Blood
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Functions of Blood
Transportation – gas, nutrients, waste, hormones
Regulation –body temp., pH, fluid volume
Protection – immune response, blood clotting
Whole Blood Separation and Composition
Plasma (55% of whole blood)
water 92% by weight
protein 7% by weight
other solutes 1% by weight
Buffy Coat (<1% of whole blood)
white blood cells and platelets
Erythrocytes (44% of whole blood)
red blood cells
Hematocrit
% formed elements (platelets, leukocytes, and erythrocytes)
females 38%-46%
males 42%-56%
Plasma Composition
92% water
1% electrolytes
7% plasma proteins
albumin (drives osmosis - movement of water)
Globulins (transport water-insoluble; antibodies)
Fibrinogen (fibrin → clots/stress or damage of tissue)
Regulatory (enzymes, hormones)
Hemopoiesis
production of formed elements
Hemopoiesis Formed Elements
Erythrocytes - Life span 120 days
Erythropoiesis - erythrocyte production; ~3 mil./sec
–under the control of hormone erythropoietin
(EPO)
Leukocytes - – life span 12 hours to years
Leukopoiesis - leukocyte production
Platelets - life span 8- 10 days
Thrombopoiesis – platelet
production
Erythrocytes ( RBCs)
Relatively small (7.5 μm in diameter, about the diameter of capillaries)
Biconcave - indent
Lacks nucleus
Transports oxygen and carbon dioxide (hemoglobin)
Hemoglobin in Erythrocytes
protein made up of four polypeptide chains
2 alpha globin chains
2 beta globin chains
Heme
ringed molecule with iron ion [Fe2+] in center
iron ions attract oxygen (O2) —> how oxygen is carried in hemoglobin
Carbon dioxide attracted to globin chains
Each erythrocyte contains ~280 million molecules of
hemoglobin (red-pigmented protein ➔ why blood is red)
Capable of reversibly transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood
Each hemoglobin molecule can bind a combination of ____ oxygen/carbon dioxide molecules.
four oxygen/carbon dioxide molecules.
Erythrocytes life cycle ~120 days
Erythrocytes from red bone marrow
Erythrocytes circulate in the bloodstream for 120 days (no nucleus)
aged Erythrocytes are phagocytized in the liver and spleen
Heme components are recycled back to bone marrow
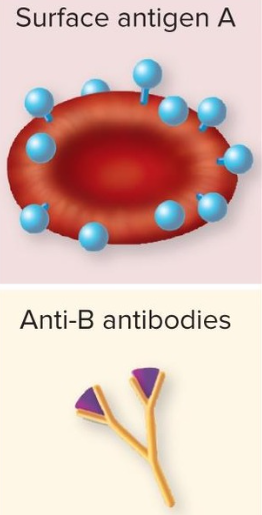
Blood Type A
Antigen A on erythrocytes
Plasma: makes Anti-B antibodies
A- 6% A+ 31%
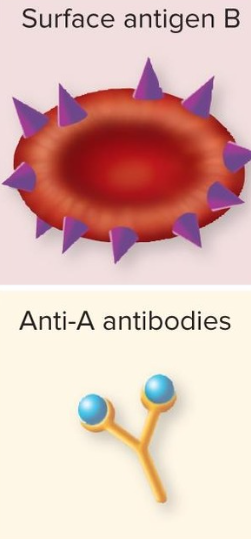
Blood Type B
surface antigen B
Plasma: makes Anti-A anitbodies antibodies
B- 2% B+ 9%
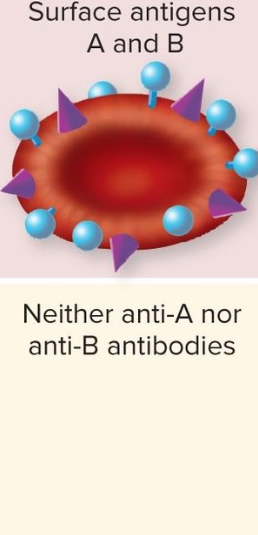
Blood Type AB
Surface antigen A and B
Plasma: Neither anti-A no anti-B antibodies
AB- 1% AB+ 3%
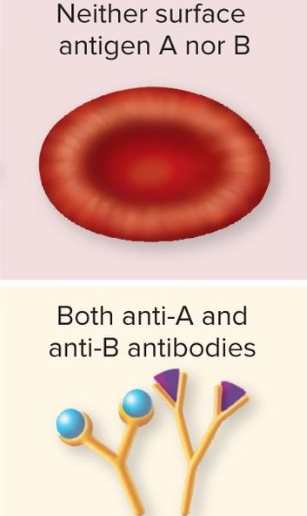
Blood Type O
Neither surface antigen A nor B
both anti-A and anti-B antibodies
O- 9% O+ 39%
“Universal Donor” ? (= can safely donate to anyone)
Type O - no antigen (no antibody agents)
“Universal Recipient” ? (= can safely receive blood from anyone)
Type AB
Erythrocyte Agglutination
Occurs if someone receives an incompatible blood transfusion
Recipient’s antibodies bind to donor erythrocytes and clump them together
–Can block blood vessels
–Can cause hemolysis (rupture erythrocytes),
organ damage
2. Leukocytes (“white blood cells”)
Immune response; defend against pathogens
1.5-3 Xs larger than erythrocytes
Granulocytes
1. Neutrophils 2. Eosinophils 3. Basophils
Agranulocytes
1. Lymphocytes 2. Monocytes
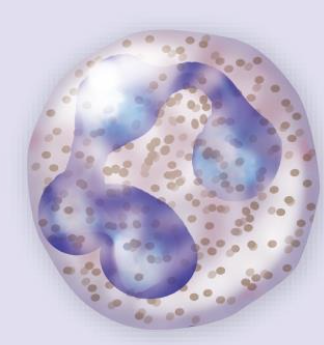
Granulocytes – Neutrophil
ca. 60% of leukocytes (most common)
Multilobed nucleus w. pale granules
Phagocytize bacteria (cell-eating harmful bacteria- infection)
function
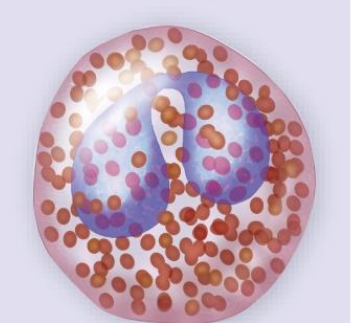
Granulocytes – Eosinophil
ca. 3% of leukocytes
Bilobed nucleus w. red
granules
Phagocytize allergens or antigen-antibody
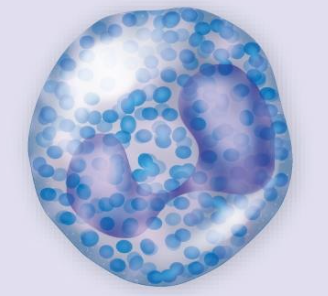
Granulocytes – Basophil
ca. 1% of leukocytes
Bilobed nucleus w. deep blue-violet granules
Release histamine during inflation (classic allergy symptoms)

Agranulocytes – Lymphocyte
ca. 30% of leukocytes
Round or slightly dented nucleus
May nearly fill the cell
Produce antibodies (b-cells)
attack antigens (T-cells)
Attack abnormal/infected cells (NK cells)
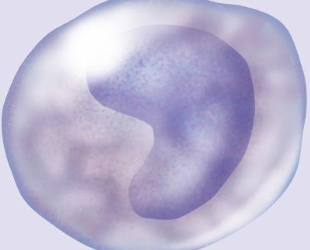
Agranulocytes – Monocyte
ca. 6% of leukocytes
Kidney-shaped nucleus
Abundant cytoplasm
Exits blood vessels & becomes a macrophage - Phagocytizes pathogens cellular debris, dead cells, viruses
Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas (descending abundance - most to least)
Neutrophil
Lymphocyte
Monocyte
Basophil
Platelets
Megakaryocytes - cellular fragments
Megakaryocytes are about 15× larger than erythrocytes
Platelets are about ¼ the size of erythrocytes
Platelets are involved in the clotting of blood
Coagulation: Blood Clotting
signal when tissue damage —> change into fibrin (net)
platelets —> stick together and hold fibrin in place (mesh network) —> hold erythrocytes back
platelets play a role in bloodclot