Ch 14: Brain-Cerebellum, Brain Stem, RF
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
Cerebrum
largest part of the brain
Divided into right and left hemispheres
Cerebellum
Inferior to cerebrum, posterior to brain stem, within cranial fossa
Brainstem
Midbrain, pons + medulla part of brain
Diancephalon
thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus part of brain
cerebrum and cerebellum
gray matter on surface (cortex) of brain
spinal cord
gray matter is deep to the white matter
hollow
much of the CNS is ____
ventricles
core spaces in the brain filled with CSF
central canal
core space in spinal cord
ectoderm
Embryology of the nervous system: NS develops from ________
neuroectoderm, neural plate
Embryology of the NS: 3rd week, dorsal streak of ___________ forms _______
primary vesicles
forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain are all ________
initial three bulges that form from the early embryonic neural tube
prosencephalon
forebrain
mesencephalon
midbrain
rhombencephalon
hindbrain
telencephalon, diencephalon, midbrain, metencephalon, myelencephalon
secondary vesicles
the five key brain regions that develop from the three primary brain vesicles during early embryonic development
adult structures
cerebrum, thalamus, 3rd ventricle, midbrain, pons, cerebellum, and medulla oblongata are all _____________
telencephalon, diencephalon
secondary vesicle(s) of forebrain
midbrain
secondary vesicle(s) of midbrain
metencephalon, myelencephalon
secondary vesicle(s) of hindbrain
cerebrum, thalamus, 3rd ventricle
adult structures of forebrain
midbrain
adult structures of midbrain
pons, cerebellum, medulla oblongata
adult structures of hindbrain
inferior, myelencephalon
spinal cord develops from neural tube _______ to _________
3, CT
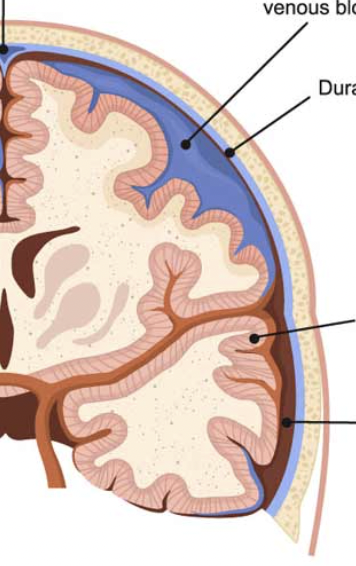
The meninges are __ layers of _ surrounding the brain and spinal cord
special features related to production, circulaiton, and absorption of CSF
related to conveying venous blood
dura mater, arachnoid, pia mater
three things meninges is divided into
dura mater
tough, fibrous, outermost meninx layer
double layer
around the brain
periosteal layer and meningeal layer = 2 layers fused over most of brain
periosteal layer
layer of dura mater: outer, adheres to skull bone forming periosteum
meningeal layer
layer of dura mater: inner, continouous w/dura mater of s.c.
dural sinuses
in certain areas of the dura mater, 2 layers are seperated forming ________
collect venous blood and empty into internal jugular veins
dural folds
places where the meningeal layer extends inward within fissures separating parts of the brain
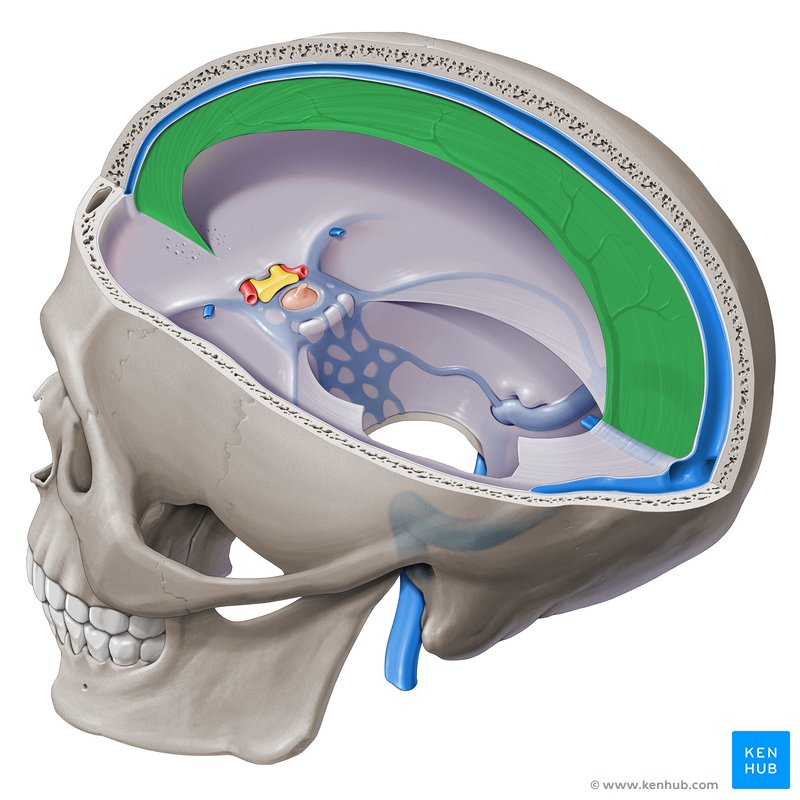
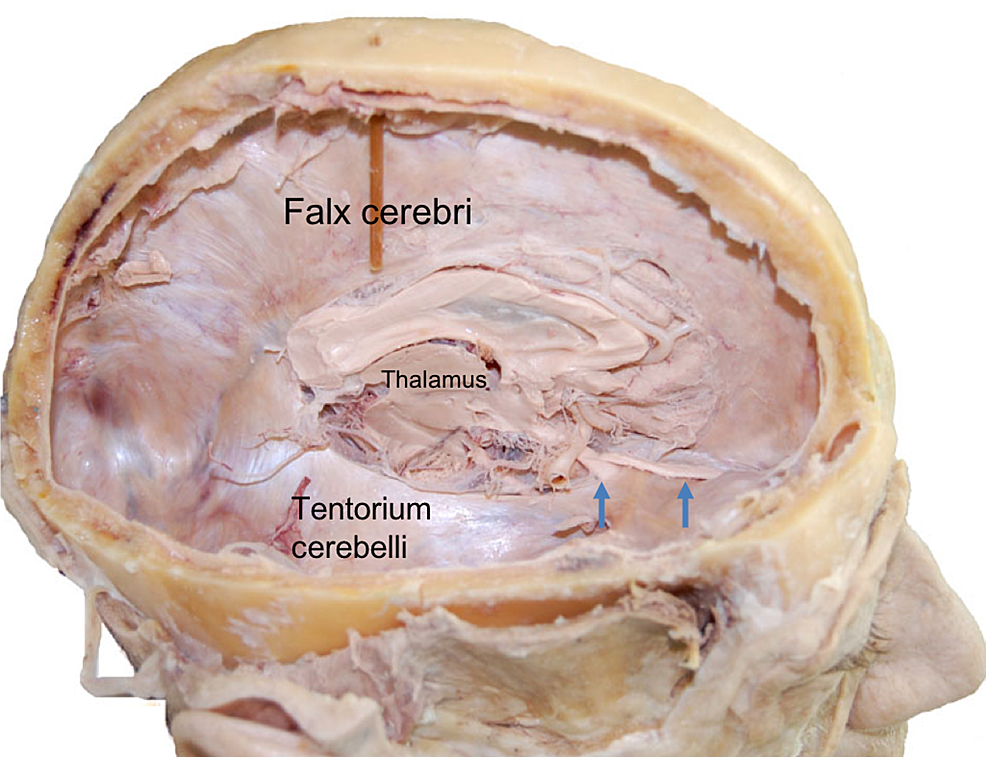
falx cerebri
in longitudinal fissure between right and left cerebral hemispheres
falx cerebelli
dural midline fold separating the two cerebellar hemispheres
tentorium cerebelli
tent-like partition in the transverse fissure separating the occipital lobes from the cerebellum
arachnoid mater
middle meninx; sends down fibrous strands
subdural space
narrow space separating the arachnoid m. from the dura m.
close adhesion to dura
subarachnoid space
wider space separating the arachnoid m. from underlying pia m.
contains CSF
contains strands of arachnoid
pia mater
inner meninx; adheres closely to brain and s.c.
meningeal
in the spinal cord, only the _______ layer is present
20
brain receives __% of our blood
internal carotid, vertebral
blood flows to the brain via _______ as & ________ as
BBB
regulates substrate exchange between blood and brain
=astrocytes + tight junctions between capillary endothelial cells and cap. B.M.
permeable to lipid soluble substrates and carrier transported substrates (ex. glucose)
makes it difficult to administer some meds to brain
trauma and inflammation can dama
CSF
clear liquid filling and surrounding the CNS
mechanical protection
function of CSF:
CSF is shock absorbing; buoyancy → effective weight of brain « actual weight
Homeostatic function
function of CSF: CSF pH affects pulmonary ventilation and blood flow; transports hormones
Circulation
function of CSF: CSF is a medium for minor exchange of nutrients and waste products between the blood and adjacent tissues
Choroid plexus
CSF is produced by the _______ within walls of each ventricle (capillaries covered by cuboidal epith.)
Blood CSF barrier
formed by the tight junctions between the ependymal cells → decreases passage of harmful substrates from blood into the CSF
ventricles
the 4 CSF filled chambers of the brain (continuous)

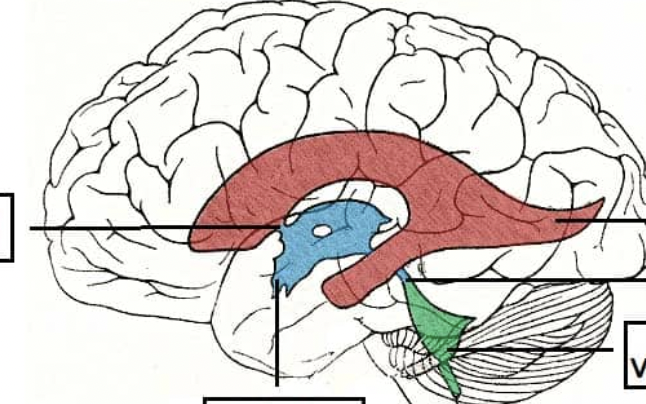
lateral ventricles
2 large ventricles; one in each cerebral hemisphere
3rd ventricle
midsagittal plane ventricle; inferior to corpus callosum
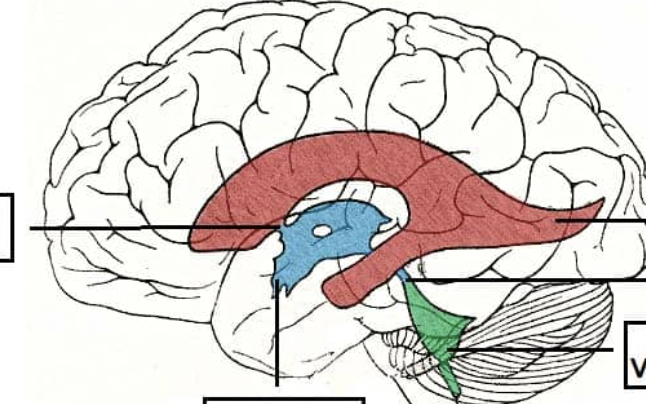
4th ventricle
small change in shape between pons and cerebellum
CSF reabsorption rate
normally CSF production rate
CSF reabsorption rate
the normal CSF production rate is also the
hydrocephalus
If increase in CSF production OR decrease in reabsorption
enlarged head
If increase in CSF production OR decrease in reaborption in childhood
ventricular dilation, compressed brain tissue
If increase in CSF production OR decrease in reabsorption in older children or adults
concussion
temporary loss of consciousness at blow to head
headache, amnesia, confusion
contusion
brain bruise
subdural hematoma
serious accumulation of blood between the brain's surface and its outer covering
epidural hematoma
bleed between dura and skull, usually middle meningeal a. bleed; rapid
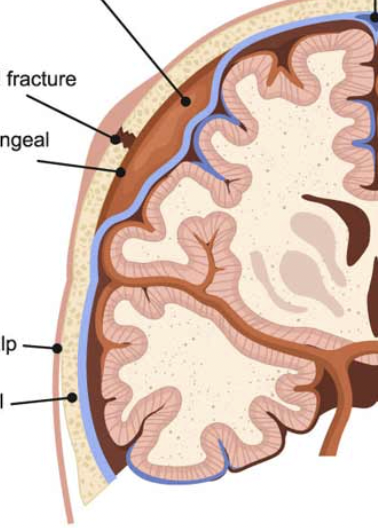
meningitis
inflammation of meninges; usually bacterial or viral infection, lumbar puncture for diagnois
brain stem
medulla, pons, and midbrain
produces programmed behaviors for survival
pathway for fiber tracts between spinal cord and cerebrum
sc, diancephalon
the brain stem is between the _______ and the _______
medulla
continuous w/superior part of spinal cord, but wider
also contains sensory nuclei and tracts
foramen magnum, pons
medulla starts at _____ and extends to _____
pyramids
2 large columns of motor neuron tracts on ventral surface of medulla
anterior median fissure
pyramids are separated by an __________
corticospinal tracts
pyramids contain _________ controlling voluntary limb movements
decussation of pyramids
at the junction of the medulla with the spinal cord, 90% of the corticospinal axons of the pyramids cross
opposite
each side of the brain controls voluntary movements on the ______ side of the body
olives
elevated areas of the medulla lateral to each pyramid
inferior olivary nuclei
olives contain ______ which send axons to cerebellum
VIII, IX, X, XI, XII
olives contain these cranial nerve nuclei:
olives
this part of the brain controls heart rate, respiration, bv diameter, coughing, swallowing, vomiting
pontine nuclei
pons contains ________ = a synaptic relay stations between the cerebrum and cerebellum
→ coordination of voluntary motor output
pons
contains ascending and descending tracts
contains “pneumotaxic” and “apneustic” areas to help control breathing
V, VI, VII, VIII
pons contains these cranial nerve nuclei
midbrain
between pons and diencephalon
contains the cerebral aqueduct (CSF from CN III→ CN IV)
made up of cerebral peduncles, substantia nigra, tegmentum, and tectum
cerebral peduncles
ventral surface of midbrain
contain corticospinal, corticopontine, and corticobulbar motor neuron tracts
substantia nigra
black nucleus between the peduncles and tegmentum
motor center containing dopamine neurons that extend to the basal nuclei → help control muscles activity (loss of these neuron ass. w/Parkinsons)
Tegmentum
contains “red nucleus” → rubrospinal tract
receive axons from cerebrum and cerebellum → some movement coordination
corpora quadrigemina
also known as tectum
corpora quadrigemina
dorsal surface of midbrain
contains 4 rounded bodies: superior and inferior colliculi
superior colliculi
upper pair of rounded bodies in tectum, some optic tract input → visual
inferior colliculi
lower pair of rounded bodies in tectum, involved in auditory reflexes
III, IV
corpora quadrigemina contain these cranial nerve nuclei
reticular formation
net-like arrangement of white and gray matter extending from the upper s.c., throughout the BS, and into the inf. diencephalon
regulate muscle tone
neurons in RF have both ascending (sensory) and descending (motor) functions:
somatic motor control
input
neurons in RF have both ascending (sensory) and descending (motor) functions:
autonomic ____
arousal
neurons in RF have both ascending (sensory) and descending (motor) functions:
_____
ascending fibers activate the cerebral cortex
Reticular activating system (RAS)
Reticular activating system
prevents sensory overload
helps arousal in RF
NO input from olfactory receptors
coma
damage to reticular activating system results in a ____
cerebellum
large, dorsal porjection in post. cranial fossa
posterior to medulla and pons
highly folded surface → increase in surface area
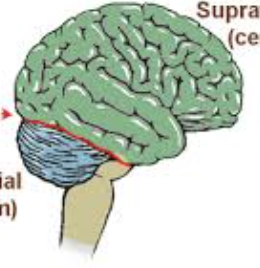
tentorium cerebelli
separates the cerebellum from occipital lobes → decrease P on cerebellum
vermis
2 lateral cerebellar hemispheres connected by
cerebellar cortex
superficial gray matter consisting of folds called folia separated by shallow sulci (grooves)
arbor vitae
tracts of white matter deep to gray matter in cerebellum
superior cerebellar peduncles
cerebellar connection: axons connecting to midbrain and thalamus
middle cerebellar peduncles
cerebellar connection: pons connection