Space physics
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what are the 8 planets in the solar system in order from the sun
-Mercury
-Venus
-Earth
-Mars
-Jupiter
-Saturn
-Uranus
-Neptune
-(Pluto)
what is the smallest planet in our solar system
mercury
what is the largest planet in our solar system
jupiter
between which planets is the asteroid belt
Mars and Jupiter
between which planets is the kepler belt
Neptune and Pluto
how do you calculate the orbital speed of a planet
v=2𝜋r/t
what is a light year
the distance travelled by light in a year
what is the speed of light
300 000 000 m/s = 3×108
how far does light travel in a year
9.46 × 1015 m a year
how do you calculate how many seconds are in a year
365 × 24 × 60 × 60
what sized star is the sun
a medium sized dwarf star
what is the sun made of
Hydrogen and Helium
what kind of rays does the sun let off into the photoshere
-infrared (heat)
-short waves (colours)
-ultraviolet (sunburn)
what protects us from harmful UVs
the ozone layer
how is a star formed
-first, it is an interstellar cloud of dust and gas containing hydrogen
-next, it becomes a protostar when the interstellar cloud collapses and increases in temperature because of its internal gravitational attraction
-finally, it becomes a stable star when the inward force of gravitational attraction is balanced by an outward force due to high temperatures in the centre
what is an interstellar cloud
cloud of dust and gas containing hydrogen
what is a protostar
when the interstellar cloud collapses and increases in temperature because of its internal gravitational attraction
when does a star become a stable star
when the inward force of gravitational attraction is balanced by an outward force due to high temperatures in the centre
when do planets die out
when the star runs out of hydrogen as fuel for the nuclear reaction
what can nebulas from a supernova do
form an new star with orbiting planets
what happens when a small mass star runs out of hydrogen
it expands into a red giant then collapses into a white dwarf and a planetary nebula
what happens when a large mass star runs out of hydrogen
it expands into a red supergiant, then creates a supernova to then become a neutron star
what happens when a very large mass star runs out of hydrogen
it expands into a red supergiant, then creates a supernova to eventually become a black hole
how big is the milky way
100 000 light years in diameter
how many galaxies is the universe made of
billions
approximately, how old is the universe
13.8 billion years old
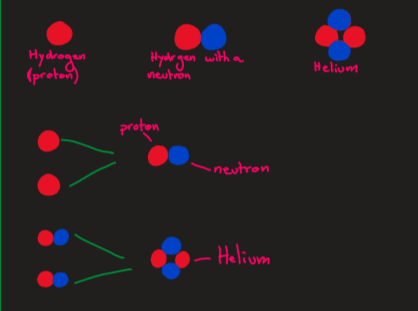
how does hydrogen create helium to power the star
how hot is the sun
15.5 million°C or 28 million°F

what is red shift
when the missing wavelengths from distant stars are shifted the red side of the colour spectrum because they are moving away from us
what is the biggest asteroid
Ceres (can be considered a dwarf planet)
what moons orbit saturn
-atlas
-laptus
-mimas
-hyperion
what moon orbits jupiter
callisto
how was the universe before
it was hot and contained gamma rays
why is the universe different now
because the universe is expanding from a single point of high density, it now contains microwave waves instead of gamma rays
how cold id the universe
-270°C