Chemistry Exam 3 (CH.12)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
States of matter in terms of K.E & P.E

Name different changes of state and identify nature of enthalpty

Understand heating/cooling curves
/ = temp is increasing on a single phase
- = phase change is occurring
adding heat increases K.E (on diagonal lines)
adding heat increase P.E (on horizontal lines)
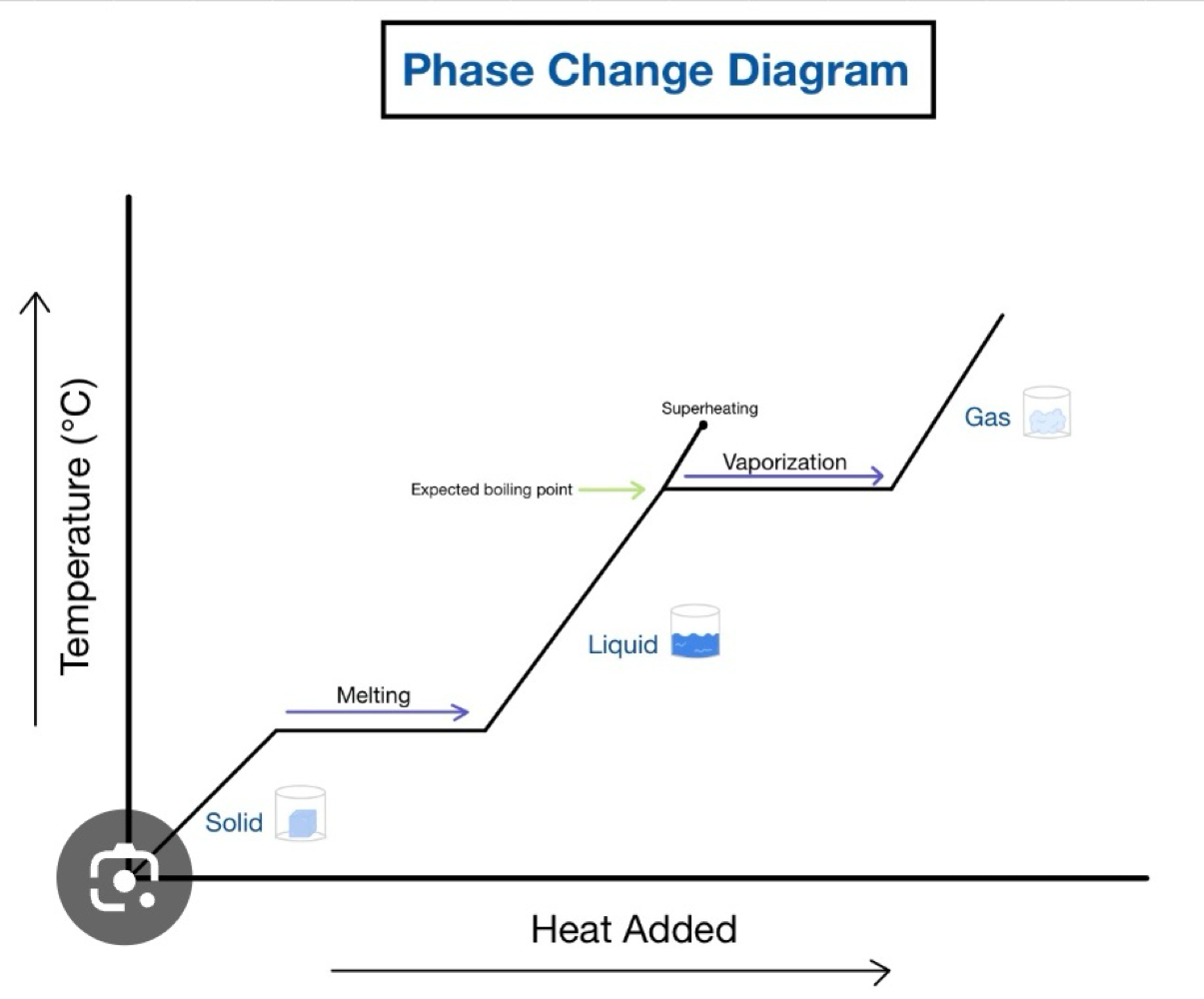
Define dynamic equilibrium and how it describes: vapor pressure, boiling point, melting point, and sublimation

Purpose of Clausius - Clapeyron equation
finding an unknown vapor pressure / boiling point

Label all parts of a Phase Diagram
Triple point: unique temp. where temp. & press. of a substance’s solid, liquid, & gas phases co-exist in equilibrium
Critical point: liquid & gas become indistinguishable

explain differences in IMF
Ion - induced dipole goes after disperson
Both dispersion and Ion - induced dipole are temporary
Surface Tension, Viscosity, & Capillarity

S.T: stronger IMF = stronger S.T | stronger Temp. = weaker S.T |
V: stronger IMF = strong V | strong Temp. = weaker V |
C: stronger IMF = weaker C | stronger Temp. = stronger C |
stronger IMF = stronger boiling/freezing point
Cohesion vs Adhesion
~ attraction of molecules from same substance
~ Attraction of molecules from different substance
Solvent, Thermal, and Surface Properties of Water
universal solvent
HIGH specific heat capacity
HIGH heat of vaporization
HIGH surface tension
Solid Water is less dense than liquid water (due to lattice structure)
Name the different types of cubic unit cells

Equations to solve different types of lattices

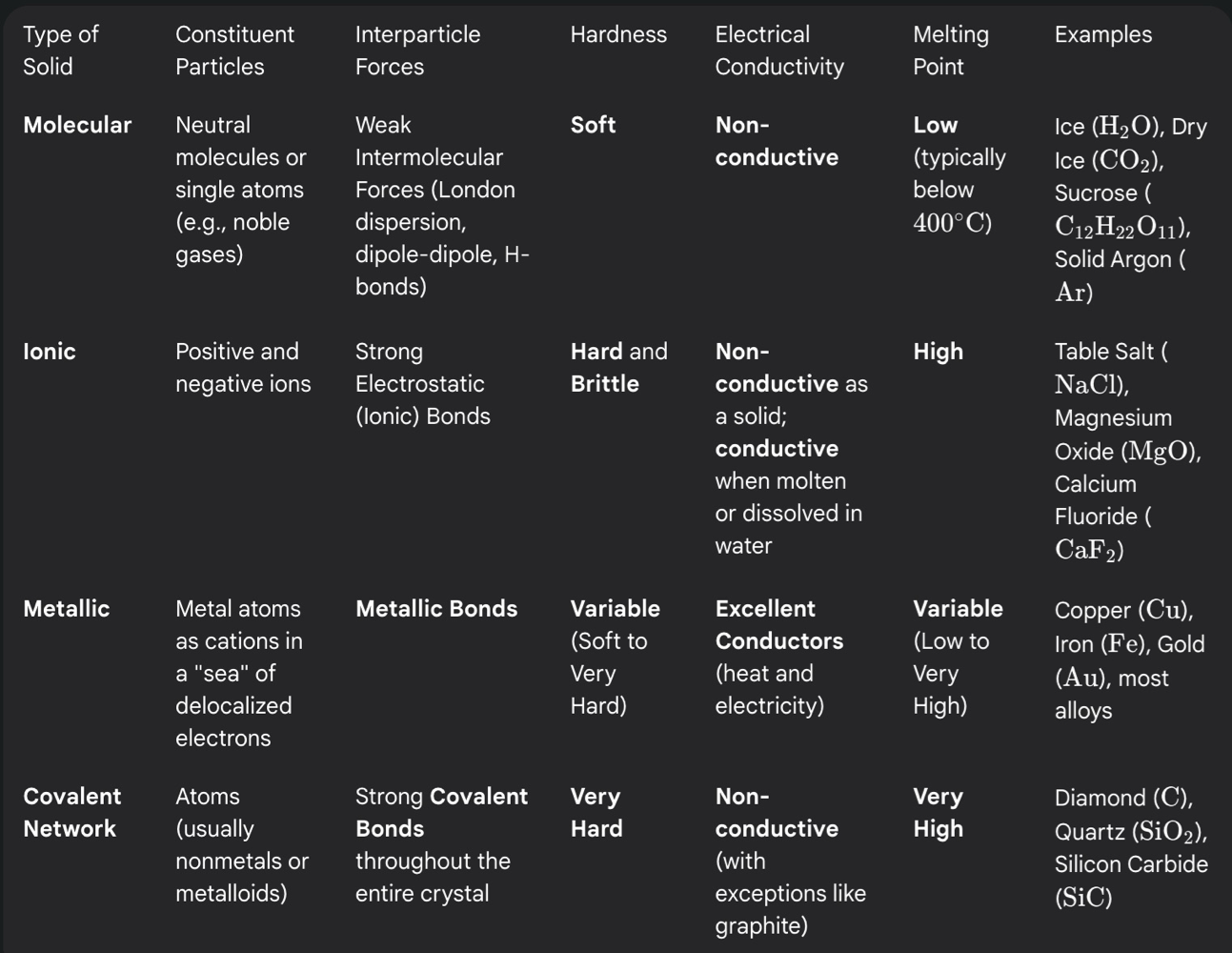
Differentiate between the different types of crystalline solids
relationship between vapor pressure and temperature
proportional (increases/ decreases together)
relationship between vaporization and IMF
inversely proportional (one increases / other decreases)