AP EUROPEAN HISTORY UNIT 1 - RENAISSANCE & EXPLORATION ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLES
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Illustrative examples to help with Unit 1 DBQs, SAQs, & LEQs
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Printing Press
Invented by Johannes Gutenberg. The Invention of the Printing Press led to the spread of Renaissance ideas and eventually the spread of Protestant Reformation ideas
Francesco Petrarch
Petrarch (1304-1374) was known as the father of humanism. He emphasized the importance of studying and learning classical texts and the language of latin.
The Courtier
Written by Baldassare Castiglione in 1528 about an ideal “renaissance man”. The Courtier was someone who knew several languages, was familiar with classical literature, and was also skilled in the arts
Filippo Brunelleschi
Created the most noteworthy architectural achievement of the Early Renaissance period, which was the building of a dome over the Cathedral of Florence
Chiaroscuro
An art technique used during the Renaissance which included the use of contrasts between light and dark

Mannerism / Late Renaissance
An art style that showed distorted figures and confusing themes and may have reflected the growing sense of crisis in the Italian world due to both religious and political problems. ( The one shown here is Parmigianio’s Madonna with the Long Neck, 1534–1540)
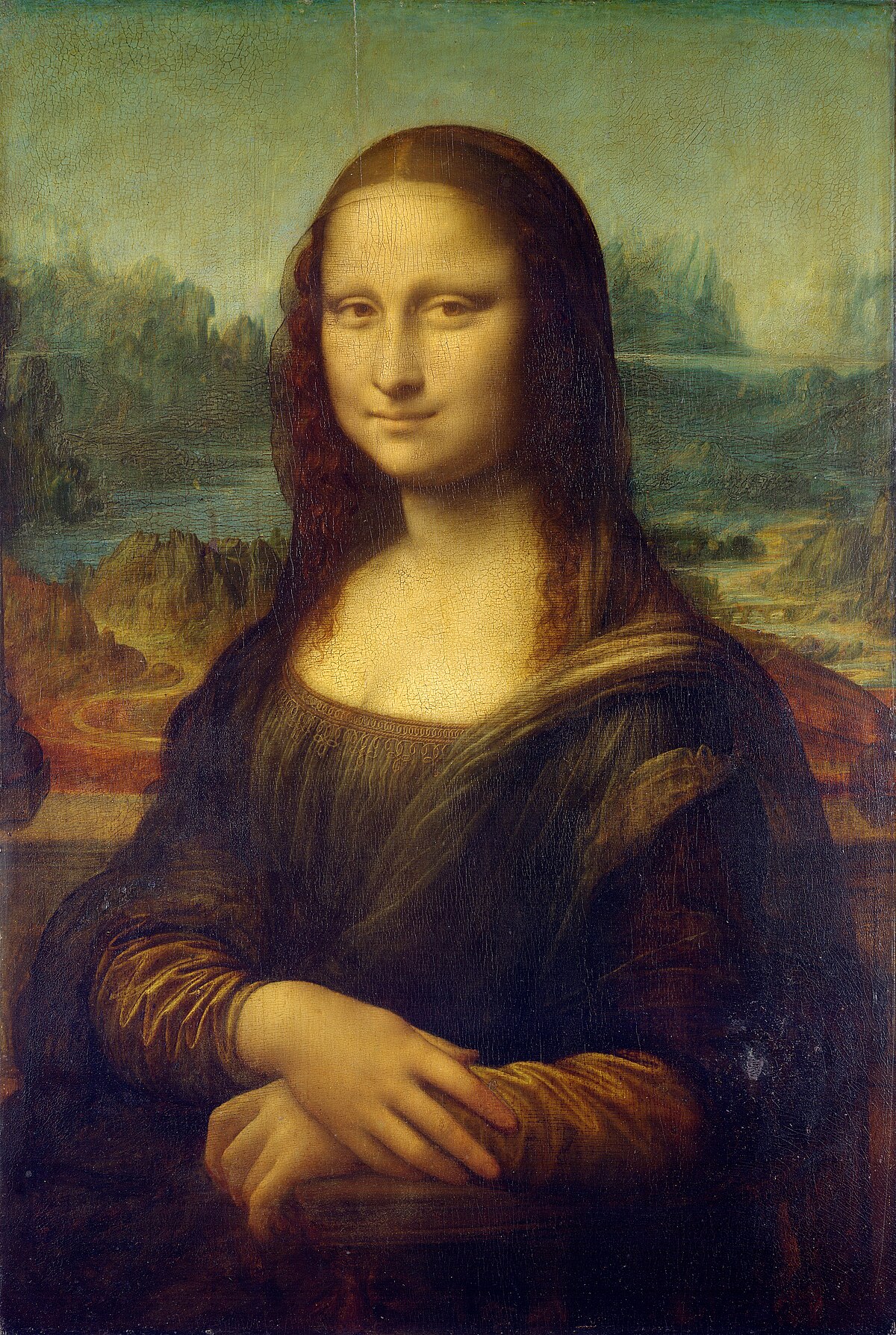

Leonardo da Vinci
The ideal Renaissance man (1452-1519). Da Vinci was a military engineer, an architect, a sculptor, a scientist, and an inventor. He created the Mona Lisa.
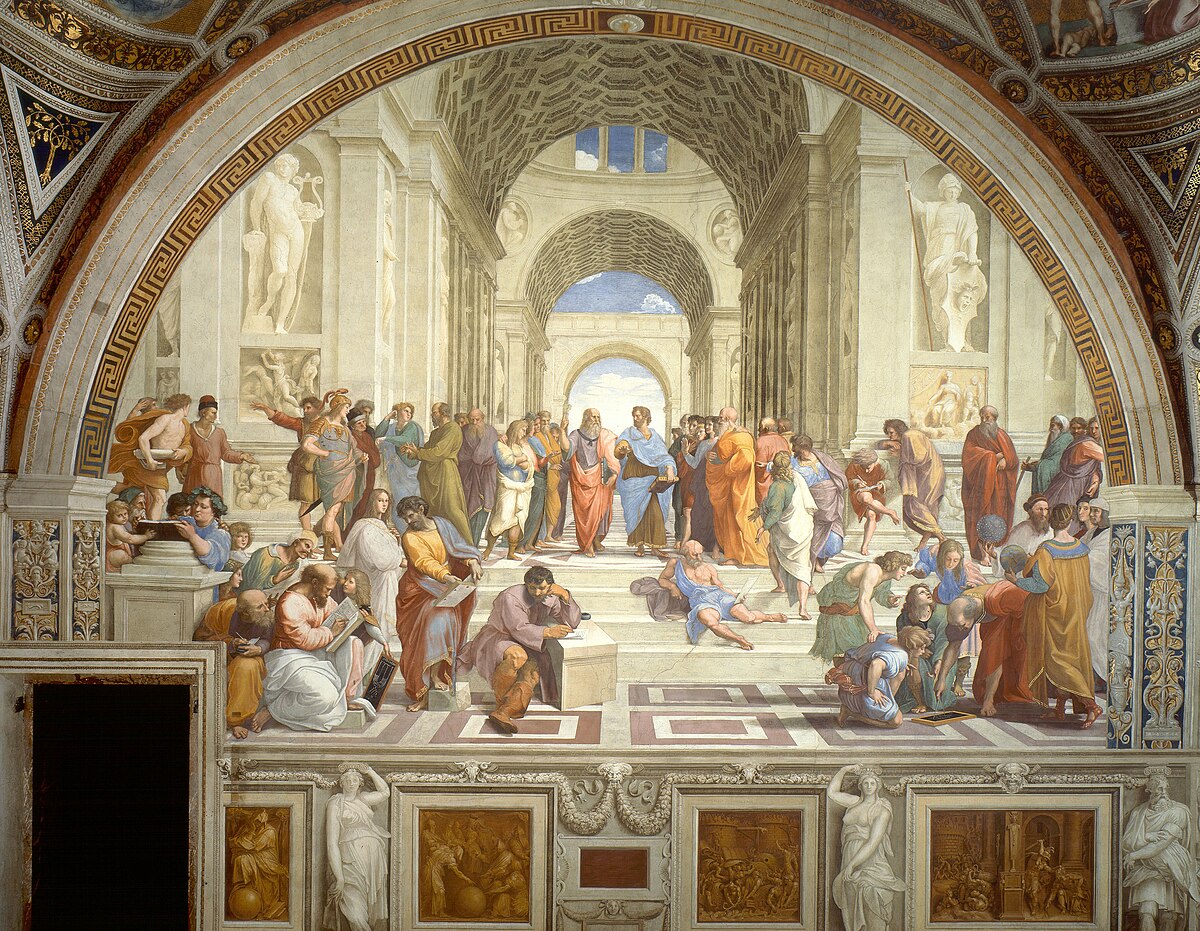

Raphael
(1483-1520) Created the School of Athens, which shows Plato and Aristotle standing together in a fanciful classical structure and uses the deep, single-point perspective characteristic of High Renaissance Style.
Michelangelo
Artist known for painting the Sistine Chapel ceiling and sculpting the David statue. Associated with the High Renaissance in Italy. (1475 - 1564)
Desiderius Erasmus
Desiderius Erasmus was a Dutch Renaissance humanist, theologian, and scholar known for his critical editions of classical texts and his satire "In Praise of Folly." (1466-1536)
Sir Thomas More
Sir Thomas More was an English lawyer, philosopher, and statesman who served as Lord Chancellor of England. He is best known for his book "Utopia" and his opposition to the Protestant Reformation (1478-1535).
Christopher Columbus
Italian explorer who completed four voyages across the Atlantic Ocean, opening the Americas to European exploration. His expeditions led to the widespread knowledge of the New World.
Ferdinand Magellan
Explorer who led the first expedition to circumnavigate the globe. Sailed from Spain in 1519, but was killed in the Philippines.
Hernán Cortés
Spanish conquistador who led the expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire in Mexico during the early 16th century.
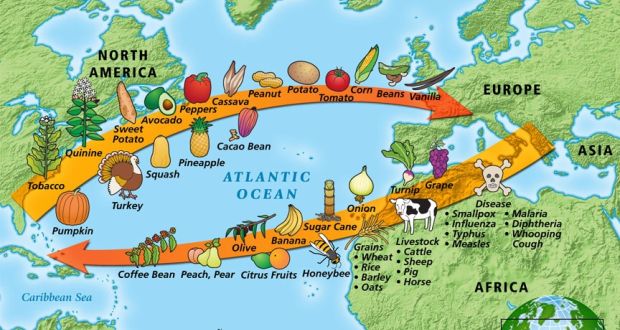
The Columbian Exchange
The widespread transfer of plants, animals, culture, human populations, technology, and ideas between the Americas and the Old World in the 15th and 16th centuries.
Niccolò Machiavelli
Italian Renaissance political philosopher known for his book "The Prince," which discusses the use of power, manipulation, and being cunning in politics. The Prince was written in the context of the collapse of the the Italian Independence (1513)