Pathology of the Kidneys and Upper Urinary Tract
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Hydronephrosis
Blockage of urine flow down the ureter.
Causes of hydronephrosis
Internal: calculi (kidney stones), scarring in the ureter, tumours blocking the vesicoureteric junction (VUJ)
External: mass effect compressing ureter
Vesicoureteric reflux: failure of bladder to empty properly

Hydronephrosis Clinical Presentation
Flank pain, haematuria, fever, Leukocytosis
Vesicoureteric reflux
Failure of the bladder to empty properly, common in babies and young children, leading to urine reflux from the bladder back into the kidney.
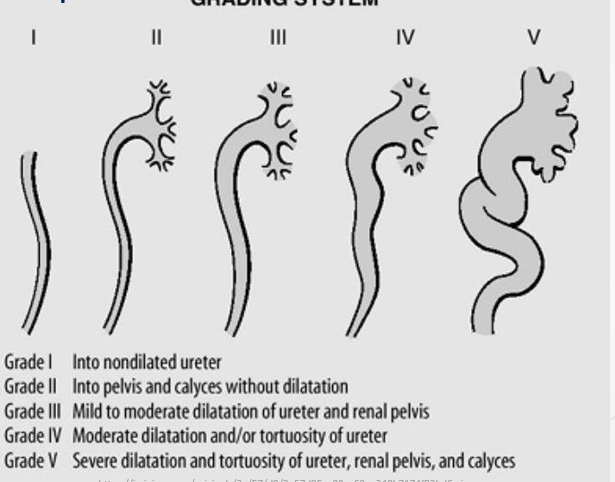
Hydronephrosis Grading System
Grade I: Into nondilated ureter.
Grade II: Into pelvis and calyces without dilatation.
Grade III: Mild to moderate dilatation of ureter and renal pelvis.
Grade IV: Moderate dilatation or tortuosity of ureter.
Grade V: Severe dilatation and tortuosity of ureter, renal pelvis, and calyces.
Pyelonephritis
Urinary tract infection that starts in the urethra or bladder and travels to the kidneys.
Main cause of pyelonephritis
Gram-negative bacteria (i.e., E. coli).
Pyelonephritis Clinical Presentation
Fever, nausea, frequent urination, and pain in the back, side, or groin.
Leukocytosis
Pyelonephritis US presentation
Can affect one or both kidneys.
Can be focal or diffuse.
Echogenic wedge defect in partial cases. - not the same as the congenital defect
Loss of blood flow seen on colour Doppler.
Renal Abscess
Complication of pyelonephritis
Can be a renal abscess or perirenal abscess
Renal abscess US presentation
Forms a distinct walled-off cavity
Perirenal abscess US presentation
Appears more diffuse between renal capsule and fascia
Renal abscess clinical presentation
Flank pain’
Fever
Leukocytosis
Pyonephrosis
Pus, debris, or haemorrhage seen within a dilated pelvicalyceal system.
Pyonephrosis US presentation
Echoes within pelvicalyceal system.
May appear solid.
Can sometimes get layering - like sludge in the GB
Put colour on to see if it moves
Glomerulonephritis
Inflammation of the glomeruli; acute or chronic
Usually affects both kidneys; early diagnosis and treatment are vital to prevent renal failure.

Causes of Glomerulonephritis
Staphylococcal infection (strep throat) and Immunologic illnesses.
Glomerulonephritis Clinical Presentation
Asymptomatic
Proteinuria
Oliguria
Hypertension
Haematuria
Fatigue
Oedema
Glomerulonephritis US presentation
Hyperechoic kidneys, collecting system not dilating
Renal Scarring
Usually due to recurrent UTIs, reflux, or pyelonephritis which causes permanent damage to renal parenchyma and reduces kidney function.
Renal Scarring US Presentation
Appears atop medullae, not between them; shows thinned parenchyma; fat fills the spot where the scarring occurs, which can lead to a characteristic echogenicity, indicating loss of normal renal architecture
Renal Atrophy
Kidneys are smaller than expected for a person's age and height
Can be congenital (renal hypoplasia) or acquired due to chronic infections or hydronephrosis.
Congenital cases typically do not require treatment unless parenchyma thickness is abnormally smaller
Acquired due to lower blood supply to the kidneys and or loss of nephrons
Renal Failure
Kidneys no longer adequately filter the blood of waste products or control fluid levels.
Renal Failure Clinical Presentation
GFR decreases significantly, with ESKD being defined as GFR <15 ml/min.
Chronic
Elevated BUN and creatinine
Proteinuria
Polyuria
Headaches
Fatigue
Weakness
Anaemia
US presentation of Renal Failure
Acute – may appear normal in size or be enlarged and hypoechoic with parenchymal disease;
Chronic – small, echogenic kidneys with loss of normal anatomy.
Duplex Kidney Pathology
Characterized by the presence of two collecting systems or ureters.
Ureters may join before the bladder or have separate openings.
Why are ectopic ureters more susceptible to reflux?
Due to abnormal placement, leading to hydronephrosis, particularly in the upper moiety.

What is the key to distinguish between pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis?
would be patient hx - urinary infection (pyelonephritis)