TEST 1 STUDY GUIDE
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
10 Rights of Patients in Medication Administration
Include right drug, patient, dose, time, route, assessment, documentation, evaluation, patient education, and refusal of care.
Conversions and Abbreviations:
Tell me ml to cm3
tell me ml to l
ml to ccc
mcg to mg
mg to g
g to kg
Liquids | Solids |
1 mL = 1 cm3 | 1,000 mcg = 1 mg |
1,000 mL = 1 L | 1,000 mg = 1 g |
1 ml=1cc | 1,000 g - 1 kg |
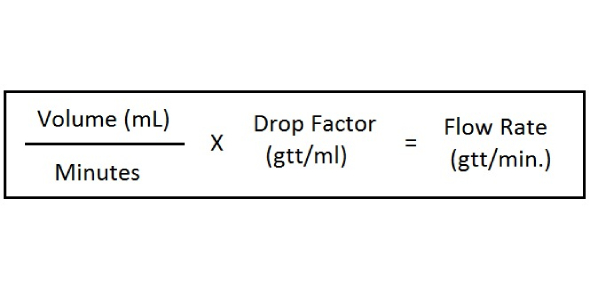
Drip rate formula
lbs to kg
2.2 lb=1kg
Properties of Ideal Drugs
Include effectiveness, safety, selectivity, predictability, ease of administration, freedom from interactions, low cost, chemical stability, and simple generic name.
Causes of Medication Errors
Include human factors, communication mistakes, and drug name confusion as common causes.
Pharmacokinetics- where do the processes work
Focus on absorption- GI tract, distribution- blood, metabolism- kidney and liver, and excretion processes in the body- bile and urine.
Pharmacodynamics
Focus on what the drug does to the body, sources of individual variation- age, gender, and weight, and drug-receptor interactions.
Passage of Drugs across membrane or BBB
Drugs must be lipophilic or lipid soluble or have a transport system
The most common anemia and what is the treatment
Oral Defienceincy anemia give oral iron (ferous sulfate)
Aplastic anemia, what are the levels
decrease in RBC, WBC, platelets
Inherrited Hemorhagic Diseases what factor is it deffiecient in and what other test wil show
Low levels of VIII and a prolonged PTT
First Pass Effect of Medications
Describes the process where drugs taken orally pass through the liver before reaching the systemic circulation.
Medication Errors - Nurse Role in Prevention
Emphasize patient education, safety culture, error prevention tools, and medication reconciliation.
Autonomic Nervous System
Differentiate between parasympathetic and sympathetic divisions and their effects on bodily functions.
Polypharmacy
Refers to the practice of taking multiple medications simultaneously.
Normal Lab Values
Include ranges for WBC, RBC, platelets, and hemoglobin and hematocrit levels.
Homeostasis
Define as the body's equilibrium and its importance in maintaining physiological functions.
Intracellular and Extracellular Fluids. Tell me the levels
Differentiate between fluids inside and outside the cell and their distribution in the body. ICF- 2/3 of fluid, EXF- 1/3 of fluid
Fluid Spacing
Explain first- normal distribution, second- edema, and third spacing of fluids in the body and their implications- pleural effusion.
To maintain a stable internal environment the body uses 4 processes
diffusion
facilitated diffusion
osmosis
active transport
Electrolytes, Define sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium normal ranges
sodium- 135-145
potassium- 3.5-4.5
calcium- 9-11
magnesium- 1.5-2.5
Sodium what are the main function
Neurological and neuromuscular
Potassium what are the main function
Neuromuscaular and cardiac
Calcium what are the main function
bones, teeth, nerve impulses, muscle contraction, clotting
If someone has a low calcium what happens
Tetany- give oral calcium
Magnesium what are the main functions
regulates metabolism, cardiac function, and nerve impulses
SLOW INFUSION RATE TO AOID CARDIAC/RESP alert (1.5 ml/min or less than 10% conc)
Treatment
Oral forms of K:The safest way to administer potassium, never exceed 10-20 mEq/hr.
Calcium
Regulates bones, teeth, nerve impulses, muscle contraction, and clotting. Tetany may require oral calcium.
Magnesium
Regulates metabolism, cardiac function, and nerve impulses. Slow infusion recommended to avoid cardiac/respiratory issues.
Acid-Base Balance
Understanding acidosis vs. alkalosis, metabolic vs. respiratory imbalances.
ABG Interpretation (ph, PACO2, Bicarboante)
what makes it metabolic or acidotic
Normal Arterial Blood Gas Values - pH (7.35-7.45), PaCO2 (35-45 mmHg), Bicarbonate (22-26 mEq/L).
If PH and CO2 are going in same direction its metabolic
If PH and CO are going opposite its respiratory
Furosemide
Loop Diuretics (Furosemide) work in the loop of Henle, adverse effects include hyponatremia, hypotension, and hypokalemia.
Hydrochlorothiazide
Widely used diuretic with adverse effect of hypokalemia.
Spironolactone
Diuretic with adverse effect of HYPER kalemia, important to monitor potassium levels.