Ciliary Body, Choroid, & Vitreous
1/181
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
182 Terms
base and apex of CB
base anteriorly at the scleral spur, iris root, and AC
apex pointing posteriorly towards the ora serrata
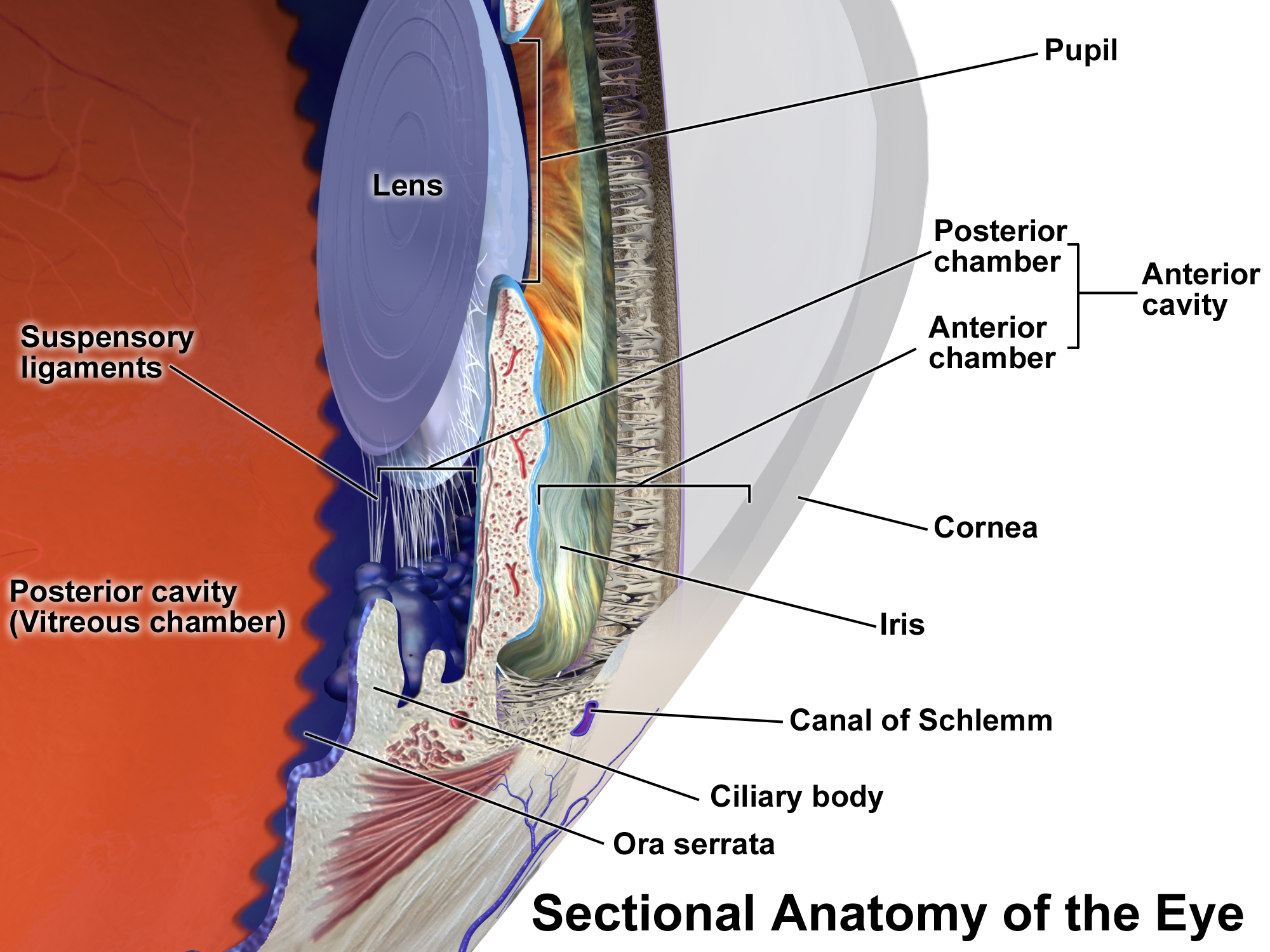
what is anterior and posterior to the CB
anterior: sclera
posterior: posterior chamber and vitreous
2 main functions of CB
aqueous humor production
accommodation
what part of the CB produces AH
non-pigmented ciliary epithelial cells
where is AH secreted
posterior chamber
ciliary body innervation
innervated by the parasympathetic fibers in the SPCNs from the ciliary ganglion
what happens when the ciliary muscle receives parasympathetic innervation and where is the innervation coming from
coming from parasympathetic fibers in the SPCNs from the ciliary ganglion
causes ciliary fibers to contract, making the lens more spherical, and causing the eye to accommodate
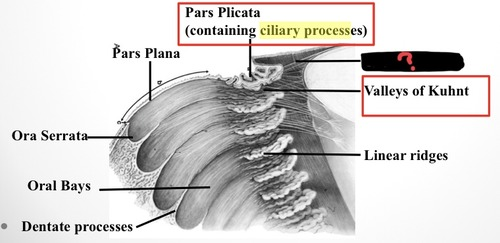
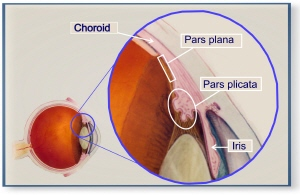
pars plicata
aka corona ciliaris
wide anterior part of CB that has 70-80 ciliary processes that extend into the posterior chamber

ciliary processes
radial folds in the pars plicata
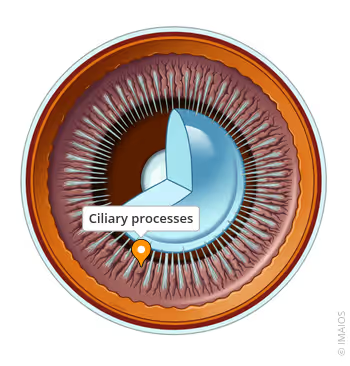
valleys of kuhnt
heavily pigmented areas between ciliary processes in pars plicata where zonular fibers of the lens attach
does AH get produced in the pars plana or pars plicata
non-pigmented ciliary epithelium of the pars plicata
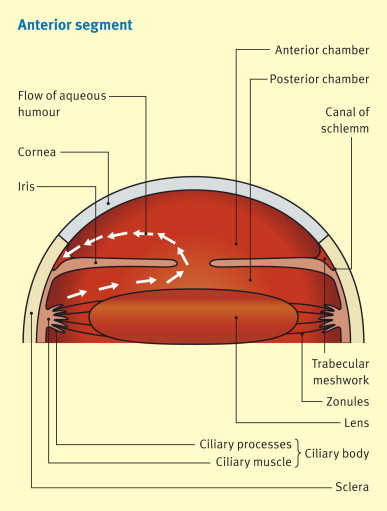
aqueous humor flow
pars plicata > posterior chamber > through pupil > anterior chamber > TM
pars plana
aka orbicularis ciliaris
flatter more posterior portion of the CB
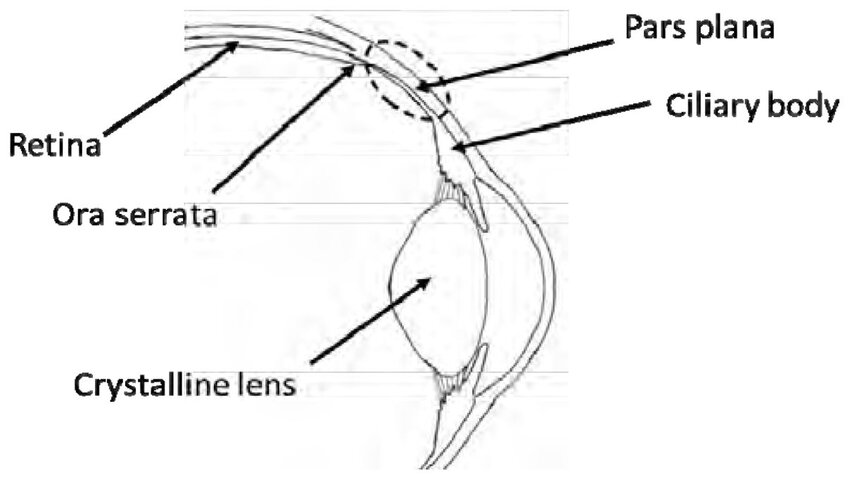
borders of pars plana
anterior: pars plicata
posterior: ora serrata
_________ serves as the anterior border to the retina
pars plana
dentate processes
parts of the peripheral retina (ora serrata) that extend onto the pars plana
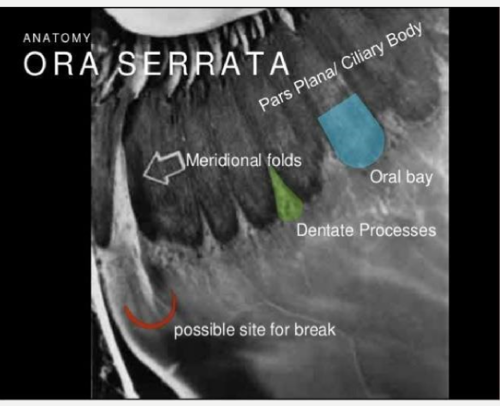
oral bays
posterior extensions of pars plana that lie between dentate processes
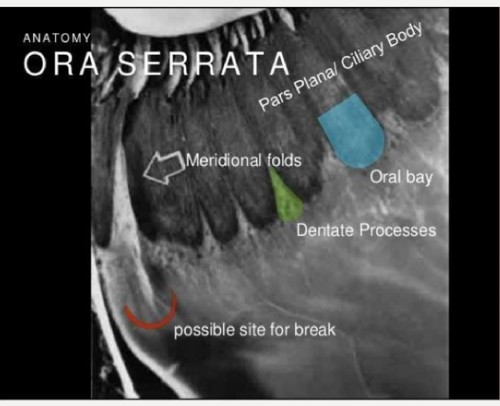
enclosed oral bay
when neighboring dentate processes join together

ruptured or damaged zonules cause _________ or _____________ of the lens
subluxation or dislocation
layers of the CB (outer to inner)
supraciliaris > ciliary muscle > ciliary stroma > pigmented ciliary epithelium > non pigmented ciliary epithelium
what is the supraciliaris attached to
loosely attached to underlying sclera but not the scleral spur
outermost layer of ciliary body
supraciliaris
composition of supraciliaris
loose CT with many collagen bonds
what is the supraciliaris continuous with and where
suprachoroid
at the ora serrata
what travels through the supraciliaris
blood vessels and nerves to reach the anterior part of the eye
what causes a ciliary body detachment
fluid build up in the supraciliaris
largest intrinsic muscle of the eye
ciliary musclewh
what kind of muscle is the ciliary muscle
smooth muscle
which layer of the CB is responsible for accommodation
ciliary muscle
innervation of the ciliary muscle
mostly parasympathetic CN III fibers
some sympathetic fibers
what anchors the ciliary muscle
anteriorly: scleral spur
posteriorly: stroma of the choroid
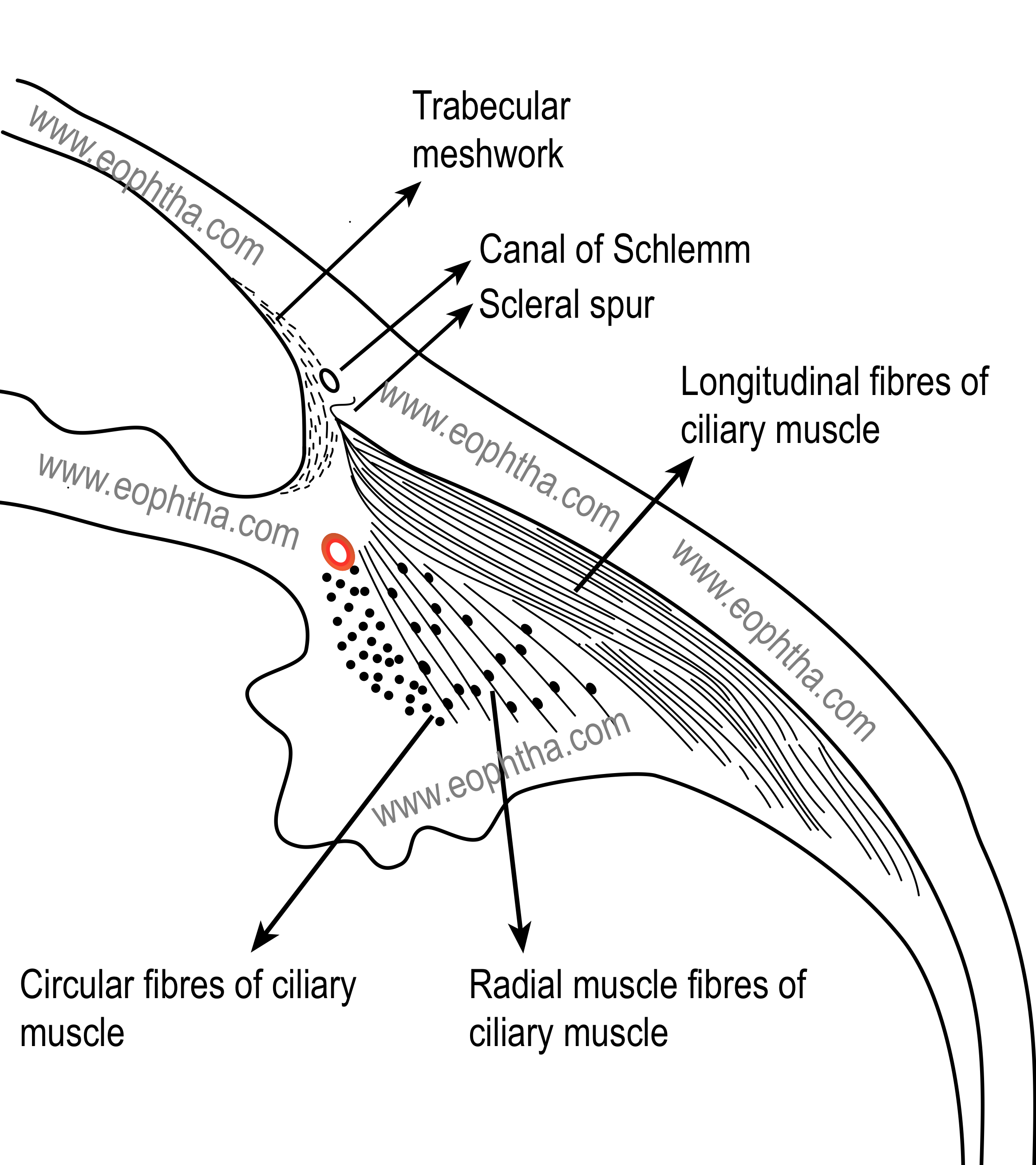
3 types of ciliary muscle fibers
longitudinal muscle fibers (of brucke)
radial fibers
Muller’s annular muscle
what muscle fibers make up the largest % of ciliary muscle fibers
longitudinal muscle fibers
what are the outermost ciliary muscle fibers
longitudinal muscle fibers
shape of longitudinal muscle fibers
long v-shaped fibers that stretch across the CM
originate at the scleral spur and TM
muscle stars
parts of the longitudinal muscle that extend into the choroid into star shaped terminations
shape, origin, and termination of radial fibers
extend in a V-shape from the scleral spur
terminate in connective tissue near the base of the ciliary processes (pars plicata)
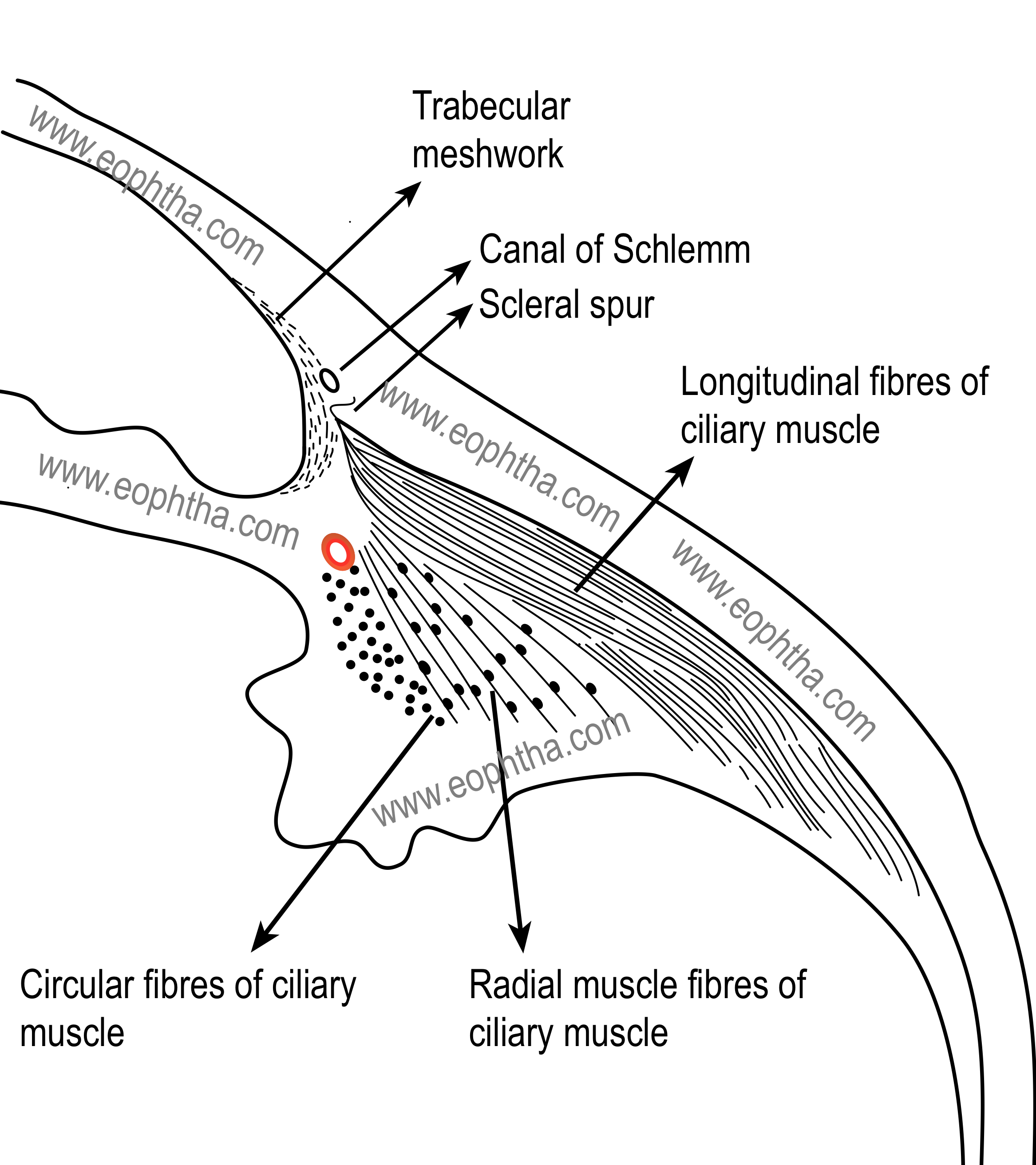
what muscle makes up the smallest portion of the CM
Muller’s annular muscle
most medial/innermost muscle of CM
Muller’s annular muscle
shape and origin of Muller’s annular muscle
circular muscle bundles that originate at the scleral spur
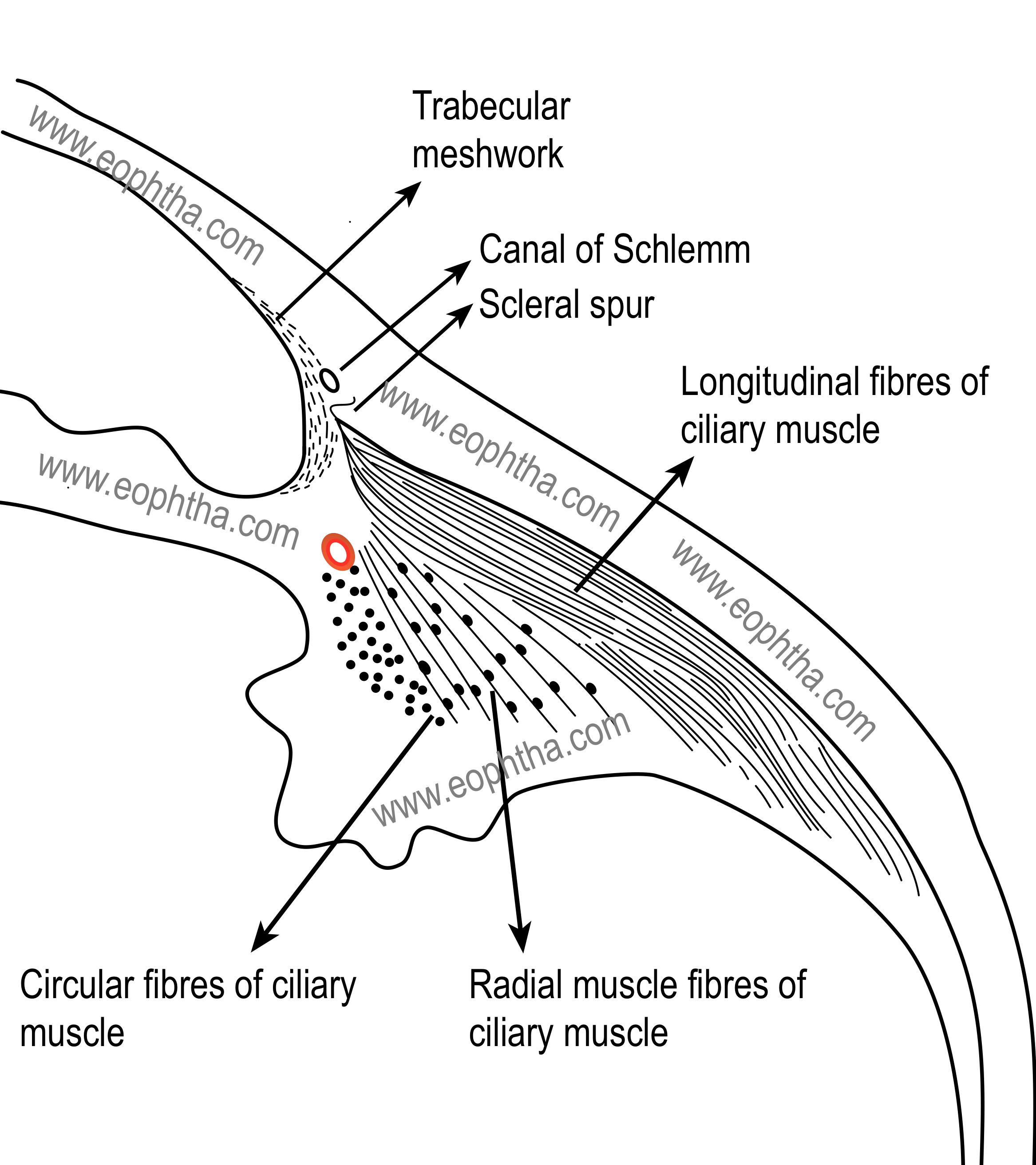
which CM muscle is near the major arterial circle of the iris
Muller’s annular muscle
what structure is Muller’s annular muscle next to
major arterial circle of the iris
what structure is in the ciliary stroma
major circle of the iris
what layers is the ciliary stroma between
ciliary muscle and ciliary epithelial layers
vascularization of ciliary stroma
highly vascularized
contains major circle of iris
location of major arterial circle of iris
inward from the CM in the ciliary stroma near the iris root
has large fenestrated capillaries near ciliary epithelium of pars plicata
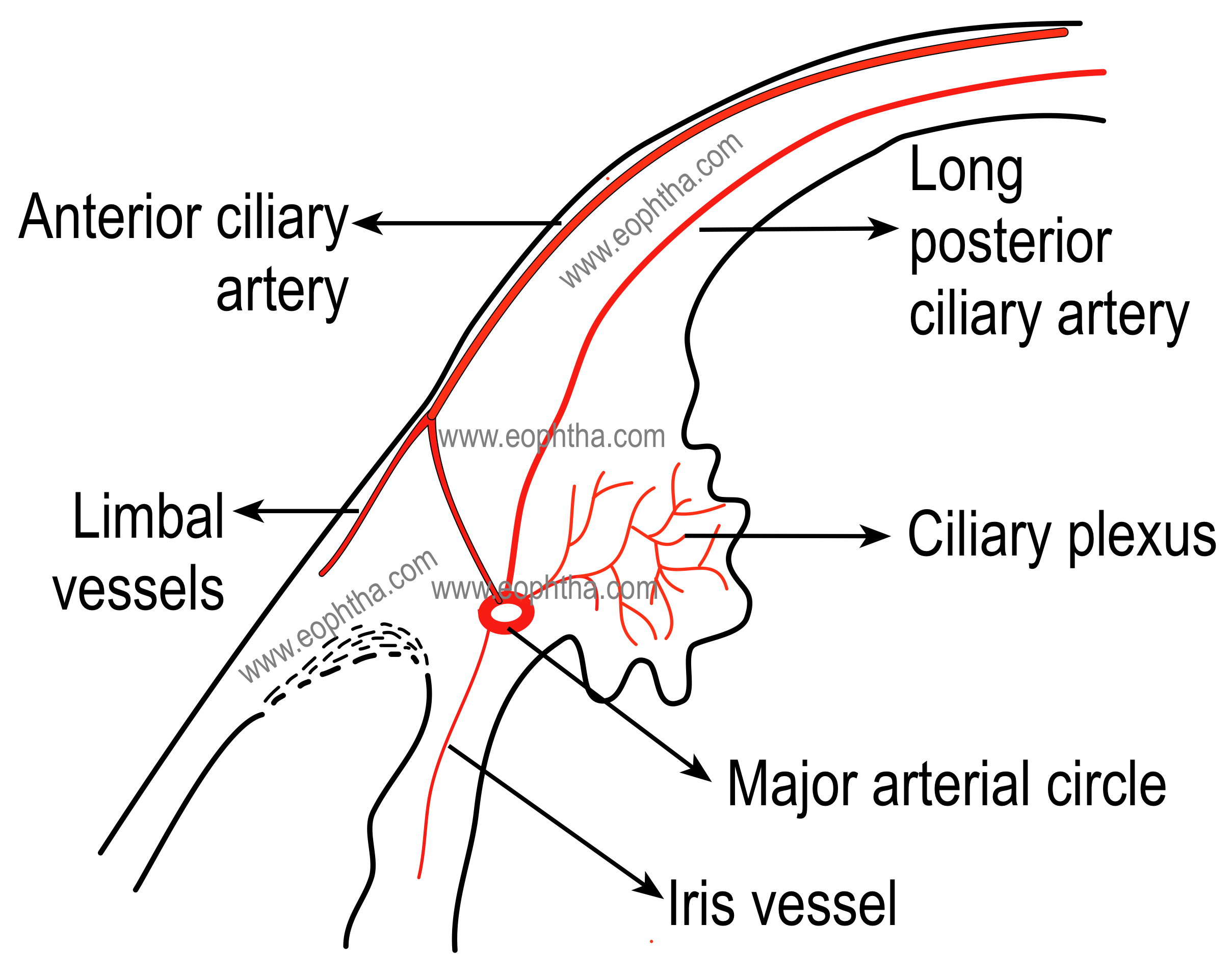
arteries that form the major arterial circle of iris
ACAs and LPCAs
what stops large molecules from getting into the anterior chamber from the fenestrated major circle of iris
large molecules are able to get through the fenestrated capillaries in the major circle of the iris
NPCE of the pars plicata contains tight zonular junctions that blocks these large molecules from entering the anterior chamber
protein concentration of the aqueous vs. blood and why
protein concentration is much lower in aqueous than blood
7% in blood, 2% in aqueous
tight junctions of non-pigmented ciliary epithelium of the CB stop protein molecules that leak out of the major circle of the iris from entering the aqueous in the anterior chamber
what is aqueous humor made from
plasma that escapes the blood stream from the fenestrated capillaries of the major arterial circle of the iris
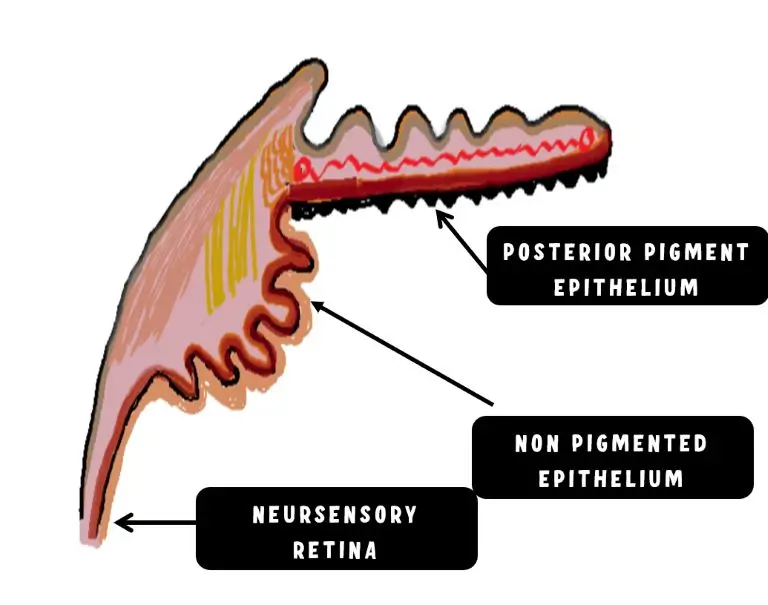
how are the 2 layers of ciliary epithelium arranged
2 layers of epithelium line the CB joined apex to apex via zonula occludens
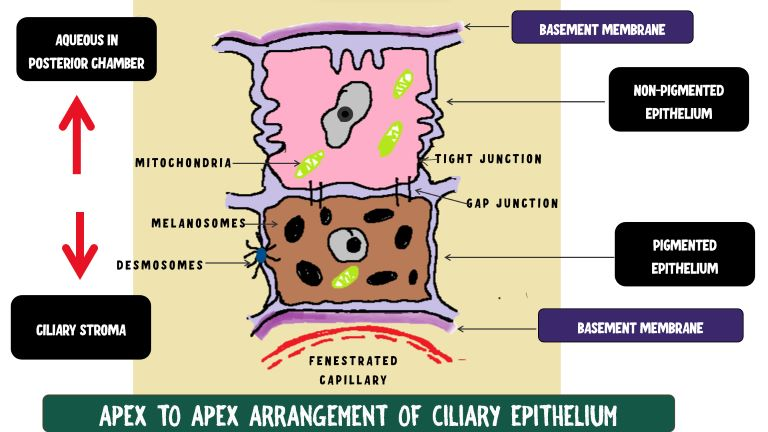
histology of pigmented ciliary epithelium
outer cuboidal epithelial layer attached to ciliary stroma via basal lamina of the its BM (apex faces NPCE)
what is the pigmented ciliary epithelium continuous with anteriorly and posteriorly
anteriorly: anterior pigmented iris epithelium and its BM
posteriorly: RPE and inner BM of Bruch’s membrane (outer retina)
histology of NPCE
inner cuboidal epithelial layer that lines the posterior chamber
2 areas lens zonules arise from
valleys of Kuhnt of pars plicata
NPCE basal lamina of pars plana
NPCE contains organelles that are necessary for ____________
aqueous secretion
what is the NPCE continuous with anteriorly and posteriorly
anteriorly: pigmented posterior epithelium of iris epithelium and its basal lamina
posteriorly: ora serrata and neural retina, basal lamina continuous with ILM of retina (inner retina)
CB blood supply
LPCAs and major arterial circle of iris
venous drainage of CB
ciliary veins drain through vortex veins
what does the parasympathetic system innervate in the CB
innervates the ciliary muscle for accommodation
what does the sympathetic system innervate in the CB
innervates arteries within the CB
where does the CB get parasympathetic innervation from
CN III parasympathetic fibers travel with SPCNs from the ciliary ganglion
where does the CB get sympathetic innervation from
sympathetic nerve fibers from the superior cervical ganglion of the sympathetic ganglion chain travel with SPCNs and LPCNs
where does the CB get sensory innervation from
sensory nerve fibers from the trigeminal ganglion of CN V1 travel with LPCNs
ganglions of sympathetic, parasympathetic, and sensory innervation of the CB
sympathetic: fibers come from the superior cervical ganglion
parasympathetic: fibers come from the ciliary ganglion
sensory: fibers come from the trigeminal ganglion of V1
what nerves do sympathetic, parasympathetic, and sensory fibers travel to the CB with
sympathetic: LPCNs and SPCNs
parasympathetic: CN III fibers travel with SPCNs
sensory: CN V1 fibers travel with LPCNs
what is the choroid positioned between
sclera and RPE of the retina (outer retina)
anterior and posterior borders of the choroid
anterior: ora serrata (where CB ends)
posterior: optic nerve
where is choroid the thickest
posterior pole (0.2 mm)
where is choroid the thinnest
ora serrata (0.1 mm)
composition of choroid
2 central vascularized layers surrounded by 2 non-vascularized membranes (4 layers total)
layers of the choroid (outer to inner)
suprachoroid lamina (next to sclera) > choroidal stroma > choriocapillaris > bruch’s membrane (next to RPE)
suprachoroid lamina
aka lamina fusca
potential space between sclera and choroidal vessels
supra choroid means above the choroid
contents of suprachoroid lamina
loosely packed with collagen fibers, fibroblasts, melanocytes, and ECM
what passes through suprachoroid lamina
LPCAs and LPCNs
where do LPCNs extend from
mid-equatorial region to ora serrata and 3 & 9 o’clock
what layer of the choroid belongs to the choroid and sclera
suprachoroid lamina
if it was split, part of it would attach to sclera and part of it would attach to choroid
choroidal stroma
loose CT layer that contains choroidal BVs, nerves, and dense melanin granules
what innervates choroidal BVs and what does it cause
sympathetic NS
causes vasoconstriction
what is the most common primary intraocular tumor in adults
choroidal melanoma
why are melanomas of the eye most common in the choroid, and what layer causes this
choroidal stroma
has extremely high density of blood vessels and melanin granules
__________ vessels in the choroidal stroma form 2 separate layers
SPCA
what 2 layers are formed by SPCAs in the stroma
Haller’s and Sattler’s layer
Haller’s layer is more (posterior/anterior) with (larger/smaller) vessels
Haller’s layer is more posterior with larger vessels
closer to sclera and suprachoroid lamina
Sattler’s layer is more (posterior/anterior) with (larger/smaller) vessels
Sattler’s layer is more anterior with smaller vessels
Haller’s layer vessels branch to form ________________
Sattler’s layer vessels branch to form __________________
Haller’s vessels branch to form smaller vessels of Sattler’s layer
Sattler’s vessels branch to form capillary beds
what drains blood from the capillary beds of Sattler’s layer
large vortex veins
tributaries of vortex veins located in Haller’su
unlike most veins, vortex veins do not contain ____________
valves
what kind of capillaries are found in the choriocapillaris and where are they most concentrated
fenestrated capillaries
most concentrated in the macula
role of choriocapillaris
supplies blood to outer retina
what cells regulate blood flow in the choriocapillaris
pericytes
where can pericytes be found and what do they do
surround capillaries of choriocapillaris
regulate blood flow
what disease can damage pericytes
diabetes mellitus
what impact does diabetes mellitus have on the choroid, and how does this cause diabetic retinopathy
diabetes damages blood vessels and pericytes of the choroid
prevents proper blood flow and regulation of blood flow, preventing nutrients and oxygen from getting to the macula, resulting in DR
innermost layer of the choroid
Bruch’s membrane
basal lamina of the choroid
Bruch’s membrane
bruch’s membrane
fusion of choriocapillaris and RPE basement membrane composed of 5 layers
5 layers of Bruch’s membrane
BM of choriocapillaris, outer collagenous layer, elastic layer, inner collagenous layer, BM of RPE
function of Bruch’s membrane
allows passage of waste and nutrients between choriocapillaris and RPE
nutrients pass from ________ through Bruch’s to __________
from choriocapillaris
to retina