Chapter 5 – Aggregate Demand and Supply
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Potential GDP/LAS (long-run aggregate supply line)
The total amount that an economy is capable of producing when all of its resources are fully utilized as represented by a vertical long-run aggregate supply line. Not dependent on price levels.
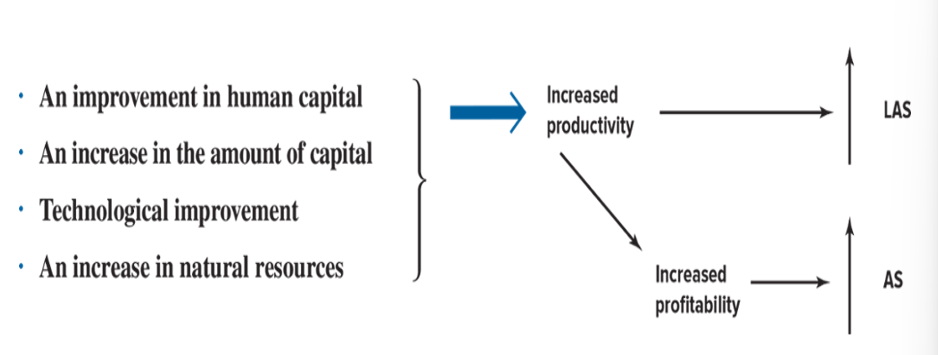
Sources of Long-Term Economic Growth
Quantity and quality of labour resources (level of human capital available)
Amount of physical capital available
Rate of technological change
Amount and quality of natural resources
Economic Growth and Potential GDP
A positive change in any of the determinants of economic growth will result in a rightward shift of the potential GDP curve, referred to as Economic Growth
On average Canada has been 2% growth of potential GDP per year
Aggregate Supply (AS)
Total quantity of goods and services produced by all sellers at various price levels, assuming the prices of factors of production remain constant. Affected by change in price levels and overall production costs.
Real Wage
Amount of goods and services that an employee can but for a given amount of nominal wage
Nominal Wage
The present day value of a current wage
Aggregate Supply (AS) and Wages
As price rise, real wages decline
Producers real wages cost of declining, resulting in higher profits
Causes an increase in aggregate quantity supplies
Aggregate Demand (AD)
The total quantity of final goods and services that consumers, businesses, government, and those living outside the country would buy at various price levels
The AD curve is downward sloping due to:
Real Balances Effect
Higher prices results in lower real wealth, lowering consumption C
Interest Rate Effect
Higher prices causes higher interest rates, lowering investments I
Foreign-trade Effect
Higher prices make Canadian exports less attractive, lowing net exports Xn
Weak Canadian dollar is attractive to other country's due to the exchange rate making it cheaper for foreign buyers
Macroeconomic Equilibrium
AD=AS.
At a price above equilibrium
A surplus will cause producers to drop prices
At a price below equilibrium
A shortage will cause buyers to bid up the price
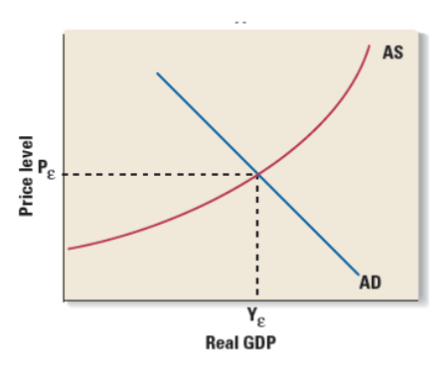
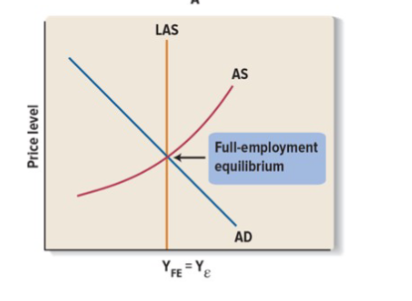
Equilibrium in the macroeconomy might occur:
Full employment
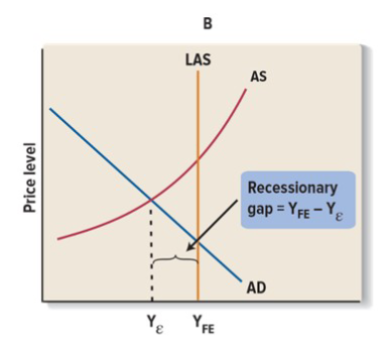
Equilibrium in the macroeconomy might occur below:
below full employment. Output level is below potential GDP. Capable of producing more if this occurs for two consecutive quarters it is a recession.
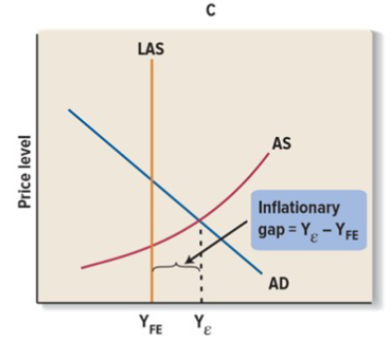
Equilibrium in the macroeconomy might occur above:
above full employment. Output level is greater than potential GDP. Producing at a greater output that is causing inflation. LAS is max output, to operate above it demand is higher than supply, there is an ability to operate at a higher capacity but not sustainable
Determinates of AD
Changes in Consumption
Individual consumer wealth, age of consumer durable, consumer confidence
Changes in Investment
Changes in interest rates, change in purchase price, age of capital goods and amount of spare capacity, business expectations, government regulation
Changes in Net Exports
Value of exchange rate, income levels abroad, price of foreign competitive goods, tastes of foreigners
Changes in Government Spending, Tax Rates and the money supply
Shifts in the AD curve
Change in an determinates of AD means that at any given price level buyers would be willing to buy more or less goods and services then before
Any change in C or I or G or Xn will cause AD to shift right or left
Determinants of Aggregate Supply
Economic growth is due to:
A change in human capital
A change in the amount of capital
Technological change
Natural resource change
What effect will the following changes have on aggregate supply and on the potential GDP (LAS).
An increase in the price of imported crude oil?
An increase in immigrants entering Canada?
Discovery of oil deposits in Canada?
Increase in wage settlements?
Increased technology efficiency?
Decrease AS
Increase AS and LAS
Increase AS and LAS
Decrease AS
Increase AS and LAS
A change in the AD – The Multiplier
When spending independently changes, total income changes more, as some of the income is spent again
One person's spending becomes another person's income
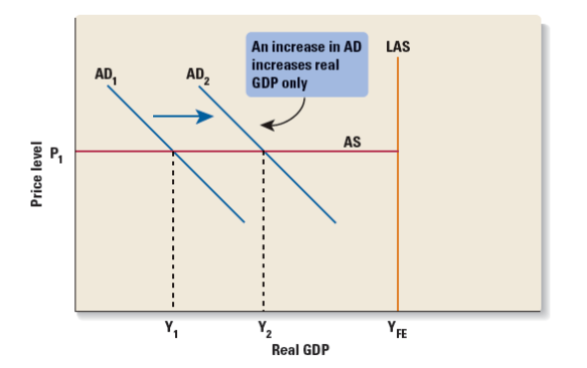
An increase in AD will increase both real GDP and price level
Increase in AS
A decrease in the price factor of production will shift the AS curve right resulting in an increase in GDP but a fall in price level
Increasing AS determinants
Wages decreasing, no effect of LAS
Factor prices decreasing, no effect of LAS
Quantity and quality of human capital increasing, increasing LAS
Quantity and quality of physical capital increasing, increasing LAS
Technology increasing, increasing LAS
Natural resources increasing, increasing LAS
Decreasing AS determinants
Wages increasing, no effect of LAS
Factor prices increasing, no effect of LAS
Quantity and quality of human capital decreasing, decreasing LAS
Quantity and quality of physical capital decreasing, decreasing LAS
Technology decreasing, decreasing LAS
Natural resources decreasing, decreasing LAS
Causes of Inflation
Inflation can be caused by an increase in AD (demand-pull) or by a decrease in AS (cost-push)
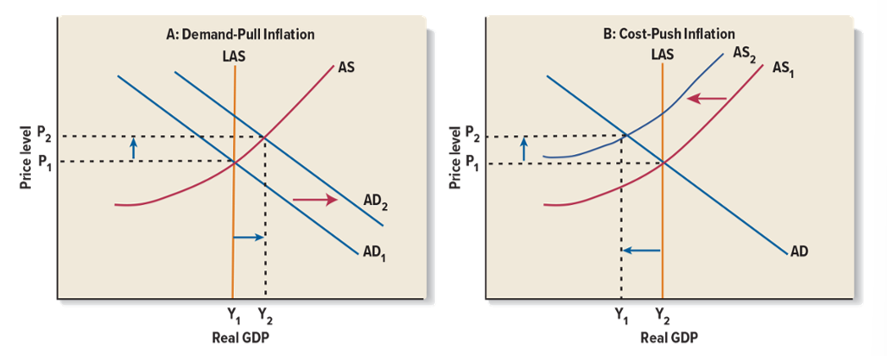
Cause of Recessions
A decrease in AD or by a decrease in AS
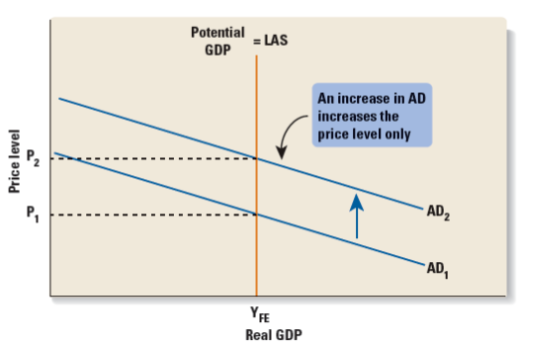
Neoclassical assumptions:
The market is competitive an efficient
Prices and wages adjust rapidly to a surplus or shortage
Economy always remains at full employment
Always operating at full potential, the only change is that prices adjust quickly to changes in demand
Output is fixed, moving the price up or down. Very simplistic
The Modern View
The impact of an increase in AS depends on the condition of the economy
In big recessions, there is a big effect on GDP
At close to potential GDP, the effect will be more inflationary
In a recession, the economy acts Keynesian
Close to potential GDP, the economy acts Neoclassical
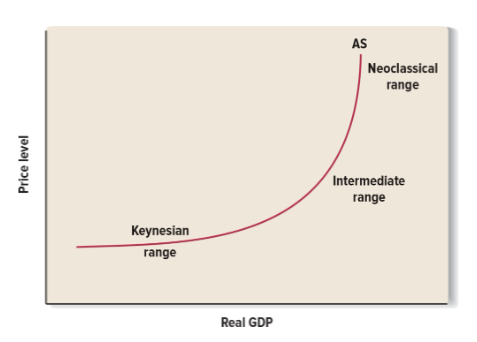
Keynesian assumptions
The more is not very competitive due to the market power of big corporations and unions
Prices and wages are sticky, adjusting slowly
Government intervention is sometimes requited to maintain full employment
Economy is underperforming, increased demand does not change price. Increasing demand on a set price level.
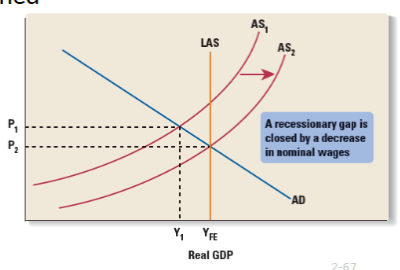
Is the Economy Self-Adjusting? R
Wages fall and AS shifts right until natural full employment is reached. Real GDP is higher, prices are lower
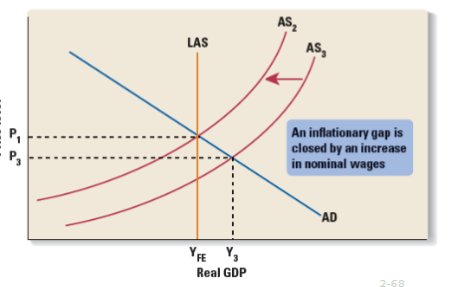
Is the Economy Self-Adjusting? I
Wages rise and AS shifts left until eventually natural full employment is reached. Real GDP is lower, prices are higher
Increase in investment spending will result in:
increased aggregate demand
Decrease in imports will result in:
increased aggregate demand
Increase in factor prices will result in:
Decreased aggregate supply as production costs rise, leading to reduced output.
Decrease in productivity will result in:
Decreased aggregate supply and potential GDP
Decrease in factor prices will result in:
Increase aggregate supply
Increase in human capital will result in:
Increased aggregate supply and potential GDP
Real GDP increases, and the price level increases. This could have occurred with a(n)
Increase in aggregate demand.
Real GDP decreases, and the price level increases. This could have occurred with a(n)
Decrease in aggregate supply
Real GDP increases, and the price level decreases. This could have occurred with a(n)
Increase in aggregate supply
Real GDP decreases, and the price level decreases. This could have occurred with a(n)
Decrease in aggregate demand
Interest rates impact:
Aggregate demand
Technology imporvemnts’s or decline impacts:
Aggregate supply
Increase or decrease in exchange rates impacts:
Aggregate demand
Increase or decrease in government spending will impact:
Aggregate demand
Increase or decrease money supply
Aggregate demand
Increase and decrease nominal wages
Aggregate supply
An appreciation of the Canadian exchange rate will ______ imports and ______ exports.
increase; decrease
If there is an injection of $5 million dollars what will be the ultimate effect on the economy?
It will increase by more than $5 million because of the multiplier. This multiplier effect occurs as the initial injection leads to increased consumption and investment, further boosting aggregate demand.
According to the modern view, at high levels of real GDP an increase in aggregate demand will have a relatively ______ effect on prices and a relatively ______ effect on real GDP.
large; small