TEST 1 STUDY GUIDE
TEST 1 STUDY GUIDE
1. Understand the factors related to drug/medication administration
a. 10 rights of patients in medication administration
Right drug
Right patient
Right dose
Right time
Right route
Right assessment
Right documentation
Right evaluation
Right of patient to education
Right of patient to refuse care
b. Conversions and abbreviations
Liquids | Solids |
|---|---|
1 mL = 1 cm3 | 1,000 mcg = 1 mg |
1,000 mL = 1 L | 1,000 mg = 1 g |
1 ml=1cc | 1,000 g - 1 kg |
Lbs / 2.2= kg
d. Properties of ideal drugs
Effectiveness: Most important property a drug can have
Safety: Drug does not produce harmful effects
Selectivity: Drug elicits only the response for which it is given
Predictability
Ease of administration
Freedom from drug interactions
Low cost
Chemical stability
Simple generic name
However, no drug is ide
2. Medication errors and what causes them
Causes of Medication Errors
Of the human factors that can cause errors, performance deficits are the most common, followed by knowledge deficits and the miscalculation of dosage
90% of all errors are due to:
Human factors
Communication mistakes
Drug name confusion
3. Difference between pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics
Pharmacokinetics
What the body does to the drug
4 processes
Absorption- GI tract
Distribution- blood
Metabolism- Kidney and liver
Excretion- bile and urine
Pharmacodynamics
What the drug does to the body
Sources of Individual Variation- impt!
Physiologic variables
Age, gender, and weight
Pathophysiology variables
kidney , liver damage
Acid- base imbalance
Altered electrolytes
Tolerance
Pharmacodynamics
What the drug does to the body
Impact of drugs on the body
Drug-receptor interaction
Patient’s functional state
Placebo effects
4. The nurse’s role in safe medication administration process
DRUG ALLERGIES
Do not administer any drug if you do not understand the reason for its use
Promoting patient adherence
Also known as compliance or concordance
Extent to which a patient’s behavior coincides with medical advice
Implementing non drug measures
6. Pharmacokinetic processes
Four major pharmacokinetic processes:
Drug absorption
Drug distribution
Drug metabolism
Drug excretion
B. Passage of Drugs Across membrane AKA BBB
Drug must be lipid soluble or lipophilic OR transport system
Plasma albumin is the most abundant and important protein in blood stream
METABOLISM- LIVER
7. First pass effect of medications
As you take medicine goes to stomach then to liver, so sometimes it can be less effective. You can bypass this by giving via different routes
8. Terms about pharmacodynamics
a. Therapeutic range- Also known as the therapeutic window, this is the range of drug concentrations in the bloodstream that is effective for treating a particular condition without causing significant adverse effects. It is the range between the minimum effective concentration and the toxic concentration.
b. Therapeutic index: Toxic dose/effective dose (formula for calculating
c. Half life
The half-life of a drug is the time it takes for the plasma concentration of a drug in your body to reduce by half.
It takes 4-5 ‘half-lives’ to reach plateau and 4-5 ‘half-lives’ for drug to be completely eliminated- on test
9. Drug-receptor
Agonist: goes to the receptor to turn it on to: START a Response
Antagonist: goes to the receptor and binds with it:
Partial agonist: binds to the receptor, weak response
interactions
10. Drug-drug reactions
Drugs can interact through four basic mechanisms:
Direct chemical or physical interaction
IV’s can precipitate( drugs did not combine well… on next page)
Pharmacokinetic interaction- what the body does to the drug
An elevated gastric pH can change absorption
Pharmacodynamic interaction- what the drug does to the body
Drugs may compete for receptor sites
Combined toxicity
*Usually caused by drug incompatibility
11. Drug-food reactions
Drug metabolism
The grapefruit juice effect (not occurring with other citrus fruits or juices)
Inhibits the metabolism of certain drugs
Raises the drugs’ blood levels
Increase in felodipine
Others: Lovastatin, cyclosporine, midazolam, and so on
Impact of food on:
Drug toxicity
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) and tyramine-containing foods
Theophylline and caffeine
Potassium-sparing diuretics and salt substitutes
Aluminum-containing antacids and citrus beverages
What is considered an empty stomach?
1 hour before meals or 2 hours after eating
13. Drug calculations, drip rage calculations
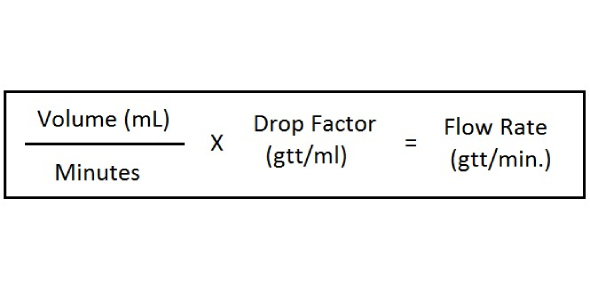
14. Medication errors- nurse role in prevention
Help and encourage patients and their families to be active and informed members of the healthcare team
Create an institutional culture that is dedicated to safety
Give healthcare providers the tools and information they need to prescribe, dispense, and administer drugs as safely as possible
Institute safety checklists for high-alert drugs Institute for Safe Medication Practices High-Alert Medications.
About 20 drugs cause 80% of medication error–related deaths
Replace handwritten medication orders with a computerized order entry system
Have a senior clinical pharmacist accompany physicians on rounds
Use a barcode system
Do not use error-prone abbreviations
Institute for Safe Medication Practices
Perform medication reconciliation
15. Drug tolerance and terms related to adverse drug reactions
Pharmacodynamic tolerance
Associated with long-term administration of drugs such as morphine and heroin
Metabolic tolerance
Results from accelerated drug metabolism
Tachyphylaxis
Reduction in drug responsiveness brought on by repeated dosing over a short time - a rapid response, ex. Afrin if you keep using it loses its effect and makes it worse
Terms Related to Adverse Drug Reactions
Side effect
Toxicity
Allergic reaction
Idiosyncratic effect- we do not know what caused it
Paradoxical effect - benodryal makes kids sleepy but sometimes it can make u hype
Iatrogenic disease - thing in medical field causes a problem
Physical dependence
Carcinogenic effect
Teratogenic effect - fetus related
Identifying Adverse Drug Reactions
Can be very difficult to determine whether a specific drug is responsible for an observed adverse event
Other factors to consider:
Underlying illness
Other drugs
Boxed Warnings- for the test
Also known as black box warnings
Strongest safety warning a drug can carry and still remain on the market
Purpose of this warning is to alert prescribers to:
Potentially severe side effects/adverse effects (eg, life-threatening dysrhythmias, suicidality, major fetal harm)
Ways to prevent or reduce harm (eg, avoiding a teratogenic drug during pregnancy)
The most dangerous that you can still give to pt, like sertraline has black box warning for suicide
Impt things to know: what's going to cause pronblems
What can you do as a nurse to prevent those from happen
16. Neuropharmacological drugs
How neurons regulate physiological processes…
Conduction of an action potential along the axon of the neuron
Release of neurotransmitter from the axon terminal and
Binding of transmitter molecules to receptors on the postsynaptic cell
17. Autonomic nervous system- parasympathetic and sympathetic -know difference
Somatic motor system – controls movement of voluntary muscles
Autonomic nervous system – regulates heart, secretory glands, smooth muscles (involuntary activities)
Parasympathetic nervous system: pear
Sympathetic nervous system- simp
Parasympathetic-”rest and digest”
Slowing of heart rate
Increased gastric secretions
Emptying of bladder
Emptying of bowel
Focusing of eye for near vision
Constriction of pupil
Constriction of bronchial smooth muscle
Sympathetic “fight or flight”
Regulation of cardiovascular system
Regulation of body temperature
Implementation of “fight-or-flight” reaction:
Increased heart rate & BP
Bronchodilation
Vasodilation in skeletal muscle and heart muscle
Vasoconstriction in superficial capillaries
Decreased gastric secretions and motility
Pupil Dilation
Receptors of the Peripheral NS -know test, understand which are which… cholernergic have three and Adrenergic have 4
Cholinergic receptors
Nicotinic n
Nicotinic m
Muscarinic - most cholinergic drugs work here, and activate parasympathetic system
Adrenergic receptors - activate sympathetic system
Alpha 1
Alpha 2
Beta 1
Beta 2
17. Polypharmacy- taking 5 or more meds
18. If your pt has a high HR bc of meds you call for doctor
19. 2.2 lb =1kg
18. Normal lab values- WBC, RBC, platelets
Formed Elements (leukocytes)
Neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, NO MONO
IMPT on TEST!: If a patient has cancer do not give them erythopoetin!
19. Understand function of WBC, RBC, platelets(Formed Elements)
Leukocyte(WBC)- neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils
Normal Range 5k-10k
Erythrocyte- RBC-
Normal Range- 4-6 million
Wear out in 120 days eaten by spleen and liver
HGB- 12-18 (men higer than women)
HCT- 39-50%
Platelet
Normal range i s150k-400k
When you have low (thrombocytopenia) you will be put on bleeding precautions
Treatmetn:oprelkin
When taking ertythropoetin HGb should not exceed 12
20. Understand importance of blood types
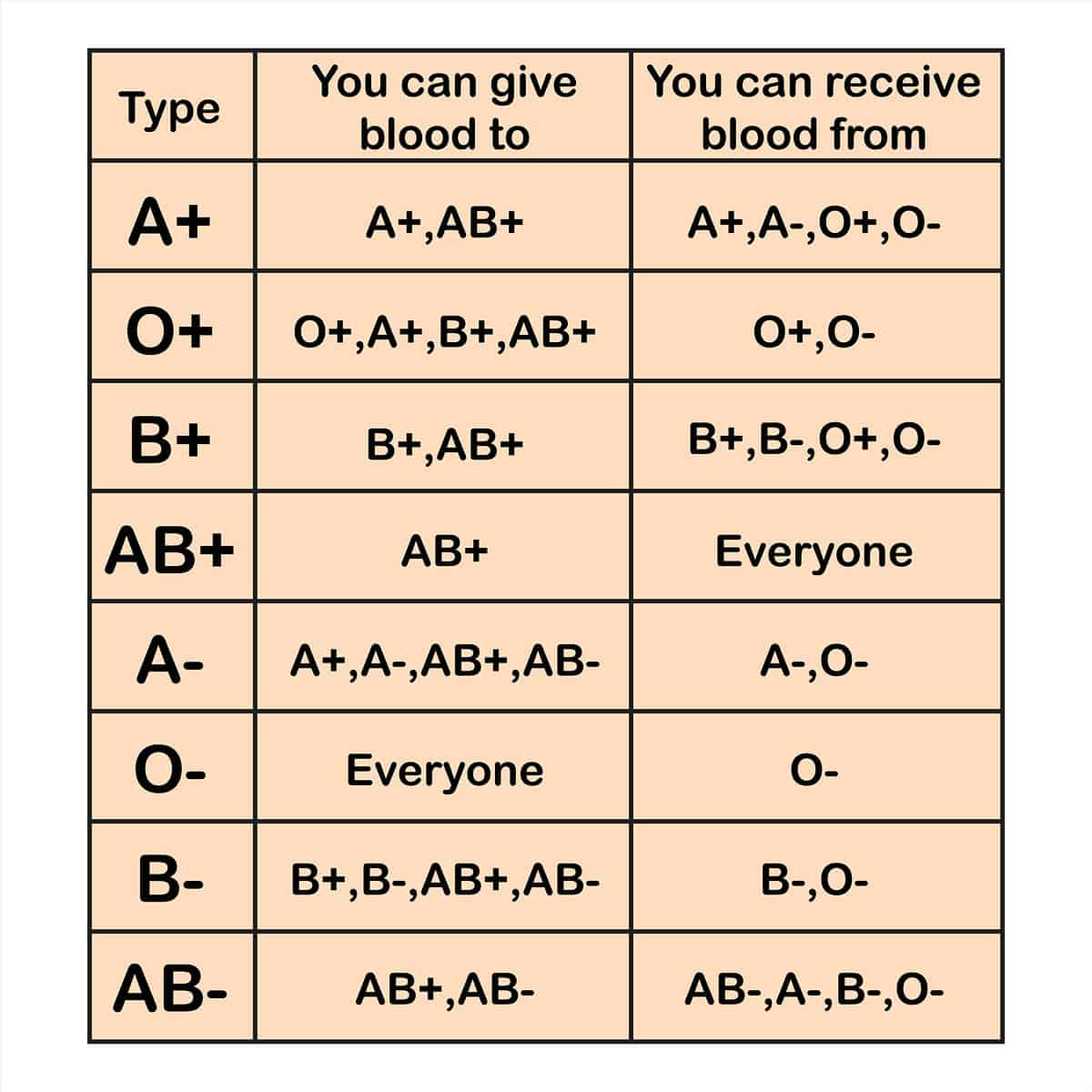
21. Differentiate the types of anemias-what causes, s/s, treatment, nursing considerations
Oral Defiency Anemia - most common
Give oral iron (ferous sulfate) but can cause staining of teeth
Anemia of chronic diseases- like HIV hepatitis
Low RBC production
Underlying disease first
Megoplastgic Anemia- impaired DNA synthesis
Results in large, fragile, defective RBC
Treatment: B12 (cobalamin)- caused by pernicious anemia
APLASTIC ANEMIA IS WHEN YOU HAVE RED AND WHITE BLOOD CELLS AND PLATELETS!!!- on test
Aplastic Anemia/ Pancytopenia
Decrease in all blood cell types
Red blood cells (RBCs)
White blood cells (WBCs)
Platelets
21. Inheritede Hemorrhagic Diseases
Classic hemophilia is factor VIII deficiency (x linked)
Manifestations: bleeding in joint, and nose
Diagnostic: Lab tests will show low levels of VIII and a prolonged PTT
22. Define homeostasis and why it is important in the body
Equilibrium in body
Who contains the highest percentage of water
Newborns (70-80)
Men have more than women
23. Intracellular fluids vs extracellular fluids
ICF- inside the cell - ⅔ of fluid
EXF- outside of the cell ⅓ od dluid
24. Fluid spacing
First spacing: normal distribution of EXF in ICF
Second spacing: edema
Third spacign : fluid trapped , pleural effusion
25. Fluid movement and disease
From plasma to interstitial
Results in edema can be from
HF
Fluid overload
Liver failure
Renal disease
Trauma
Burns
Results from intersititual to plasma
Medications (mannitol)
Compression hose
To maintain a stable internal environment the body uses 4 processes
Diffusion
Facilitated Difusion
Osmosis
Active Transport
26. Fluid volume deficit vs fluid volume overload- what causes, s/s treatment, nursing considerations
Fluid Volume Imbalance
Hypovolemia
Isotonic : need isotonic fluids
Hypertonic: meed hypotonic fluid
Hypotonic: need hypertonic solution
Hypervolemia
Inreased extracellular fluid (edema)
Treat with diuretic or fluid restriction
27. Understand difference between electrolytes and effect on body- normal vs abnormal and how to treat
Electroyltes
Sodium: 135-145 (odd)
Potassium 3.5-5 (pot is ass)
Calcium 9-11 (call 911)
Magnesium 1.5-2.5 (lil maggie is 1.5)
Sodium
Neurological and neuromusclar function
Signs and Symptoms:
Hyper: Thrist, lethargy, dry mouth, sticky mucous, brain damage, disorientationn, hallucination, muscle instability, convulsions
Hypo: Headache, confusion, anorexia, SOB with exertion, fatigue, confusion, deliriium, shock, coma
Potassium
Neuromuscular and cardiac
Signs and Symtoms (most abundant)
Hyper: nausea, vomiting, diarhea, weak and flacid muscles, Arrhythmias, v fib/ arrest, T wave heighetens, PR interval prolongs, numbness and tingleness
Hypocalemia: Nausea, vomiting, Abd distension, decreased motiility, weakness than flacid, decrease standing BP , syrhithmias, PVCs, twaves lower, Cardiac arrest,
Treatment: Oral forms of K are the safest, never exceeed 10-20 mEQ/hr
ALERT: patients with RENAL FAILURE
Calcium
Regulates bones and teeth, nerve impulses, muscle contraction, clotting
TETANY- ON TEST- sustained muscle contraction- GIVE ORAL CALCIUM
Magnesium
Regulates metabolism, cardiac funciotn, nerve impulses
SLOW INFUSION TO AVOID CARDIAC/ RESP ALERT (1.5 ML/MIN OR LESS OF A 10% CONC)
28. Acid-base balance-acidosis vs alkalosis, metabolic vs respiratory
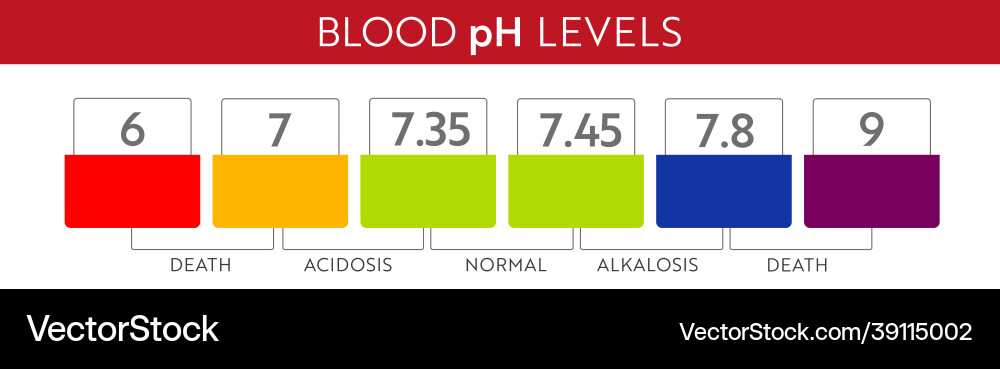
Test:
m R acidosisi: increased CO2 (hypoventilaition), R depression- COPD or oversdose
R alkalsis is : decreased CO2 (hyperventilation) (anxiety- al is anxious
Food going up ph going up (vomit = alkalosis
Food going down ph going down= acidosis
Bufffers are used to maintain acid- base homeostasis
29. ABG interpretation
Normal Arterial Blood Gas Values
(Table 17.15, p. 323 Lewis’s Med/Surg Text , 12th Ed)
*remember these top three
pH = 7.35 to 7.45
PaCO2 = 35 to 45 mmHg
Bicarbonate (HCO3-) = 22-26mEq/L - tells us if it is metabolic
If PH and CO2 are going in same direction its metabolic
If PH and CO are going opposite its respiratory
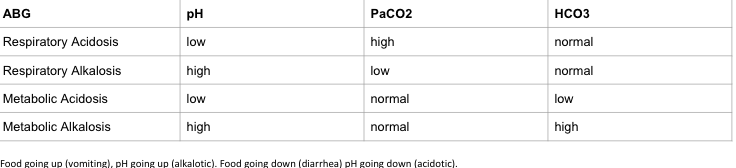
30. Diuretic functions, side effects, adverse effects, nursing considerations
Loop Dieuretic (Fursosemide)
Adverse effects: LOWWWWWWW (hyponatremia, hypotensions, HypoKALEMIA)
Works in loop of henle
Hydrochlorothiazide
Most widely used
Adverse effects: Hypokalemia
Spirnolactorne
Adverse effects: HYPERKALEMIA, HYPER, HYPER - tesT!!!
31. Understand/befamiliar with drugs in the drug tables