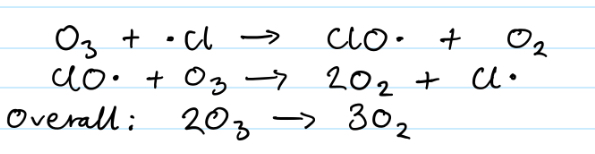Alkenes and Haloalkanes
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Describe the structure of alkenes
Unsaturated hydrocarbons (C=C double bond)
Why are alkenes more reactive than alkanes?
C=C bond is an area of high electron density making it susceptible to attack from electrophiles
What are the two bonds in C=C?
A covalent bond and a pi bond
What is the test for alkenes?
Bromine water - orange-brown to colourless
What are electrophiles?
Electron acceptors
What area of molecules are electrophiles attracted to?
Areas of high electron density
Examples of electrophiles
HBr, Br2, H2SO4
What is formed when a double bond is broken during electrophilic addition?
A carbocation
What is a carbocation?
A carbon atom with only 3 bonds (+ charge)
Which carbocations are most to least stable?
Primary are least stable, tertiary are most stable
Which carbocations are more likely to form in reactions?
The most stable (tertiary)
Electrophilic addition of alkenes to haloalkanes
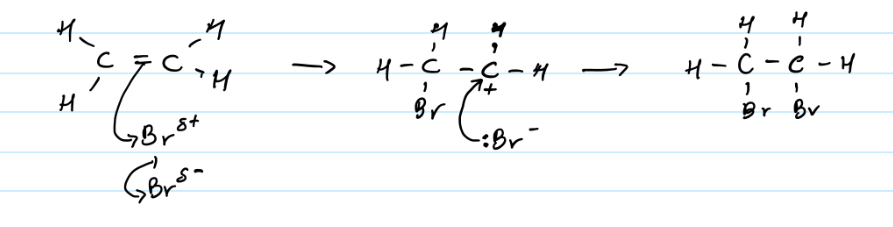
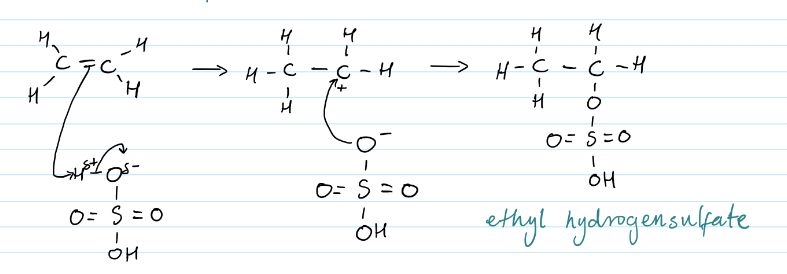
Electrophilic addition of alkenes to alkyl hydrogensulfates
What is an addition polymer?
A larger molecule produced from alkenes where double bond is broken to form a repeating unit
What type of polymers do high pressures and temperatures produce?
Branched chain polymers with weak intermolecular forces
What type of polymers do lower pressures and temperatures produce?
Straight chain polymers with stronger intermolecular forces
What is a disadvantage of polymers being unreactive?
Means that polymers are not biodegradable
Why do haloalkanes contain polar bonds?
The halogens are more electronegative than carbon atoms
Which area of the haloalkane is drawn to the halogen?
The area of high electron density
What are nucleophiles?
Positive liking molecules
what property of nucleophiles make them positive-liking?
They contain a lone electron pair that is attracted to slightly positive regions of molecules
Examples of nucleophiles
CN-, NH3, OH-
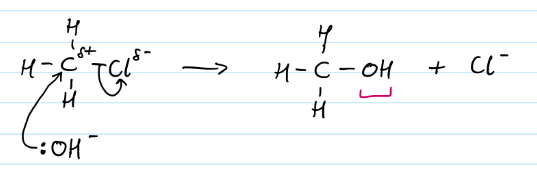
Nucleophilic substitution of haloalkanes to make alcohols
Nucleophilic substitution of haloalkanes to make amines
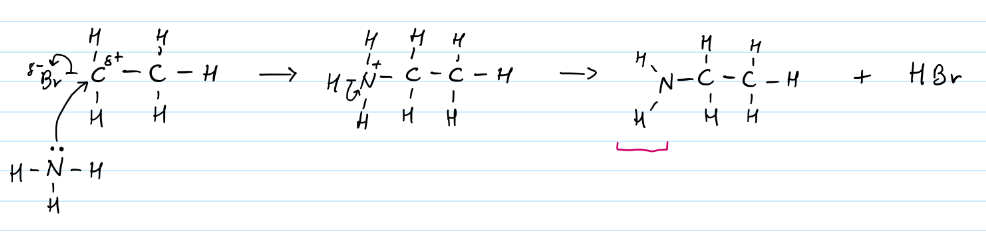
How does the Mr of the halogen in the polar bond of haloalkanes affect how easily the bond can be broken?
The greater the Mr, the lower the bond enthalpy meaning it can be broken more easily
What reaction conditions are required for elimination of haloalkanes?
High temperatures, ethanol solvent, strong base
What reaction conditions are required for nucleophilic substitution of haloalkanes?
Low temperatures, aqueous solvent, weak base
What does the nucleophile in elimination reactions do?
Acts as a base and accepts a proton, removing a H from the molecules
What does elimination of haloalkanes result in?
The removal of a halide to produce a C=C bond (alkene)
What types of haloalkanes does elimination reactions only occur in?
2° and 3°
What type of haloalkanes does nucleophilic substitution only occur in?
1° and 2°
Elimination of haloalkanes to form alkenes
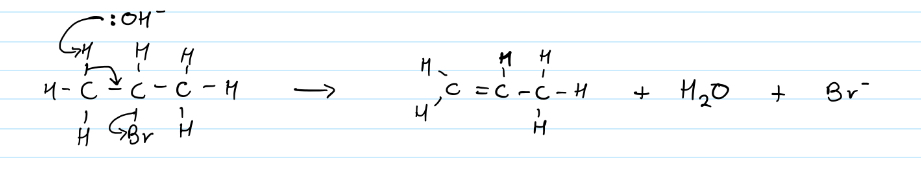
Describe the test for halide ions
Add acidified silver nitrate
Br - cream pcp
Cl - white pcp
I - yellow pcp
Ozone equation