AP Physics 1 1.1-1.2 Review
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
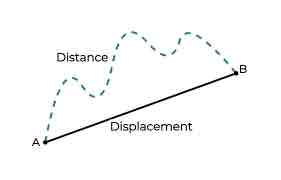
Distance
The measure of length between objects or points without regard for direction.
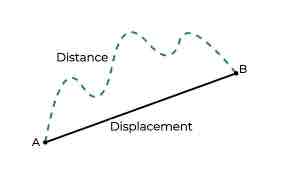
Displacement
The change in position of an object.
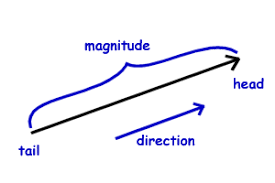
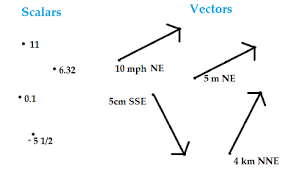
Vector
A quantity that has direction as well as magnitude.
Example: Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration
Scalar
Quantities that have no direction associated with them.
Example: Distance and Speed
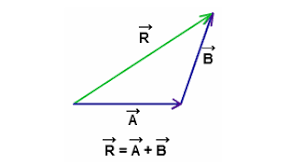
Resultant Vector
The single vector that represents the sum of two or more individual vectors.
Speed
The magnitude of the change of its position per unit of time.
Aka a positive number with units.
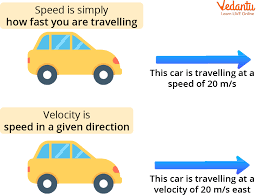
Velocity
The magnitude of how fast an object is moving and the direction in which it’s moving.
Acceleration
How rapidly the velocity of an object is changing.
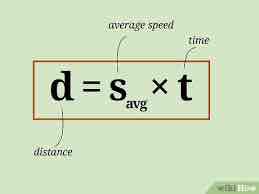
Distance Formula
Distance= Speed x Time
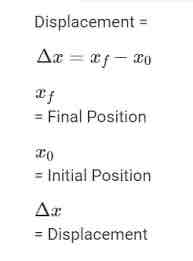
Displacement Formula
Δx= x2-x1
Displacement= Final - Initial
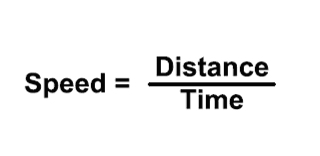
Speed Formula
Speed= Distance Traveled/Time Elapsed
s= d/t
Velocity Formula
v= Δx / Δt
Velocity= Displacement / Time Elapsed
*Average speed is not necessarily equal to the magnitude of the average velocity
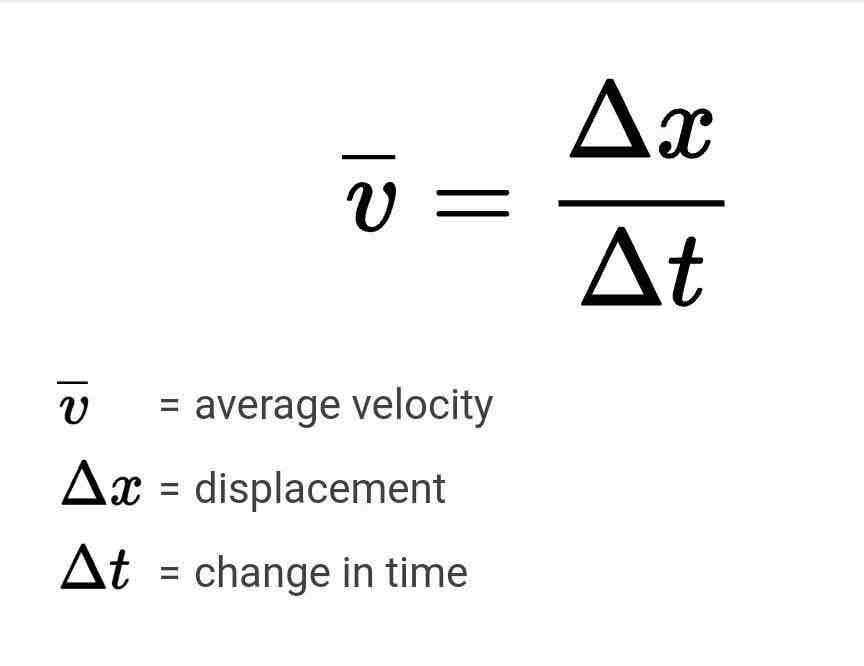
Acceleration Formula
a= Δv / Δt
Acceleration= Change in Velocity / Time Elapsed
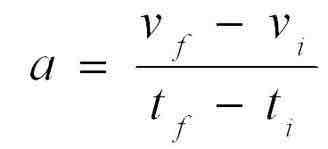
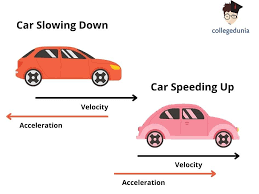
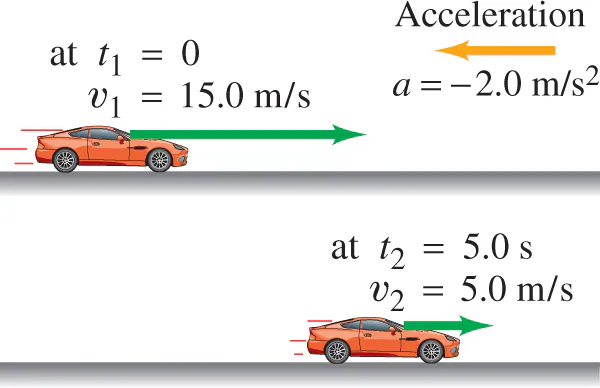
Positive/Negative Acceleration
Positive= right
Negative= left
The acceleration vector (orange) points to the left because the car slows down as it moves to the right.
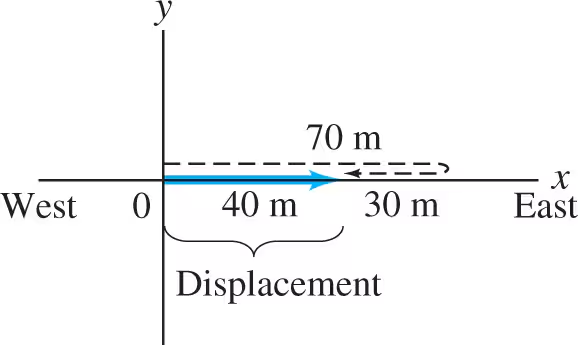
Positive/Negative Displacement
Positive Displacement= Right
Example: Δx= 30.0m - 10.0m = 20.0m
Negative Displacement= Left
Example: Δx= 10,0m - 30.0m= -20.0m
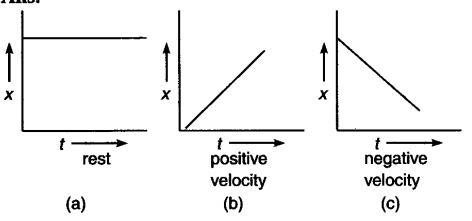
Positive/Negative Velocity
The average velocity is positive for an object moving to the right along the x axis and negative when the object moves to the left.
*The direction of the average velocity is always the same as the direction of the displacement.