Chapter 16 Quest
1/34
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Arrhenius acid definition
increase [H+]in aqueous solution
Arrhenius base definition
increase [OH-] in aqueous solution
Arrhenius acid-base equation
acid + base → salt + water
Bronstead-Lowry acid definition
donates H+
Bronstead-Lowry base definition
accepts H+; does not need to contain OH-
Amphiprotic
any molecule or ion that can gain or lose a proton; can behave as acids and bases
Amphoteric
reserved for insoluble oxides that dissolve in acidic or basic solutions; can behave as acids and bases
How to determine concentration of hydronium/hydroxide?
pOH = -log[OH-] or pH3O = -log[H3O]
Kw
ion-product constant of water; autoionization of water; 1 × 10-14
Kw »
more water molecules are ionizing; a more basic or acidic solution
Kw «
only a very small amount of water molecules are ionizing; predominately neutral solution
Kw with temperature
increases with increasing temperature; more water molecules ionize at higher temperatures
What conditions makes the autoionization of water a source of H+?
at 25 degrees C
Conjugate base
whatever is left of the acid after the proton is donated
Conjugate acid
whatever remains of the base after it accepts a proton
Conjugate acid-base pairs differ by
one proton
7 Strong Acids
HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, HClO3, HClO4, and H2SO4

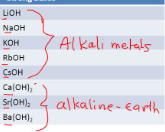
6 strong bases
group 1 hydroxides: LiOH, NaOH, KOH, RbOH, CsOH; heavy group 2 metal hydroxides: Ca(OH)2, Sr(OH)2, Ba(OH)2
How do you calculate pH and pOH from strong acid and base concentrations?
put the strongest acid concentration into the pH equation (if acid M < 10-6 M then pH = initial molarity) and the strongest base concentration into the pOH equation
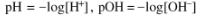
How can you use conjugate pairs to classify acids/bases as strong or weak?
stronger acid, negligible conjugate base; weak acid, weak conjugate base; negligible acid, strong base
Leveling effect of water
places strong acid/base in dilute acetic acid to find different in their strengths; H+ is strongest acid and OH- is strongest base in equilibrium in aq
Equilibrium in acid-base reactions
favors transfer of proton from stronger acid to stronger base; strong acid → favors right side and weak acid → favors left side- bc favors weak electrolyte production
Acidic Solutions
[H+] > 1.0 × 10-7 and pH < 7.00
in neutral water at 25C, pH =
pH = pOH = 7.00
basic solutions
[H+] < 1.0 × 10-7 and pH > 7.00
pH/pOH sig figs
use concentration’s sig fig (what you take the log of)
Ka » in terms of acids
stronger the acid
Ka > 1 in terms of acids
acid is a strong acid and is completely ionized
What does pH give?
the equilibrium concentration of H+
If you have an Ka or Kb value of 10-5 or less, you can
usually make an assumption; make sure to double check though
Percent ionization
[H3O+]eqm / [HA]0 × 100 or [OH-]eqm / [A-]0 × 100
What does a higher percent ionization mean?
stronger the acid
Percent ionization of a weak acid decreases as the molarity
increases
If the successive Ka values differ by a factor of _____ or more, pH can be determined by considering only ___
103; Ka1
weak acids are only
partially ionized