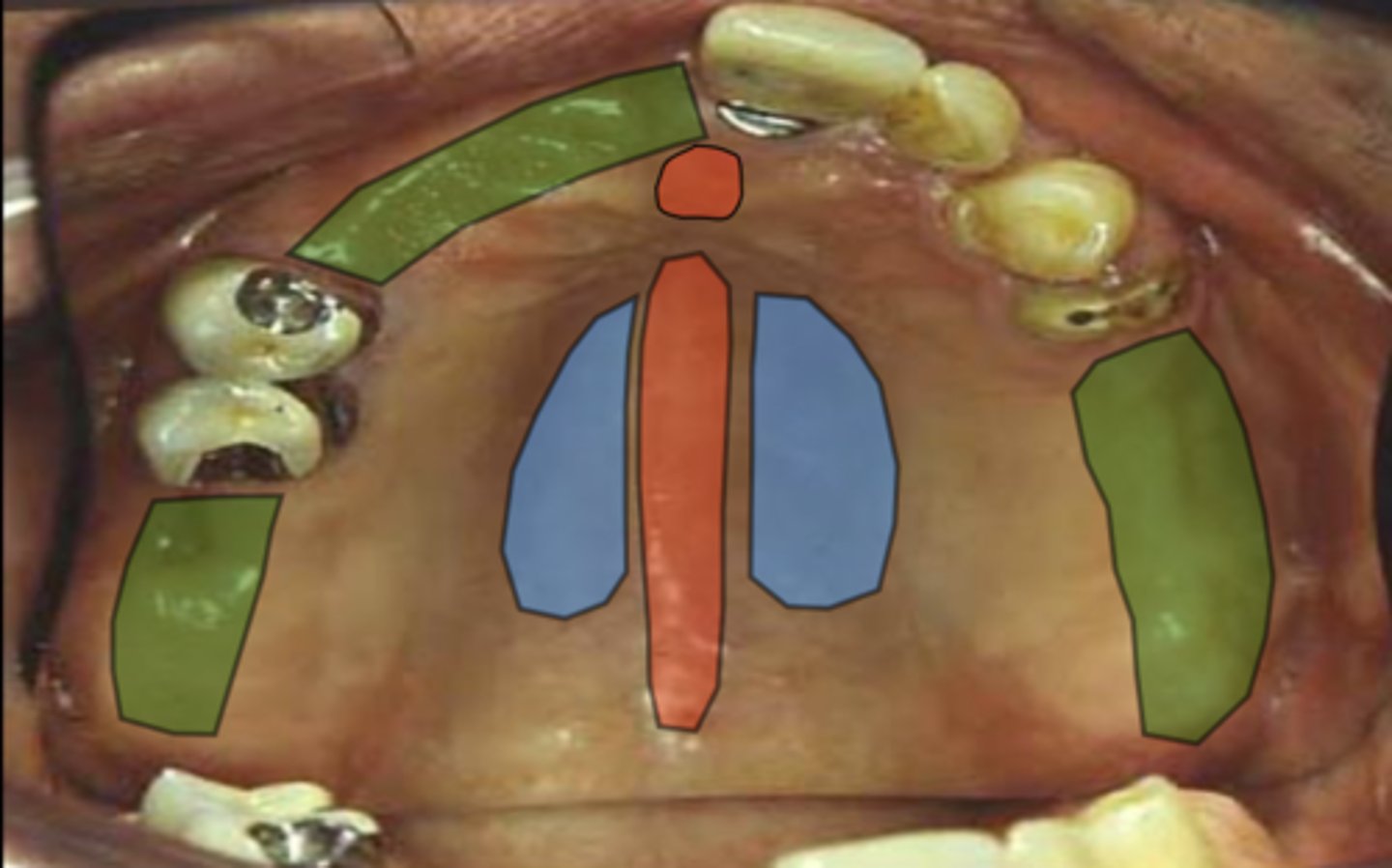
What does the area in green represent in terms of stress-bearing areas?
Residual ridge crest - secondary bearing area
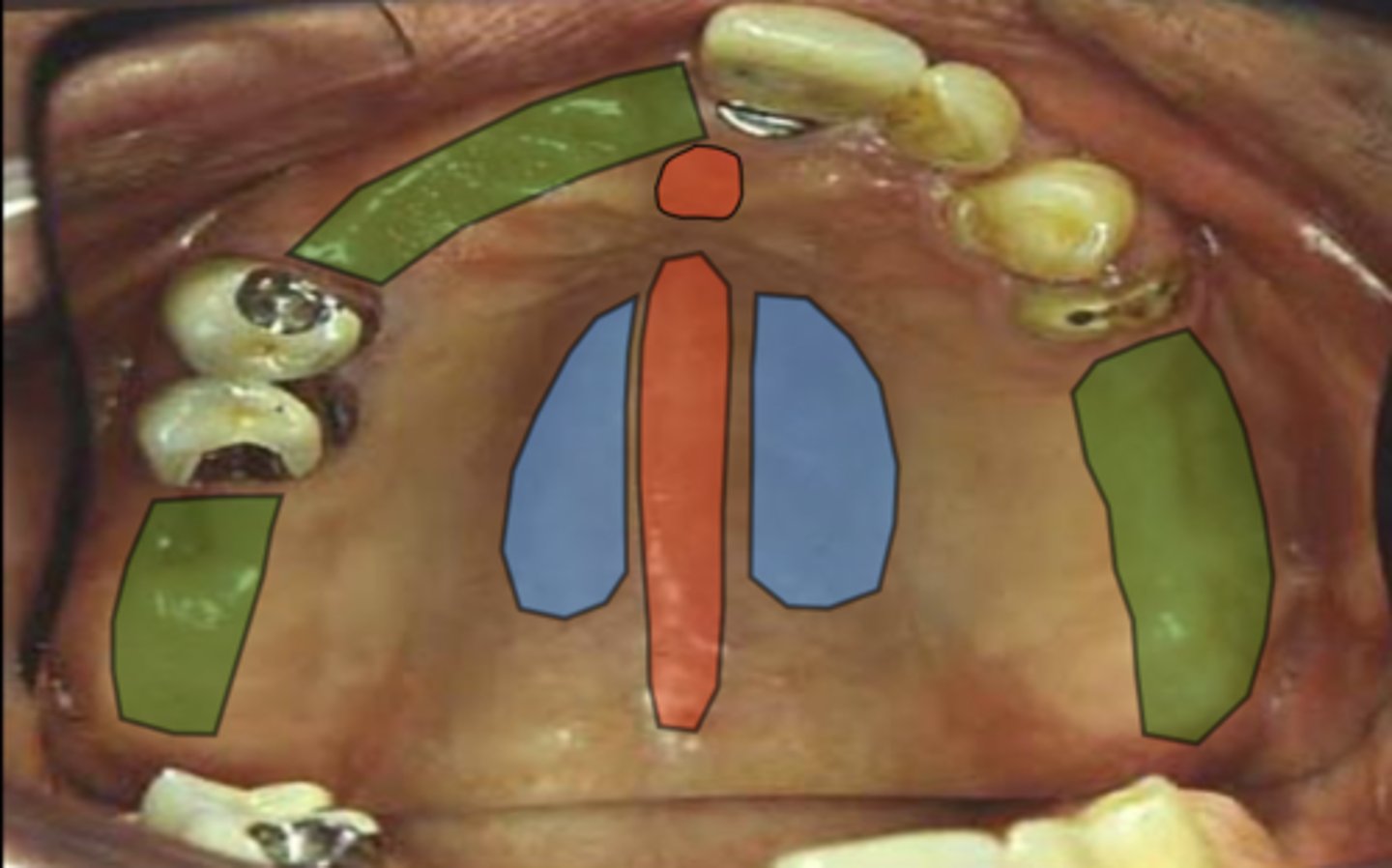
What does the area in red represent in terms of stress-bearing areas?
Areas to be relieved - median palatal raphe and incisive papilla
what are the primary bearing ares of the mandible?
- Buccal shelf
- Retromolar pad
what is the secondary bearing area of the mandible?
crest of residual ridge
Define the following:
By both the nature of the bone and its position at right angles to the denture base, affords the primary support for the mandibular denture.
Buccal shelf
Define the following:
Triangle of soft tissue. The anterior portion of the _________ is keratinized with a remnant of the third molar called the pear-shaped pad. The posterior aspect of the _________ is composed of non-keratinized epithelium, loose connective tissue, glandular tissue; fibers of the temporals tendon and of the superior constrictor of the pharynx, the buccinator, the pterygo-mandibular raphe. The underlying bone is cortical and does not resorb.
Retromolar pad
Define the following:
Covered by keratinized fibrous soft tissue but the bone underneath is mainly comprised of cancellous bone with a thin cortical plate. Considered a secondary bearing area.
Crest of the residual ridge
what are the different parts of the buccal shelf?
- External oblique ridge
- Ridge crest
- Buccal frenum
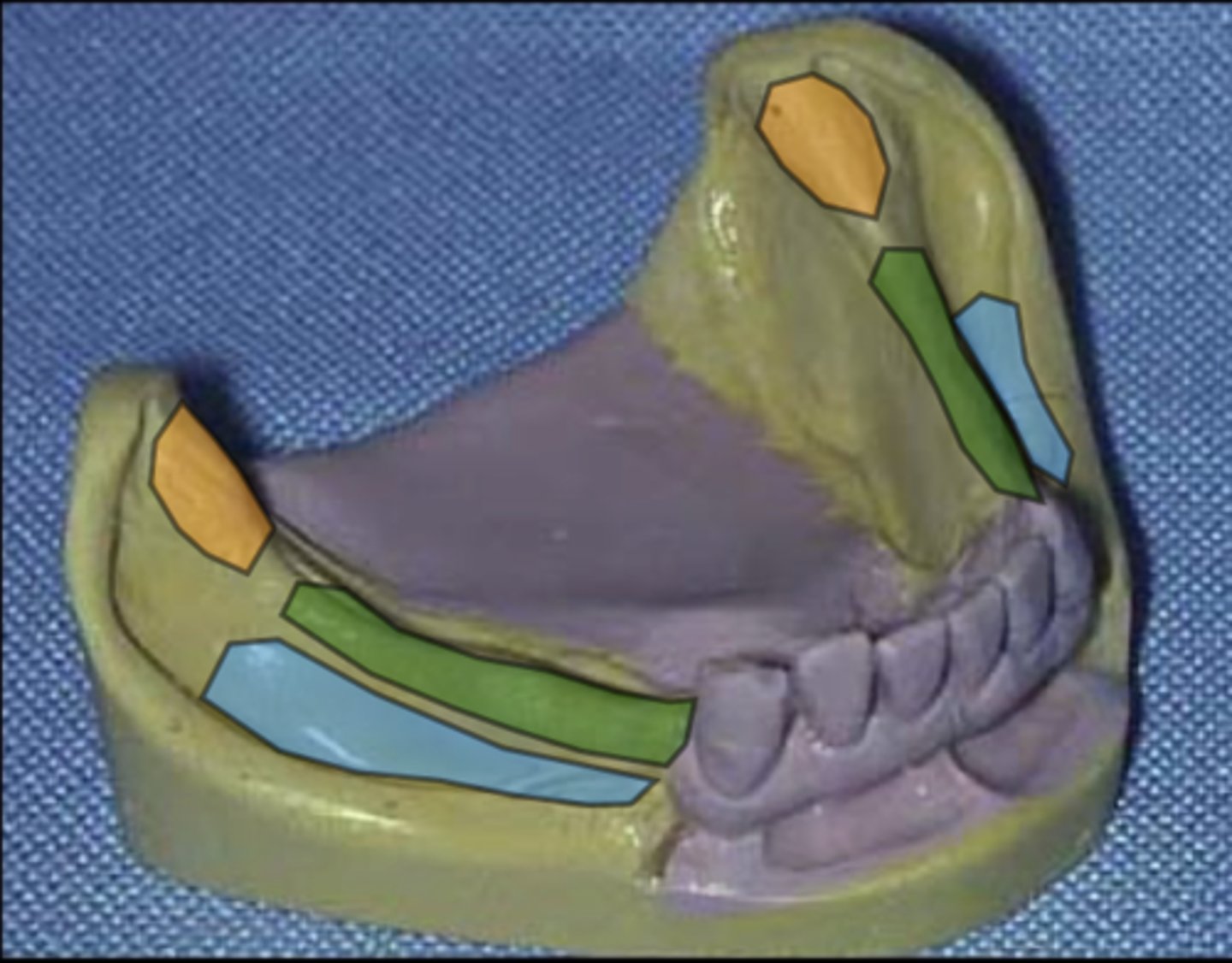
What does the area in blue represent?
Buccal shelf
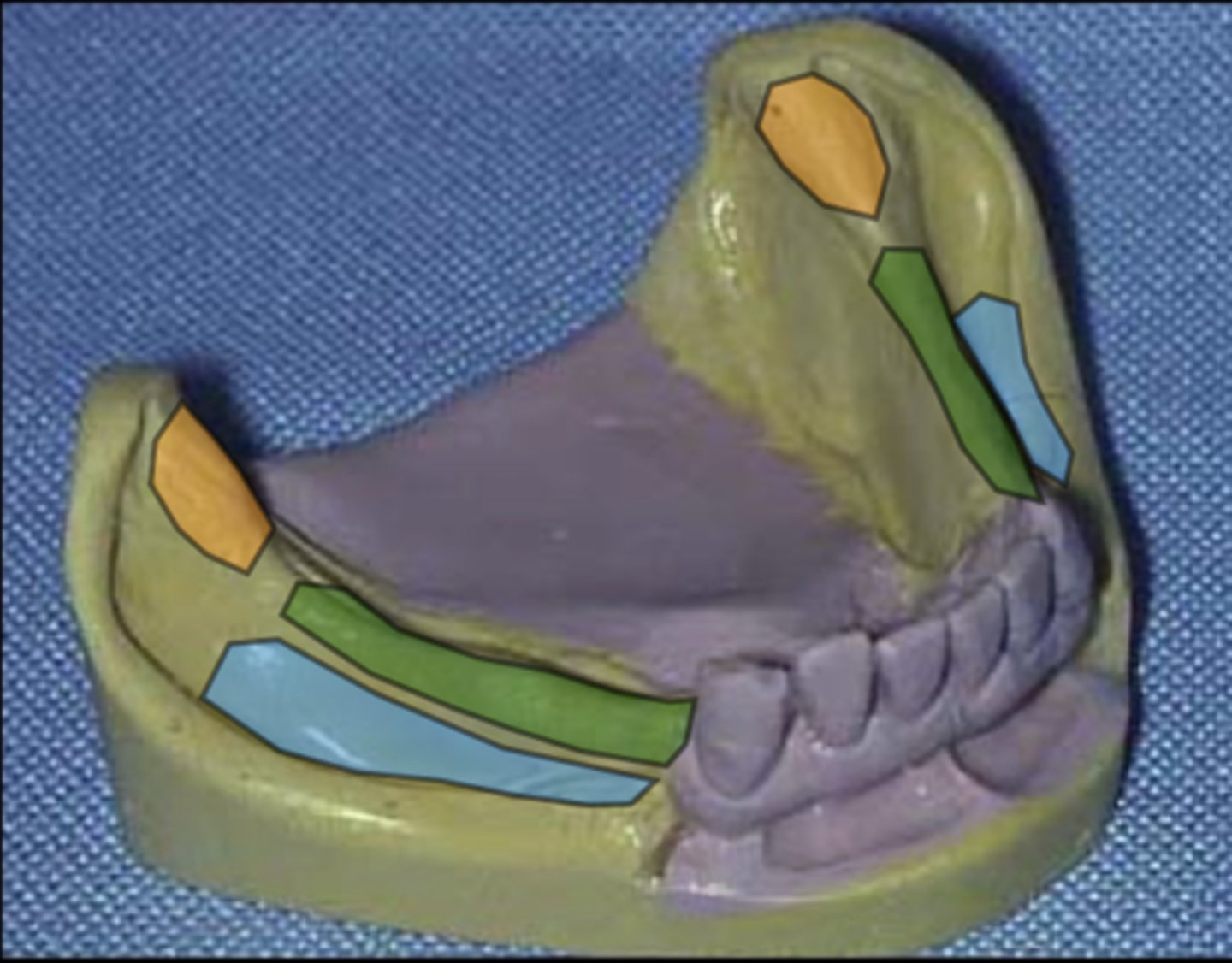
What does the area in orange represent?
Retromolar pad
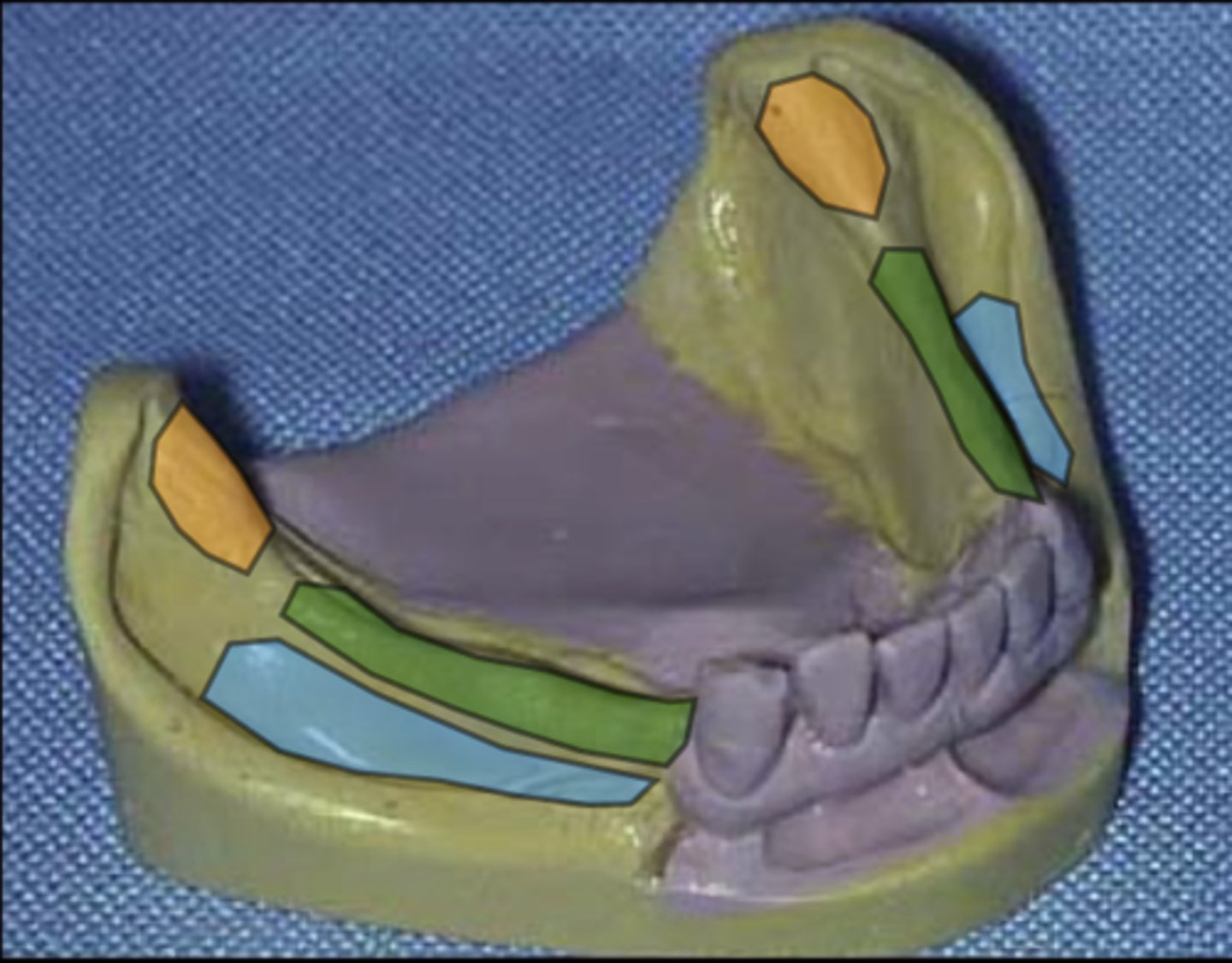
What does the area in green represent?
Residual ridge crest
what are the four factors that affect partial denture movement?
- Direction of load
- Type of load
- Ridge angle
- Fit of casting
what are the anatomical factors that affect partial denture movement?
- Direction of load
- Ridge angle
As a dentist, which of the following can you control? (2)
- Direction of load
- Type of load
- Ridge angle
- Fit of casting
- Type of load
- Fit of casting
how does the length of the edentulous span affect the force transmitted to the abutment?
longer edentulous span = greater leverage force applied to abutment teeth
how can you combat the amount of force transmitted to abutment teeth when the edentulous span is long?
preserving a posterior tooth or placing an implant for vertical support
how does the quality of ridge support affect force transmitted to the abutment?
large, well-formed ridges (at least 1mm) can withstand greater loads
how does clasp flexibility affect the amount of force transmitted to the abutment and ridge?
more flexible clasp = less stress on abutment and more stress to ridge
in terms of flexibility, how do cast clasps differ from wrought wire?
wrought wire is more flexible (and therefore transmits less force on the abutment tooth)
to minimize the amount of force transmitted to the abutment, the clasp should be ________ at the terminal position
passive
to neutralize the load to the abutment tooth, the reciprocating arm should contact the tooth before what?
the retentive tip passes over the greatest bulge of the abutment
how does the length of the clasp affect the amount of force transmitted to the abutment?
long and curved clasps are more flexible, which means they transmit less force to the abutment
what material is best to use in clasp construction to minimize the force transmitted to the abutment?
gold alloy (instead of chrome-cobalt)