chem U3AOS1 p1
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
specific heat capacity definition and SI unit
Amount of energy needed to raise temp of 1g by 1°C
J/g°C
How to reduce heat loss in calorimetry
Add insulation around setup
Add lid (with hole for thermometer)
Change material of test tube
CF formula
CF=E/delta T
Fossil fuel define
Non renewable resources derived from ancient remains of plants and animals
define renewable resource
can be replenished faster than it is consumed
Made from
Tryglyceride components
Glycerol molecule with 3 fatty acids
fatty acid composition
Carboxylic acid with long carbon chains
Condensation reaction
Two molecules combine to form one with the loss of water
bioethanol
ethanol that is made from the anaerobic fermentation of sugar and starch products by yeast
biodiesel
fatty acid methyl esters
fuel that is made from the transesterification of fats and oils in organic matter
carbon neutral
does not result in net production of carbon dioxide from sourcing or consumption
coal
combustible carbonized plant matter (fossil fuel), formed by the partial decay of plant matter
natural gas
coal seam gas sourced from coal deposits (fossil fuel)
fuel
substance that is used, usually combusted, that has energy stored in its bonds
Fossil fuel
a natural fuel such as coal or gas, formed in the earth, in the past, from the remains of living organisms.
non renewable- cannot be produced as quickly as it is consumed
Renewable resource
replenished by natural processes within a relatively short period of time
partially oxidised fuel meaning
higher or lower heat of combustion?
fuel with oxygens already present in molecular formula
lower heat of combustion
cellular respiration equation
C6H12O6(aq) +6O2(g) → 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l)
biogas
CH4 and CO2, formed through anaerobic breakdown of organic materials by bacteria
bioethanol formation equation
C6H12O6 → 2C2H5OH(aq) + 6CO2(aq)
what is calorimetrry
method used to determine the changes in energy of a system by measuring heat exchanges with surroundings
calorimetry calculation steps
find energy (chemical/electrical)
E=VIt or E = H*n
CF = E/t
E=CF*t
H=q/n
Why do calorimeters need to be calibrated
imperfect insulation/absorbance of heat
energy from the reaction is not solely transferred to the water
heat is absorbed by internal components of calorimeter as well
calibration means the factors are taken into account
relationship of temp to heat can more accurately be calculated
without calibration, the enthalpy value obtained will always be less than the true value for a given calorimeter using a fixed quantity of solution.
features of electrodes which allow fuel cells to function properly
porous to gases
allow conduction of a current
have embedded catalysts
direct contact spontaneous energy transformation
chem → thermal
why? bc needs and external circuit for electrons to go through
indirect contact spontaneous energy transformation
chem → electrical
Why is molten electrolysis not viable?
Difficult/dangerous to maintain required temperature
Lack of proper equipment to safely collect toxic gases
Difficult to keep reactants from coming into contact (violent spontaneous reactions)
Issues sourcing suitable electrodes
Issues maintaining electric ciruit at high temperature
hydrogen fuel cell equations
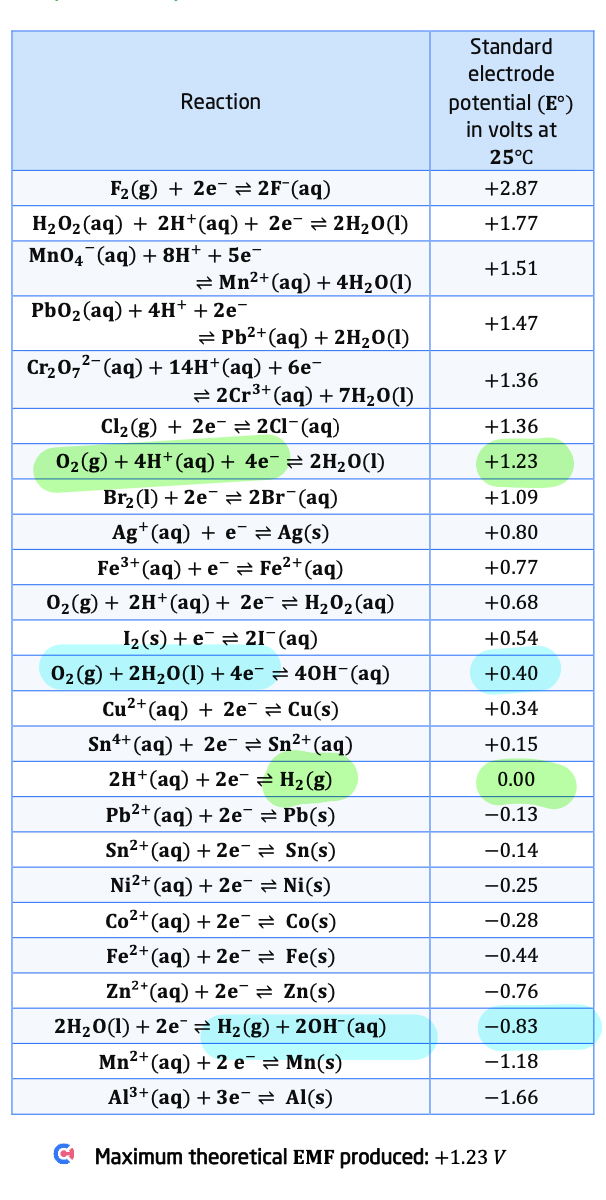
what is denaturation?
disruption of bonds within quaternary/tertiary/secondary structure
shape and structure of the active sites are altered.
results from high temp or ph
effect of ph on enzyme activity?
low ph, high h+ conc
results in protonation of acidic and basic groups -COOH and -NH3+
high ph, low h+ conc
results in deprotonation
both extremes result in denaturation
ionisation of R groups can affect substrate binding as:
An altered tertiary structure can change confirmation of the active site.
Amino acid residues within the active site may no longer be able to bind to the substrate.