Bio Study Quizlet: Organelles
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Membrane lipids are made here.
Important in breaking down toxins.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Proteins for cellular export are made here.
Covered in ribosomes.
Golgi Apparatus
Has a cis and trans face. The cis face receives protein and lipids, and the trans face sends them out. Packages and modifies things sent from the ER for transport in or out of the cell.
Vesicle
Made of phospholipids and holds macromolecules to send to places in and out of the cell.
When and who discovered the Golgi Apparatus
Discovered in 1898 by Camillo Golgi
Cell Wall
A rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides support to plant cells (square shape). (Literally just a wall).
Cell Membrane
A flexible barrier around a cell that regulates what enters and leaves the cell.
Vacuole
A sac inside a cell that acts as a storage area (multiple small ones in animal cells, one large one in plant cells).
Lysosomes
An organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down certain materials in the cell, such as nutrients, old organelles, and dangerous outside stuff like pathogens.
Modified Vesicle.
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that produces energy (ATP).
Chloroplasts
Organelle that captures the energy from sunlight and convert it into chemical energy in a process called photosynthesis.
Ribosomes
Makes proteins
Cytoplasm
The fluid that surrounds all the organelles and... idk i know what it is its what everything floats in.
Discovery Made by Alexander Fleming
Discovered Penicillin and the Lysozyme.
Theory that Lynn Margulis popularized
The Theory of Symbiogenesis, which states that complex life started when two independent organisms somehow merged. Pointing at the mitochondria and chloroplasts, which may have originally been independent organisms.
Proteins produced by free ribosomes
Proteins used for use within the cell: Enzymes and structural proteins (Cytosolic), proteins for chloroplasts, mitochondira, peroxisomes, and nucleus.
Proteins produced by ribosomes attached to the Rough ER.
Proteins destined for export outside of a cell: enzymes, hormones, antibodies, etc.
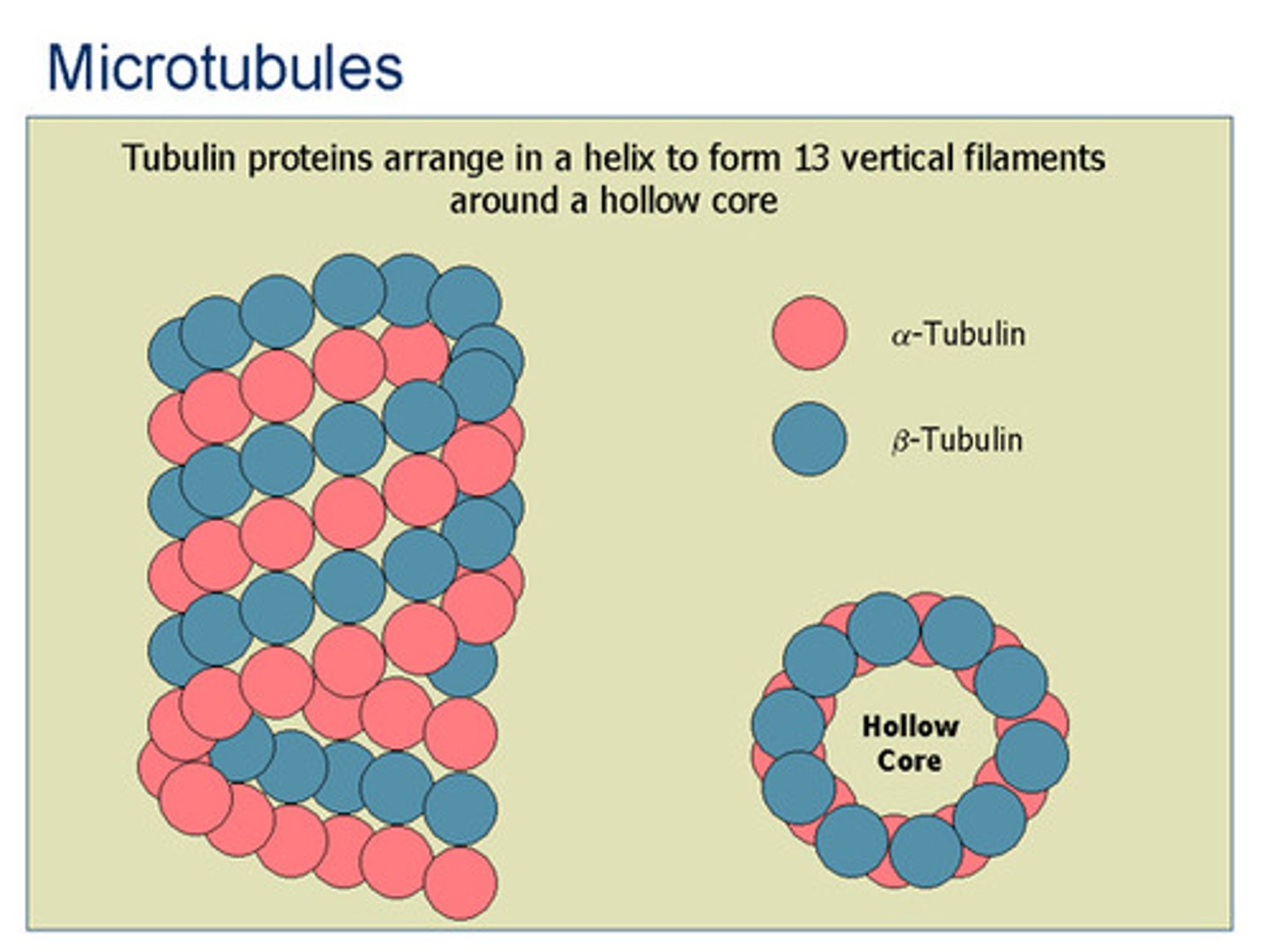
Microtubules
25 nanometers, provide structural support and transport within a cell and help with cell division and movement.
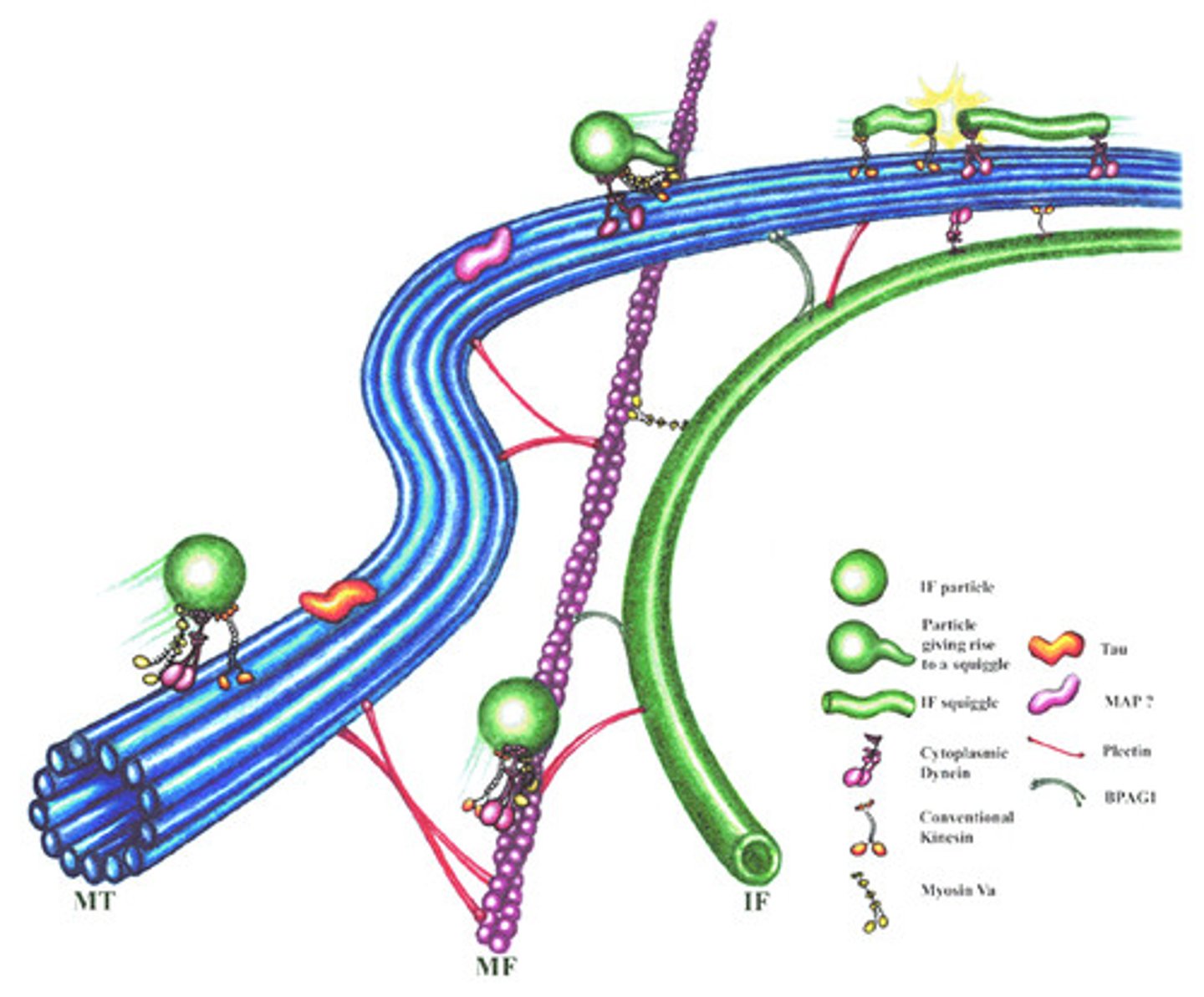
Intermediate filaments.
10 nanometers, provides structural support by reinforcing cell shape and anchoring nucleus and helps with tension and stress in muscle and nerve cells. helps connect structures in a cell.
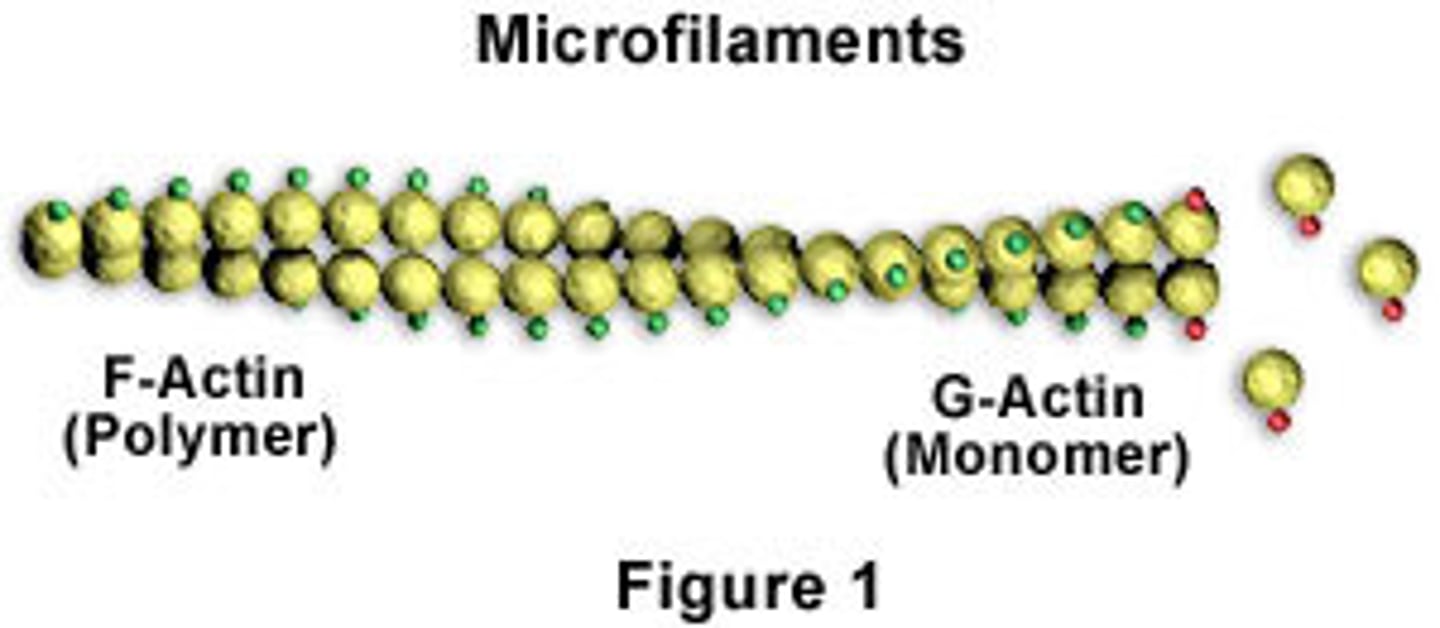
Microfilaments
7 nanometers, responsible for cell movement, shape changes, and muscle contraction.
Endosymbiont Theory
The theory that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated as independent prokaryotic cells and somehow became engulfed by another cell, and then evolved to be one organism with the other cell.
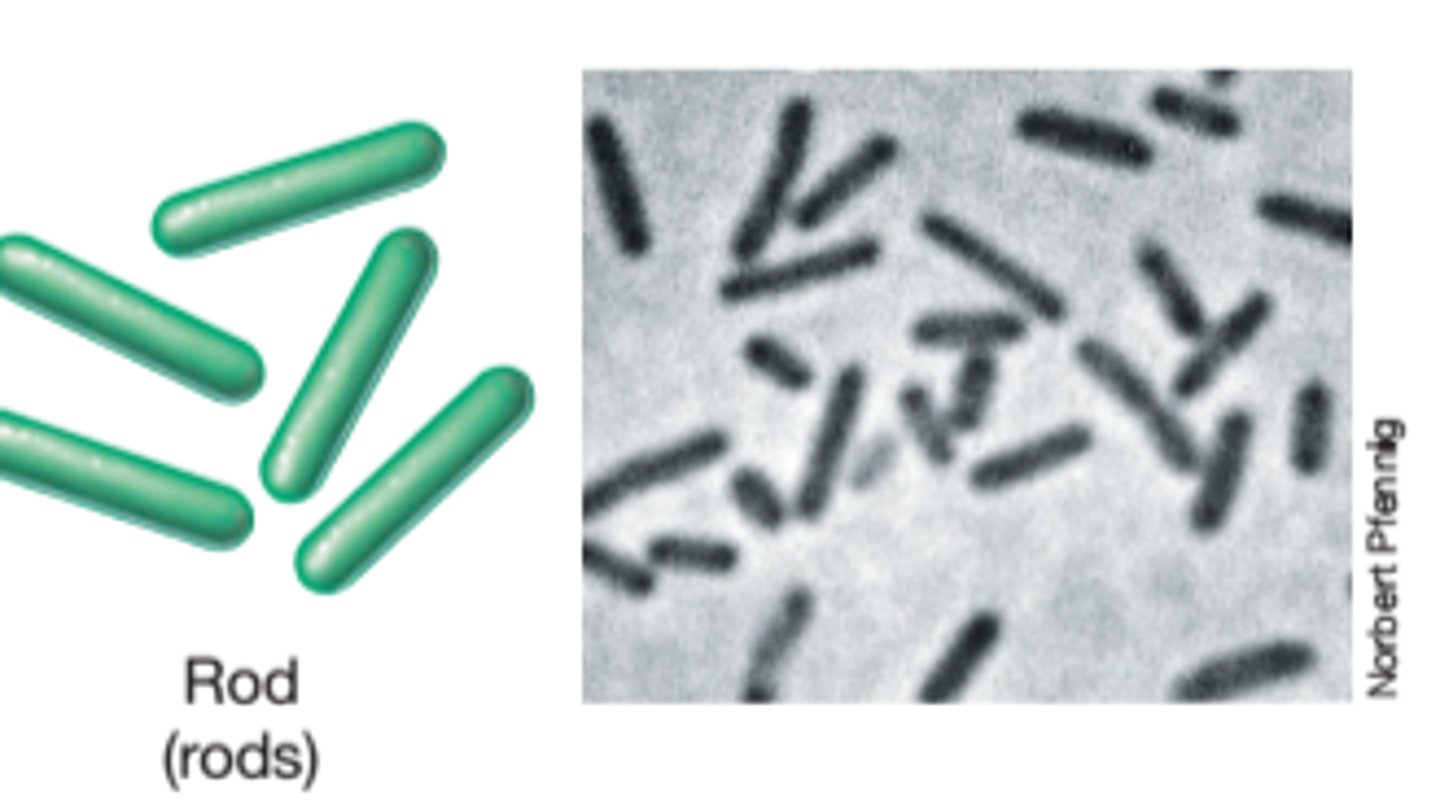
Bacillus Shape Bacteria
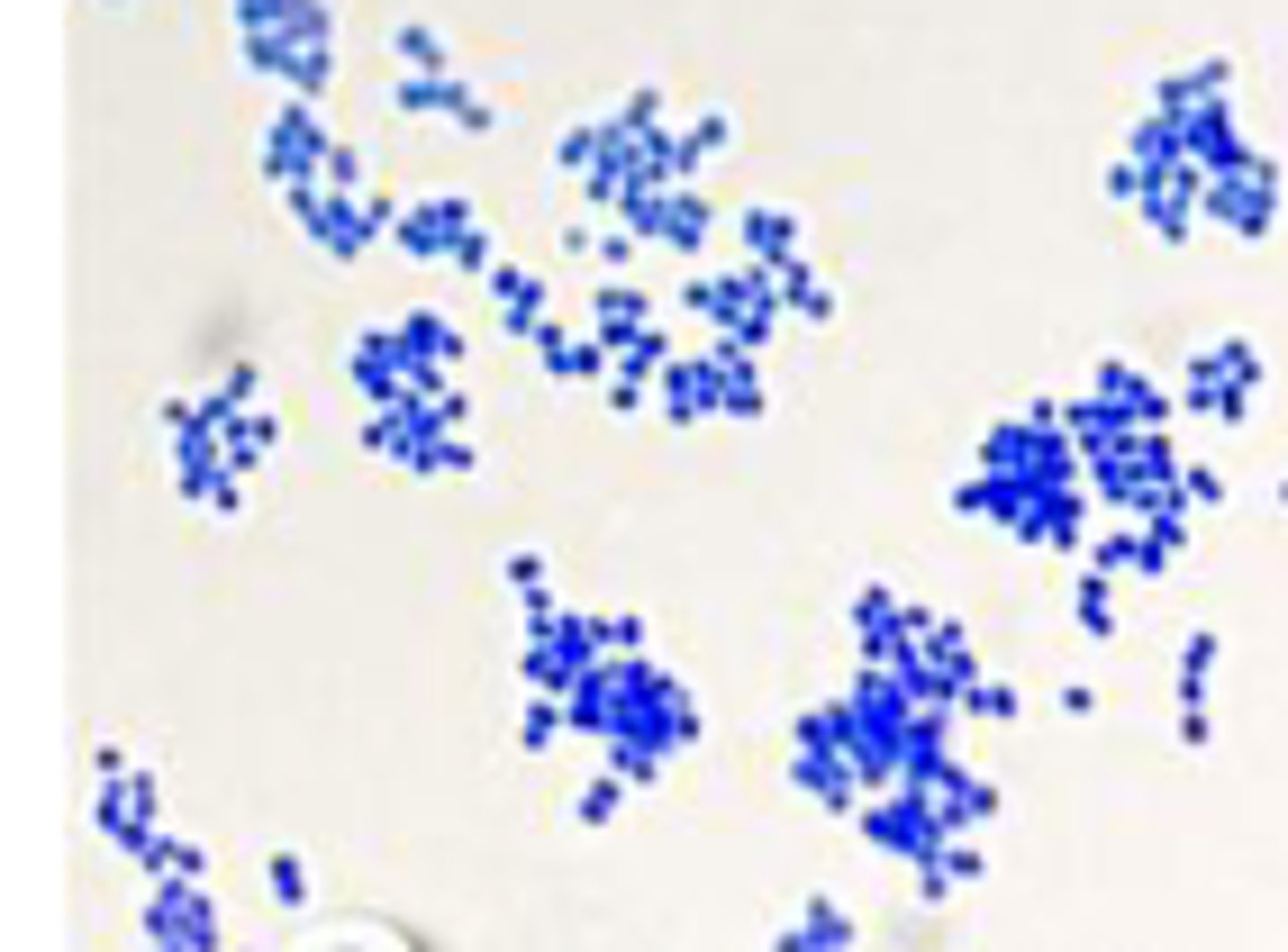
Coccus shaped bacteria
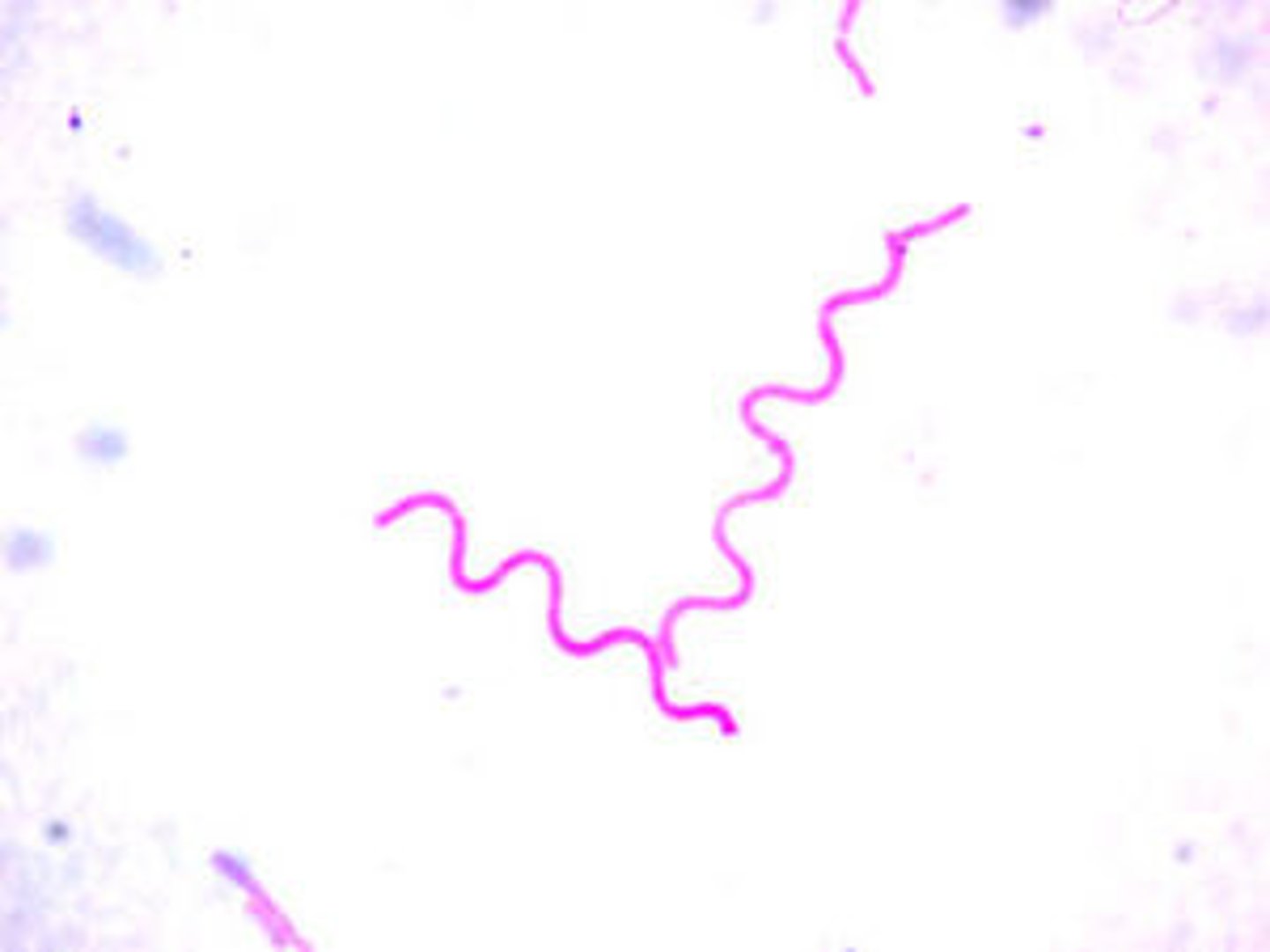
Spirullum shaped bacteria
- Protists
- Plants
- Fungi
- Animals
Kingdoms of Eukaryotes
- Archaebacteria
- Eubacteria
Kingdoms of Prokaryotes
Peroxisomes
breaks down and produces hydrogen peroxide, breaks down fatty acids.
Phagocytosis
A process in which extensions of cytoplasm surround and engulf large particles and take them into the cell
- White Blood Cells, amoeba movement.
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
Nuclear Membrane
A highly-porous membrane that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm
Nuclear Pore
Passageway for molecules into and out of the nucleus.
Chromosomes
Threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes, for splitting.
Chromatin
Substance found in eukaryotic chromosomes that consists of DNA, flowy.
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
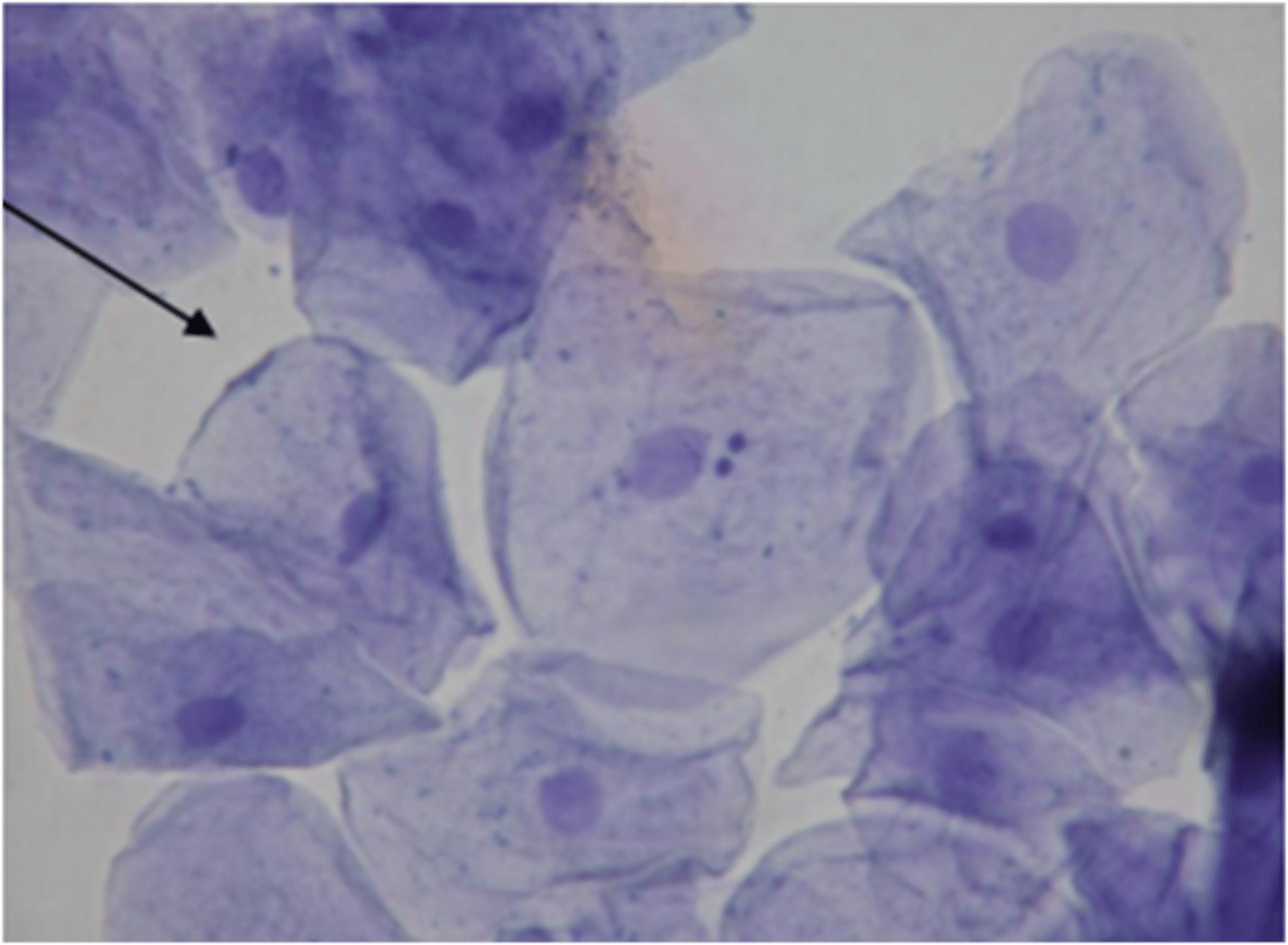
Human Cheek Cell
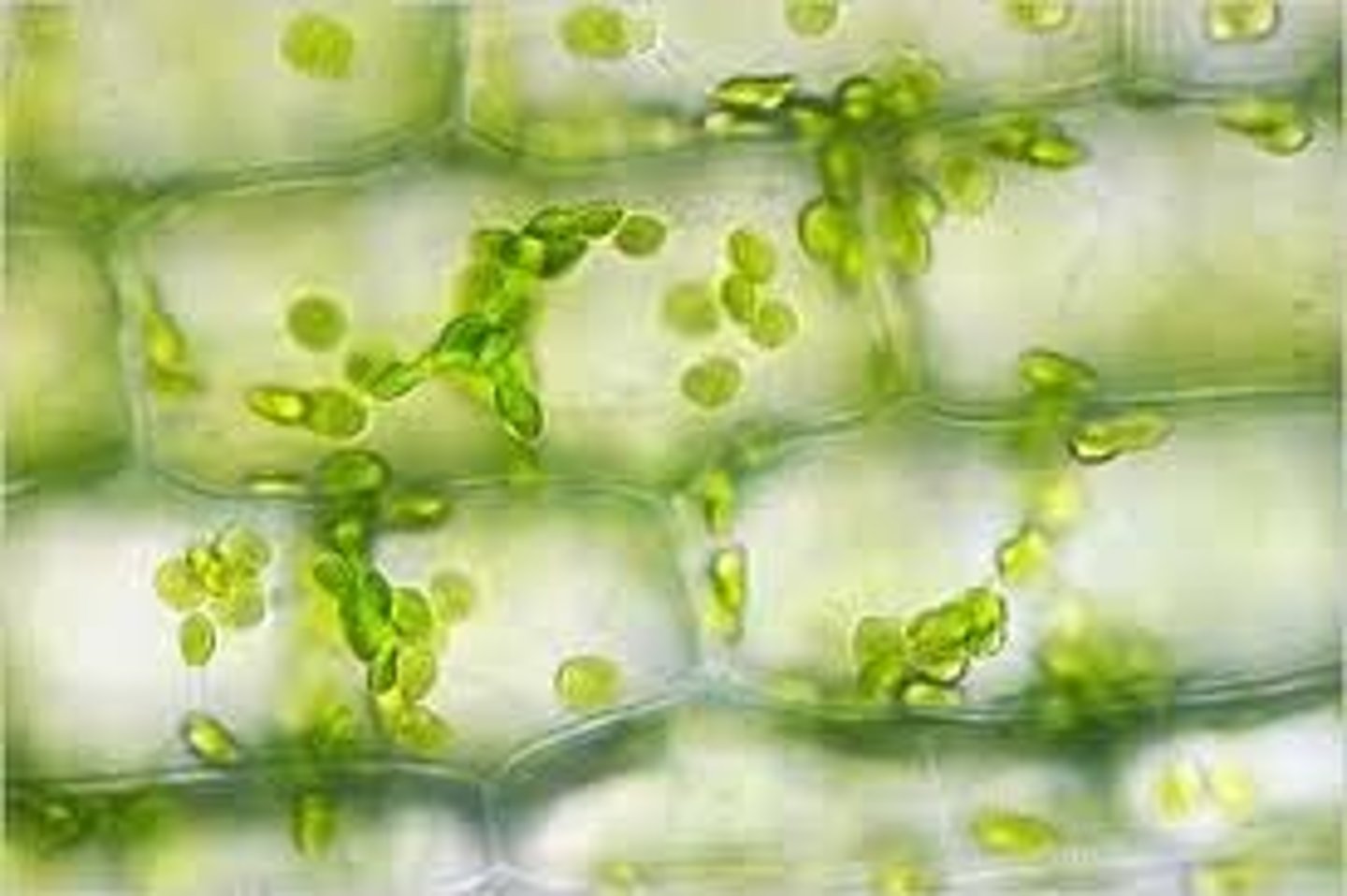
Elodea
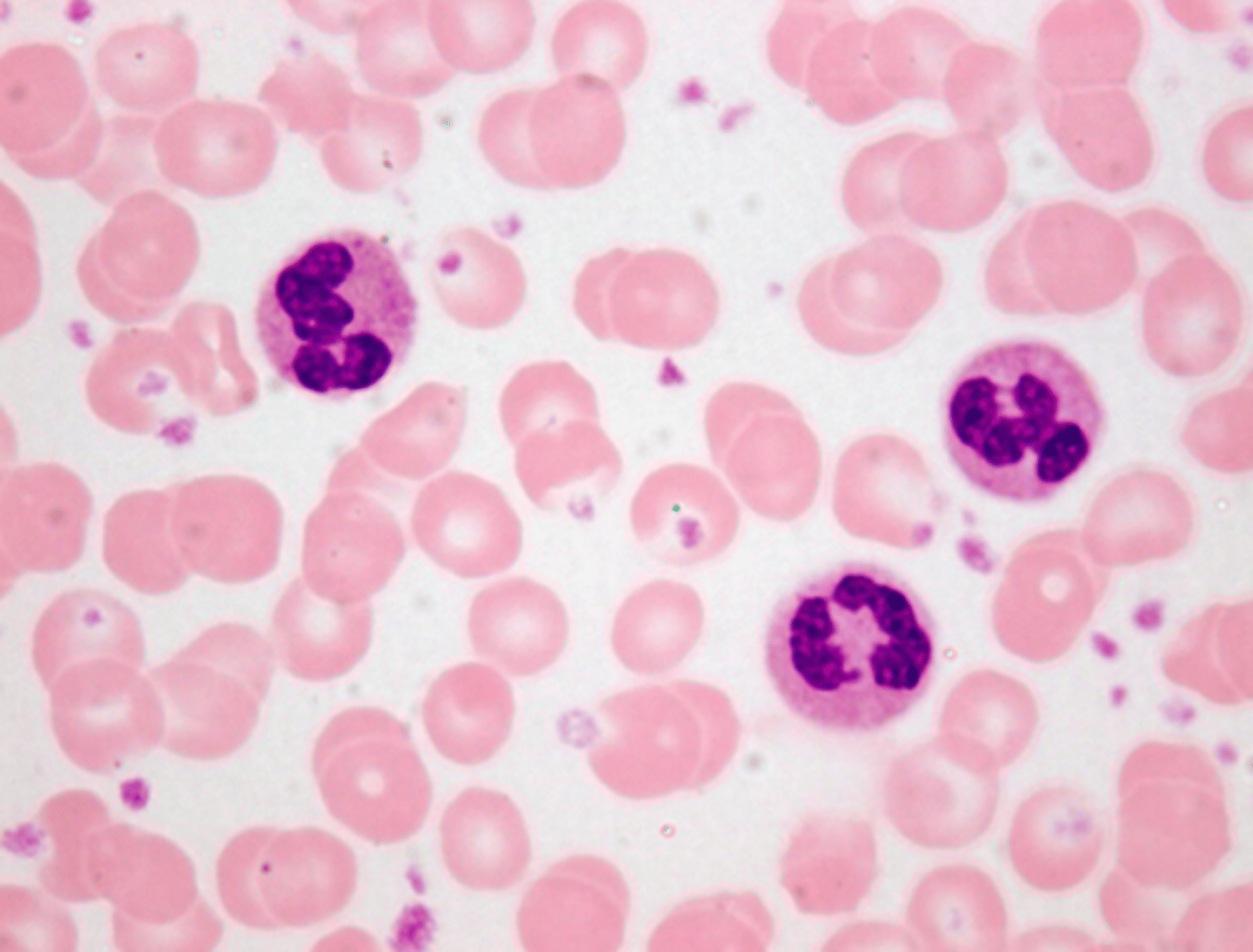
Human Blood Cells
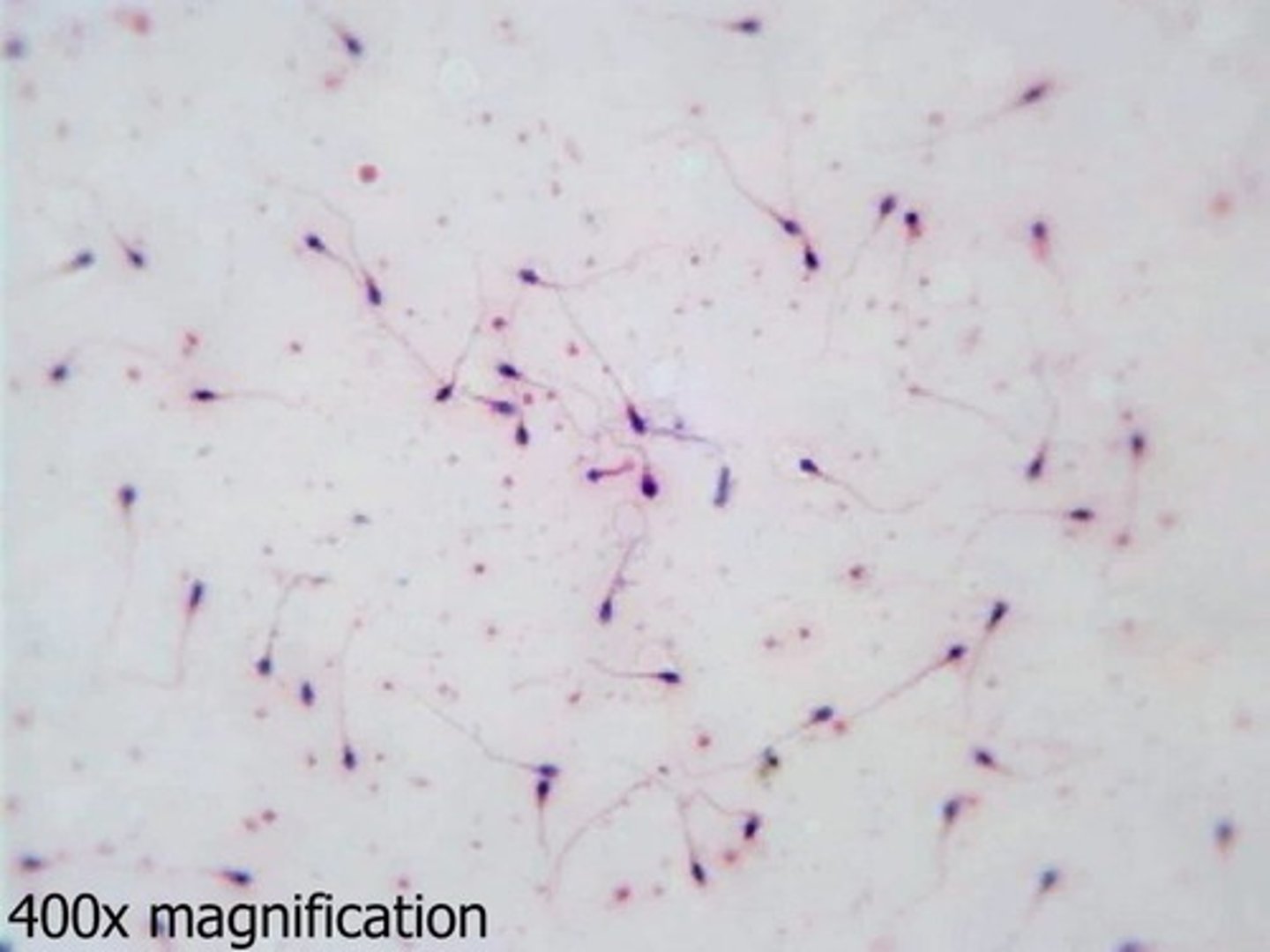
Human Sperm Cell
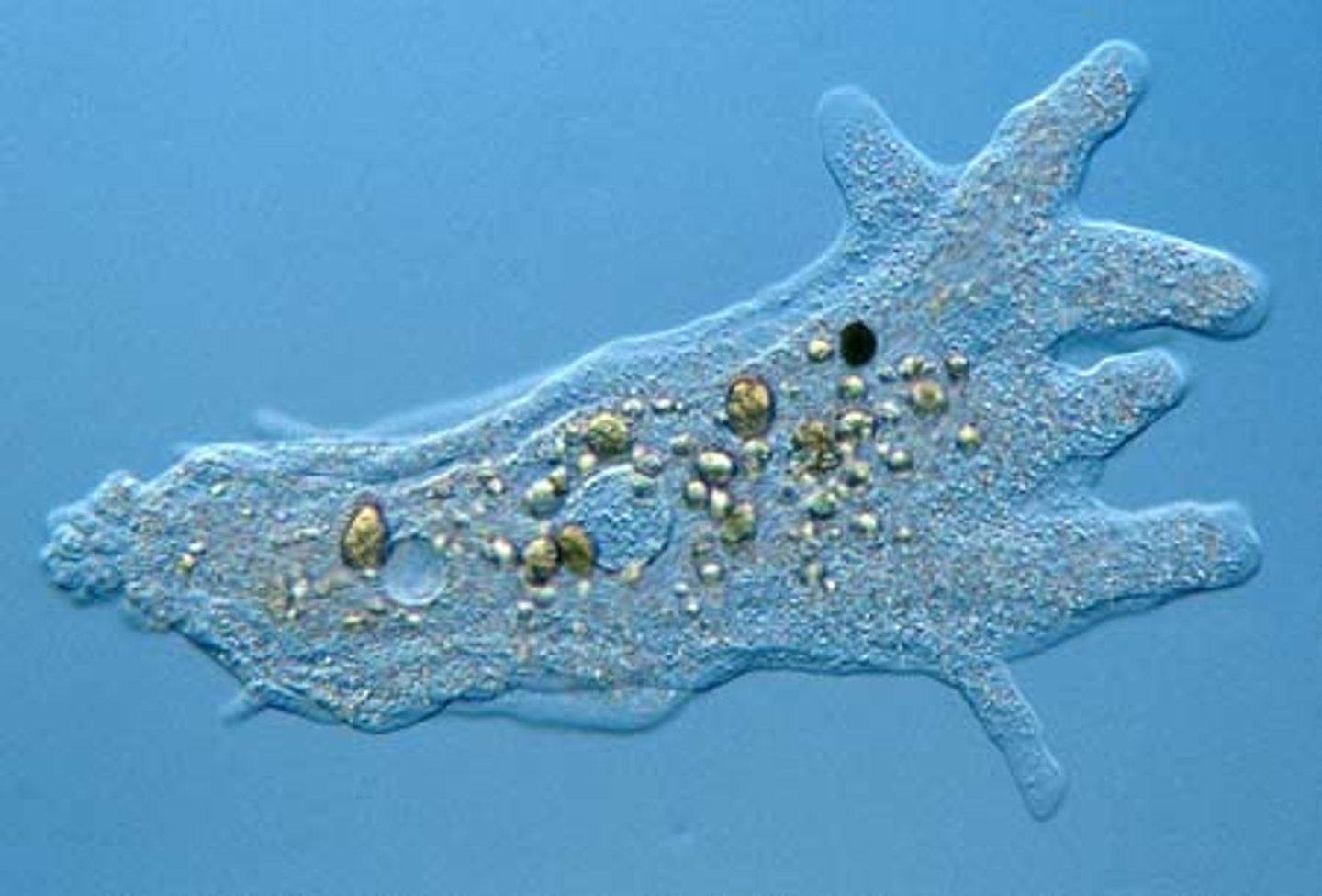
Amoeba
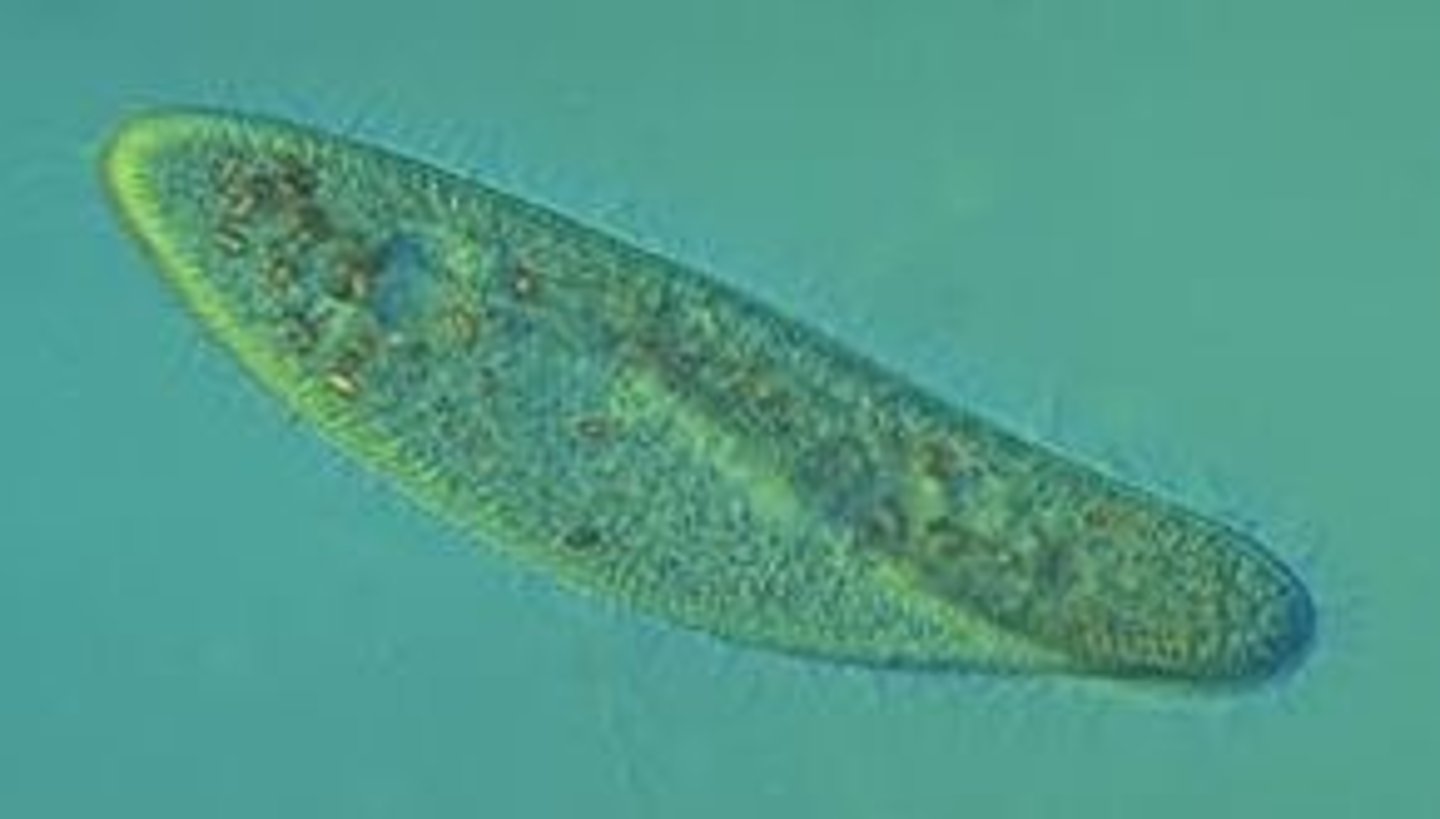
Paramecium

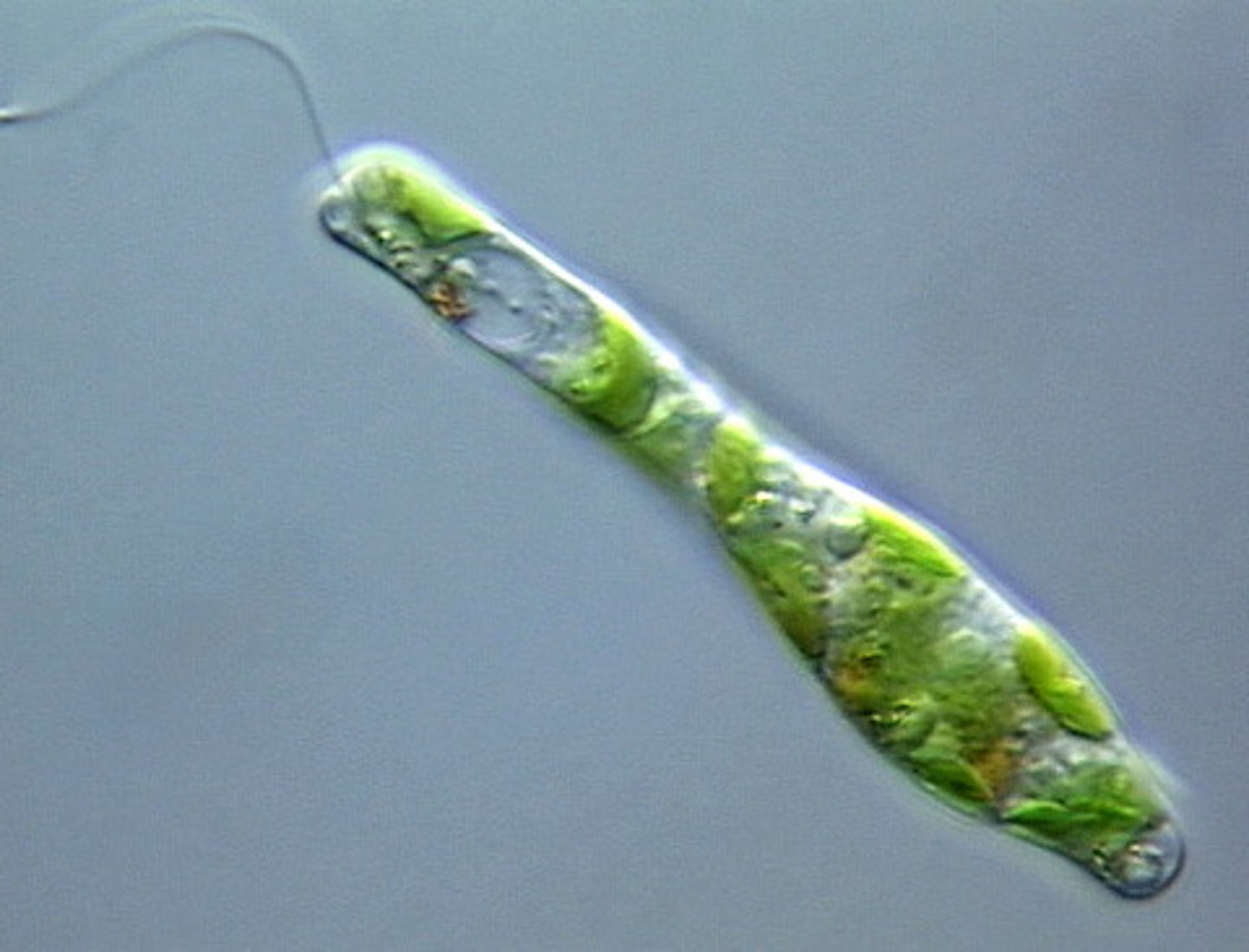
Euglena
Penicillium
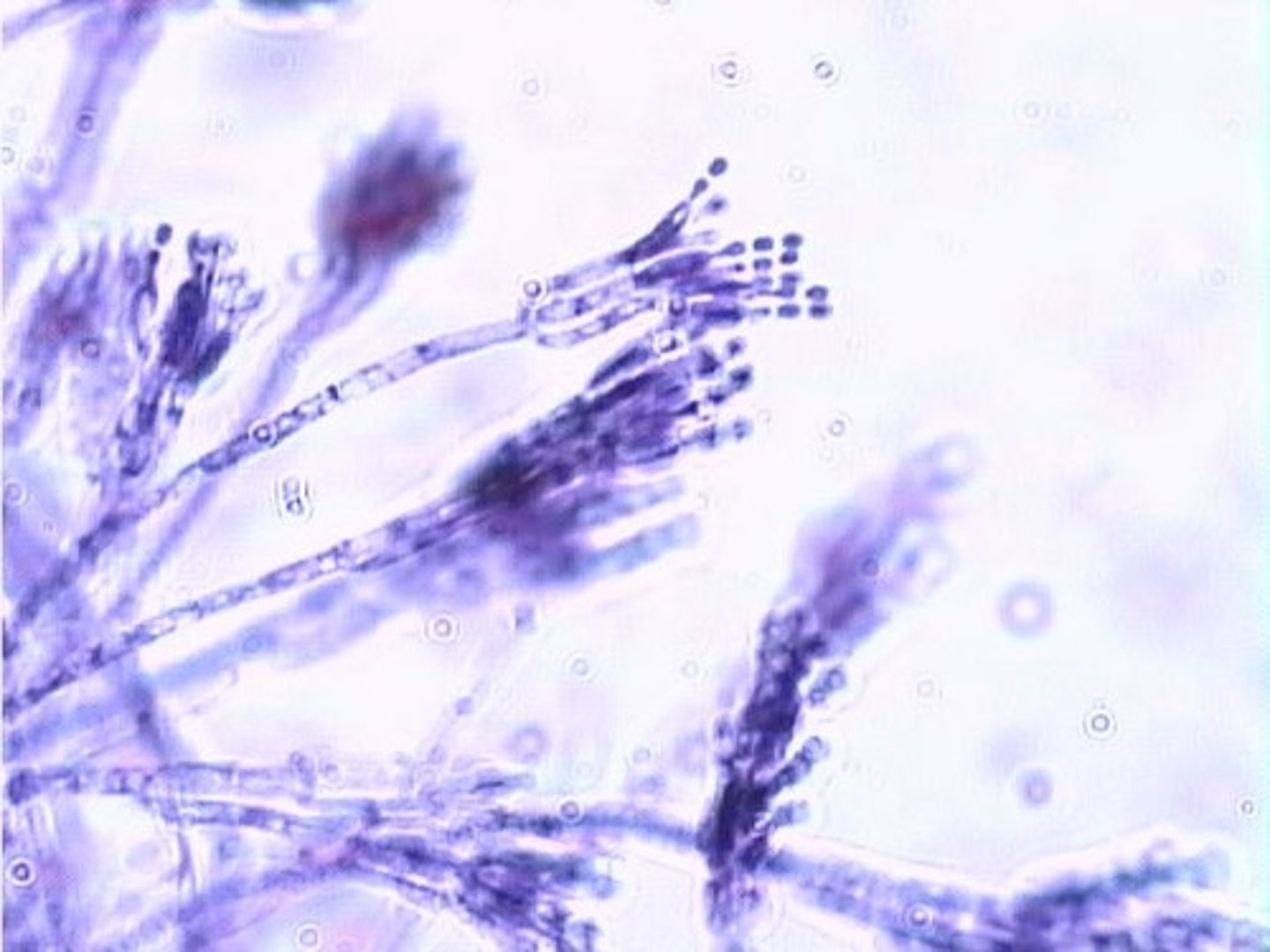
Lactobacillus bulgaricus
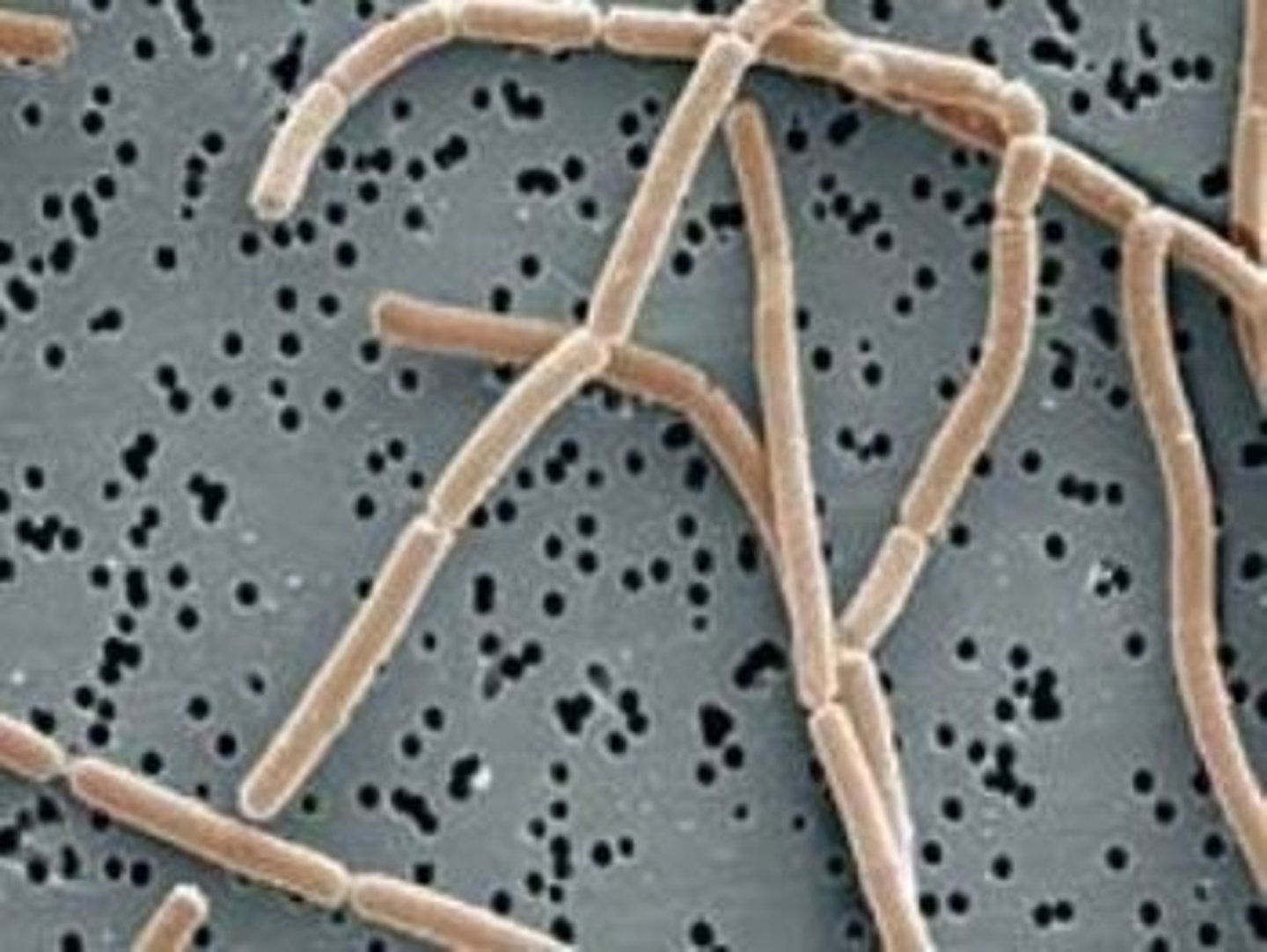
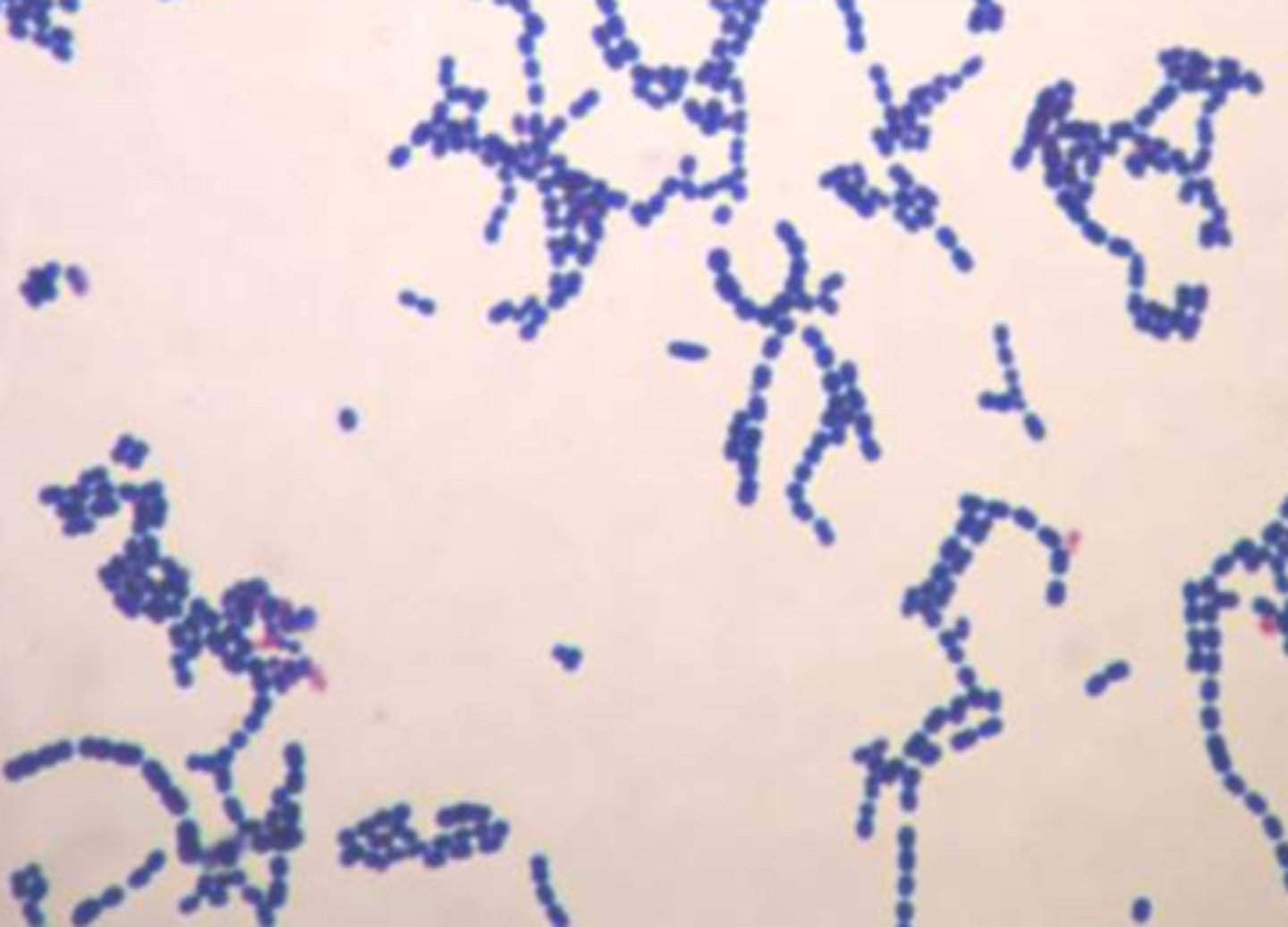
Streptococcus thermophilus
Tight Junctions
Bind cells to form leak proof sheets.
Anchoring Junctions
Rivet cells into strong tissues
Gap Junctions
Allow for ions and small molecules to flow from cell to cell
Plasmodesmata
Allows plant tissues to share water, nourishment, and chemical messages