Chapter 14 - Market Failures and the Role of the Government
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
The marginal social cost of pollution
Is the additional cost imposed on society as a whole by an additional unit of pollution.
The marginal social benefit of pollution
The additional gain to society as a whole from an additional unit of pollution.
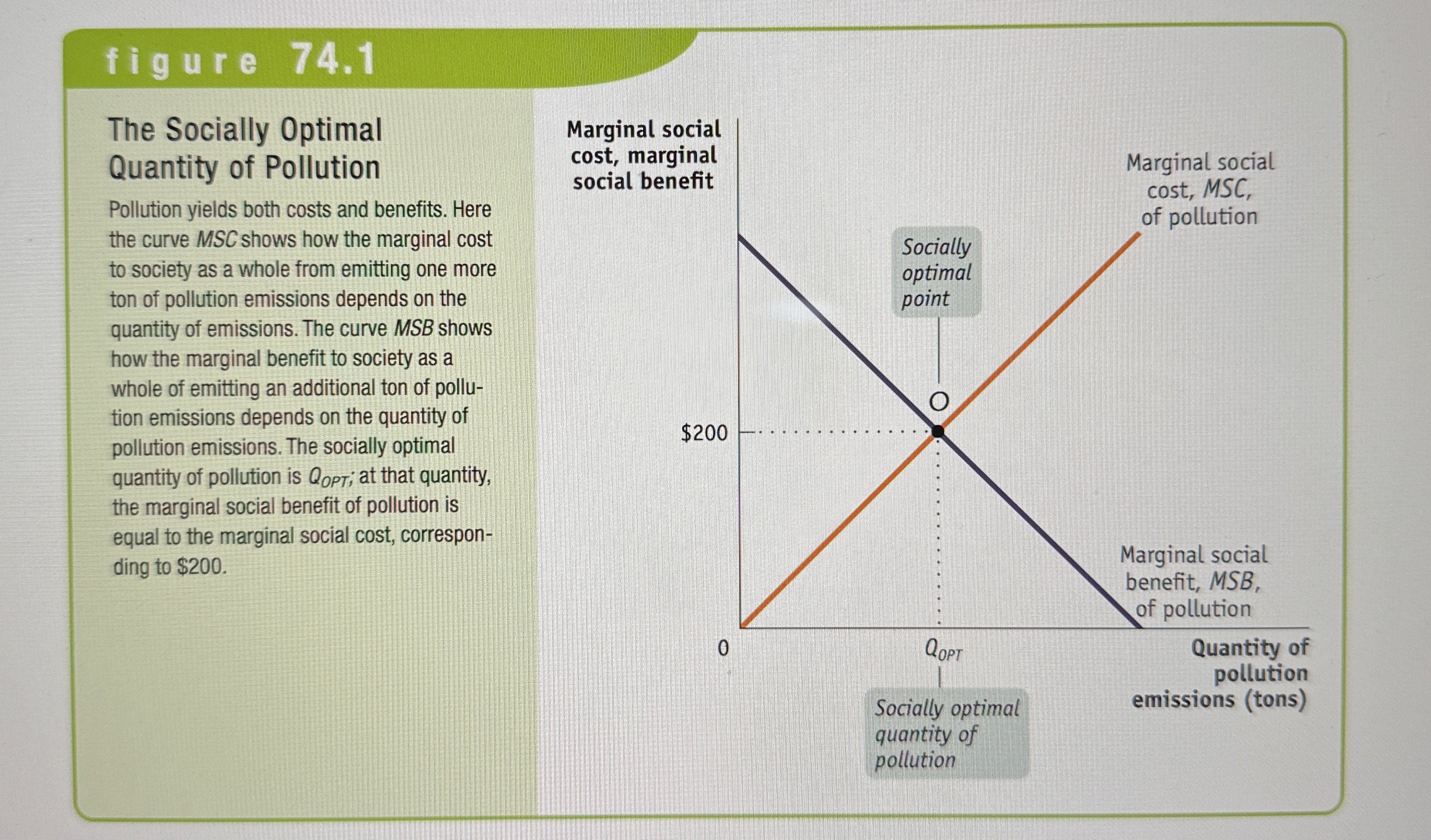
The socially optimal quantity of pollution
The quantity of pollution that society would choose if all the costs and benefits of pollution were fully accounted for.
External cost
An uncompensated cost that an individual or firm imposes on others.
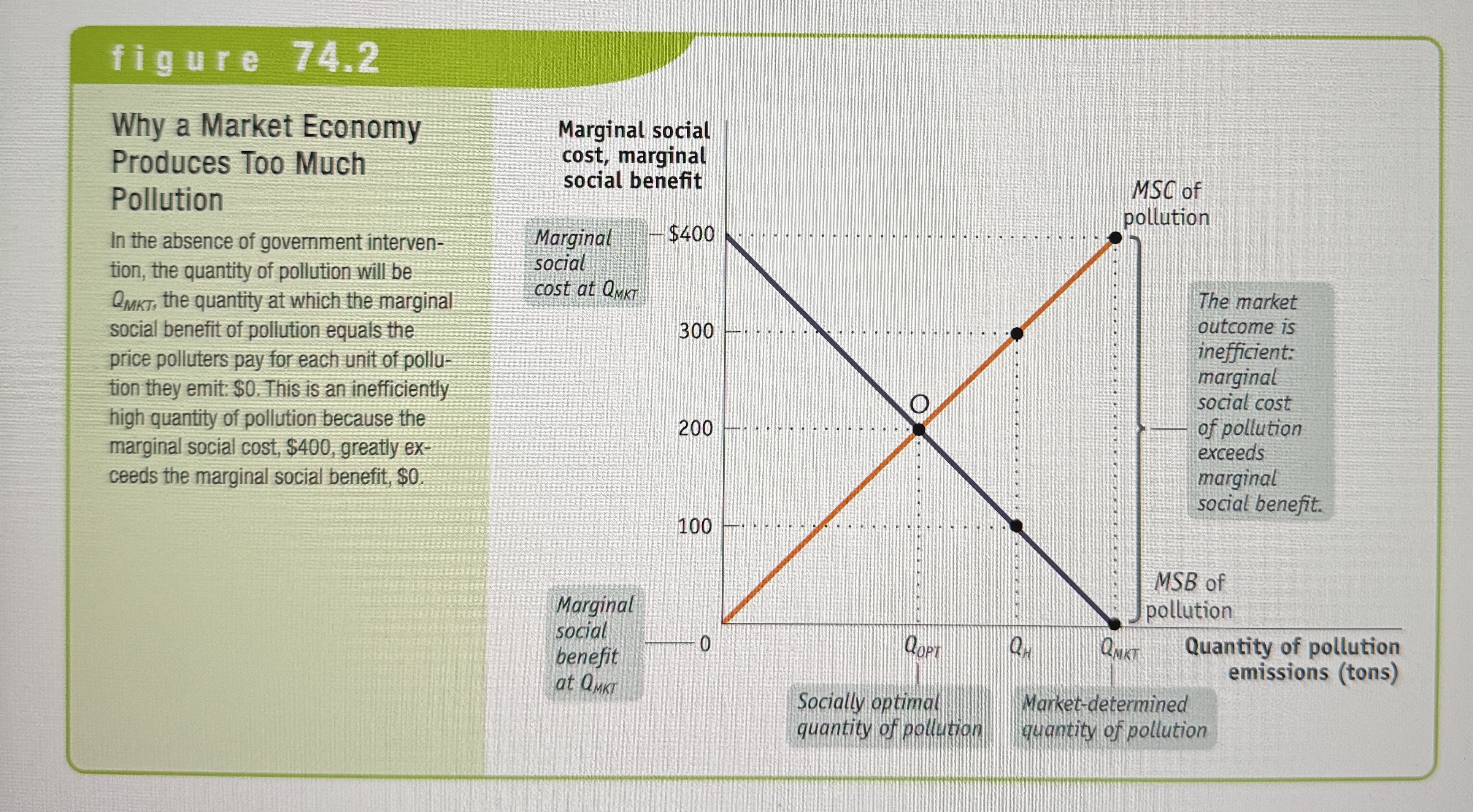
Why a Market Economy Produces Too Much Pollution
Ex.
External benefit
A benefit that an individual or firm confers on others without receiving compensation
Externalities
External costs and benefits
Negative and Positive Externalities
External Costs are Negative, External Benefits are positive.
Coase Theorem
According to the Coase theorem, even in the presence of externalities, an economy can always reach an efficient solution as long as transaction costs - the costs to individuals of making a deal - are sufficiently low. When individuals take external costs or benefits into account, they internalize the externalities.
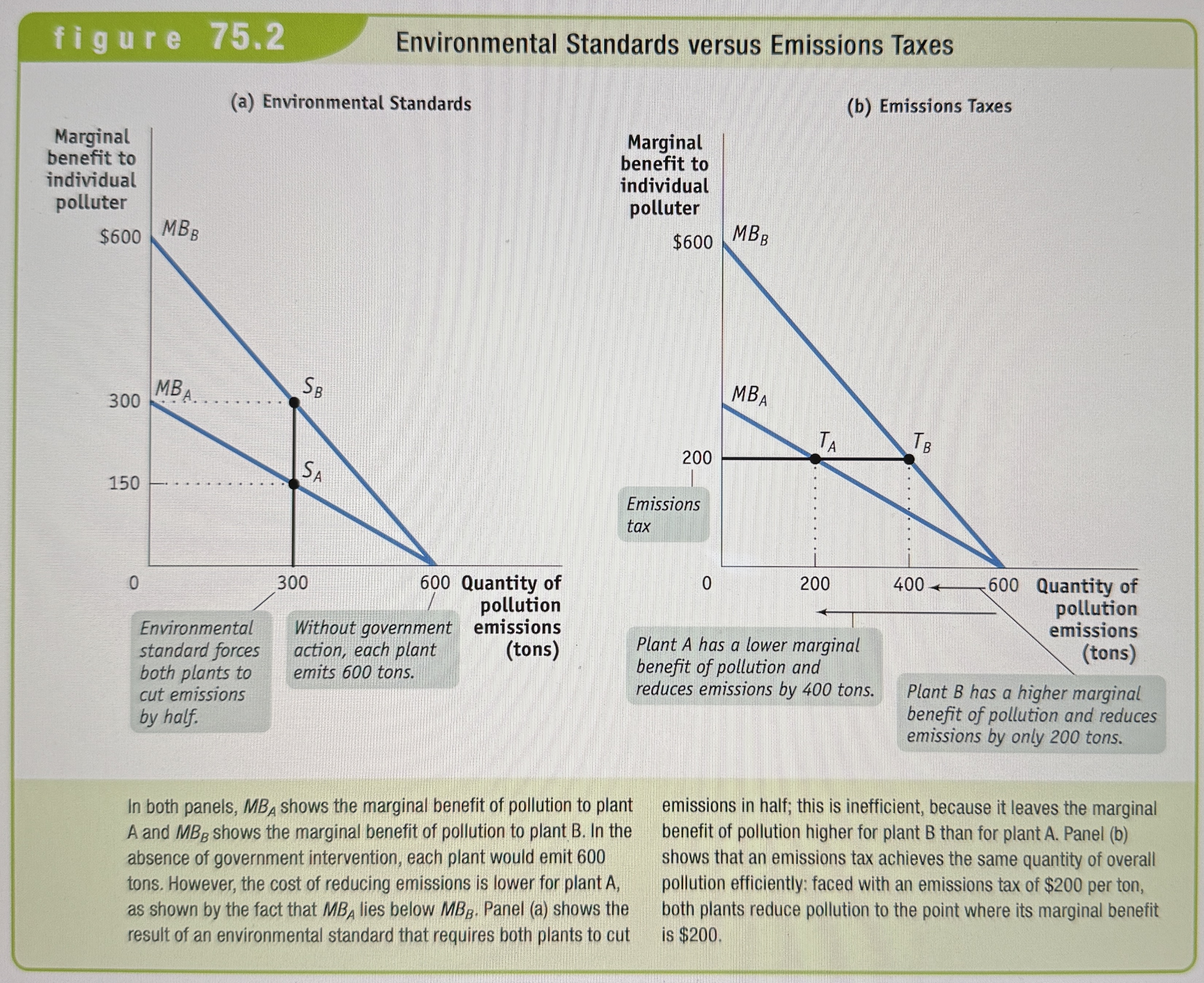
Environmental standards
Rules that protect the environment by specifying limits or actions for producers and consumers.
Emissions tax
A tax that depends on the amount of pollution a firm produces.
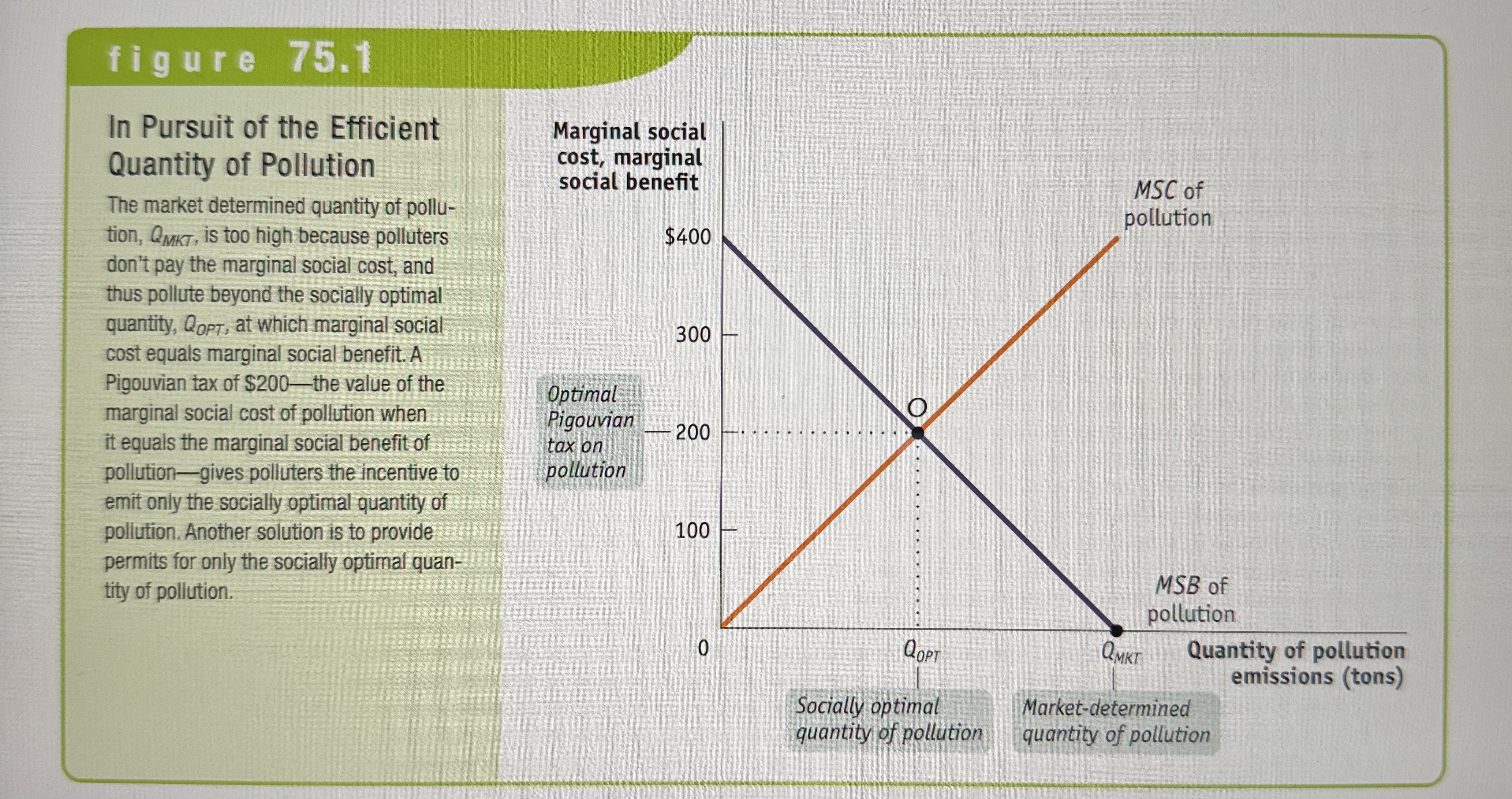
In Pursuit of the Efficient Quantity of Pollution
Ex.
Environmental Standards versus Emissions Taxes
Ex.
Pigouvian Taxes
Taxes designed to reduce external costs
Tradable emissions permits
Licenses to emit limited quantities of pollutants that can be bought and sold by polluters.
Positive Externalities and Consumption
Ex.
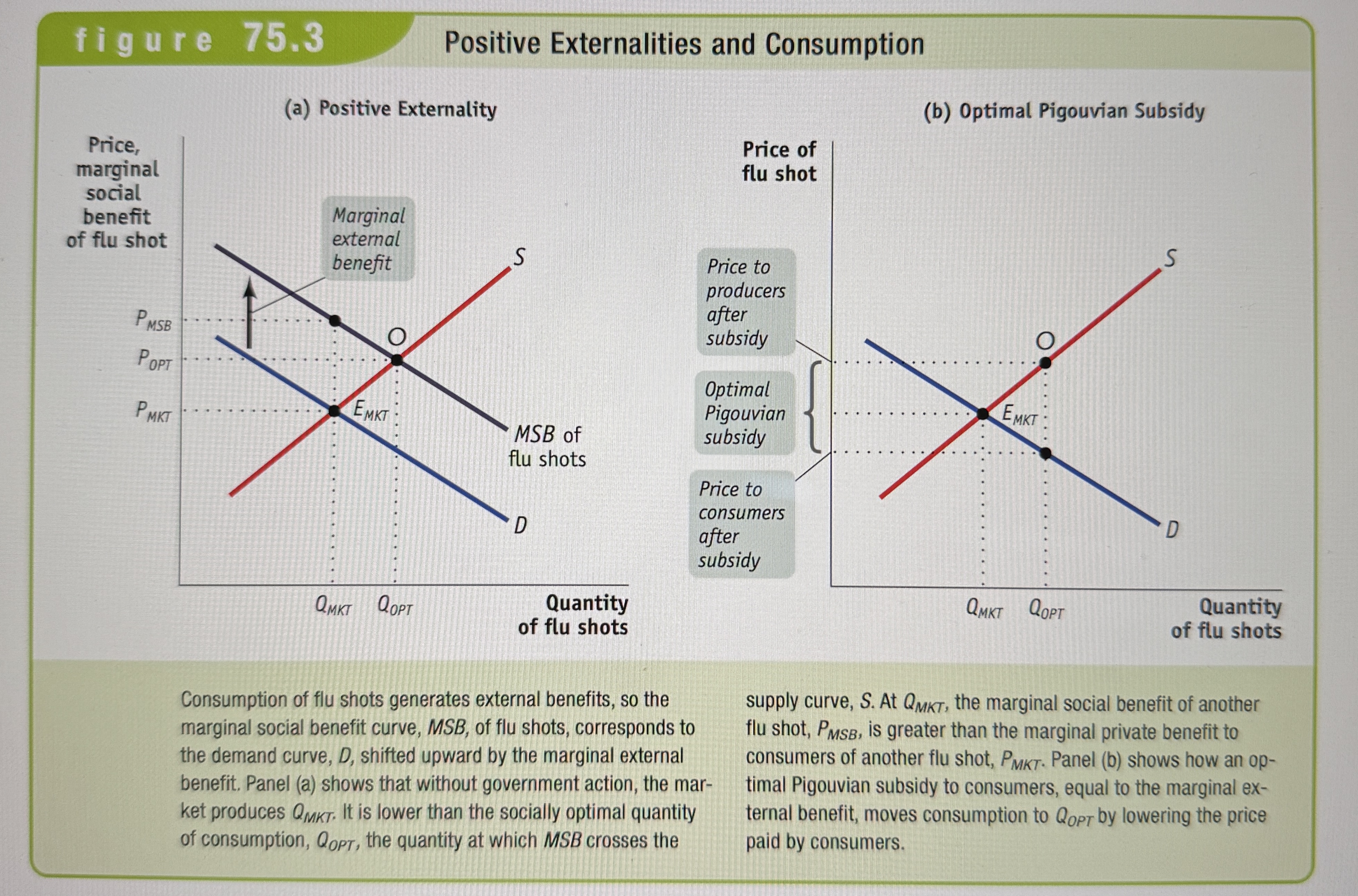
Marginal private benefit
The marginal benefit that accrues to consumers of a good, not including any external benefits.
Marginal social benefit of a good
The marginal private benefit plus the marginal external benefit. MSB = MPB + MEB
Marginal external benefit
The addition to external benefits created by one more unit of the good.
Pigouvian Subsidy
A payment designed to encourage purchases and activities that yield external benefits.
Technology spillover
An external benefit that results when knowledge spreads among individuals and firms.
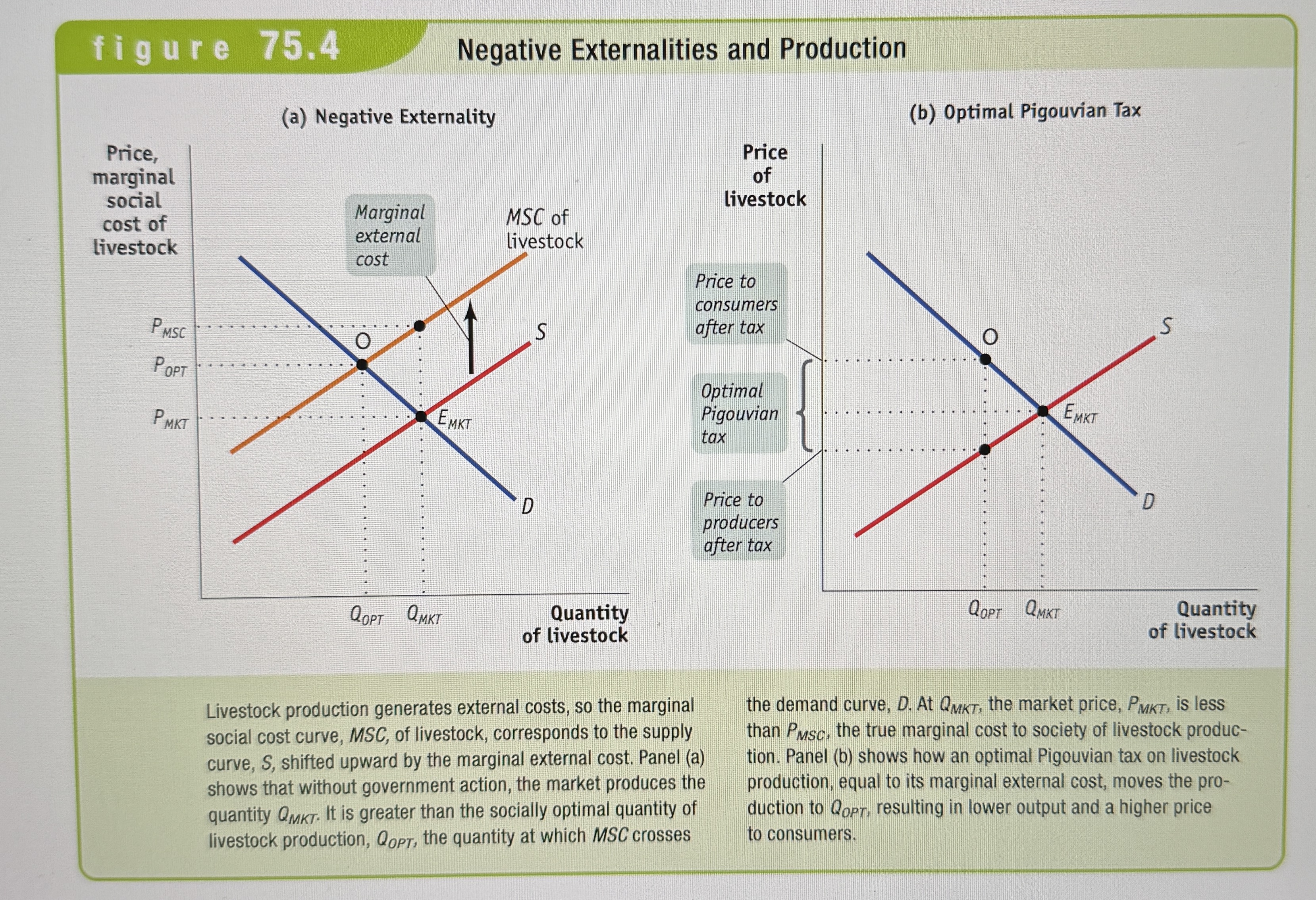
Marginal private cost
The marginal cost of producing that good, not including any external costs.
Marginal social cost of a good
Equal to the marginal private cost of production plus its marginal external cost. MSC = MPC + MEC
Marginal external cost
An increase in external costs created by one more unit of the good.
Negative Externalities and Production
Ex.
Network externality
When the value of a good to an individual is greater when more other people also use the good.
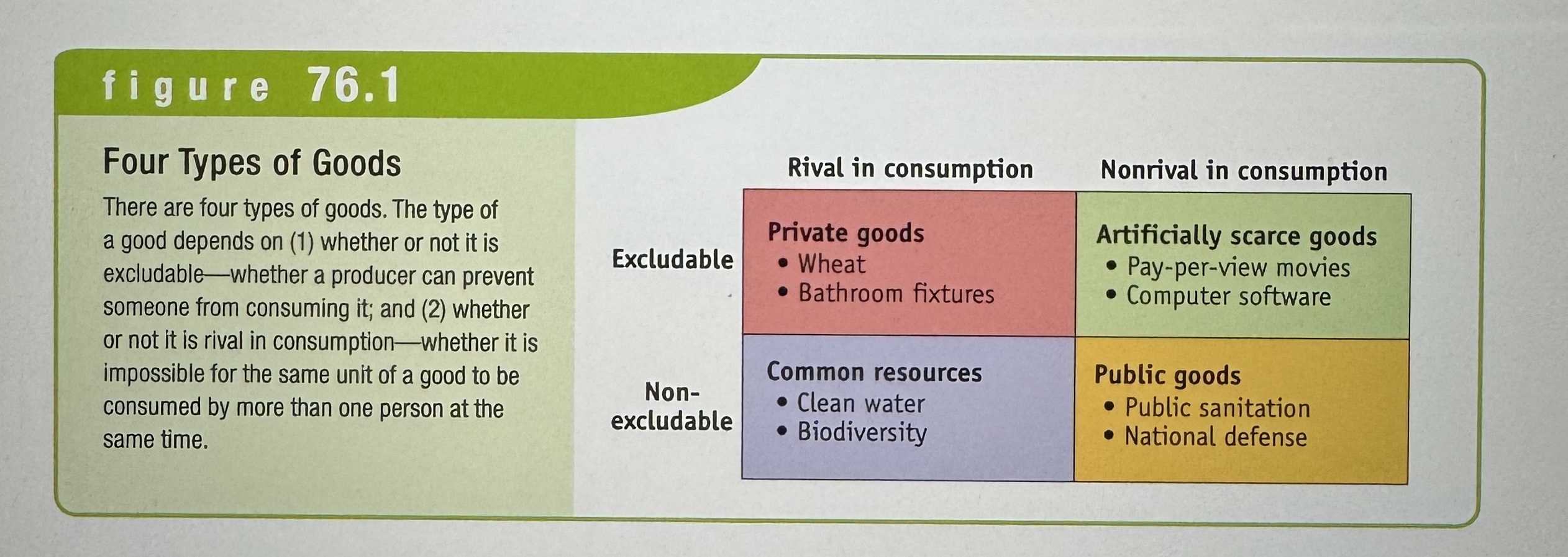
Excludable
A good is excludable if the supplier of that good can prevent people who do not pay from consuming it.
Rival in consumption
A good is rival in consumption if the same unit of the good cannot be consumed by more than one person at the same time.
Private good
A good that is both excludable and rival in consumption.
Nonexcludable
A good is nonexcludable when the supplier cannot prevent consumption by people who do not pay for it.
Nonrival in consumption
A good is nonrival in consumption if more than one person can consume the same unit of the good at the same time.
Four Types of Goods
Ex.
Free-rider Problem
Individual have no incentive to pay for their own consumption and instead will take a “free ride“ on anyone who does pay. Nonexcludable goods suffer from this.
Public good
A good that is both nonexcludable and nonrival in consumption.
A Public Good Graph
Ex.
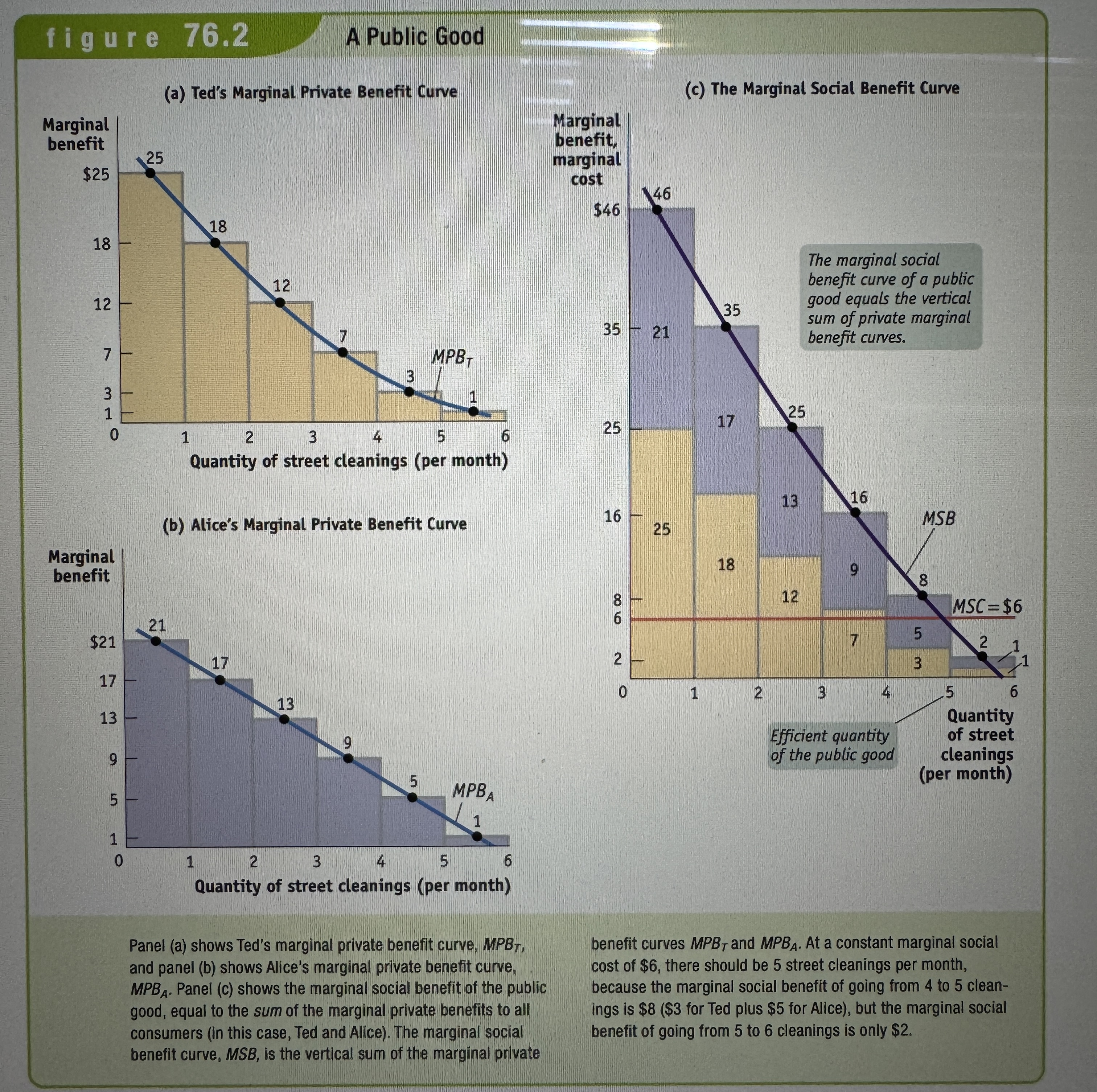
Common resource
A good that is nonexcludable and rival in consumption: you can’t stop me from consuming the good, and more consumption by me means less of the good available for you.
Overuse
Is the depletion of a common resource that occurs when individuals ignore the fact that there use depletes the amount of the resource remaining for others.
A Common Resource Graph
Ex.
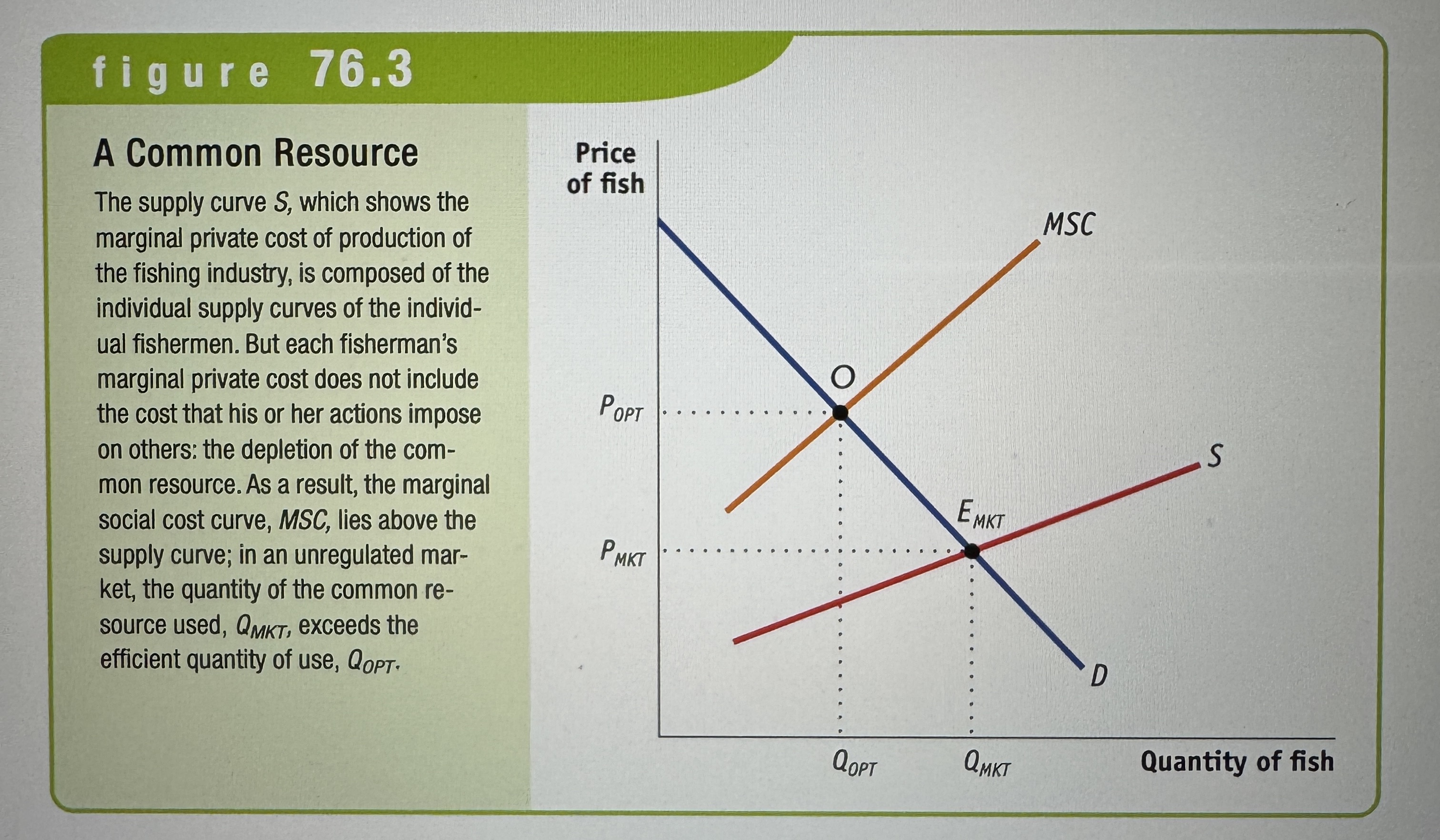
Artificially scarce good
A good that is excludable, but nonrival in consumption.
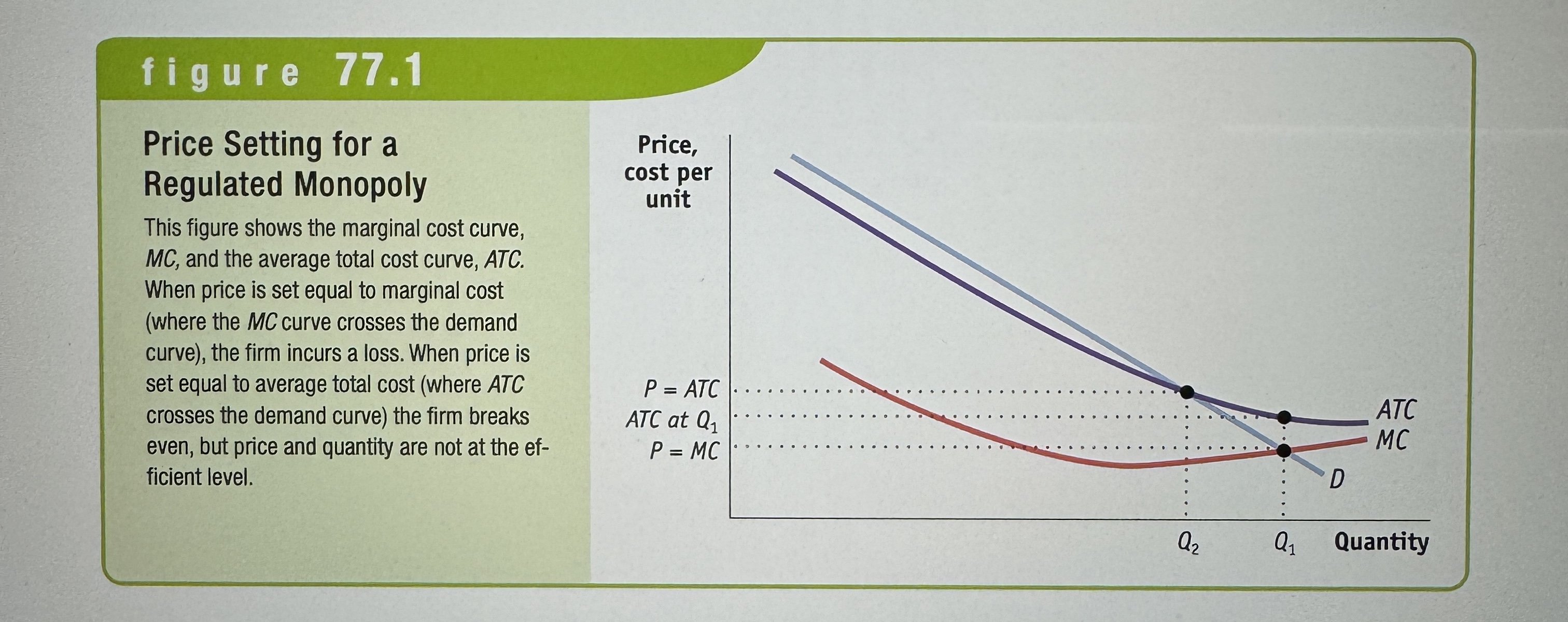
Marginal cost pricing
Occurs when regulators set a monopolies price equal to its marginal cost to achieve efficiency.
Average cost pricing
Occurs when regulators set a monopolies price equal to its average cost to prevent the firm from incurring a loss.
Price setting for a regulated monopoly
Ex.
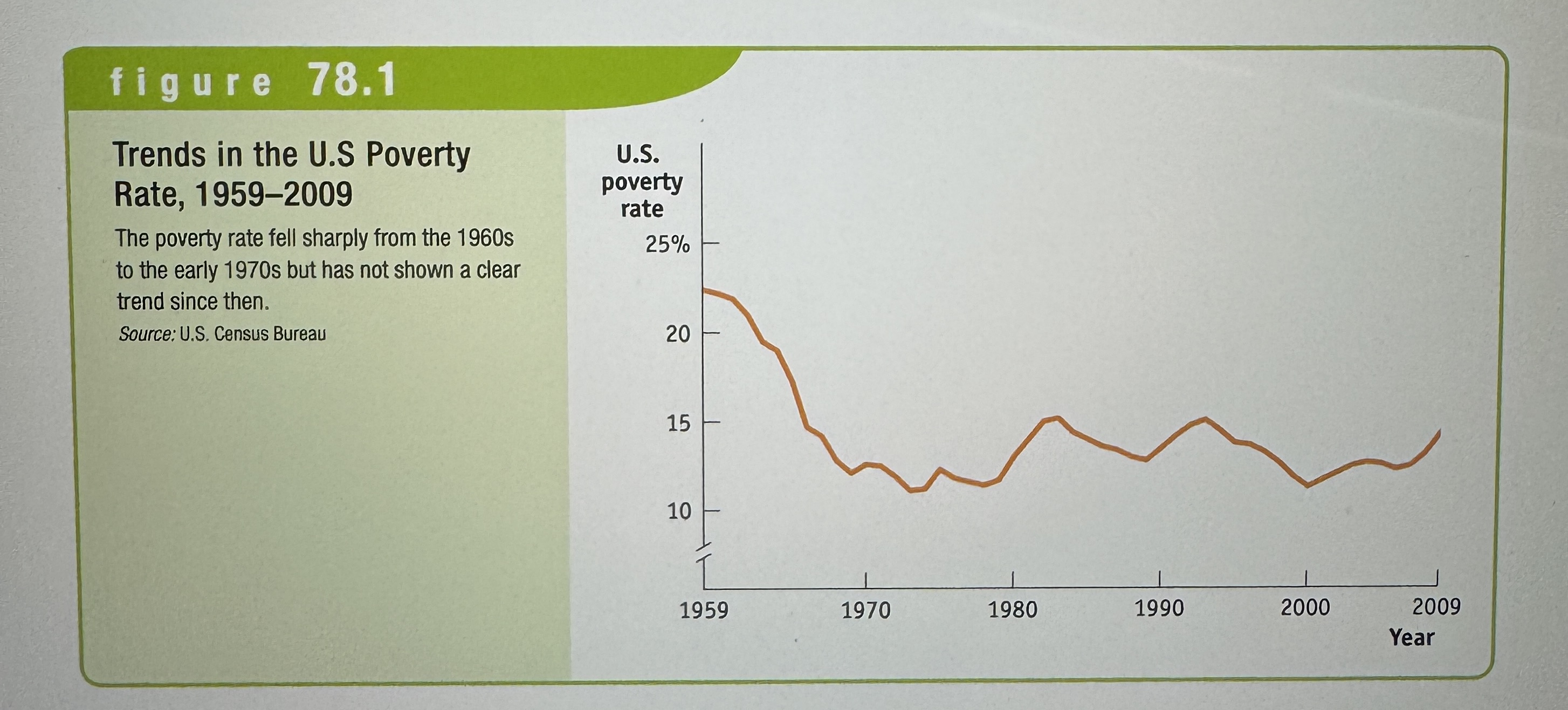
poverty threshold
The annual income below which a family is officially considered poor.
Poverty rate
The percentage of the population with incomes below the poverty threshold.
Percent of Eighth-Graders Finishing College, 1988
Ex.

U.S. Income Distribution in 2008
Ex.
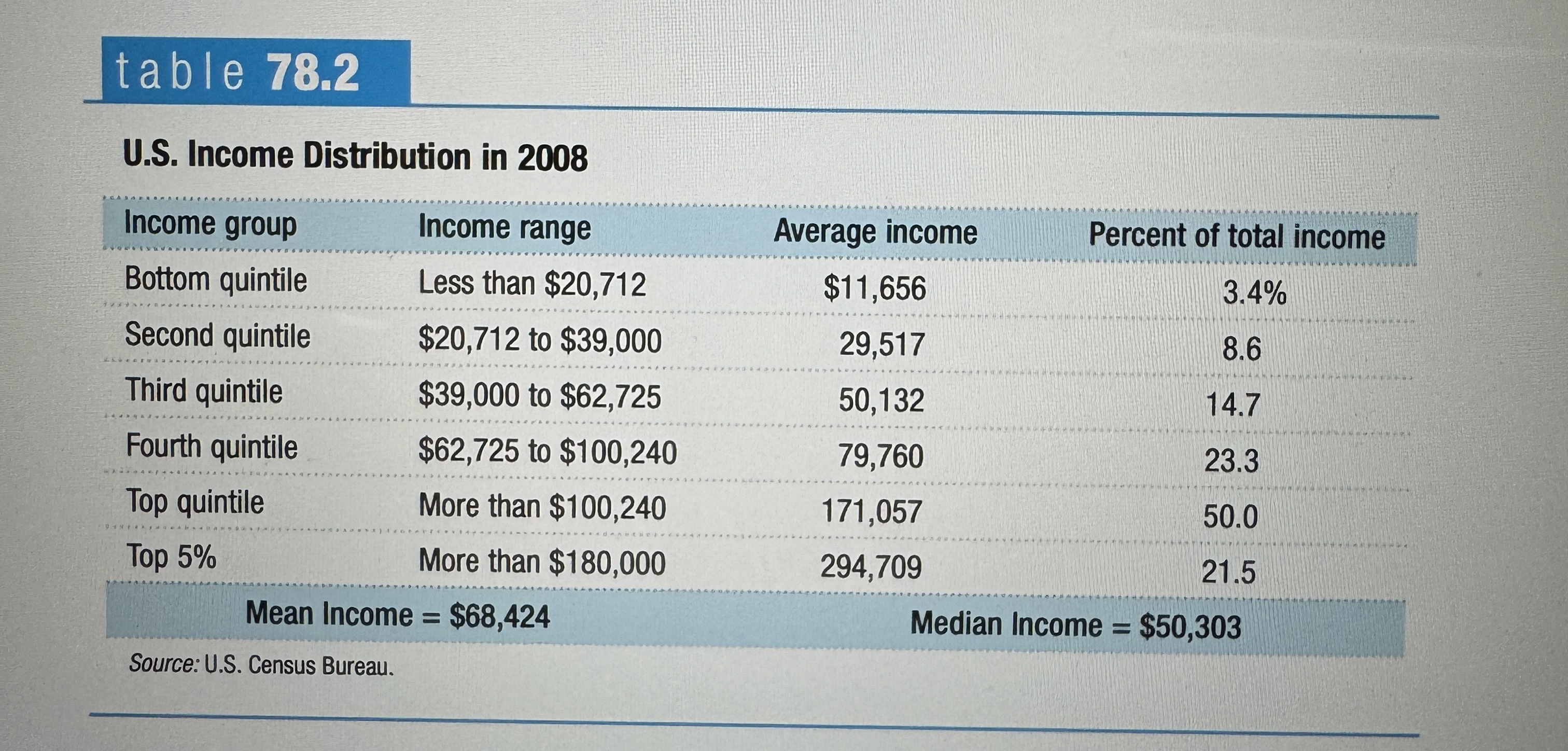
Mean household income
The average income across all households
Median household income
The income of the household lying in the middle of the income distribution
Gini Coefficent
A number that summarizes a country’s level of income inequality based on how unequally income is distributed across the quintiles.
Income inequality around the world
Ex.
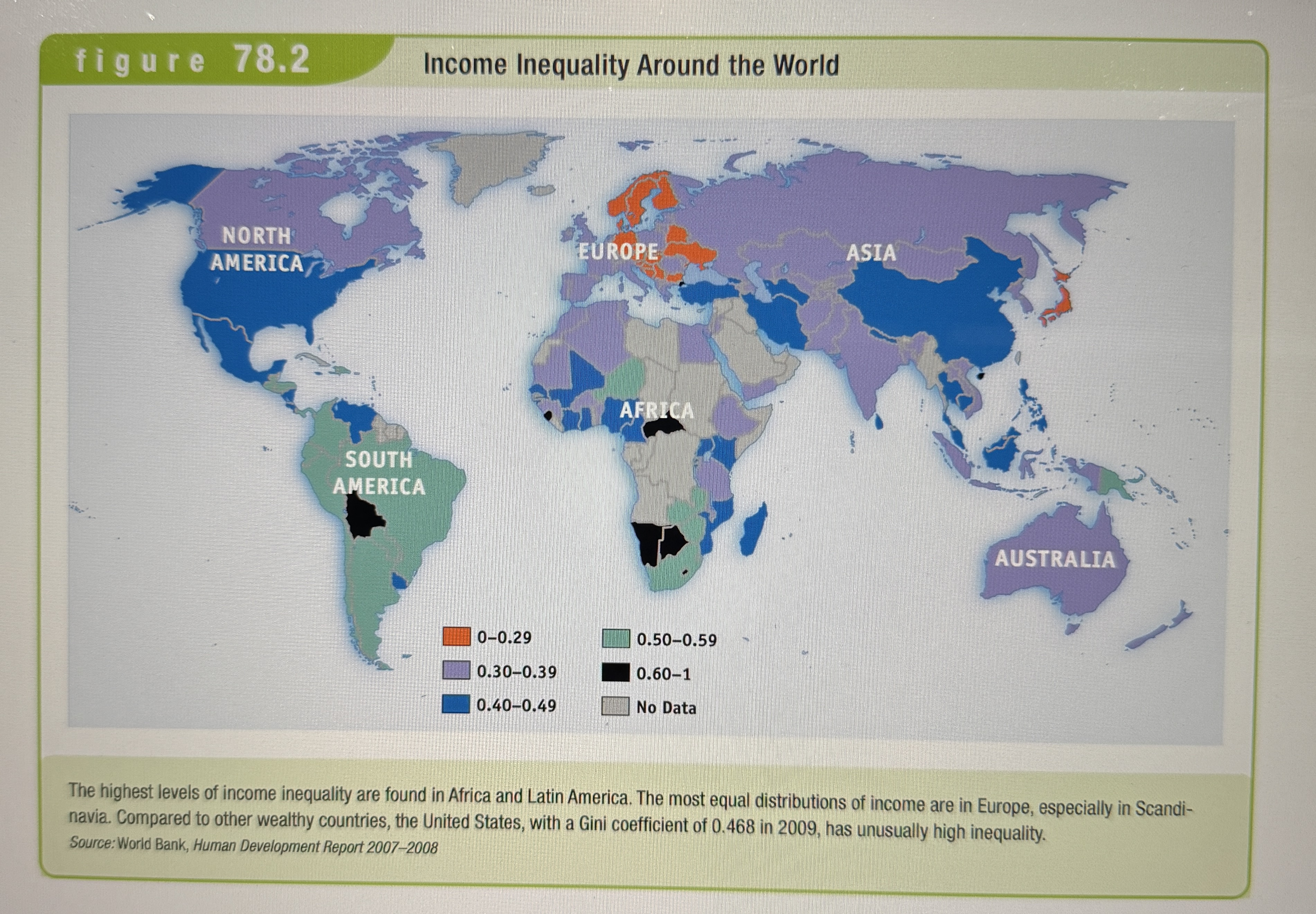
Means-tested
A Program that is available only to individuals or families whose incomes fall below a certain level.
In-kind Benifit
A benefit given in the form of goods or services.
Major U.S. Welfare State Programs, 2009
Ex.
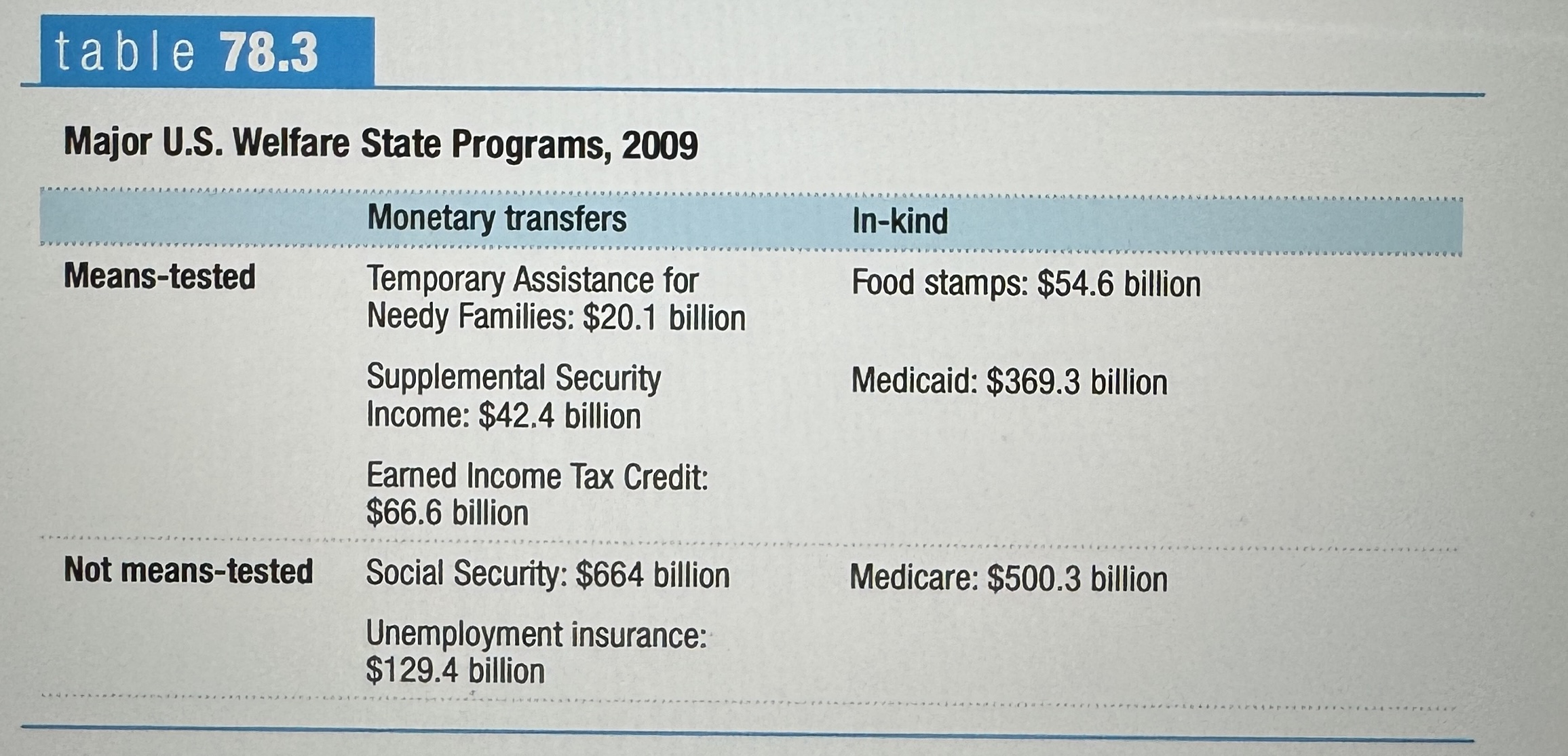
Negative income tax
A program that supplements the income of low income workers.
Effects of Taxes and Transfers on the Poverty Rate, 2008
Ex.
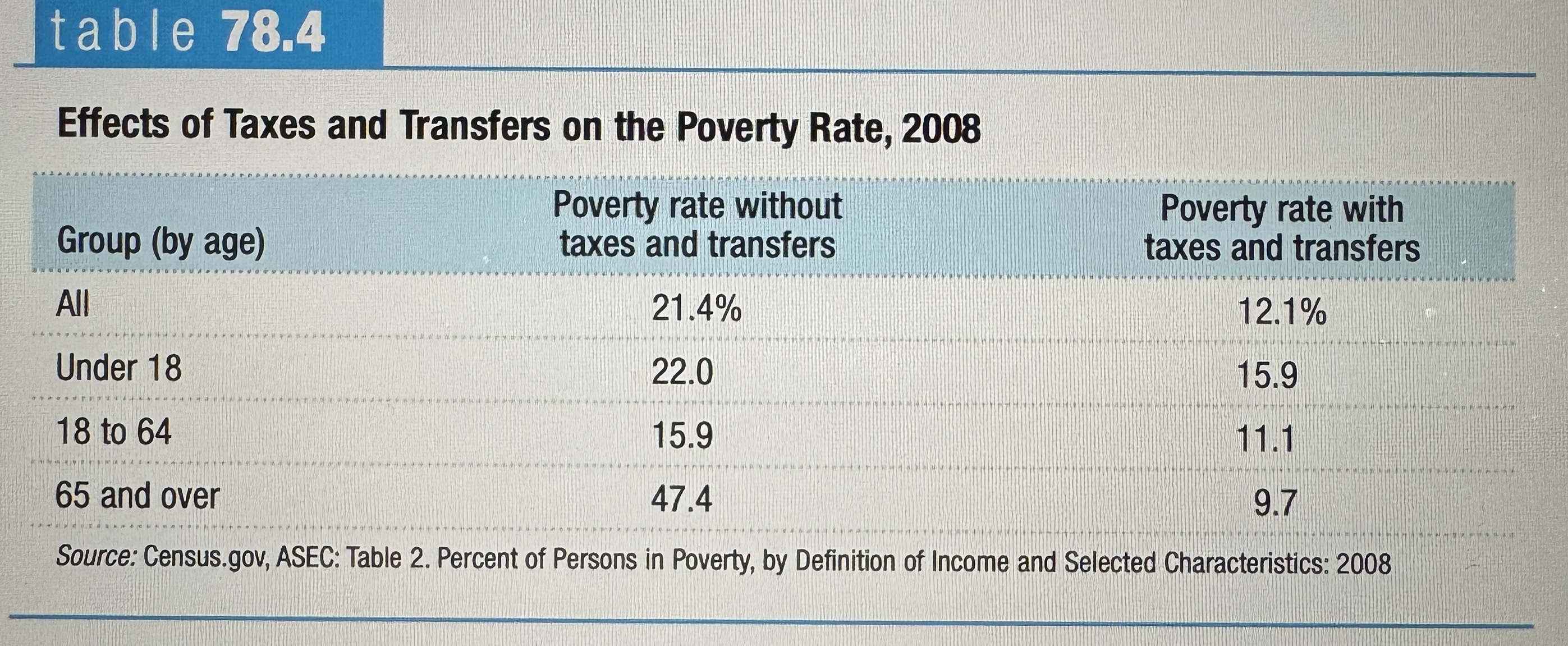
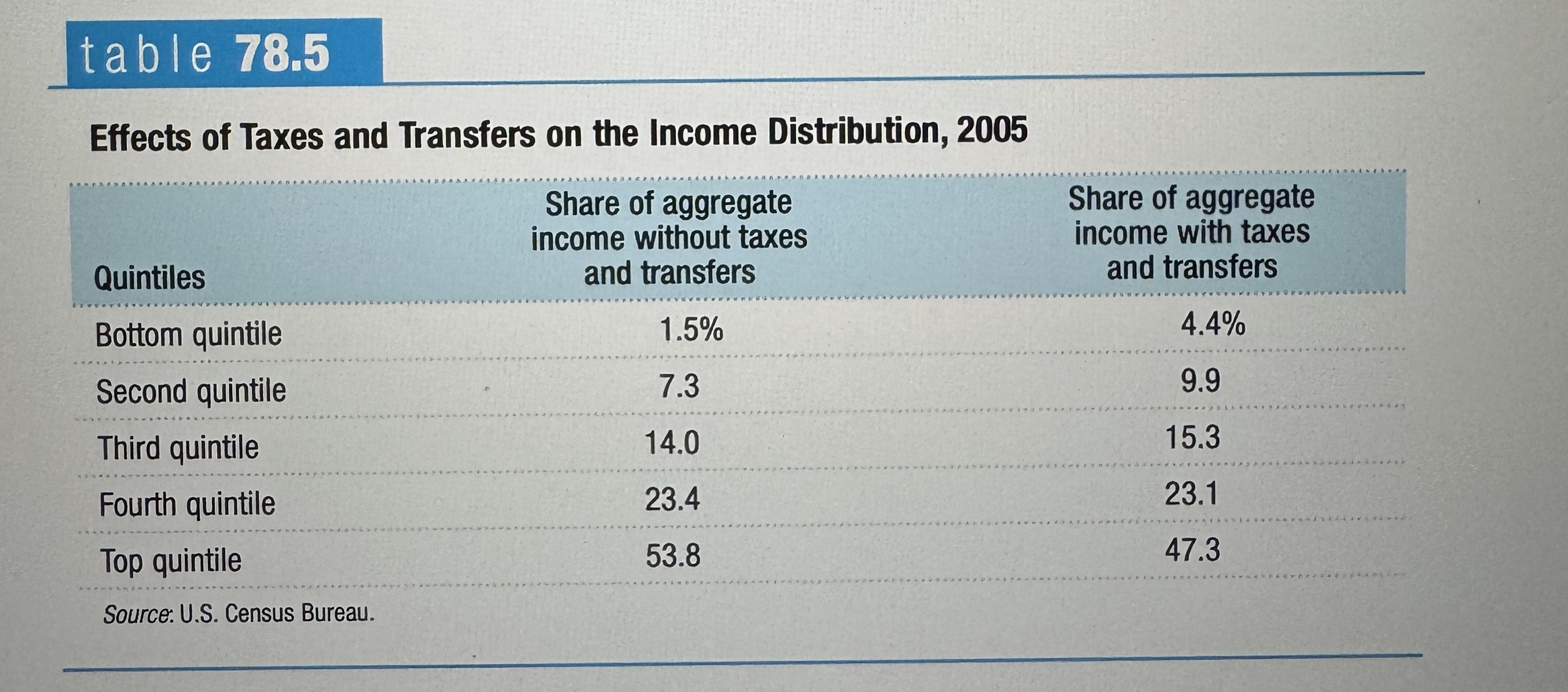
Effects of Taxes and Transfers on the Income Distribution, 2005
Ex.
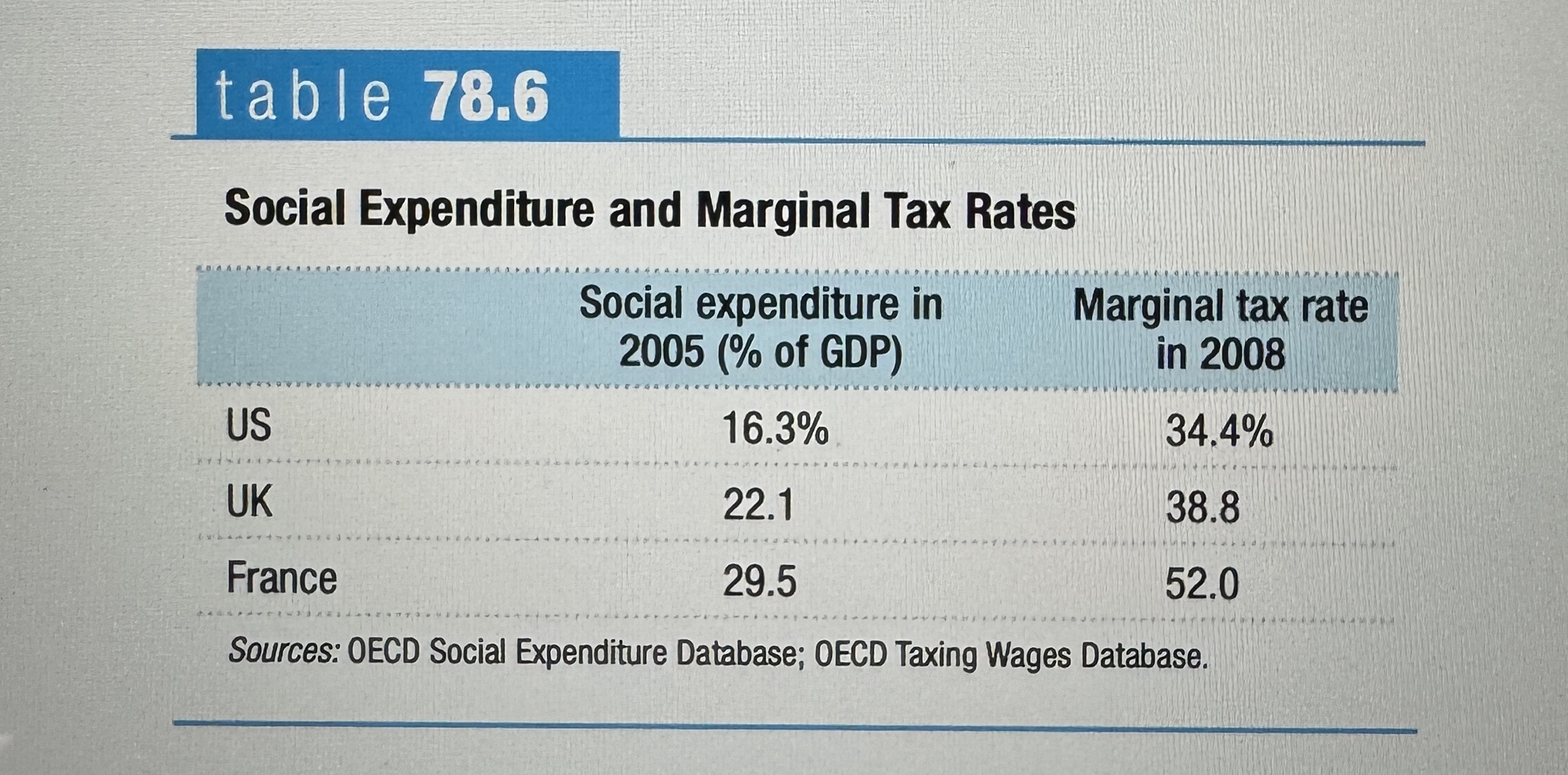
Social Expenditure and Marginal Tax Rates
Ex.