L02 Atomic bonding
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Valence electrons
The electrons in the outermost shell of an atom that participate in bond formation.
What is bond formation?
Bond formation is the process by which atoms join together to form molecules or compounds through various types of interactions, such as ionic, covalent, or metallic bonding.
Ionic bond
A bond formed between cations and anions through the exchange of electrons, exemplified by NaCl.
Covalent bond
A bond formed between non-metal atoms through the sharing of electrons, as seen in molecules like CH4 and H2O.
Metallic bond
A bond found in metals where electrons are delocalized in a 'sea of electrons' around positively charged metal ions.
Van der Waals bond
A weak bond resulting from the interaction between induced dipoles in nearby atoms or molecules.
Hydrogen bond
A type of weak bond that forms between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an electronegative atom and another electronegative atom.
Primary bonds
Bonds that are strong and typically include ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds.
Secondary bonds
Weaker bonds than primary bonds, such as van der Waals and hydrogen bonds, which can be easily broken.
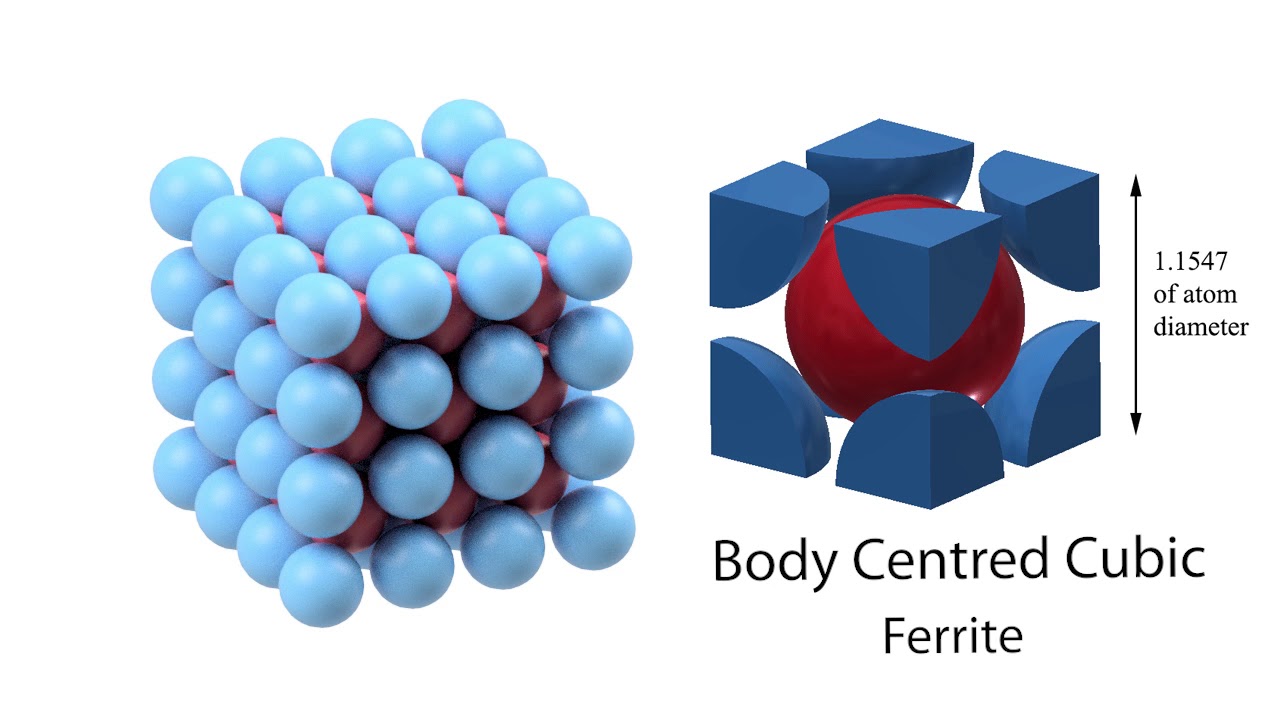
Body-centered-cubic (BCC)
One of the three principal crystal structures for metals; atoms are located at the corners and one atom at the center.
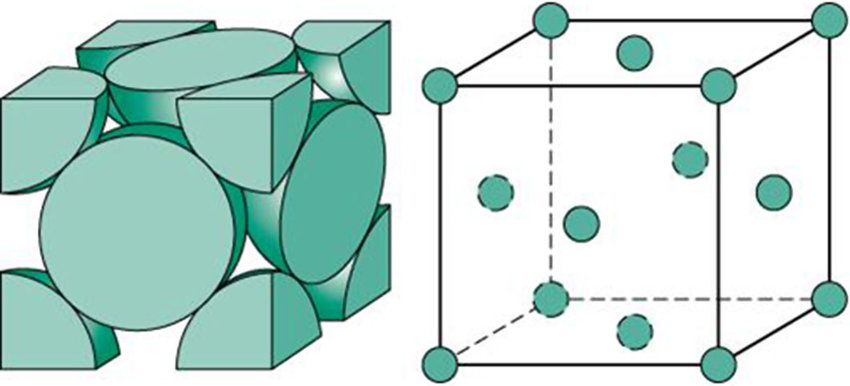
Face-centered-cubic (FCC)
A crystal structure where atoms are located at each corner and the center of each face of the cube.
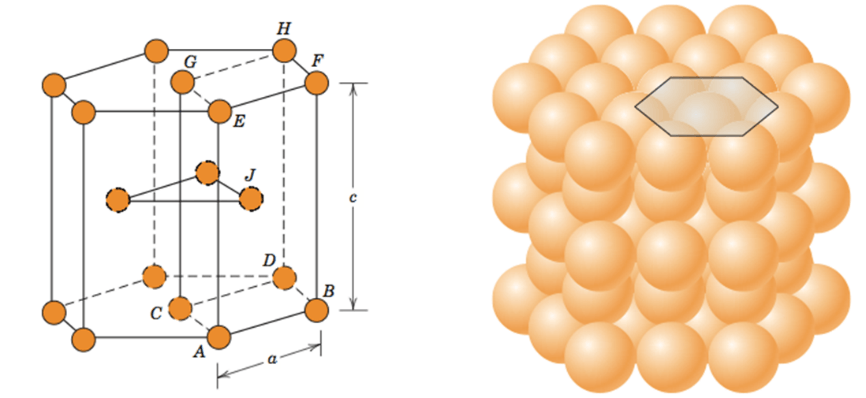
Hexagonal closed packed (HCP)
A crystal structure where the atoms are packed closely in a hexagonal pattern.
Crystalline materials
Materials with atoms arranged in patterns that exhibit long-range order.
Amorphous materials
Materials that are non-crystalline and lack a well-defined long-range order.
Electronegativity
A measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons.
Charge neutrality
The condition where the total positive charge is equal to the total negative charge within an ionic compound.
Electrostatic attraction
The force that attracts oppositely charged ions toward each other.
Crystal defects
Irregularities in the crystal structure of materials that can affect their strength and properties.
Crystallinity in polymers
The degree to which the molecular chains in a polymer are ordered or packed in a regular pattern.
Ductile materials
Materials that can undergo significant plastic deformation before rupture, often characterized by low melting points.
Brittle materials
Materials that fracture without significant plastic deformation, usually having high modulus and high melting points.