Chapter 6: Acellular Pathogens
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Characteristics of Viruses
Infectious, acellular pathogens
Obligate intracellular parasites with host and cell-type specificity
DNA or RNA genome (never both)
Genome is surrounded by a protein capsid and, in some cases, a phospholipid membrane studded with viral glycoproteins.
Lack genes for many products needed for successful reproduction, requiring exploitation of host-cell genomes to reproduce.
Viruses infect all types of organisms, including microorganisms.
Parvoviruses
All DNA viruses are ds except for
Reoviruses
All RNA viruses are single-stranded except for dsRNA
Viral Structure
Virus Particle
Covering
Capsid
Envelope (not found in all viruses)
Central Core
Nucleic Acid Molecule(s) (DNA or RNA)
Matrix proteins enzymes (not found in all viruses)
Naked Nucleocapsid Virus
virus composed of a nucleic acid core, either DNA or RNA, surrounded by a capsid.
More resistant than enveloped virus.
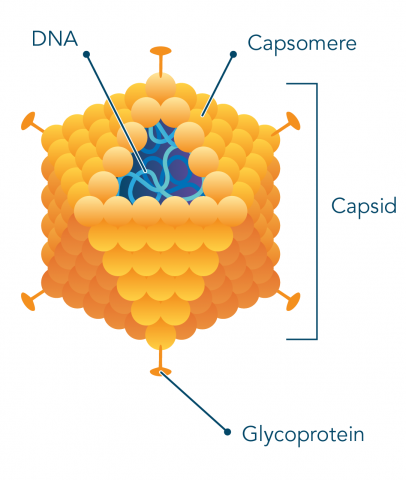
Capsids
(Protein Coat)
Nucleocapsid
Capsid + Nucleic Acid
Capsomers/Capsomeres
Protein Subunits of the Capsid
Enveloped Virus
Nonenveloped virus/Naked virus
Spikes; protein extensions.
Helical
cylindrical or rod shaped
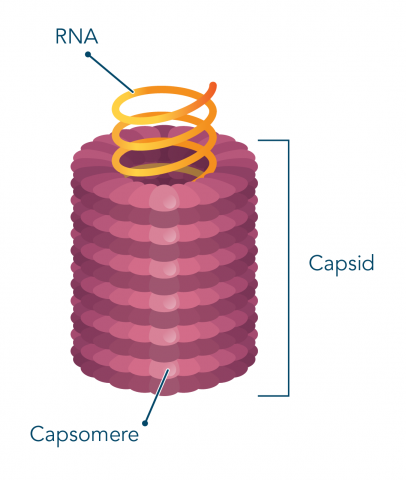
Icosahedral/Polyhedral
three-dimensional, 20-sided structure with 12 vertices
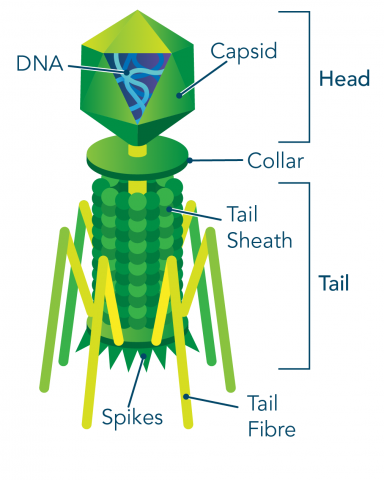
Complex Virus
virus shape that often includes intricate characteristics not seen in the other categories of capsid.
Atypical viruses
Poxviruses
Bacteriophages
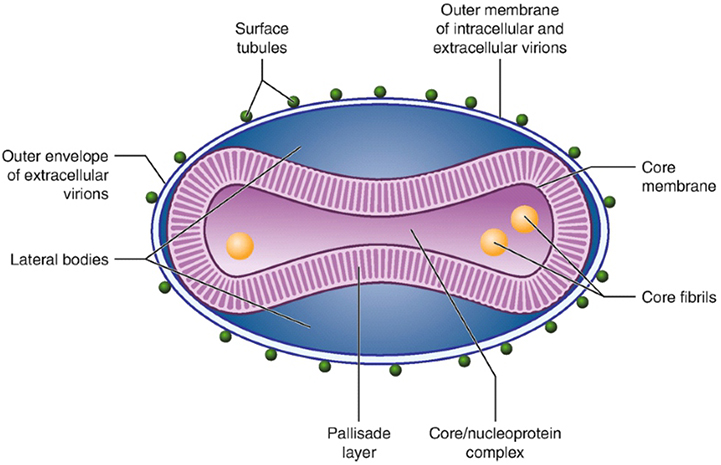
Poxvirus
Lack a typical capsid and are covered by a dense layer of lipoproteins.
Viral Envelope
Mostly animal viruses
Acquired when the virus leaves the host cell
Exposed proteins on the outside of the envelope; spikes.
Sensitive to extreme pH, heat, dryness, and simple disinfectant.
Viral Genome
Either DNA or RNA (never both)
DNA Viruses
usually double stranded (ds)
Circular or linear
Eg. Herpes, smallpox
RNA viruses
Usually single stranded (ss)
Eg. Influenza, HIV
Virus Classified
Morphology
Size of virion
Genome composition
ssDNA, dsDNA, ssRNA, or dsRNA
Type of host
Virion
inert particle that is the reproductive form of a virus
Complete infective form of a virus outside a host cell.
Bacteriophages Infection
Attach with tail fibers attach to cell wall proteins
Viral DNA injected into host cell
Uncoating is not required
Biosynthesis in cytoplasm
Lysogeny during release
Host cell becomes lysed.
Animal Viruses
Attachment sites are plasma membrane proteins
Capsid enters by endocytosis or fusion
Uncoating occurs during enzymatic removal of capsid proteins
Biosynthesis occurs in the nucleus (DNA viruses) or cytoplasm (RNA viruses)
Lysogeny: Latency; slow viral infection; cancer
Enveloped viruses bud out; nonenveloped viruses rupture plasma membrane.
Attachment
Many viruses are host specific: attach specifically to receptor sites on the host cell membrane.
Host Range
Spectrum of cells a virus can infect
Hepatitis B
Poliovirus
Rabies
Tissue Tropism
Specific to certain tissues
Eg. Flu → Respiratory tract only
DNA Virus
Replicate in the Nucleus
RNA Virus
Replicate in the cytoplasm
Genome
The nature of the ____ determines how the ___ is replicated and expressed as viral proteins
dsDNA
Normal flow of genetic information
DNA → RNA → Protein
ssDNA
Produce dsDNA using host enzymes to process
dsRNA
Translated into protein
+ssRNA
Can be translated directly to make viral proteins
-ssRNA
Must be converted into +ssRNA to proceed
Budding
unequal reproductive division in which a smaller cell detaches from the parent cell
exocytosis
Lysis
Nonenveloped and complex viruses release when cell dies and ruptures
Persistent infections
Virus present continuously at usually low level over an extended period after the acute infection and disease have ended.
Latent Infections
Maintain viral genome in the host cell without replicating (Latency)
Herpes simple virus
Herpes zoster virus
Epstein-Barr virus
Chronic Infections
Shed the virus continuously for a long period of time.
Hepatitis C Virus
HIV → Interfere with immune function
In vitro
Outside living organism in a test tube or artificial environment.
In vivo
In living organism
Cytopathic Effects
Distinct observable cell abnormalities due to viral infection.
Changes in size and shape
Cytoplasmic inclusion bodies
Cells fuse to form multinucleated cells
Cell lysis
Alter DNA
Transform cells into cancerous cells
Transformation Cells
Animal viruses enter the host cell and permanently alter its genetic material resulting in cancer - _______ of the cell
______ ____ have an increased rate of growth, alterations in chromosomes, and the capacity to divide for indefinite time periods resulting in tumors.
Oncovirus
Papillomavirus (HPV)
Epstein-Barr Virus
Oncovirus
Mammalian viruses capable of initiating tumors
Importance of Viruses
Cause many diseases in animals, plants, and humans to balance nature.
Used a a vector in biotechnology (to transfer genes)
Development of vaccines, phage therapy, etc.
Major participants in earth’s ecosystem.
Viroid’s, Virusoids, and Prions
Nonliving disease agents quite different from viruses.
Particles consisting of only RNA or only Protein.
Viroid
An infectious RNA particle, smaller than a virus, lacking a capsid that causes various plant diseases.
Virusoid
(Satellite nucleic acids/viruses)
Same as viroid; small ssRNA molecule lacking a capsid
Lacks genes required for the replication; therefore it requires a helper (satellite) virus to replicate
Causes various plant diseases.
Prions
Misfolded proteins; no nucleic acid
Extremely resistant to usual sterilization techniques
Cause transmissible spongiform encephalopathies
Fatal neurodegenerative diseases
Prions Disease
Scrapie
Sheep and goats
Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathies (BSE)
Mad Cow Disease
Wasting Disease
Elk, Moose, Deer
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Syndrome (CJS) & Kuru
Munching on humans