Locally Dynamic Synaptic learning rules in pyramidal neuron dendrites
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What does “synapse-specific LTP” mean?
Only the stimulated synapse undergoes potentiation, meaning each synapse can act as an independent learning unit.
What is heterosynaptic spread of LTP?
When LTP at one synapse also affects or “spreads” to neighboring synapses nearby on the dendrite, reducing their independence.
What does heterosynaptic metaplasticity predict?
LTP at one group of synapses makes it harder (raises the threshold) for nearby synapses to undergo LTP.
What does clustered plasticity predict?
LTP at one spine makes it easier (lowers the threshold) for nearby spines to undergo LTP, possibly through local tagging mechanisms.
What was the main experimental goal of this study?
To test whether LTP in one synapse makes nearby synapses:
Harder to potentiate (metaplasticity), or
Easier to potentiate (clustered plasticity).
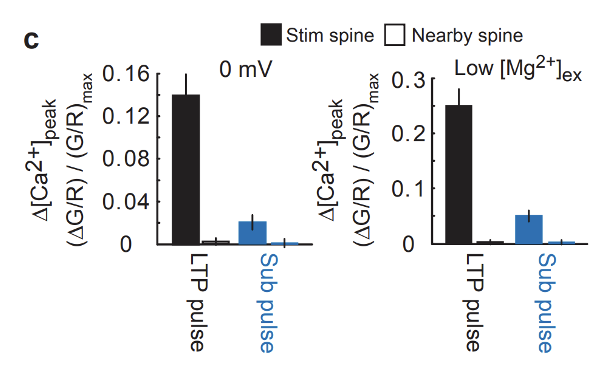
What happens when they stimulated Spine 1 with a strong stimulus and a neighbouring spine with a weak stimulus
They held the neuron at 0MV to remove the Mg block + uncaging and stimulated the spine (protocol pairing) to induce a strong LTP, then they applied a weak stimulus (usually too weak to cause LTP) in the neighbouring spine which also undergoes FULL LTP because the first spine’s potentiation lowered the threshold for the neighbouring spine
What happened when they held the cell at -70mV and what did this indicate
At -70mV, the LTP protocol LTP failed to LTP in either the stimulated spine or its neighbor. This meant that crosstalk requires actual LTP induction via NMDA receptor mediated Ca influx, not just the uncaging procedure
In the uncaging only experiment (no depolarization, Mg removed), what happened when one spine received strong stimulation and a neighbouring spine later received subthreshold stimulation?
The first spine showed full, long lasting LTP, and the neighbouring spine also underwent full, persistent LTP, just as strong as the LTP spine
This showed that LTP and crosstalk can occur with just NMDAr Ca entry, without artifical depolarization. Meaning clustered plasticity is a realistic natural mechanism
In this paper, how did they prove that crosstalk happens under physiological (normal conditions)
They stimulated schaffer collatetral cells which mimics what would actually happen in the brain
This triggered LTP and volume increase. Two minutes later a subthreshold stimulus (usually too weak to cause LTP) was applied to the neighbouring spine which caused a full, persisten LTP
Proving that crosstalk can occur in natural conditions
What is STDP (Spike-timing-dependent-plasticity)
A plasticity rule where the itming between an EPSP and a postsynaptic AP determines LTP.
If the time between EPSP and postsynaptic AP = tens of ms = LTP
If the time between EPSP and postynaptic AP = 30-40 ms = No LTP
What happens in normal STDP at single spines
At Δt = 5 ms, spines show strong LTP
At Δt = 35 ms, no LTP occurs
How does crosstalk affect STDP
After one spine undergoes LTP with Δt = 5 ms, a nearby spine can also now undergo full LTP even with Δt = 35ms
Meaning crosstalk broadens the STDP window and lower the threshold for potentiation at neighbouring spine
What are the time and distance limits of crosstalk between spines?
Crosstalk lasts about 10 mins and spreads only 8-10um along the SAME dendritic branch. Beyond this time or distance, subthrehold inputs no longer induce LTP
Is crosstalk mediated by extracellular or intracellular factors? How was this tested?
It requires intracellular signaling spread. When two spines were close in space BUT on DIFFERENT dendritic branches = no cross talk
Meaning crosstalk depended on intracellular factors like calcium ions, kinases, and second messenger
Does crosstalk rely on Ca release from intracellular stores?
No. Blocking ER Ca release with thapsigargin and ryanodine had no effect, showing crosstalk does not depend on intracellular Ca stores
(remember, Ca entry through NMDAr is still needed)
Compare and contrast order of weak and strong stimulus for crosstalk and synaptic tagging
Crosstalk = order matters = strong LTP first, then weak
Synaptic tagging = works in both orders → weak can come before or after a strong stimulus because tagged synapses can capture proteins later
Compare and contrast synaptic tagging and crosstalk in terms of protein synthesis
Corsstalk does NOT require new protein synthesis - LTP still happens when protein synthesis inhibitors are applied
Synaptic tagging = needs protein synthesis because weakly stimulated synapses depend on capturing plasticity related proteins (PRPs)
How is crosstalk different from synaptic tagging
Crosstalk is order dependent | Tagging isnt order dependent
Crosstalk doesnt depend on PRPs | Tagging depends on PRPs
Crosstalk is short lived | Tagging lasts for hours
After blocking multiple mechanisms (CPP, Thaps + ryanodine, and anisomycin) what did they conclude about how these affected crosstalk
CPP (NMDAR blocker): Completely blocked crosstalk -> shows NMDAR calcium entry is required
Thap + ryanodine (blocks Ca release from internal stores): no effect -> intracellular stores are not required
Anisomycin (protein synthesis inhbitor): No effect -> protein synthesis is not required
How does corsstalk contribute to memory storage?
Crosstalk lowers the threshold for LTP in nearby spines, crosstalk allows clusters of synapses on the same dendritic branch to potentiate together
This binding of related inputs creates coherent memory traces (engrams) and icnreases learning efficiency
What does crosstalk imply for plasticity models
Synapses arent fully independent, instead, groups of 10-20 spines on the same dendritic branch can act together. This supports clustered plasticity models where spines in the same area store memory traces
How does Calcium signals digger between stimulates spines, subthreshold spines, and neighbouring spines
Stmulated = large Ca influx
Stimulated neighbouring spines: Smaller Ca influx, not enough for LTP
Unstimulated spines: No Ca signal