Plant basics
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
sporophyte
2n
gametophyte
n
sporangium
structure that produces spores through meiosis
gametangia
structure that makes gametes through mitosis (2 types)
Archegonia
Female gametangia
Antheridiais
Male gametangia (sperm)
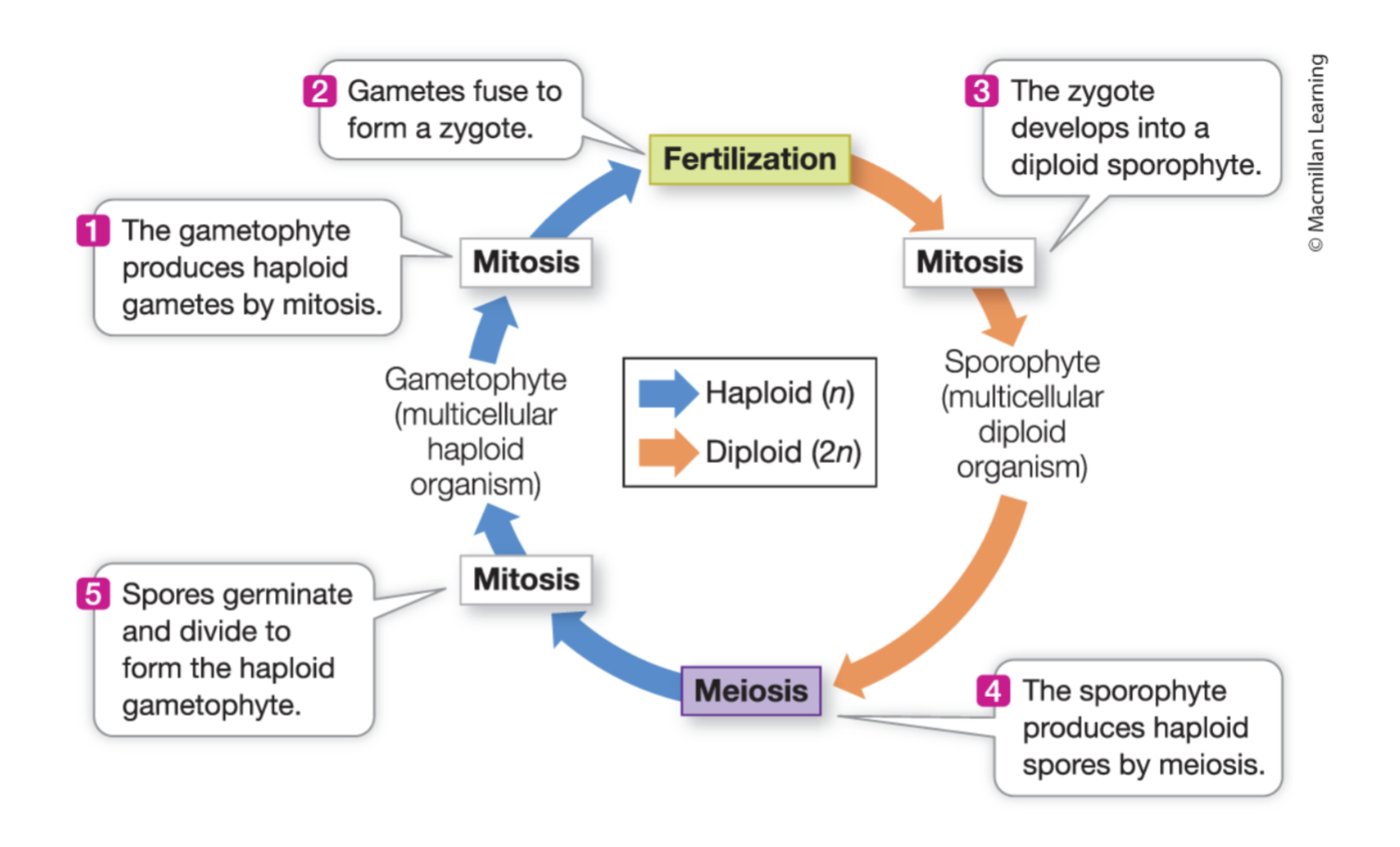
Sporophyte to gametophyte
Meiosis
Gametophyte to sporophyte
Fertilization
Synapomorphy of land plants
A protected embryo by tissues of parent plant
Land plants can also be called
Embryophytes
Vascular plants
Has tracheophytes
tracheophytes
Fluids conducting cells called traceids
Fusion of gametes results in
diploid zygote
Zygote (for plants) develops into:
Multicellular sporophyte
Non-vascular plants
Plants that don’t have tracheids
What do plants need on land?
- water transport mechanisms
- physical support
- mechanisms to distribute gametes and progeny
- avoid desiccation (drying out)
Adaptations of plants
- cuticle
- stomata
- gametangia
- embryos in a protective structure
- thick spore walls that prevent desiccation and decay
- pigments that protect against UV radiation
- mutually beneficial associations with fungi (mycorrhizae) that provide nutrient uptake from the soil
Cuticle
Waxy coating that retards water loss
Stomata
Openings in stems and leaves regulate gas exchange and water loss
Basic plant life cycle
:)
Sharded derived trait of plantae
Primary endosymbiosis
2 types of land plants
Vascular and nonvascular
Key synapomorphy of vascular plants
Tracheid and Branching independent sporophytes
Vascular system parts
Xylem and Phloem
Xylem
Conducts water and minerals from soil up to the rest of the plant
What provides support in Xylem
Lignin
Phloem
Conducts products of photosynthesis through the plant
Transport of water and minerals and rigid structural support allows plants to ________
Grow tall to compete for light and aids in spore dispersal
Branching independent sporophytes (in vascular plants)
- produce more spores
- develop in complex ways
The most ancient vascular plants were
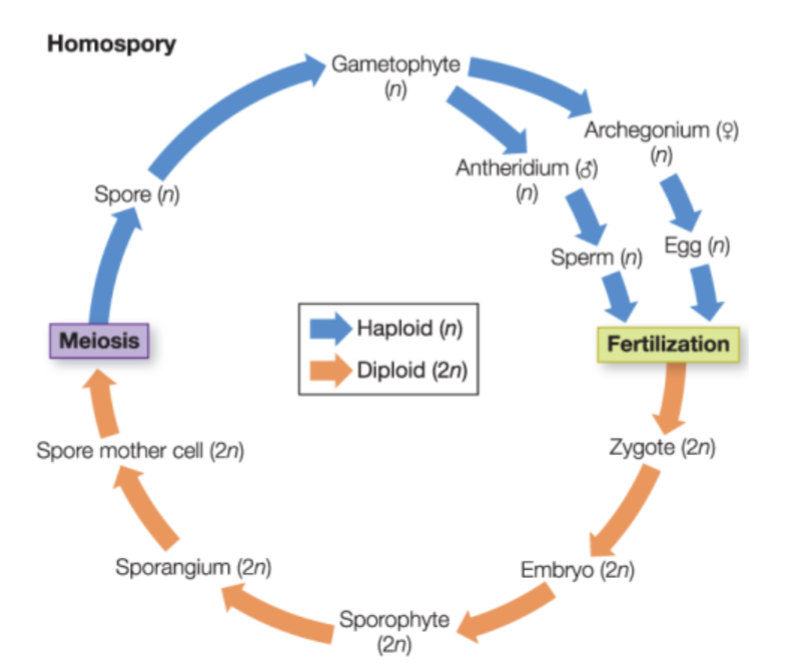
homosporous
homosporous
one type of spore
heterosporous
multiple types of spores
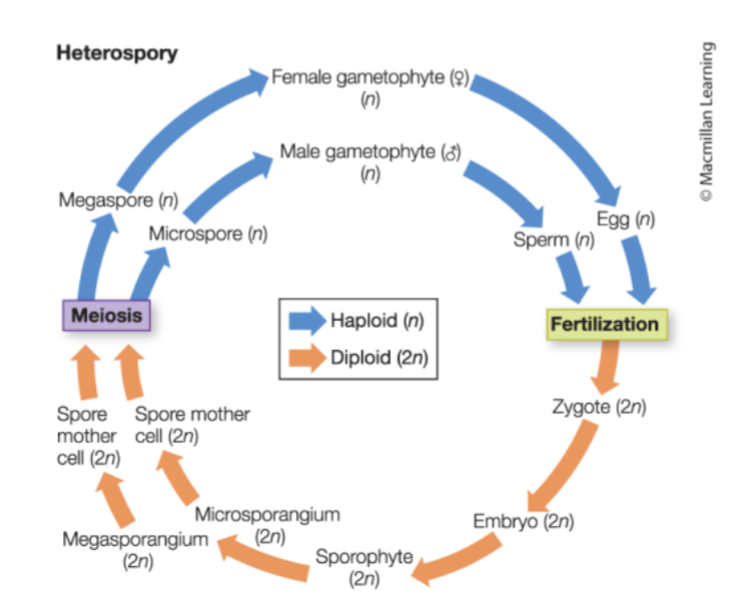
megaspore
develop into female gametophyte - megagametophytes (eggs only)
Ovule
Megasporangium and the integument
microspore
divide mitotically to form male gamerophytes (pollen grain)- microgametophytes (sperm only)
Pollen grain
male gamerophytes
Seeded plants (vascular)
Gymnosporms and Angiosperms
3 new features in seeded plants
woody stem - pollen - seeds
Woody stem
Secondary growth that gives support and allows plants to grow above their competitors - many plants have lost this
Pollen
Sperm transfer that doesn’t require water
sporopollenin
in pollen grain walls - most resistant biological compound - prevents dehydration and chemical change
Seeds
embryo is protected until ready to germinate - has tissue from 3 generations
tissue in seeds
Seed coat that develops from integument (from the sporophyte parent) - Haploid female gametophyte tissue supplies nutrients for developing embryo - Embryo is the new diploid sporophyte generation
What is the evolutionary trend about the size of the sporophyte and the gametophyte?
Trend towards reduction of gametophyte generation in plant evolution
Pollination
When a pollen grain lands near a female gametophyte
Pollen tube
tube from the pollen grain that elongates and digests its way through the sporophyte tissue to the megagametophyte
Angiosperms
Protected/enclosed seeds
Gymnosperms
naked/unprotected seeds (no flowers or fruits)
Megastrobilus
Female cone - houses megasporangium
Microstrobulis
Male cone - houses microsporangium
Synapomorphies of angiosperms
- germination of pollen on stigma
- double fertilization
- endosperm (nutritive tissue for embryo
- phloem with companion cells
Corolla
Petals plural
Calyx
Sepals plural
Tepals
undifferentiated flowers (petals and sepals)
Perfect flowers
Both mega and microsporangia - can self pollinate
Imperfect flowers
Either mega or microsporangia - monoecious and dioecious
Red and odorless flowers are mostly pollinated by ____
Birds
Flowers that smell are often pollinated by ____
Insects
Flowers with conspicuous markings, or nectar guides are often pollinated by ___
Bees
Simple fruits
Develop from one carpel (plum or cherries)
Aggregate fruits
Develop from several carpels of a single flower (raspberry)
Multiple fruits
Develop from a cluster of flowers (pineapple or figs)
Accessory fruits
Develop from parts in additon to carpels and seeds (apple, pears, or strawberry)
Monocots
One cotyledon - vascular bundles arranged in scattered/no arrangement
Dicots/eudicots
two cotyledons - vascular bundles arranged in a circular bundle
Monoecious
Male and female flowers occur on the same plant
Dioecious
Male and female flowers are on different plants
genetic self-incompatibility
reject pollen from their own flowers - S locus genes encodes proteins in the pollen and style that interact during the recognition process
Nonvascular plant traits:
no vascular transport system - plants are short
water transport is via diffusion
thin cuticle or no cuticle; most live in moist habitats
lack true leaves, stems, and roots
Sporophyte is nutritionally dependent on gametophyte
water needed for reproduction
Multicellular diploid plant generation
Sporophyte
Multicellular haploid plant generation
Gametophyte