badm 2301 quiz 4
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
1
New cards
e business
in addition to the buying and selling of goods and services, e business refers to servicing customer, collaborating with business partners and performing electronic transaction with in an organization
2
New cards
virtual (pure play) organizations
companies engaged only in e commerce
3
New cards
degree of digitization
the extent to which the commerce has been transformed from physical to digital
concept can relate to both the product or service being sold and the delivery agent or intermediary
concept can relate to both the product or service being sold and the delivery agent or intermediary
4
New cards
brick and mortar orgs
purely physical orgspa
5
New cards
partial EC companies
organizations that are a combo of digital and physical dimensions
book from amazon
book from amazon
6
New cards
click and mortar orgs/clicks and bricks
conduct some e commerce activites, yet their primary business is carried out in the physical world
example of partial ec
example of partial ec
7
New cards
e commerce
process of buying selling, transferring, exchanging products, services, or info through computer networks, including the internet
8
New cards
7 common types of e commerce
b2b (business to business); b2c (business to consumer); c2c (consumer to consumer); b2e (business to employee); egov (e government, refers to gov to citizen and gov to business); mobile commerce; social commerce; conversational commerce
9
New cards
C2C
consumer to consumer (etsy, ebay)
10
New cards
gig job
org contracts with independent workers for short-term engagements where the worker is paid for each engagement
11
New cards
B2E
business to employee; an org using electronic commerce internally to provide info and services to its employees
benefits and training classes, insurance, travel, etc.
benefits and training classes, insurance, travel, etc.
12
New cards
e government
to deliver info and public services to citizens (gov to citizen) and business partners/suppliers (gov to business)
gov is regulating; efficient way of conducting business transactions with citizens and businesses and within the gov themselves. e gov makes gov more efficient and effective, esp in delivery of public services
gov is regulating; efficient way of conducting business transactions with citizens and businesses and within the gov themselves. e gov makes gov more efficient and effective, esp in delivery of public services
13
New cards
mobile commerce
e commerce that is conducted entirely in a wireless environment. cell phones to shop
14
New cards
social commerce
delivery of electronic commerce activities and transactions through social computing
15
New cards
conversational commerce
conversational commerce (chat commerce) refers to e commerce using messaging and chat apps to offer a daily choice, often personalized, of a meal, product, or serviceb
16
New cards
business model
method by which a company generates revenue to sustain itself (each type of EC is a business model)
17
New cards
electronic catalogs
consist of a product database, a directory, and search capabilities, and a presentation function. backbone of most e commerce sites
18
New cards
auction
competitive buying and selling process in which prices are determined dynamically by competitive bidding
19
New cards
e auction
generally increase revenues for sellers by broadening the customer base and shortening the cycle time of the auction
buyers generally benefit because they can bargain for lower prices. they also do not have to travel to a physical location
internet provides efficient infrastructure for conduction auctions at lower admin costs and with more involved sellers and buyers. both individual consumers and corporations can participate in auctions
buyers generally benefit because they can bargain for lower prices. they also do not have to travel to a physical location
internet provides efficient infrastructure for conduction auctions at lower admin costs and with more involved sellers and buyers. both individual consumers and corporations can participate in auctions
20
New cards
2 types of auctions
forward and reverse
21
New cards
forward auctions
auctions that sellers use as a selling channel to many potential buyers, the highest bidder wins (eBay)
22
New cards
reverse auctions
auctions in which 1 buyer, usually an organization, seeks to buy a product or service, and supplier submit bids, lowest bidder wins
gov and large corps use this approach, can provide large savings for buyer
gov and large corps use this approach, can provide large savings for buyer
23
New cards
electronic storefront
website that represents a single store
24
New cards
electronic mall (cybermall/emall)
collection of individual shops consolidated under 1 internet address
25
New cards
e marketplacd
virtual market space on web where many buyers and seller conduct e business
26
New cards
electronic payments
what ECs accept for money
27
New cards
electronic payment machanisms
enable buyers to pay for goods/services electronically, rather than writing a check or using cash
28
New cards
online direct market
manufacturers or retailers selling directly to consumers
29
New cards
electronic tendering system
business requests quotes from suppliers, uses B2B with a reverse auction mechanism
30
New cards
name your own pricd
customer decides how much they want to pay, intermediary tries to match a provider
31
New cards
find the best price
customers specify a need and intermediary compares providers and shows lowest price
customer must accept offer in short time or they may lose the deal
customer must accept offer in short time or they may lose the deal
32
New cards
affiliate marketing
vendors ask partners to place logos or banners on site; if customers click on logo, go to vendor site, and buy, then vendor pays commission to partners
33
New cards
viral marketing
recipients of your marketing notices/info send info about your product to friends
34
New cards
group purchasing
small buyers aggregate demand to get a large volume, then the group conducts tendering or negotiates a lower price
35
New cards
product customization
customers use internet to self configure products or services, sellers then price them and fulfill them quickly
36
New cards
electronic marketplaces and exchanges
transactions are conducted efficiently (more info to buyers and seller, lower transaction costs) in electronic marketplaces (private or public)
37
New cards
bartering online
intermediary administers online exchange of surplus products or company receives "points" for its contribution, which it can use to purchase other needed items
38
New cards
deep discounters
company offers steep price discounts
39
New cards
e credit cards
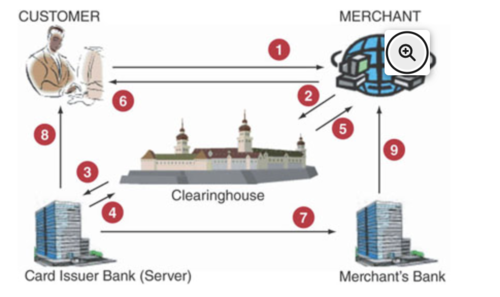
1: purchase book from amazon, your credit card info and purchase amount are encrypted in browser. this ensures the information is safe while it is "travelling" to the internet to amazon
2: info arrives at amazon, it is not opened. it is automatically transferred (in encrypted form) to clearinghouse, where it is decrypted for verification and authorization
3: clearinghouse asks bank that issued credit card (BofA, Chase, etc.) to verify CC info
4: card issuer bank verifies CC info and reports this to the clearinghouse
5: clearinghouse reports result of verification of CC to amazon
6: amazon reports successful purchase and amount to you
7: card issuer sends bank funds of purchase amount to amazon's bank
8: card issuer bank notifies me of debit on CC
9: amazon's bank notifies them of funds credited to its acct
2: info arrives at amazon, it is not opened. it is automatically transferred (in encrypted form) to clearinghouse, where it is decrypted for verification and authorization
3: clearinghouse asks bank that issued credit card (BofA, Chase, etc.) to verify CC info
4: card issuer bank verifies CC info and reports this to the clearinghouse
5: clearinghouse reports result of verification of CC to amazon
6: amazon reports successful purchase and amount to you
7: card issuer sends bank funds of purchase amount to amazon's bank
8: card issuer bank notifies me of debit on CC
9: amazon's bank notifies them of funds credited to its acct
40
New cards
stored value money cards
form of e cash on which a fixed amount of prepaid money is stored, amount is reduced each time card is used (visa gift card)
41
New cards
EMV smart cards
contain a chip that can store a large amount of info as well as on a magnetic strip for backwards compatibility
42
New cards
payment gateway
e commerce application that facilitates online shopping by mediating the interconnections to the merchant's bank, card issuer bank, then back to original website to approve/decline purchase
43
New cards
e commerce benefits
good customer service, more options, more convenient
44
New cards
e commerce limits
lack of universally accepted security measures, insufficient telecommunications bandwidth in some regions, accessing web can be expensive.
EC is perceived as nonsecure
EC is perceived as nonsecure
45
New cards
b2b is larger than b2c by volume, but b2c is more complex
slay
46
New cards
electronic retailing
direct sale of products and services through storefronts or electronic malls, usually designed around an electronic catalog format and auctions
47
New cards
long tail
retailing strategy of selling a large number of unique items in small quantities
48
New cards
e mall
collection of individual shops group under 1 url (amazon)
49
New cards
disintermediation
2 function: provide info (can be fully automated) & perform value added services (such as consulting) (requires expertise, can only be partially automated)
50
New cards
fintech (fuck this)
industry composed of companies that use tech to compete in the marketplace with traditional financial institutions and intermediaries in the delivery of financial services, which include banking, insurance, real estate, and investment
51
New cards
native advertising
ads disguised as content (those tiktok fuckwads)
52
New cards
ad blockers
my beloved
53
New cards
e tailing issues
1) channel conflict
2) order fulfillment
3) personalized pricing
2) order fulfillment
3) personalized pricing
54
New cards
multichanneling
process in which a company integrates its online and offlilne channels
55
New cards
showrooming
occurs when shoppers visit brick and mortar store to examine product in person. then conduct online research. often purchase product from website, for lower price
56
New cards
order fulfillment
Any time a company sells directly to customers, it is involved in various order-fulfillment activities; makes it harder to be effective and efficient in B2C
57
New cards
standardized pricing
when a product is sold through multiple channels, the cost should not vary by more than the difference in shipping, taxation, and distribution costs. If the price is higher for a product at a certain retailer, then customers can easily use the Internet to compare prices and features among a huge number of retailers to purchase that product from another retailer, a process known as showrooming.
58
New cards
personalized pricing
practice of pricing items at a point determined by a particular customer's perceived ability to pay
59
New cards
reservation price
max price a consumer is willing to pay for a product or service based on total perceived consumer benefits
60
New cards
spamming
indiscriminate distribution of email without receiver's permission
61
New cards
sell side marketplace
B2B model in which organizations sell their products or services to other organizations electronically from their own private e-marketplace website or from a third-party website
- This model is similar to the B2C model in which the buyer is expected to come to the seller’s site, view catalogs, and place an order. In the B2B sell-side marketplace, however, the buyer is an organization.
- suitable for customization
- seller can be a manufacturers, distributor or a retailer
-key mechanisms in the sell-side model are forward auctions and electronic catalogs that can be customized for each large buyer
kinda like a bidding war
- This model is similar to the B2C model in which the buyer is expected to come to the seller’s site, view catalogs, and place an order. In the B2B sell-side marketplace, however, the buyer is an organization.
- suitable for customization
- seller can be a manufacturers, distributor or a retailer
-key mechanisms in the sell-side model are forward auctions and electronic catalogs that can be customized for each large buyer
kinda like a bidding war
62
New cards
procurement
Procurement is the overarching function that describes the activities and processes to acquire goods and services. Distinct from purchasing, procurement involves the activities necessary to establish requirements, sourcing activities such as market research and vendor evaluation, and negotiation of contracts.
63
New cards
buy side marketplace
a model in which organizations attempt to procure needed products or services from other organizations electronically. A major method of procuring goods and services in the buy-side model is the reverse auction.
- uses EC technology to streamline the procurement process. The goal is to reduce both the costs of items procured and the administrative expenses involved in procuring them. EC technology can also shorten the procurement cycle time.
- uses EC technology to streamline the procurement process. The goal is to reduce both the costs of items procured and the administrative expenses involved in procuring them. EC technology can also shorten the procurement cycle time.
64
New cards
e procurement
uses reverse auctions, particularly group purchasing
65
New cards
group purchasing
multiple buyers combine their orders so that they constitute a large volume and therefore attract more seller attention. When buyers place their combined orders on a reverse auction, they can also negotiate a volume discount
66
New cards
public exchanges
Electronic marketplaces in which there are many sellers and many buyers, and entry is open to all; frequently owned and operated by a third party
-buyers and sellers merely have to “plug in” to trade. B2B public exchanges are often the initial points of contact between business partners. Once the partners make contact, they may move to a private exchange or to private trading rooms provided by many public exchanges to conduct their subsequent trading activities (etsy, amazon for b2c)
-buyers and sellers merely have to “plug in” to trade. B2B public exchanges are often the initial points of contact between business partners. Once the partners make contact, they may move to a private exchange or to private trading rooms provided by many public exchanges to conduct their subsequent trading activities (etsy, amazon for b2c)
67
New cards
direct materials
inputs to the manufacturing process, such as safety glass used in car windshields
68
New cards
indirect materials
girl you know what this is
69
New cards
3 types of public exchanges (vertical, horizontal, and functional)
1) Vertical exchanges connect buyers and sellers in a given industry; offer services that are particularly suited to the community they serve. Vertical exchanges are frequently owned and managed by a consortium, a term for a group of major players in an industry. For example, Marriott and Hyatt own a procurement consortium for the hotel industry, and Chevron owns an energy e-marketplace
2) horizontal exchanges: connect buyers and sellers across many industries. They are used primarily for MRO (maintenance, repair, operations) materials
3) functional exchanges, needed services such as temporary help or extra office space are traded on an “as-needed” basis. For example, Employease (www.employeaseinc.com)s can find temporary labor by searching employers in its Employease Network.
2) horizontal exchanges: connect buyers and sellers across many industries. They are used primarily for MRO (maintenance, repair, operations) materials
3) functional exchanges, needed services such as temporary help or extra office space are traded on an “as-needed” basis. For example, Employease (www.employeaseinc.com)s can find temporary labor by searching employers in its Employease Network.
70
New cards
cloud computing
technology in which tasks are performed by computers physically removed from the user and accessed over a network, in particular the internet
71
New cards
IT infrastructure evolved
1) stand alone mainframes
2) mainframe and dumb terminals
3) stand alone PCs
4) local area networks (client/servier computing)
5) enterprise computing
6) cloud computing
2) mainframe and dumb terminals
3) stand alone PCs
4) local area networks (client/servier computing)
5) enterprise computing
6) cloud computing
72
New cards
stand along mainframes
Organizations initially used mainframe computers in their engineering and accounting departments. The mainframe was typically housed in a secure area, and only MIS personnel had access to it. (like mad men)
73
New cards
mainframes and dumb terminals
Forcing users to go to wherever the mainframe was located was time consuming and inefficient. As a result, firms began placing so-called "dumb terminals"—essentially electronic typewriters with limited processing power—in user departments. This arrangement enabled users to input computer programs into the mainframe from their departments, a process called remote job entry.
74
New cards
stand alone PCs
In the late 1970s, the first personal computers appeared. The IBM PC's debut in 1981 legitimized the entire personal computer market. Users began bringing personal computers to the workplace to improve their productivity—for example, by using spreadsheet and word processing applications. These computers were not initially supported by the firm's MIS department. However, as the number of personal computers increased dramatically, organizations decided to support these devices, and they established policies as to which PCs and soft ware they would support.
75
New cards
local area networks
organizations began to connect personal computers to local area networks and then those LANs to the mainframe
76
New cards
enterprise computing
In the early 1990s, organizations began to use networking standards to integrate different kinds of networks throughout the firm, thereby creating enterprise computing. As the Internet became widespread after 1995, organizations began using the TCP/IP networking protocol to integrate different types of networks. All types of hardware were networked, including mainframes, personal computers, smartphones, printers, and many others. Software applications and data now flow seamlessly throughout the enterprise and among organizations.
77
New cards
on premise computing
A model of IT management where companies own their IT infrastructure (their software, hardware, networks, and data management) and maintain it in their data centers.
- incurs expenses for IT infrastructure; orgz usually do not use their infrastructure to its full capacity
- on-premise system meant that its technology group spent too much time managing its information technology infrastructure and not enough time developing innovative projects that could enhance the firm’s future growth. Furthermore, Photobox had difficulty keeping up with the large amount of new digital photos from its customers.
- incurs expenses for IT infrastructure; orgz usually do not use their infrastructure to its full capacity
- on-premise system meant that its technology group spent too much time managing its information technology infrastructure and not enough time developing innovative projects that could enhance the firm’s future growth. Furthermore, Photobox had difficulty keeping up with the large amount of new digital photos from its customers.
78
New cards
cloud computing characteristics
1. provides on demand self service
2. considers retailers
3. encompasses the characteristics of grid computing
4. encompasses the characteristics of utility computing
5. utilizes broad network access
6. pools computing resources
7. often occurs on virtualized servers
2. considers retailers
3. encompasses the characteristics of grid computing
4. encompasses the characteristics of utility computing
5. utilizes broad network access
6. pools computing resources
7. often occurs on virtualized servers
79
New cards
provides ono demand self service
A customer can access needed computing resources automatically. This characteristic gives customers elasticity and flexibility—that is, customers can increase (scale up) or decrease (scale down) the amount of computing they need.
80
New cards
consider retailers
During the Christmas buying season, these firms need much more computational capacity than at other times of the year. Therefore, if they use cloud computing, they can scale up during peak periods of business activity and scale down at other times.
81
New cards
encompasses the characteristics of grid computing
Grid computing enables organizations to use their computing resources more efficiently.
Grid computing provides fault tolerance and redundancy, meaning that there is no single point of failure, so the failure of one computer will not stop an application from executing.
Grid computing makes it easy to scale up—that is, to access increased computing resources (add more servers)—to meet the processing demands of complex applications.
Grid computing makes it easy to scale down (remove computers) if extensive processing is not needed.
Grid computing provides fault tolerance and redundancy, meaning that there is no single point of failure, so the failure of one computer will not stop an application from executing.
Grid computing makes it easy to scale up—that is, to access increased computing resources (add more servers)—to meet the processing demands of complex applications.
Grid computing makes it easy to scale down (remove computers) if extensive processing is not needed.
82
New cards
grid computing
A technology that applies the unused processing resources of many geographically dispersed computers in a network to form a virtual supercomputer.
83
New cards
cloud computing encompasses the characteristics of utility computing
A technology whereby a service provider makes computing resources and infrastructure management available to a customer as needed. The provider then charges the customer for its specific usage rather than a flat rate.
84
New cards
cloud computing uses broad network access
cloud provider's computing resources are available over a network, accessed with a web browser, and they are configured so that they can be used with any computing device
85
New cards
cloud computing pools computing resources
provider's computing resources are available to serve multiple customers. These resources are dynamically assigned and reassigned according to customer demand
86
New cards
cloud computing often occurs on virtualized servers
server virtualization --> A technology that uses software-based partitions to create multiple virtual servers (called virtual machines) on a single physical server.
-each server no longer has to be dedicated to a particular task. Multiple applications can run instead on a single physical server, with each application running within its own software environment. As a result, virtualization enables companies to increase server usage. Companies can also realize cost savings in two areas. First, they do not have to buy additional servers to meet peak demand. Second, they reduce their utility costs because they are using less energy
-each server no longer has to be dedicated to a particular task. Multiple applications can run instead on a single physical server, with each application running within its own software environment. As a result, virtualization enables companies to increase server usage. Companies can also realize cost savings in two areas. First, they do not have to buy additional servers to meet peak demand. Second, they reduce their utility costs because they are using less energy
87
New cards
cloud computing
eases the difficult tasks of procuring, configuring, and maintaining hardware and software environments. It also allows enterprises to get their applications up and running faster, with easier manageability and less maintenance. It also enables IT to adjust IT resources (e.g., servers, storage, and networking) more rapidly to meet fluctuating and unpredictable business demand.
88
New cards
public clouds are...
shared, easily accessible, multi-customer IT infrastructures that are available non exclusively to any entity in the general public (individuals, groups, orgs), over the internet
89
New cards
private cloud/internal/corporate
IT infrastructures that are accessible only by a single entity or by an exclusive group of related entities that share the same purpose and requirements, such as all the business units within a single organization.
- Private clouds provide IT activities and applications as a service over an intranet within an enterprise. Enterprises adopt private clouds to ensure system and data security. For this reason, these systems are implemented behind the corporate firewall.
- Private clouds provide IT activities and applications as a service over an intranet within an enterprise. Enterprises adopt private clouds to ensure system and data security. For this reason, these systems are implemented behind the corporate firewall.
90
New cards
hybrid clouds
clouds composed of public and private clouds that remain unique entities but are bound together, offering the benefits of multiple deployment models.
customers may need to maintain some of their data in a private cloud for security and privacy reasons while storing other, less-sensitive data in a public cloud because it is less expensive.
customers may need to maintain some of their data in a private cloud for security and privacy reasons while storing other, less-sensitive data in a public cloud because it is less expensive.
91
New cards
vertical clouds
building cloud infrastructure and applications for different businesses - construction, finance, or insurance businesses
92
New cards
cloud computing services are based ono three models:
infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
platform as a service (PaaS)
software as a service (SaaS)
platform as a service (PaaS)
software as a service (SaaS)
93
New cards
3 types of computing generally required by consumers
infrastructure to run software and store data (IaaS), platforms to develop applications (PaaS), and software applications to process their data (SaaS).
94
New cards
infrastructure as a service
model with which cloud computing providers offer remotely accessible servers, networks, and storage capacity
bills on a utility computing basis
bills on a utility computing basis
95
New cards
platform as a service
A model in which customers rent servers, operating systems, storage, a database, software development technologies such as Java and .NET, and network capacity over the Internet.
PaaS model allows the customer to both run existing applications and to develop and test new applications. PaaS offers customers several advantages, which include the following:
Application developers can develop and run their software solutions on a cloud platform without the cost and complexity of buying and managing the underlying hardware and software layers.
Underlying computing and storage resources automatically scale to match application demand.
Operating system features can be upgraded frequently.
Geographically distributed development teams can work together on software development projects.
PaaS services can be provided by diverse sources located throughout the world.
Initial and ongoing costs can be reduced by the use of infrastructure services from a single vendor rather than maintaining multiple hardware facilities that often perform duplicate functions or suffer from incompatibility problems.
PaaS model allows the customer to both run existing applications and to develop and test new applications. PaaS offers customers several advantages, which include the following:
Application developers can develop and run their software solutions on a cloud platform without the cost and complexity of buying and managing the underlying hardware and software layers.
Underlying computing and storage resources automatically scale to match application demand.
Operating system features can be upgraded frequently.
Geographically distributed development teams can work together on software development projects.
PaaS services can be provided by diverse sources located throughout the world.
Initial and ongoing costs can be reduced by the use of infrastructure services from a single vendor rather than maintaining multiple hardware facilities that often perform duplicate functions or suffer from incompatibility problems.
96
New cards
software as a service
A delivery model in which cloud computing vendors provide software that is specific to their customers’ requirements.
- typically charge their customers a monthly or yearly subscription fee.
SaaS applications reside in the cloud instead of on a user’s hard drive
- What differentiates SaaS applications from other applications is their ability to scale. As a result, applications can run on as many servers as is necessary to meet changing demands. This process is transparent to the user; back up their customer's data
- typically charge their customers a monthly or yearly subscription fee.
SaaS applications reside in the cloud instead of on a user’s hard drive
- What differentiates SaaS applications from other applications is their ability to scale. As a result, applications can run on as many servers as is necessary to meet changing demands. This process is transparent to the user; back up their customer's data
97
New cards
3 benefits of cloud computing
1) positive impact on employees
- enables companies to provide their employees with access to all the information they need no matter where they are, what device they are using, or with whom they are working
2) can save money
- cost of building and operating an on-premise IT infrastructure will typically be more expensive than adopting the cloud computing model. Cloud providers purchase massive amounts of IT infrastructure (e.g., hardware and bandwidth) and gain cost savings by buying in large quantity; cloud computing can reduce or eliminate the need to purchase hardware, build and install software, and pay software licensing fees. The organization pays only for the computing resources it needs, and then only when it needs them
3) Can improve organizational flexibility and competitiveness
- allows organizations to use only the amount of computing resources they need at a given time; companies can efficiently scale their operations up or down as needed to meet rapidly changing business conditions. Cloud computing is also able to deliver computing services faster than the on-premise computing can
- enables companies to provide their employees with access to all the information they need no matter where they are, what device they are using, or with whom they are working
2) can save money
- cost of building and operating an on-premise IT infrastructure will typically be more expensive than adopting the cloud computing model. Cloud providers purchase massive amounts of IT infrastructure (e.g., hardware and bandwidth) and gain cost savings by buying in large quantity; cloud computing can reduce or eliminate the need to purchase hardware, build and install software, and pay software licensing fees. The organization pays only for the computing resources it needs, and then only when it needs them
3) Can improve organizational flexibility and competitiveness
- allows organizations to use only the amount of computing resources they need at a given time; companies can efficiently scale their operations up or down as needed to meet rapidly changing business conditions. Cloud computing is also able to deliver computing services faster than the on-premise computing can
98
New cards
risks with cloud computing
legacy IT systems, reliability, privacy, security, legal and regulatory environment, and criminal use of cloud computing
99
New cards
Legacy IT systems (in reference to cloud computing)
IT systems that have been in use for an extended time period; can not be transferred to the cloud easily; organizational IT systems have accumulated a diversity of hardware, operating systems, and applications. When bundled together, these systems are called “legacy spaghetti"
100
New cards
reliability (in reference to cloud computing)
not as reliable as well managed IT infrastructure