Chapter 10 BIO MITOSIS
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
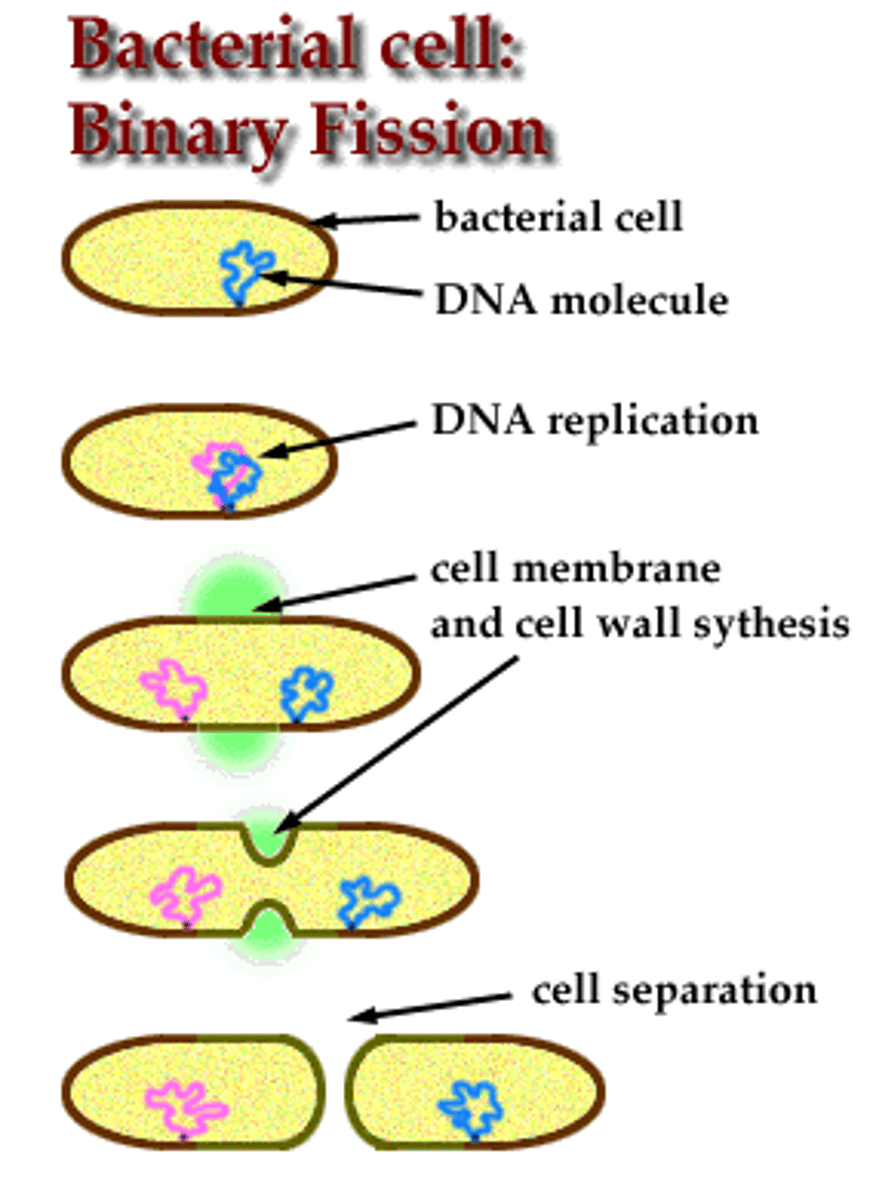
binary fission
Binary fission starts with origin of replication on one circular chromosome, grow in two opposite directions, forms two strands of DNA. FtsZ proteins scattered around the cell, form a ring structure bringing in material from cell wall and cell membrane to form separation. Separation forms septum. Two daughter cells are the result.
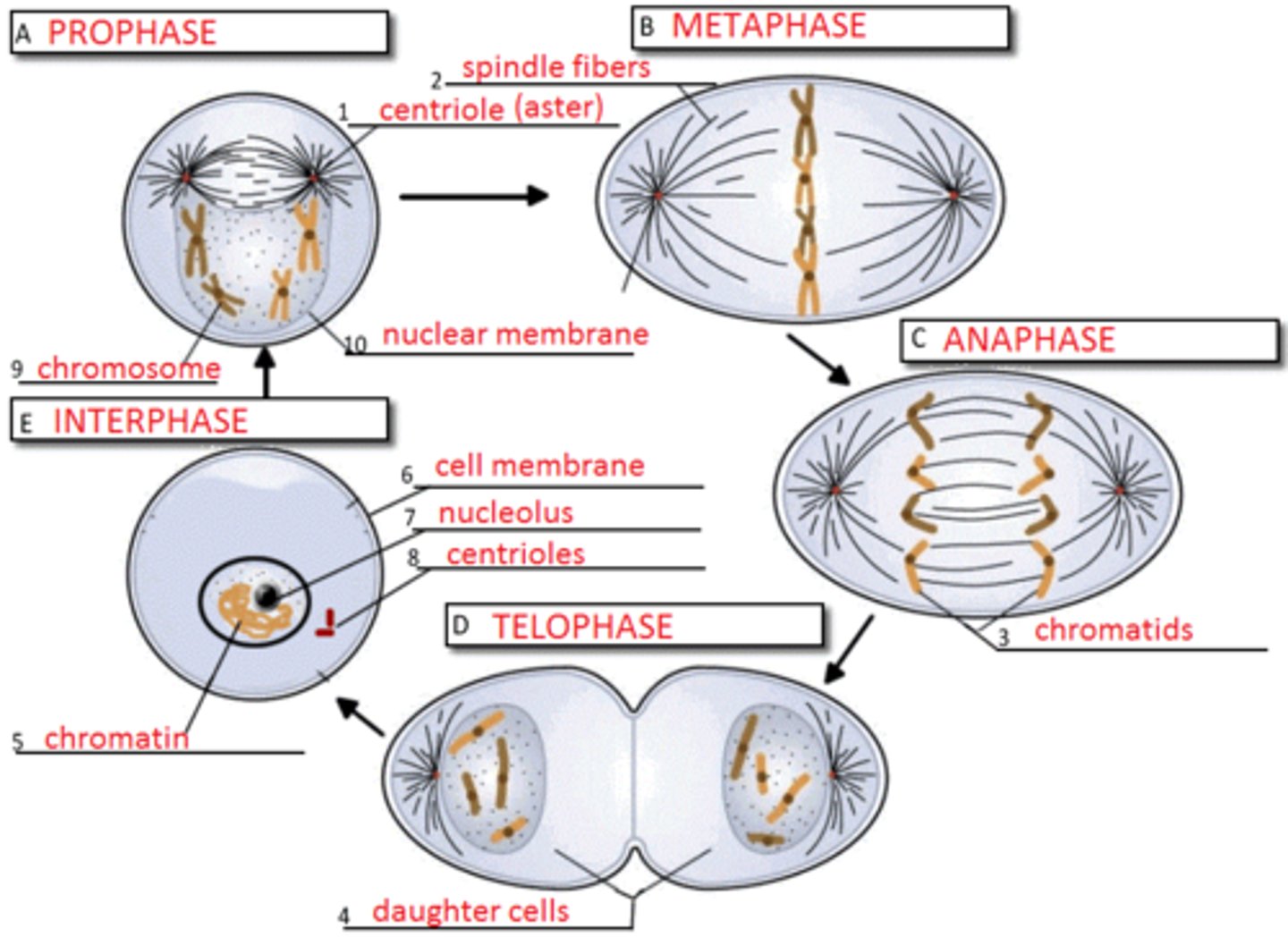
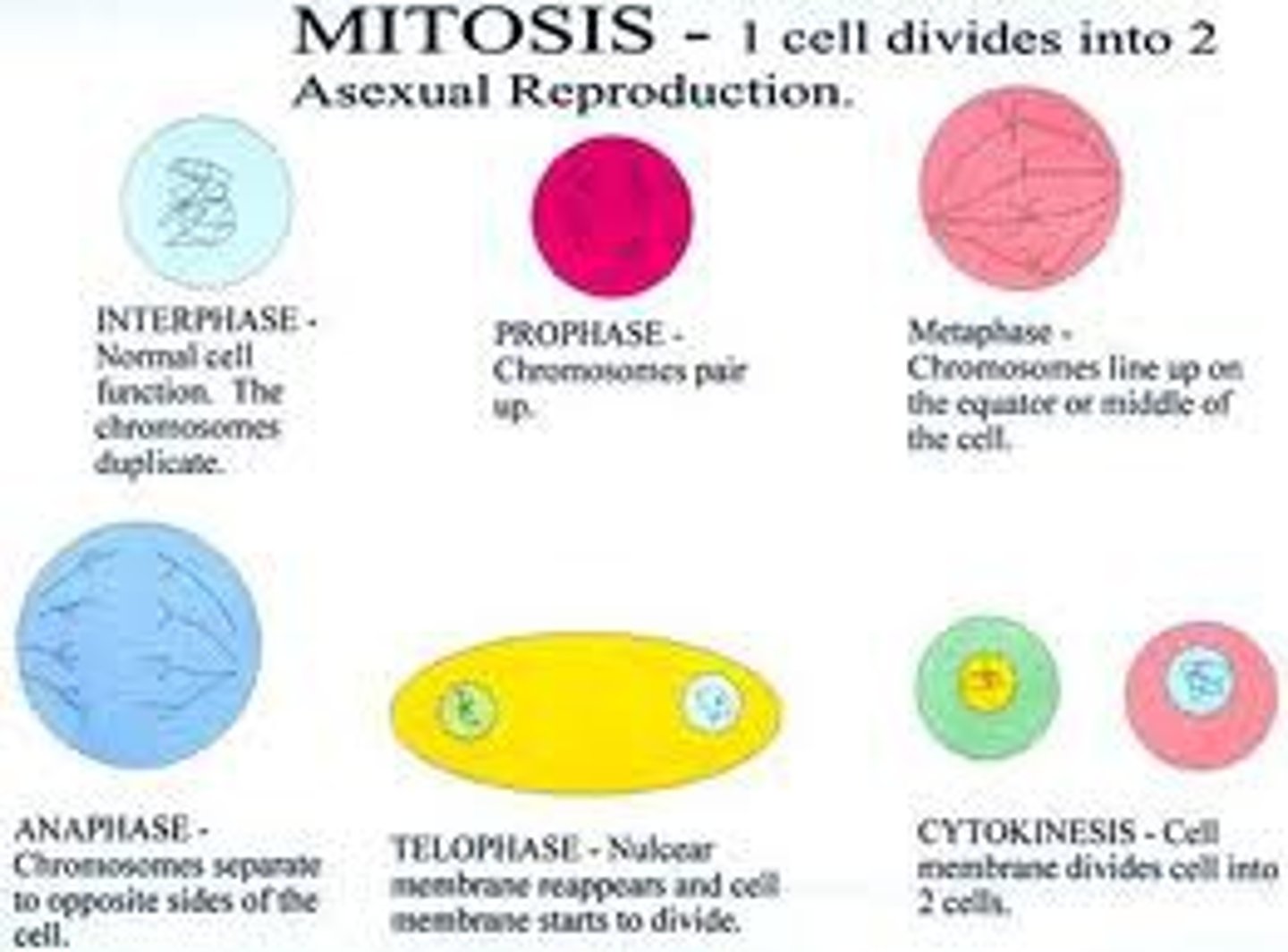
interphase
cell growth and copying chromosomes in preperation for cell division (spends most of its time there)
mitotic phase
mitosis and cytokinesis
G1 phase
cell is biochemically active, cell is growing, obtaining nutrients, preparing organelles for s phase
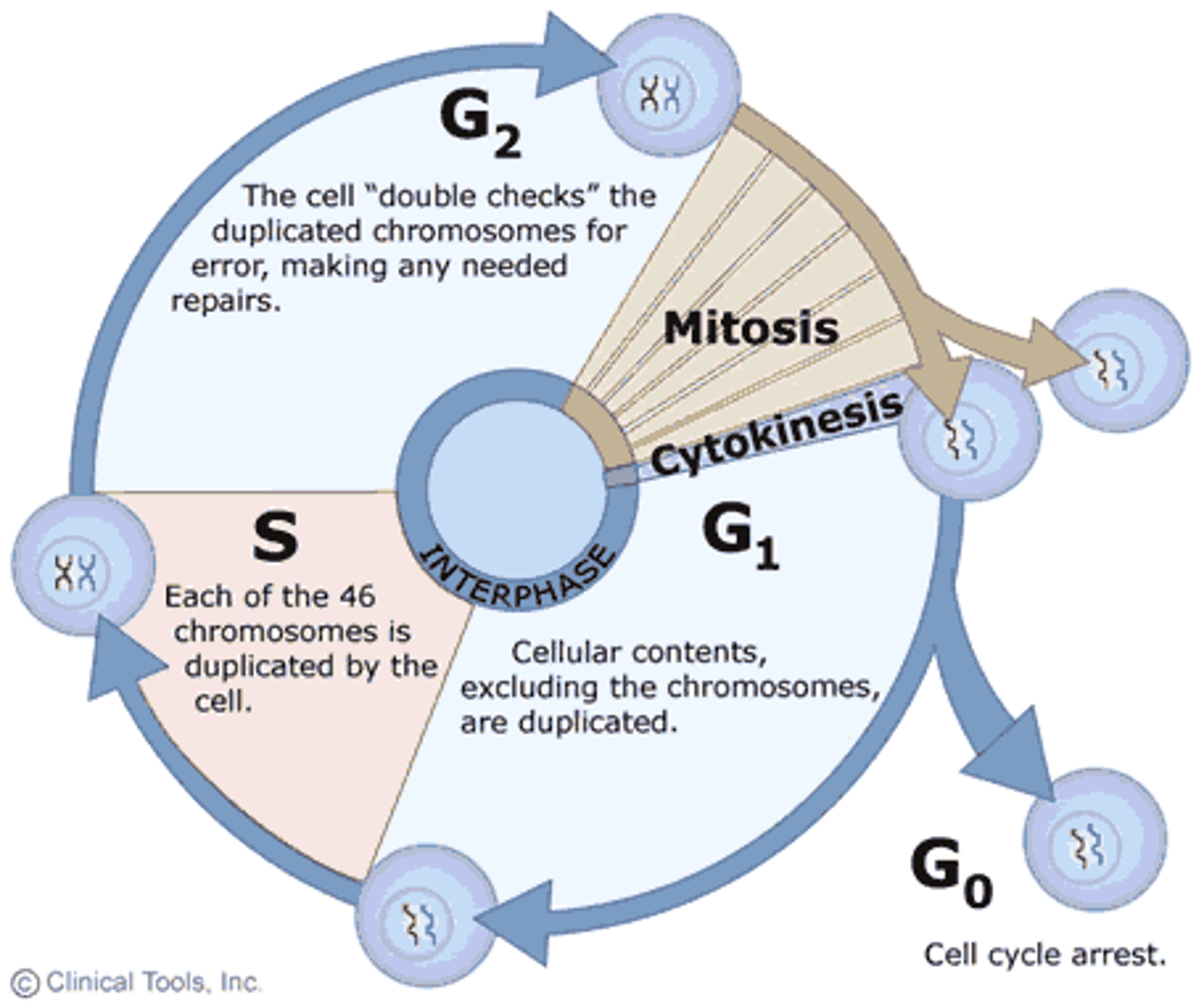
S phase
dna replication, histone production, centrosome production
G2 phase
cell continues to grow, energy replenished, cytokeleton begins to breaks, organelles replicate
nucleosomes are composed of -----
8 histones
nucleosomes are separated by
linker DNA
prophase
-nuclear envelope begins to break down,
-spindle fibers begin to form,
-nucleolus disappears,
-chromosomes start condensing
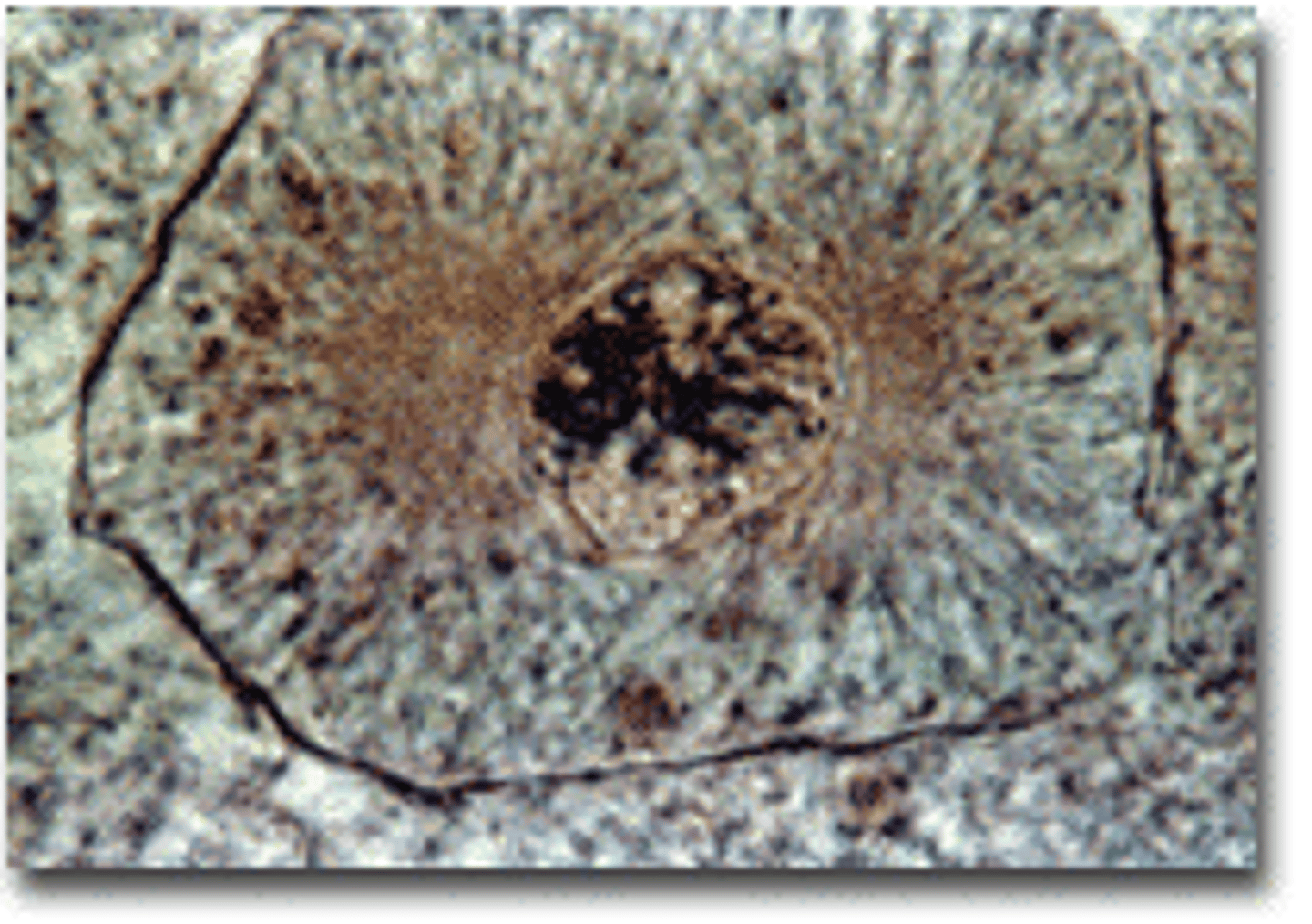
prometaphase
-centrosomes continue to condense,
-kinetochores appear,
-mitotic spindle begins to form at centromeres,
-centrosomes move to opposite poles
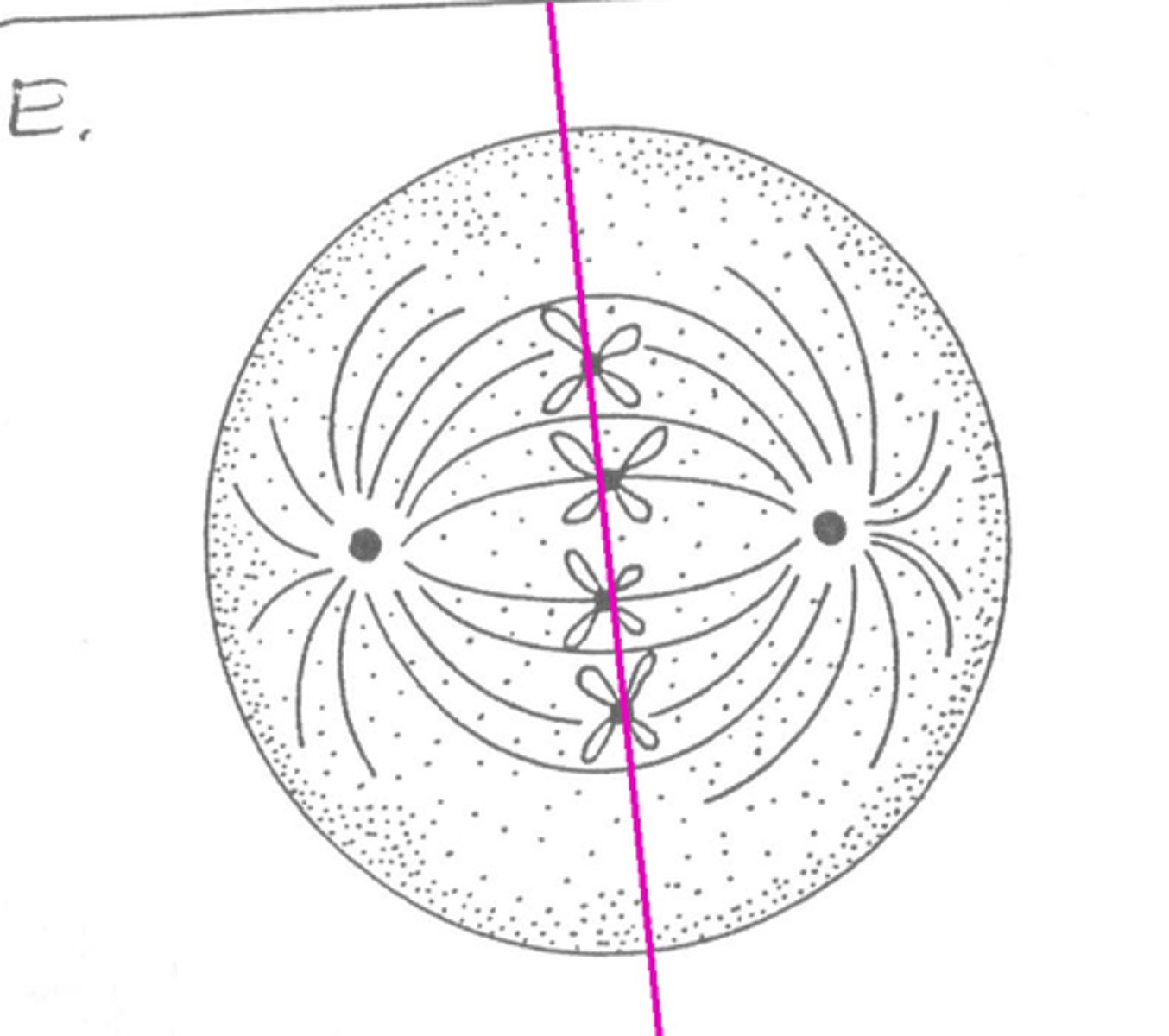
metaphase
-spindle fibers are fully forms,
-chromosomes line up at metaphase plate,
-nuclear envelope is absorbed in er,
-sister chromatids are attached to spindle fibers on opposite ends
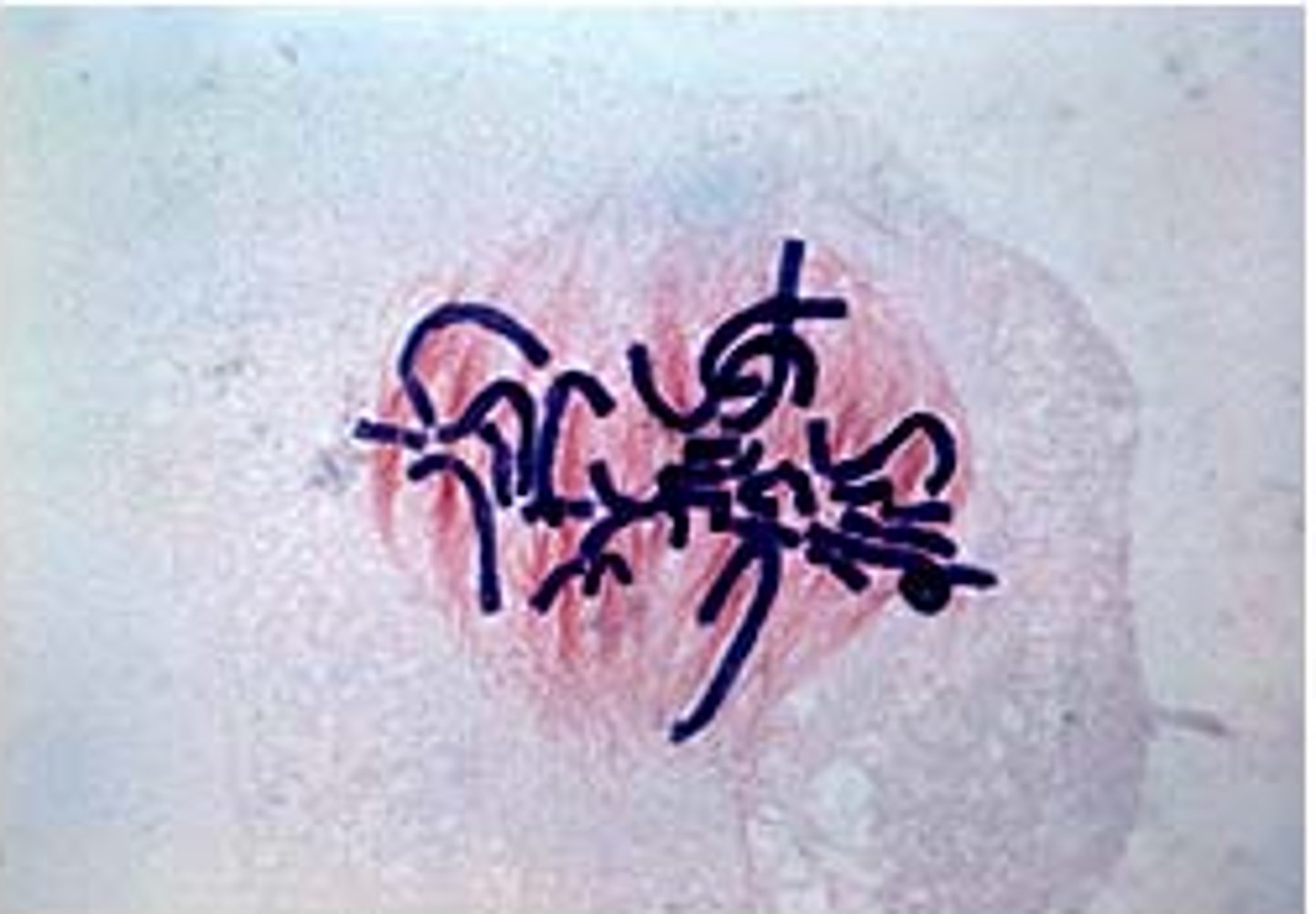
anaphase
-sister chromatids are puled apart,
-cohesions begin to break down,
-nonkinetochores glide against each other to help elongate the cell
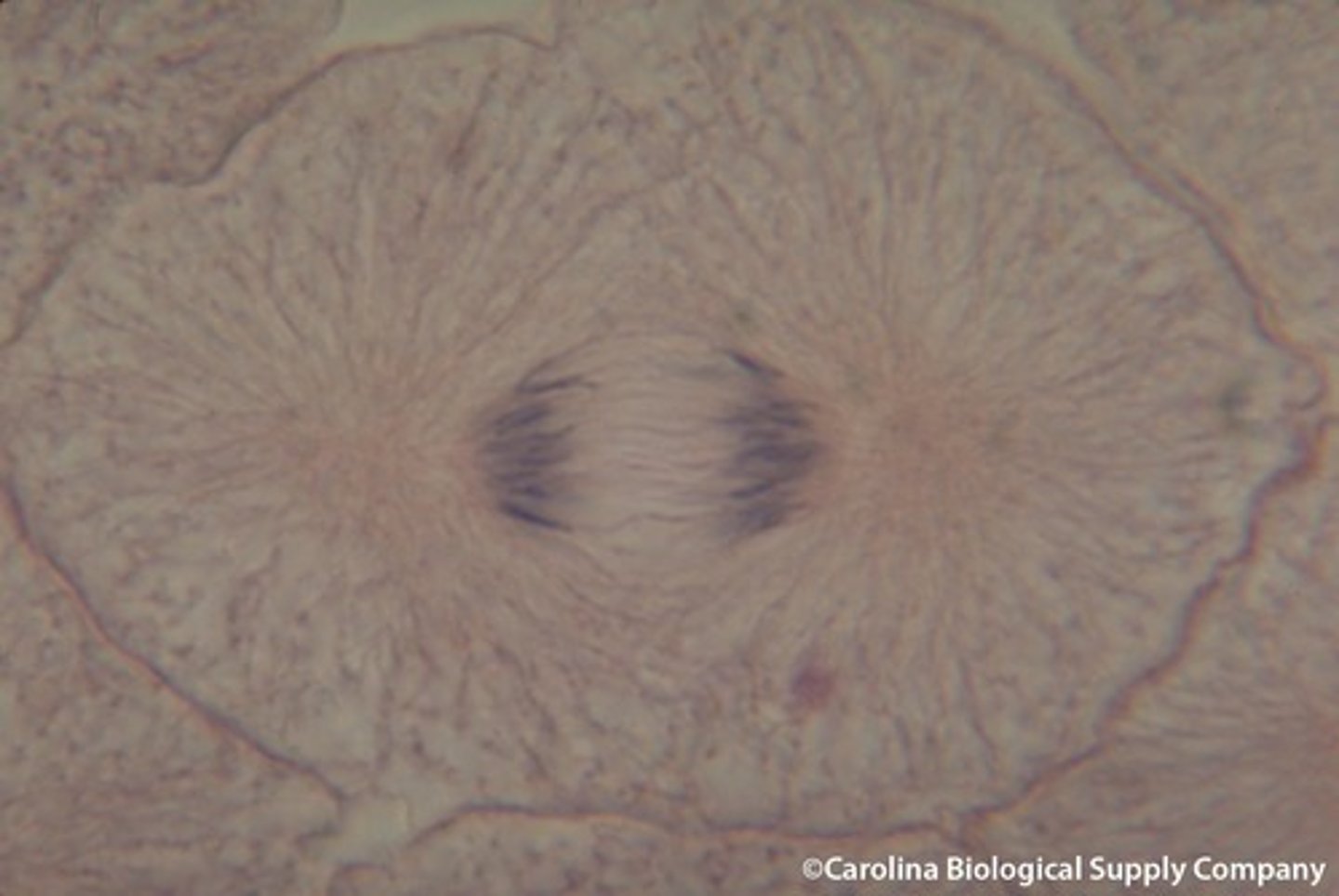
Telophase
-nuclear envelope reforms,
-mitotic spindle break down,
-chromosomes are at opposite ends and are decondensing
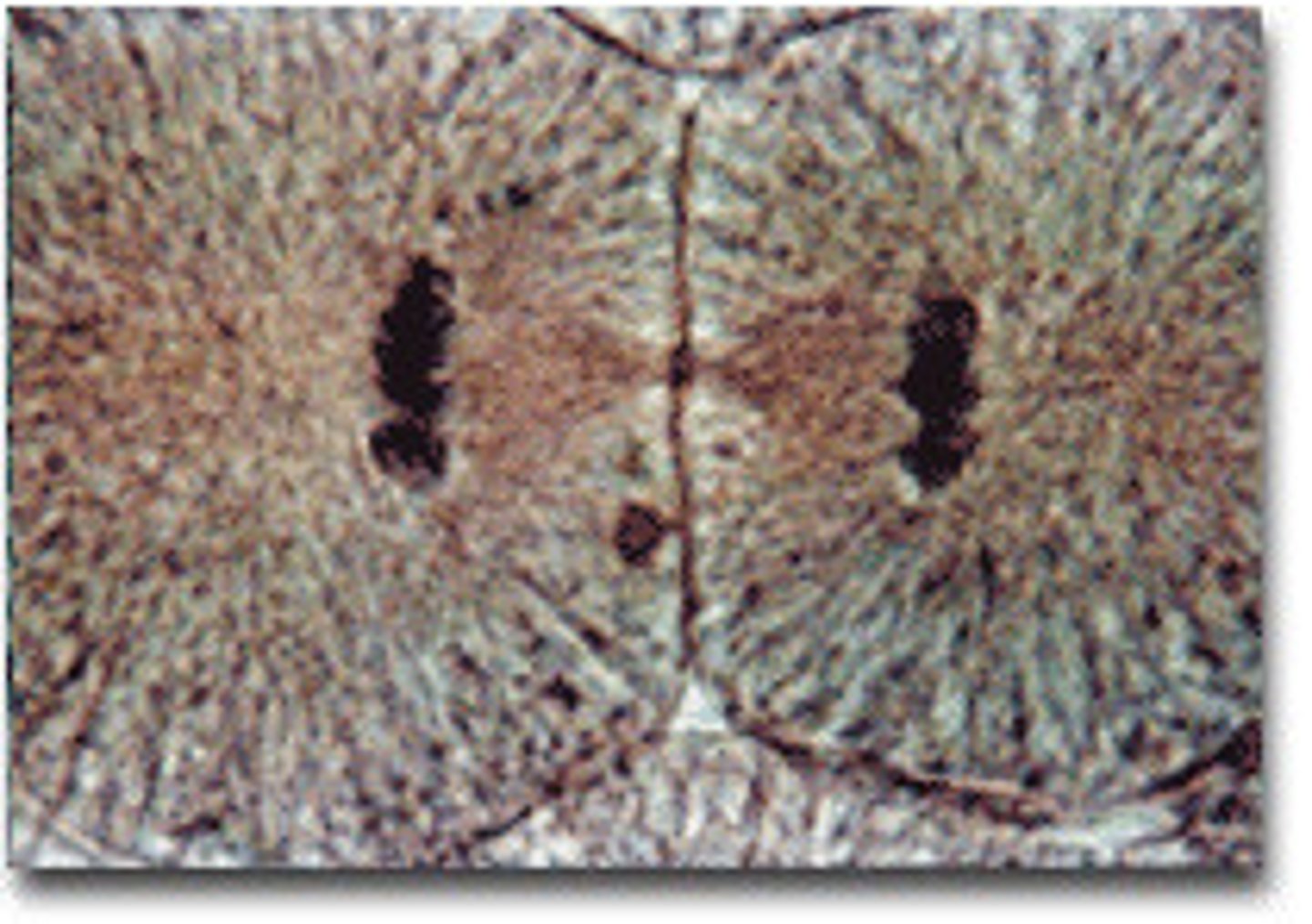
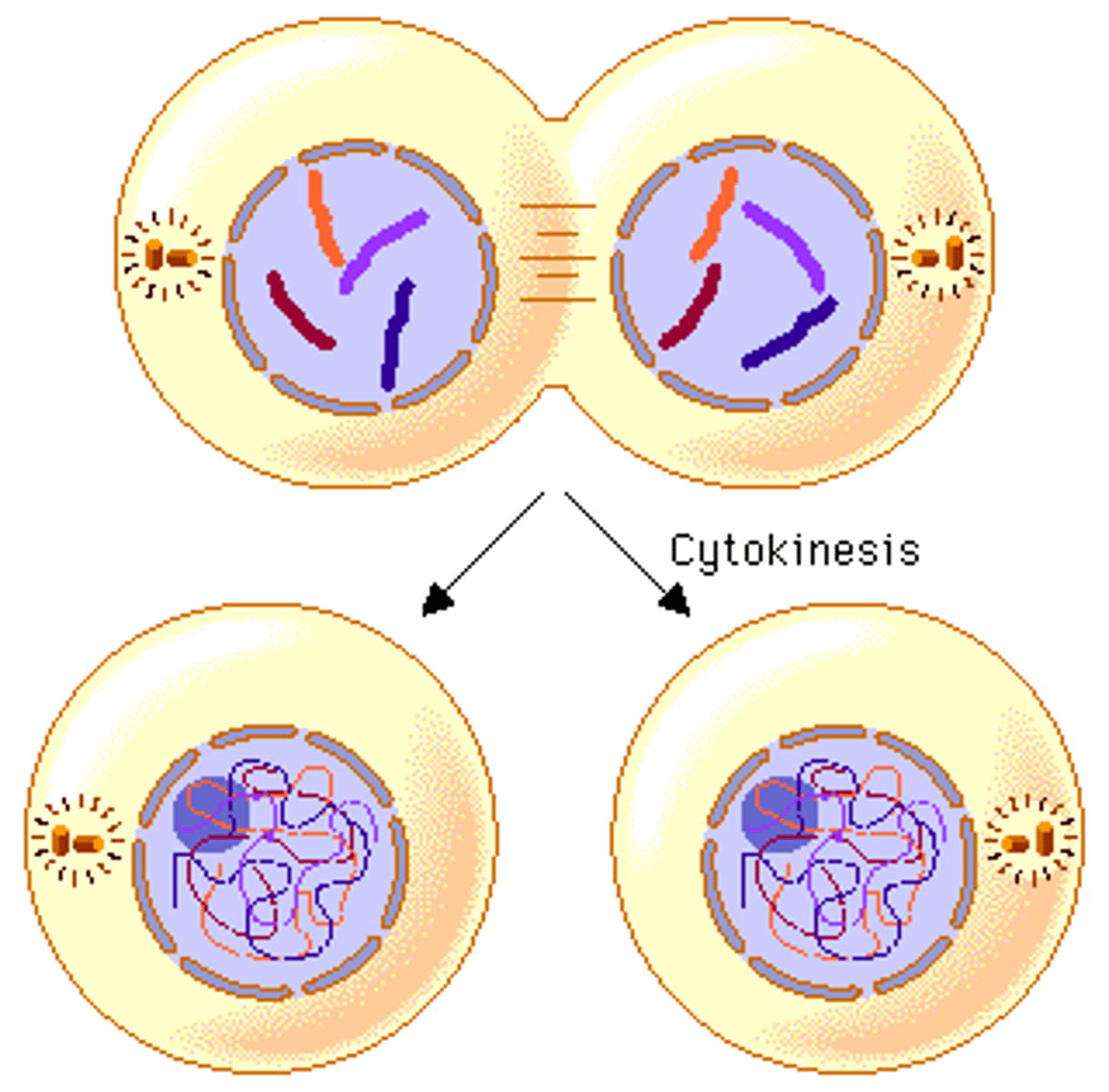
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm, forming two new cells
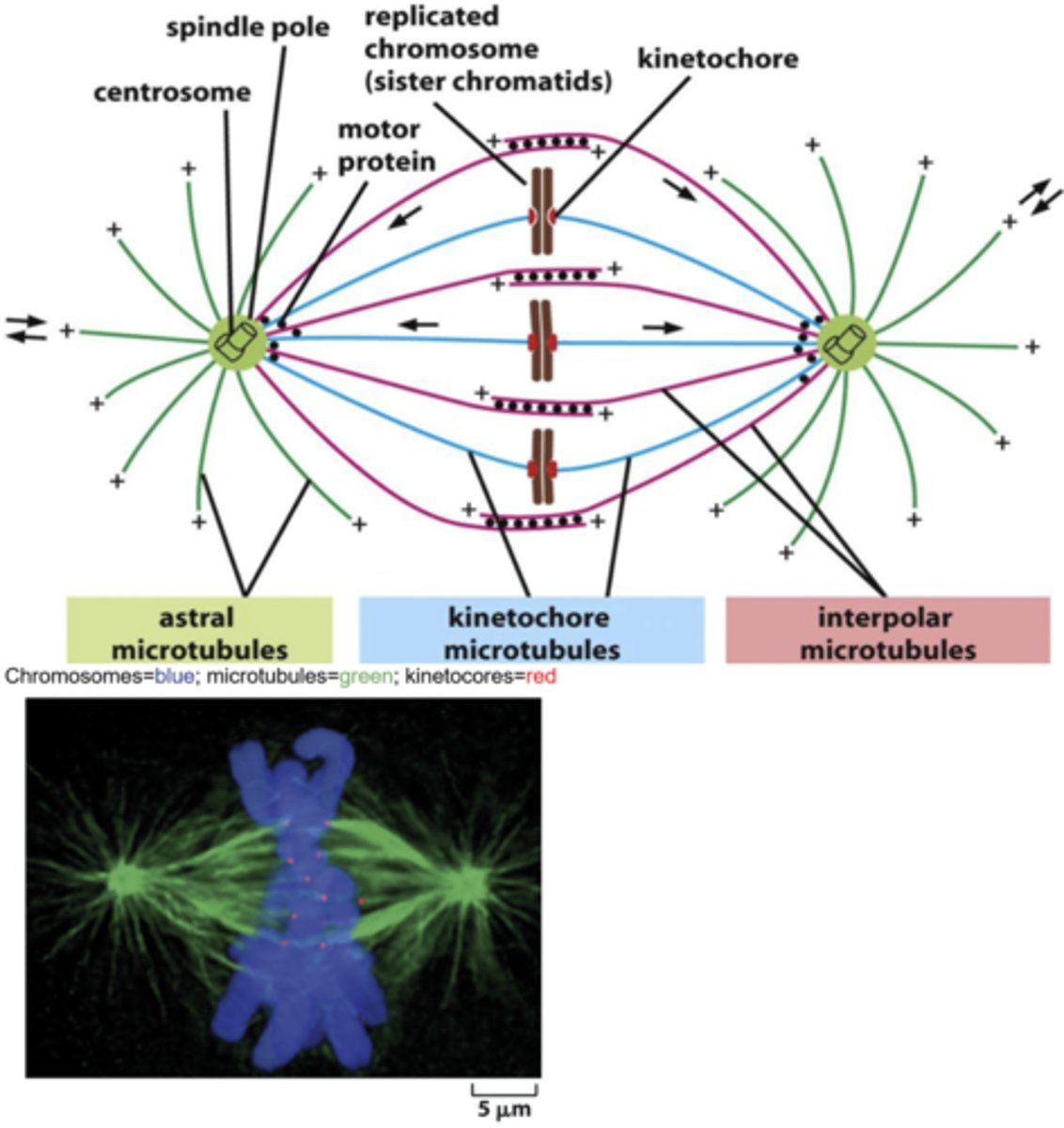
kinetochore
A structure of proteins attached to the centromere that links each sister chromatid to the mitotic spindle.
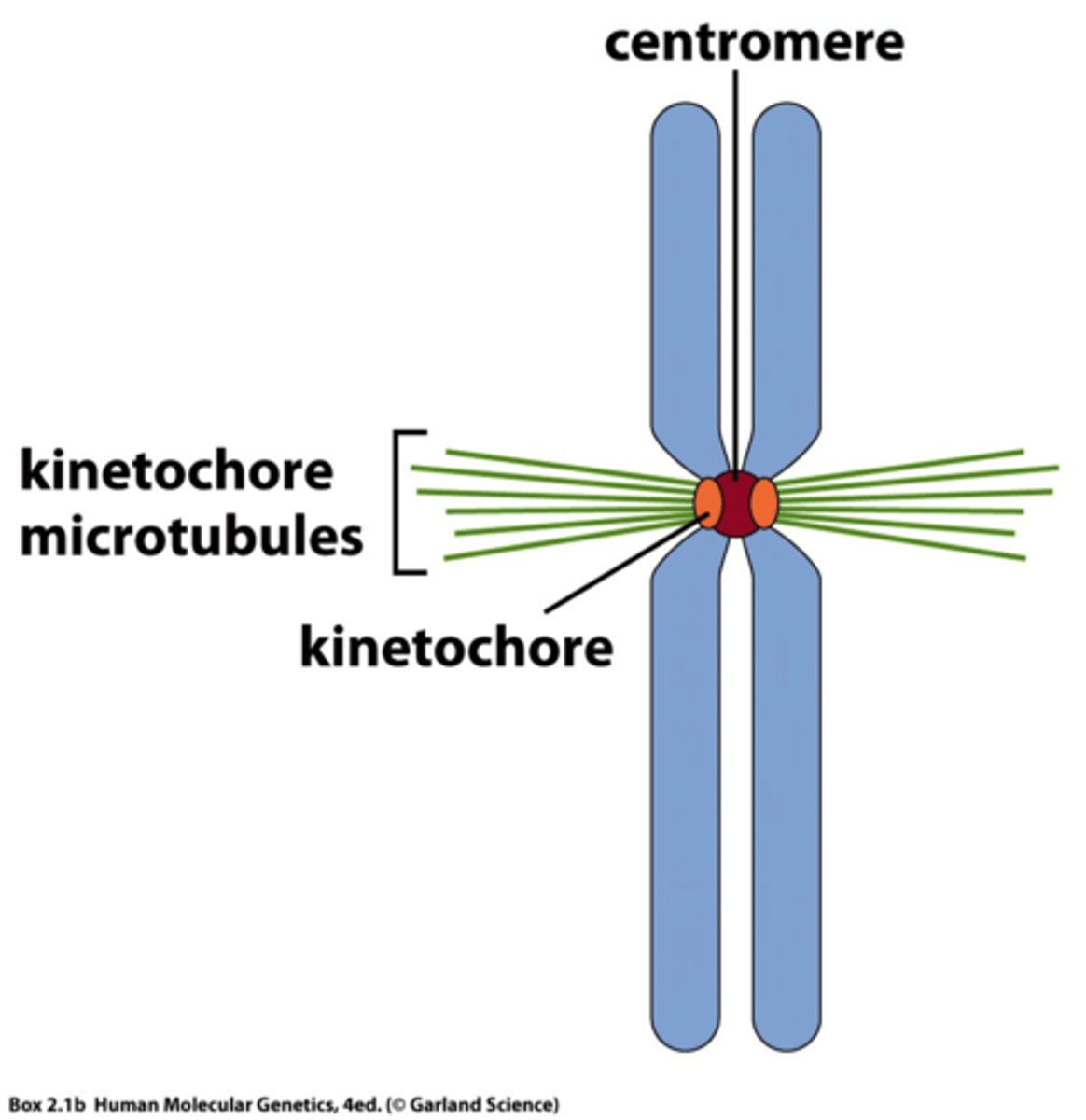
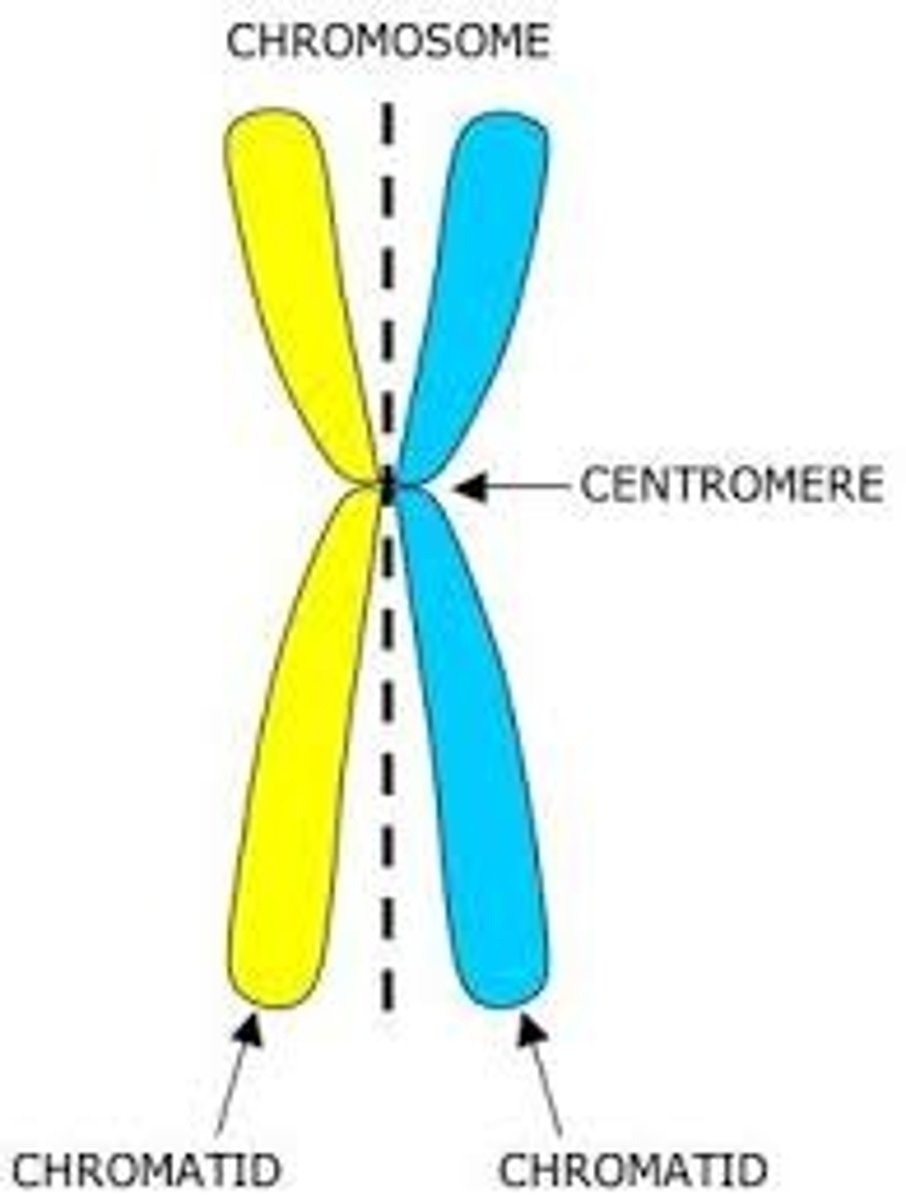
Centromere
the region of the chromosome that holds the two sister chromatids together during mitosis
Centrosomes in Mitosis
organize microtubules of the mitiotic spindle
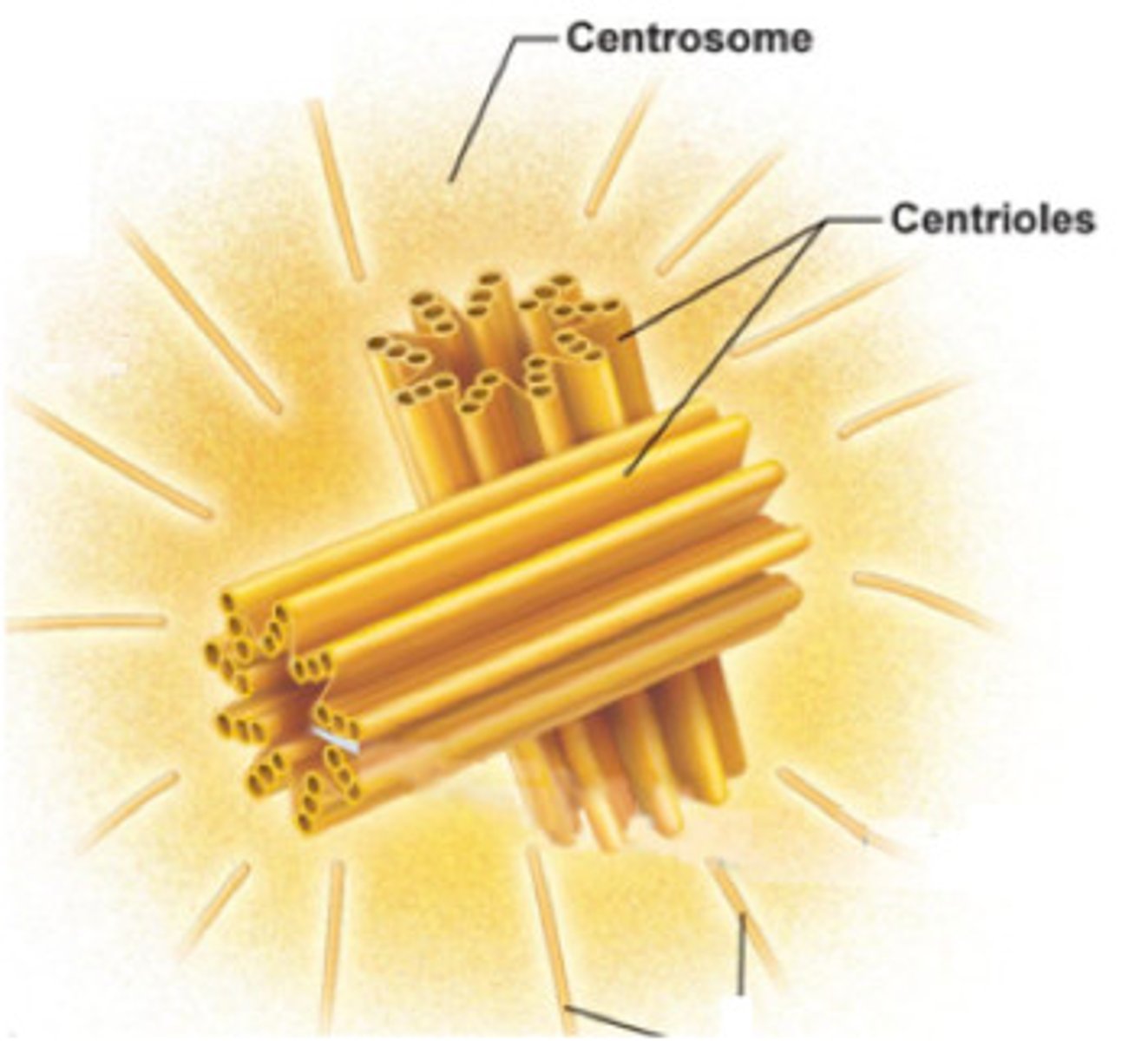
centrioles in mitosis
barrel shape organnelle that lives within the centrosome
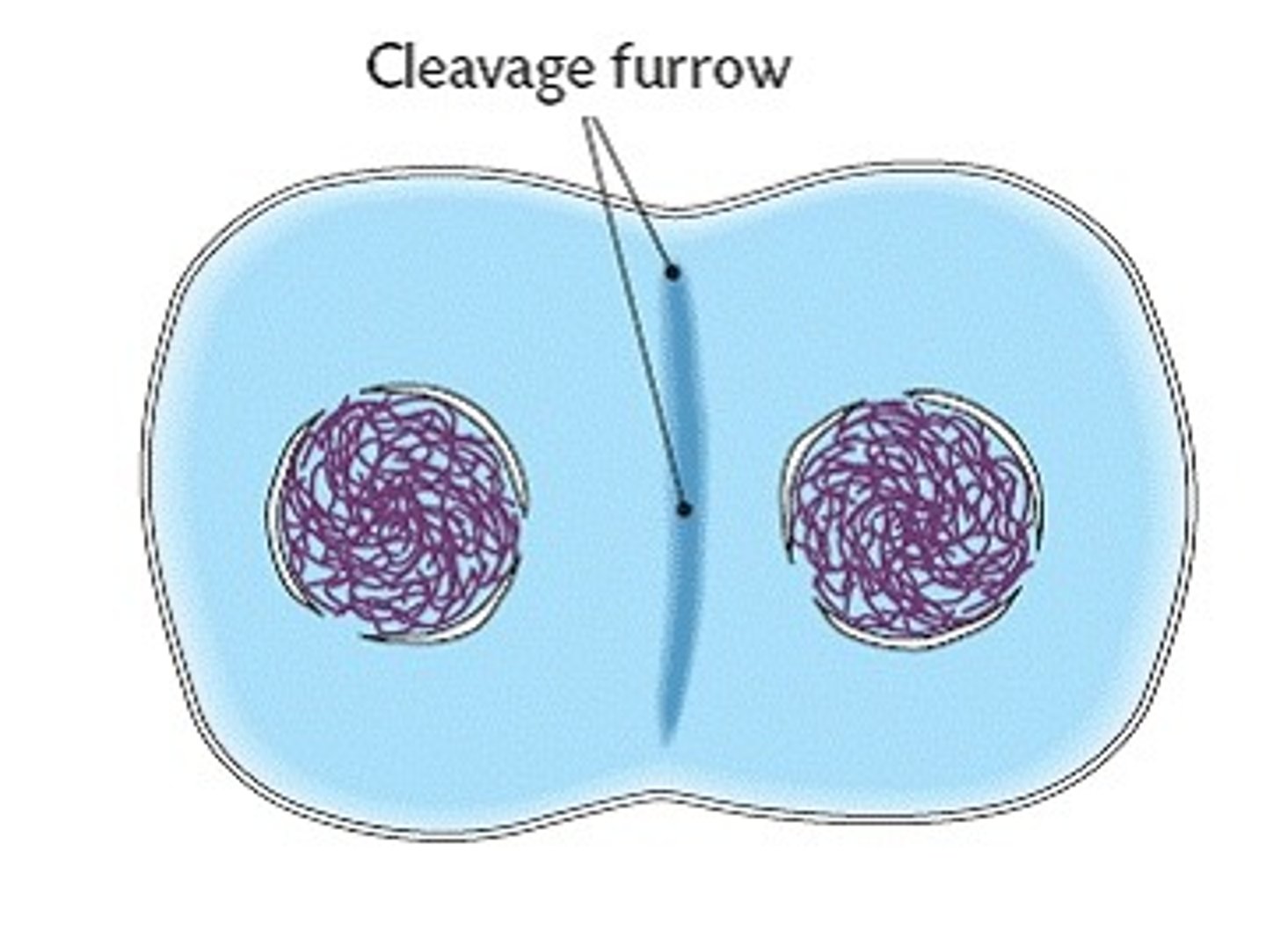
clevage furrow
-formation of contractile ring made up of actin fiilaments are going to squeeze middle part and pinch it in the center --> get two separate cells
* only works in animals and some protists because plants have cell walls so cant pinch it
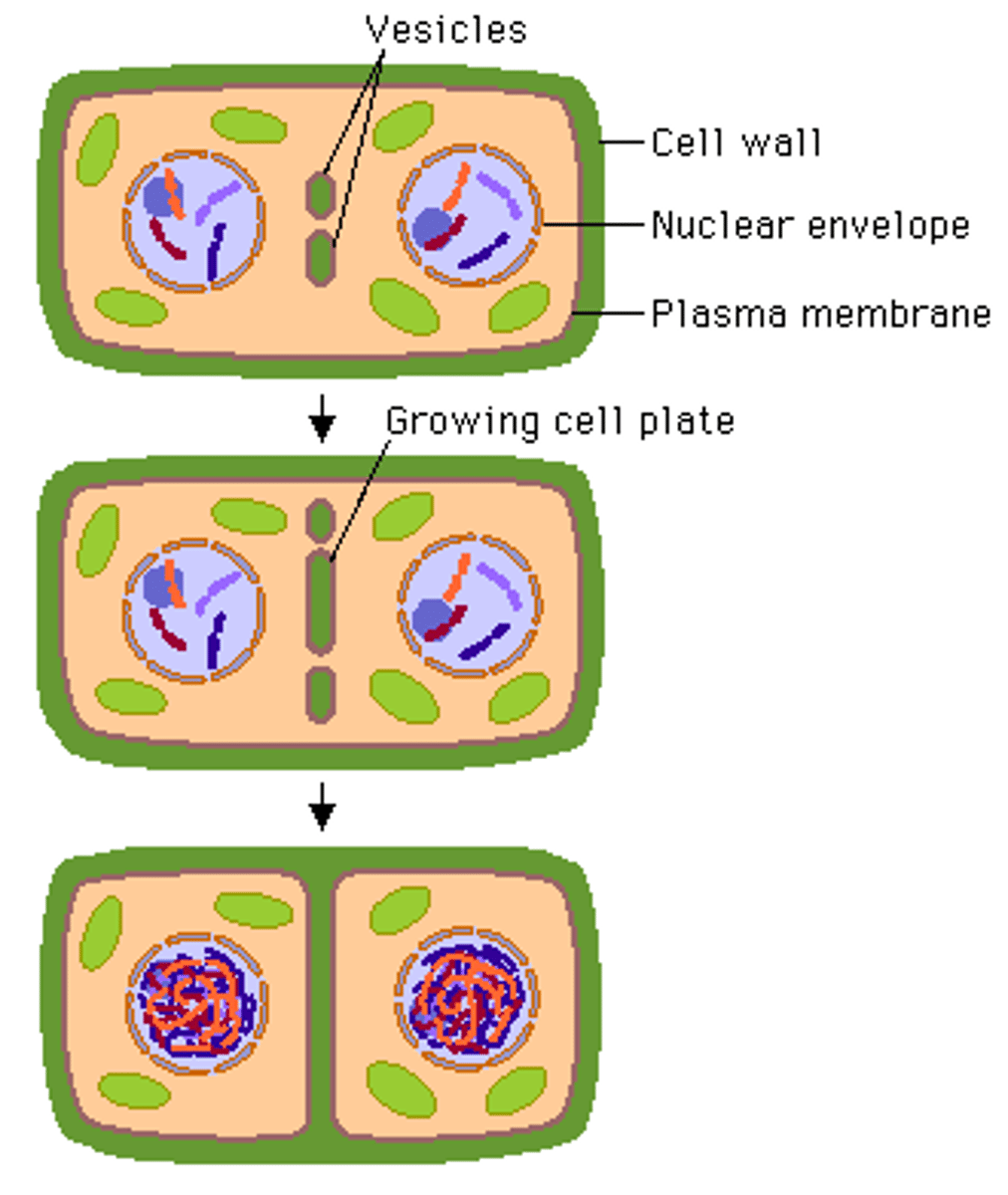
cell plate formation
Golgi vesicles align together and fuse to create the cell plate bringing in material from the cell wall and cell membrane. The membranes of these vesicles then form the new plasma membrane.
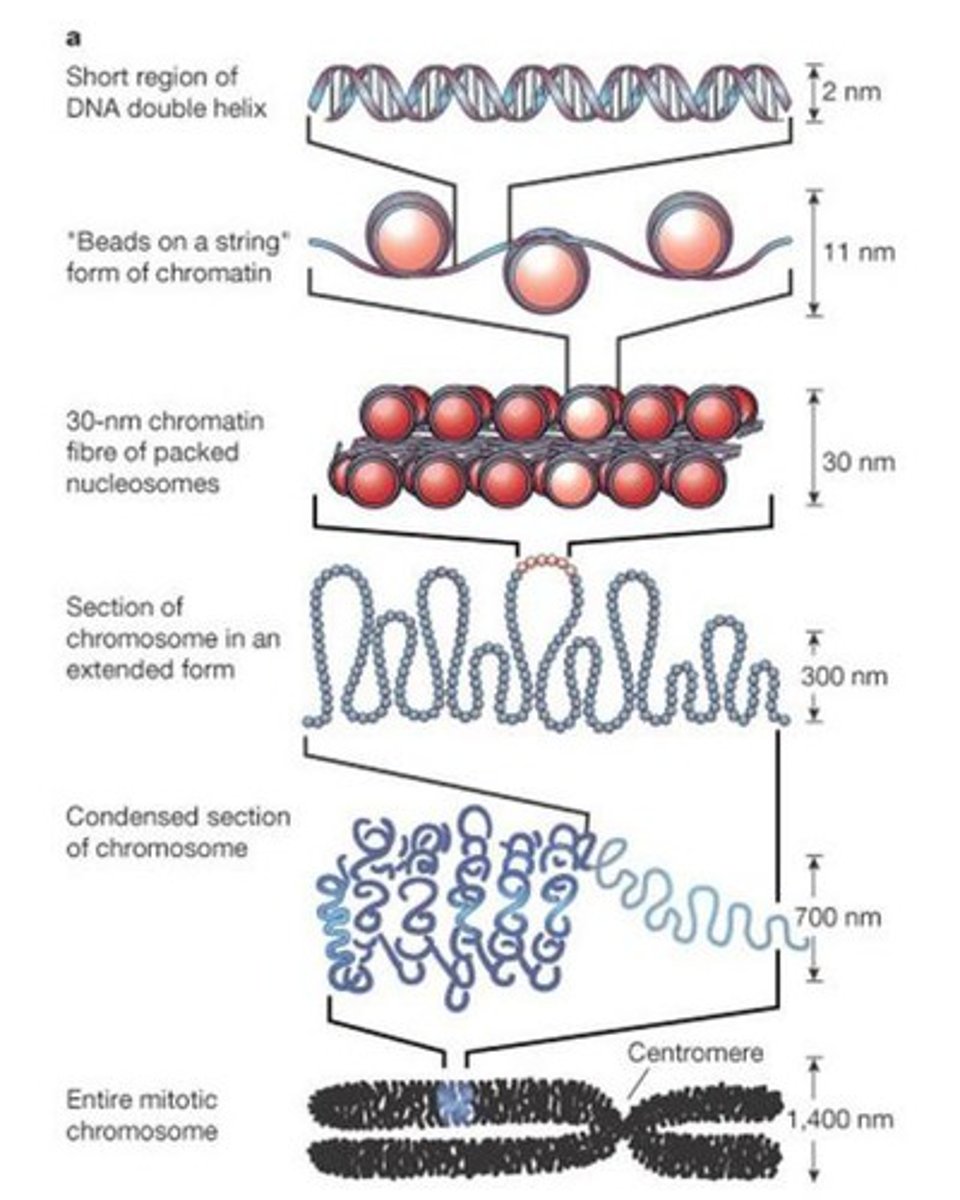
levels of packaging DNA in chromatin
-most DNA is at 30nm fiber stage
-at 300 nm: loop because scaffolding proteins that can hold loops together--> more condensed
-at 700nm they are fully condensed
- we condense because it makes it easier to move things around, need condesing of chromosome to replicate
-each region of nucleus has a specific chromosomes (they are not just tangled and floating)
functions of mitosis
growth and development of embryo and tissue renewal