IB Physics E5
1/6
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Luminosity
the total energy emitted by the star every second (also, the emitted power)
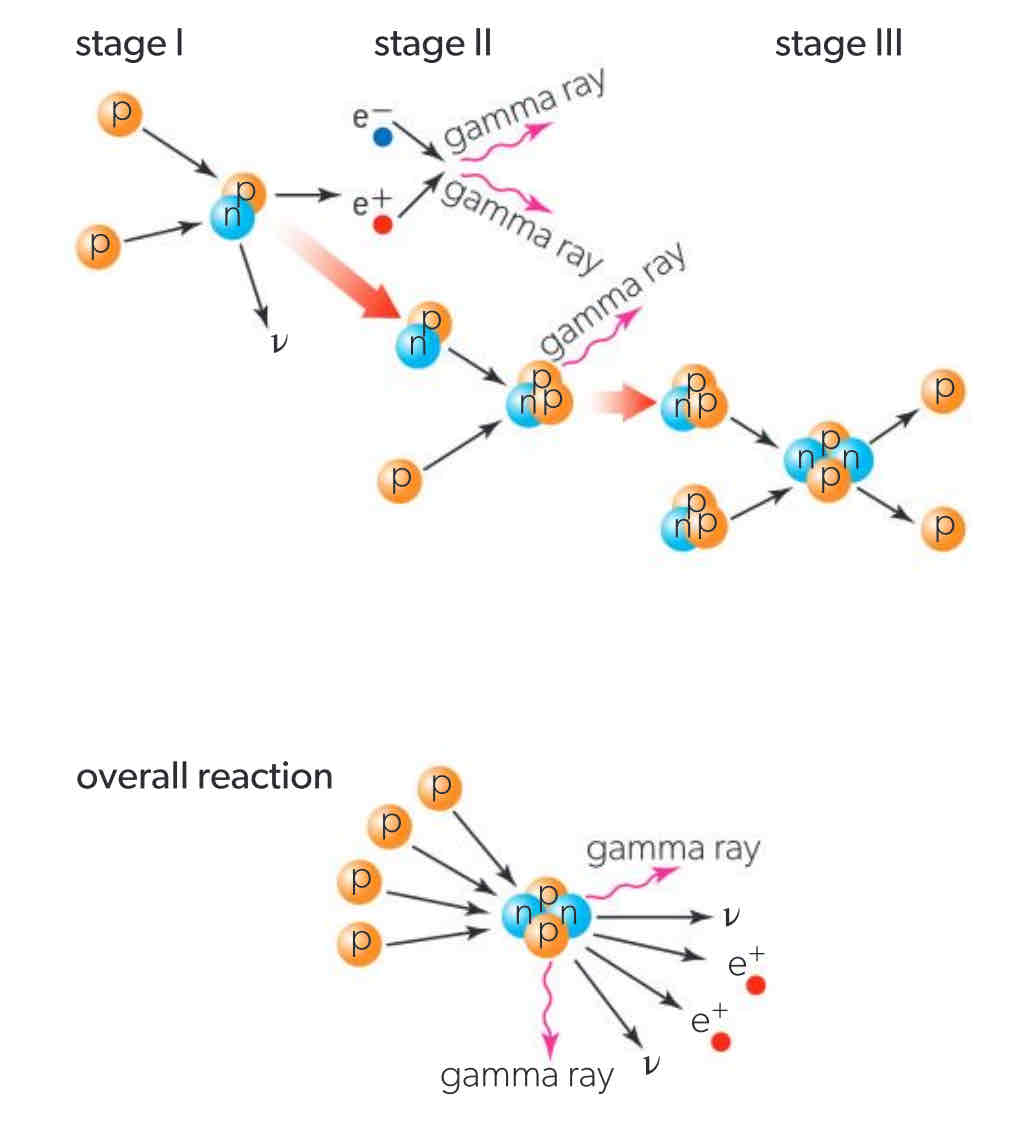
Nuclear fusion in stars
a star on the main sequence is fusing hydrogen to produce helium nuclei, proton-proton cycle
proton-proton (p-p) cycle
4 hydrogen nuclei fuse to give one helium atom until no hydrogen remains uncovered) in small mass stars, happens at high temperatures
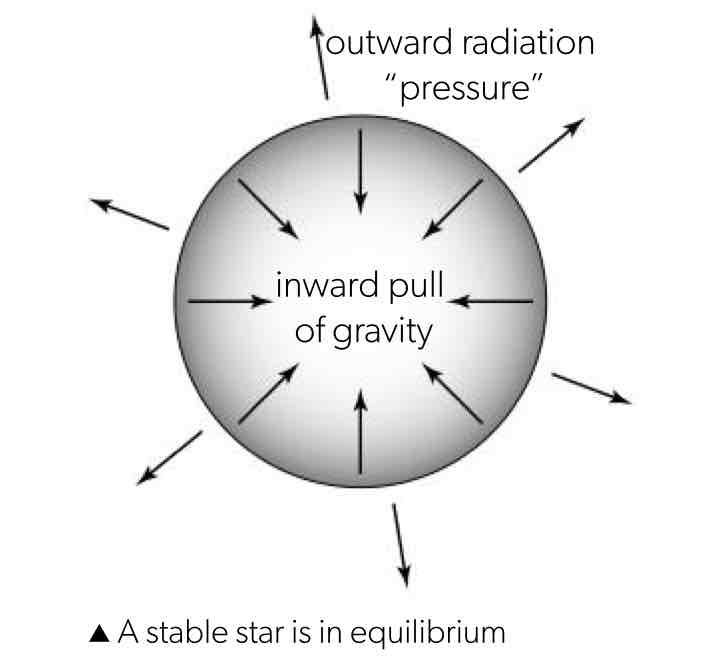
Hydrostatic equilibrium
the equilibrium between the gravitational attraction between the interior of the star and the outer layers pulling inwards and the thermal and radiation pressure pulling inwards
Basics of stellar evolution
a gas cloud comes together, and due to increasing temperature and pressure form a proto-star
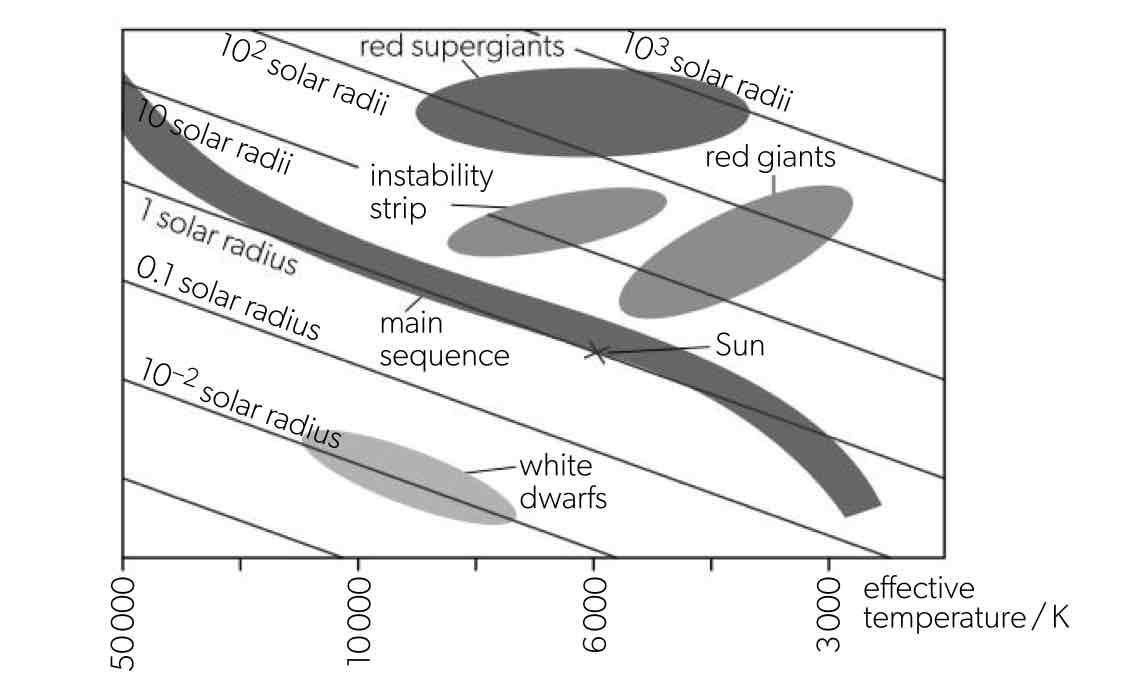
When the temperature is high enough, the star can start nuclear fusion and moves into the HR diagram as a main sequence star. The larger the mass, the shorter the time the star remains on the main sequence.
The star runs out of hydrogen and moves off the main sequence and becomes a red giant with a much greater diameter but a smaller core.
Further evolution of small mass stars
eventually form a planetary nebula, transforming into a white dwarf kept stable by the electron degeneracy pressure
The Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) diagram
the luminosity of the stars (vertical axis) plotted against the temperature (decreasing, horizontal axis)