Diagnostic Imaging Midterm
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
When are real-time U/S imaging produced?
when tissues reflect sound waves back to transducer
What do piezoelectric crystals do/produce?
They produce high frequency sound in transducer
What is something U/S is better at than radiograph?
U/S is better at visualizing soft tissues.
Application in vet. med.
small animal→
Equine→
Ruminant→
Swine→
Cattle→
abdominal organs & cardiac
used in tendons
reproduction
measurement for back fat, reproduction
measurement for rib eye, reproduction
Advantages of ultrasound?
no ionizing radiation, non-invasive, clearer picture of soft tissues, repeated, used for guiding minimally invasive procedures
Disadvantages of U/S?
waves are disrupted by gas, larger patients more difficult, difficult to penetrate bone
In a abdominal U/S where do you clip hair?
clip hair→ costal arch to flanks, caudal to pubic bone.
Uses isopropyl alcohol
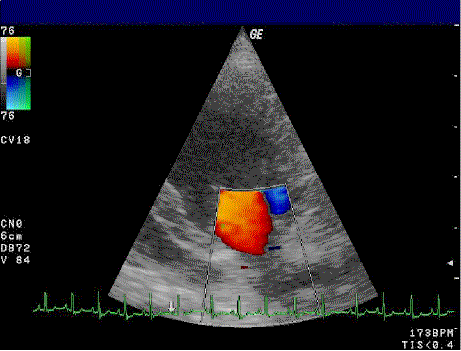
What does BART stand for?
blue away from probe, red towards probe
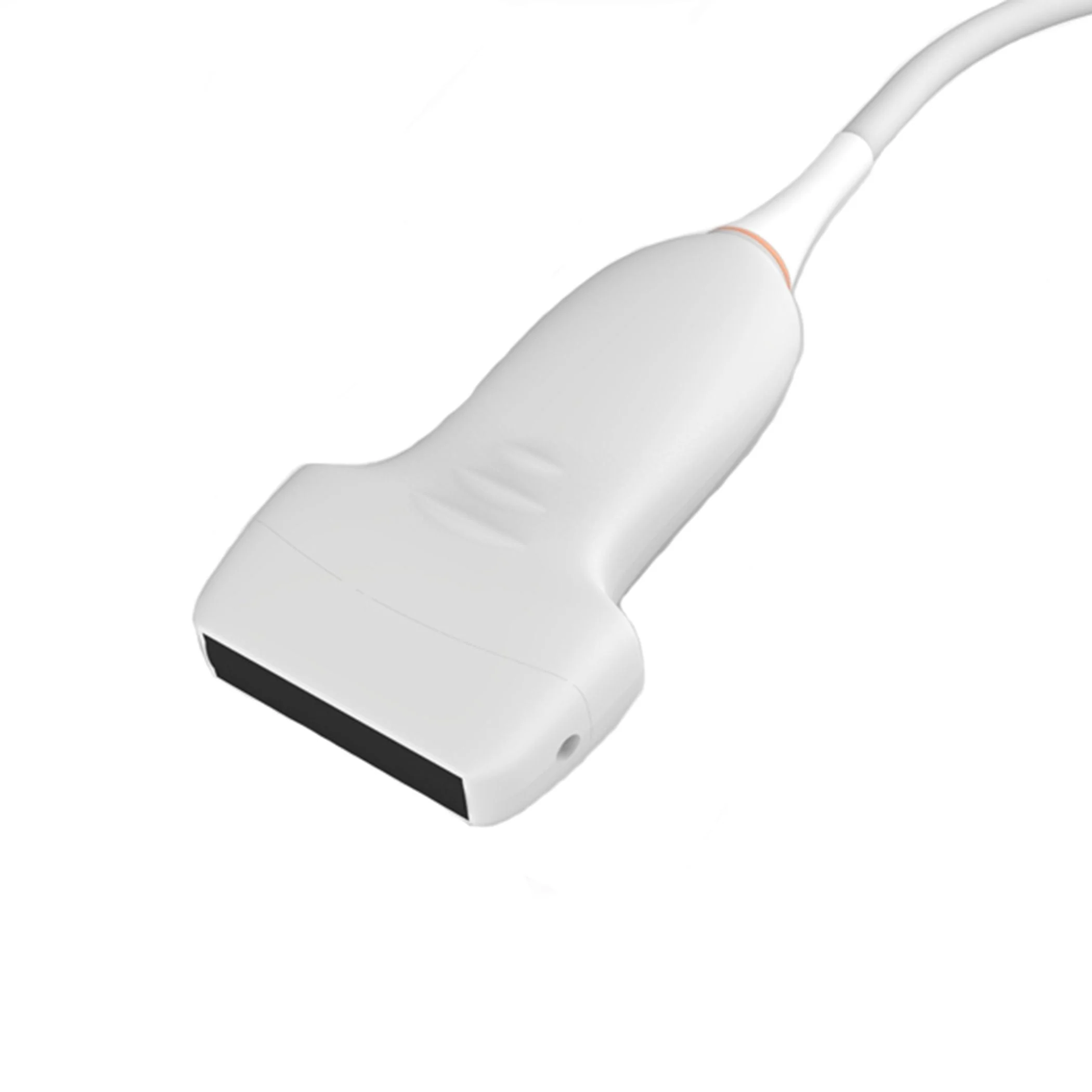

What is this type of transducer and what does it do
A-linear transducer
results of high resolution but only used for tendons
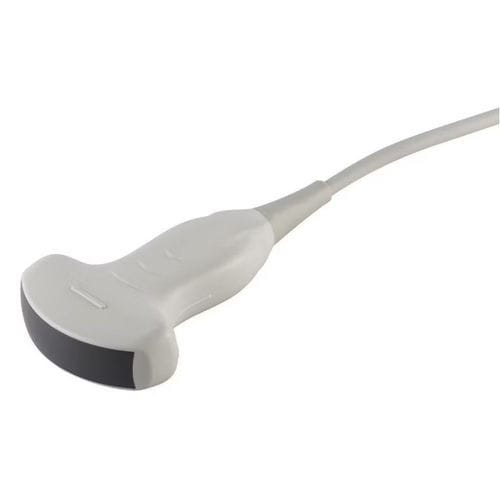

What is this type of transducer and what does it do
B-corvex
gives wider view
greater depth but less detail

What is this type of transducer and what does it do?
C-microcorvex
more narrow
used for smaller animals
When is fanning a transducer used?
to identify shape of structure
What does roll/rocking a transducer do?
it brings an object at the edge of screen to center of screen
With what should you clean with for transducers
70% of isopropyl PRN JUST the head
The two conepts of Knobology are?
Depth- controls amount of tissue displayed, greater depth but less detail
Gain- alter brightness
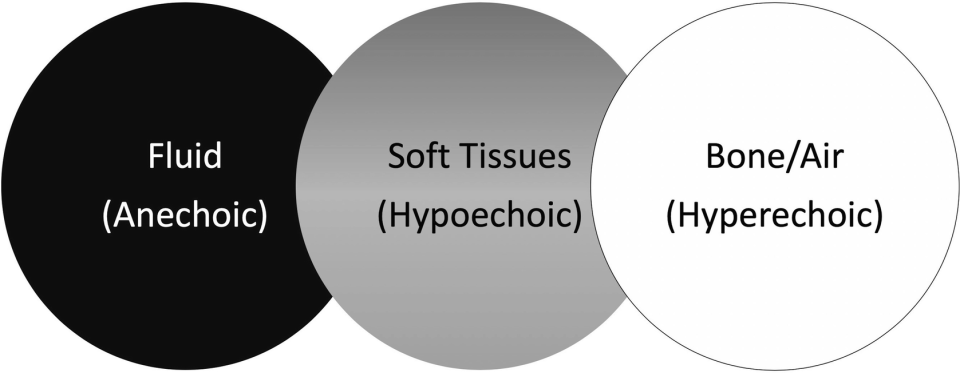
Echogenicity- Anechoic
echo free, its all black
air in lungs or fluid in bladder
Echogenicity- Hypoechoic
echo poor, dark grey
less dense soft tissue
Echogenicity- hyperechoic
echo rich, bright white
areas of increased density
in bone and metal
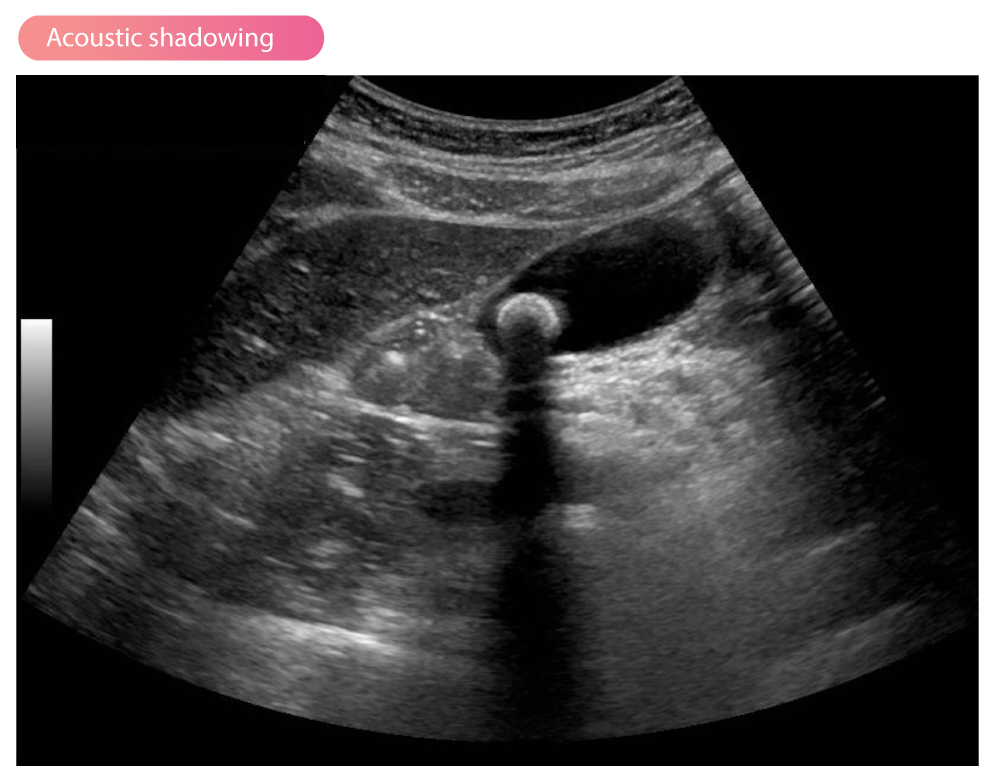
ID this artifact
Acoustic Shadowing
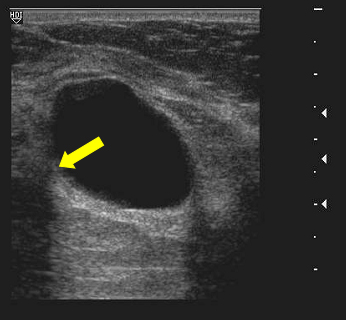
ID this artifact
edge shadow
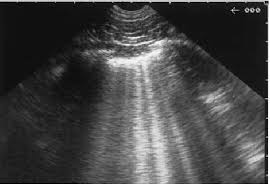
ID this artifact
comet tail
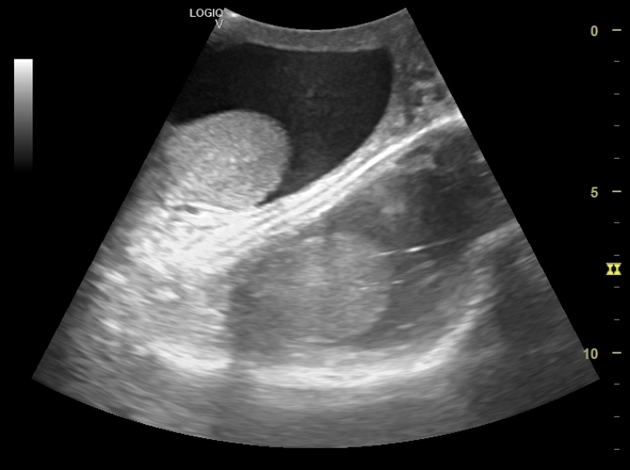
This artifact is?
mirror image
What are the two types of anode (+)
Stationary: portable units but lower voltage, less powerful
Rotating: NOT portable, in X-ray machines, prolongs life of tube, spreads heat
Name the 5 radiographic densities
gas
fat
soft tissues/ fluid
bone
metal
What is summation?
organs that overlap each other
kVp=
penetrating power
mA=
total # of x rays produced
contrast=
dark or light, low kVp, high contrast
Differences b/w:
Digital radiography=
computed radiography=
Digital imaging, fewer retakes
Indirect digital imaging using photostimulable phosphor (PSP)
What does DICOM stand for?
Digital image communications in medicine
is global view
not altered
where are x-rays on the electromagnetic spectrum?
between ultraviolet light and gamma rays
are radiant energy
What are ways in which x-rays can interact with matter?
it can occur thru penetration, absorption and scatter
What is scatter radiation?
Lower-energy photons do not help produce image
Depends on intensity of beam, density of object, field size
Reduces image quality
What are the difference of matter and energy
Matter has mass and occupies space
Energy is the capacity to do work
What startles the patient more?
spinning anode
Where should marker be placed for lat limb?
cranial/dorsal
lateral
corresponding side
cranial/dorsal
Where should marker be placed for CrCd, CdCr, DV limb?
cranial/dorsal
lateral
corresponding side
lateral aspect
Where should marker be placed for lateral body?
cranial/dorsal
lateral
corresponding side
dorsal
dorsal aspect
Where should marker be placed for DV, VD?
cranial/dorsal
lateral
corresponding side
on corresponding side
How should the image be displayed for Lateral limb?
proximal aspect at top of screen, cranial/dorsal aspect on left side of screen
How should image be displayed for CrCd, CdCr, DV limb
proximal aspect at top of screen, lateral aspect on left side of screen
How should image be displayed for lateral body?
dorsal surface at top of screen, cranial end on left side of screen (as if animal is walking to the left)
How should image be displayed for DV or VD body?
cranial end at top of screen, left side of patient on left side of screen