Unit 4: Social Psychology and Personality
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Attributions
how people explain behavior and mental processes of themselves and others
Attribution Theory
the theory that we explain someone's behavior by crediting either the situation or the person's stable, enduring traits.
Dispositional Attribution
relate to internal qualities of others (such as intelligence or personality)
Situational Attribution
relate to external circumstances that are experienced
Explanatory Style
how people explain good and bad events in their lives and in the lives of others.
-can be optimistic or pessimistic
Attribution Biases
people are subject to biases in their attributions.
-these biases can affect behavior and mental processes
Actor/Observe Bias
the tendency for those acting in a situation to attribute their behavior to external causes, but for observes to attribute others' behavior to internal causes
Fundamental Attribution Error
the tendency for observers, when analyzing others' behavior, to underestimate the impact of the situation and to overestimate the impact of personal disposition
Self-serving Bias
the tendency to attribute our successes to internal causes, and our failure to external causes.
-take credit for triumphs and blame others for failures
Locus of Control
a psychological concept that describes a person's belief about whether they have control over the events in their life
External Locus of Control
perception that chance or outside beyond our personal control determines our fate
Internal locus of Control
perception that we control our own fate
Mere Exposure Effect
occurs when people are exposed to a stimulus repeatedly over time, which causes them to like the stimulus more
-reduces uncertainty
-makes understanding and interpreting easier
Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
the process by which a person's expectations about someone else can lead to that someone else behaving in ways that confirm the expectations
Social Comparison
evaluating one's opinions and abilities by comparing oneself with others
Upward Comparison
we compare ourselves with those who we believe are better or superior to us.
-often focus on the desire to improve ourselves, our current status, or our level of ability
Downward Comparison
we compare ourselves to others who are worse off than us
-make us feel better about our abilities or traits
Relative Deprivation
the perception by an individual that the amount of a desired resource they have is less than some comparison standard.
Stereotype
A generalized belief about a group of people
-can help reduce cognitive load
Prejudice
an unjustifiable (and usually negative) attitude toward a group and its members. Prejudice generally involves stereotyped beliefs, negative feelings, and a predisposition to discriminatory action.
Discrimination
unjustifiable negative behavior toward a group and its members
Implicit Attitudes
those that individuals hold may be unaware of or may not acknowledge
-unconscious
Just World Phonomenon
tendency to believe that the world is just and that people get what they deserve
-believe its the victim's fault
Out-group Homogeneity Bias
-tendency to assume that the members of other groups are very similar to each other

In-group Bias
"us"- people with whom they share a common identity
-tendency to favor own group
Ethnocentrism
-measuring or judging one's own culture against another culture
-can lead to judging someone else's culture negatively
Belief Perseverance
the persistence of one's initial conceptions even after the basis on which they were formed has been discredited.
Confirmation Bias
a tendency to search for information that supports our preconceptions and to ignore or distort contradictory evidence
Cognitive Dissonance Theory
we act to reduce the discomfort we feel when our thoughts are inconsistent with our behavior
-rationalizing
-changing attitude
-or change behavior
Social Norms
defined expectations and roles a society may have for its members in individual and social situations
Norms
a society's understood rules for accepted and expected behavior
-prescribe "proper" in individual and social situations
Social Influence Theory
talks about how people are more likely to do whatever they see as being the norm
-people have the tendency to change their behavior according to those around them
Normative Social Influence
influence resulting from a person's desire to gain approval or avoid disapproval
-changing one's behavior in order to fit in with the group
Informational Social Influence
Influence resulting from one's willingness to accept other's opinions about reality
-happens when a person lacks the knowledge and looks to the group for information and direction
Persuasion
The process by which a person's attitudes or behavior are without duress, influenced by communications from other people
Elaboration Likelihood Model
Theory of persuasion that suggests that there are two different ways people can be persuaded of something, depending on how invested they are in the topic
Central Route
When people are strongly motivated and have the time to think over a decision
-carefully weighs the pros and cons of a choice
Peripheral Route
When people are rushed or the decision is less important to them, they tend to be more easily persuaded by the peripheral route
-incidental cues
The Halo Effect
A type of cognitive bias in which our overall impression of a person influences how we feel and think about their character
Foot-In-The-Door
The tendency for people who have first agreed to a small request to comply later with a larger request
Door in the Face
-based on initially asking an excessive request and then reduce it
Conformity
Adjusting our behavior or thinking to coincide with a group standard
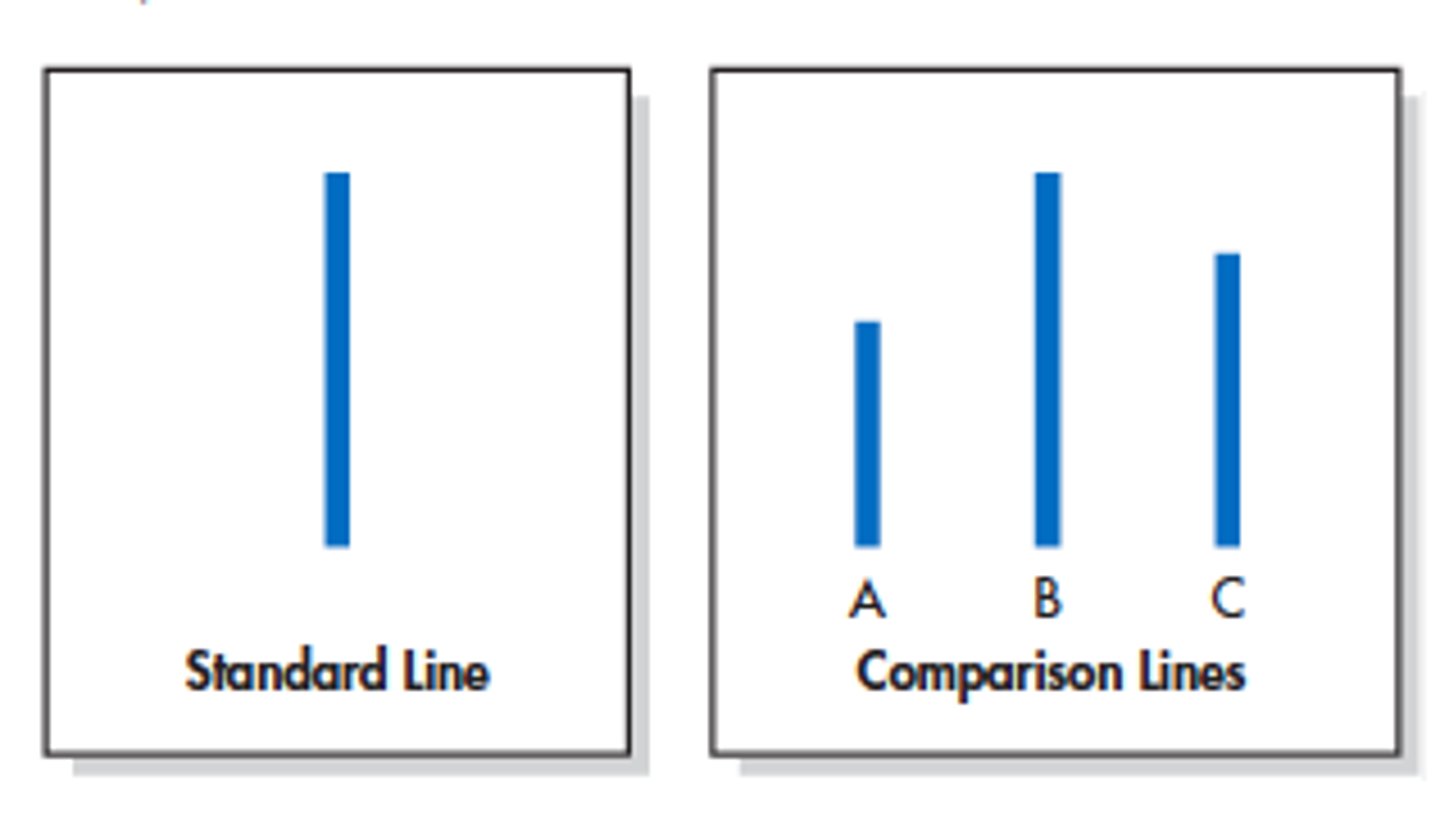
Solomon Asch Conformity Experiment
group of participants said wrong lines and were trying to see if the actual participant would also say the wrong answer
Obedience
tendency to comply with the commands of those in authority
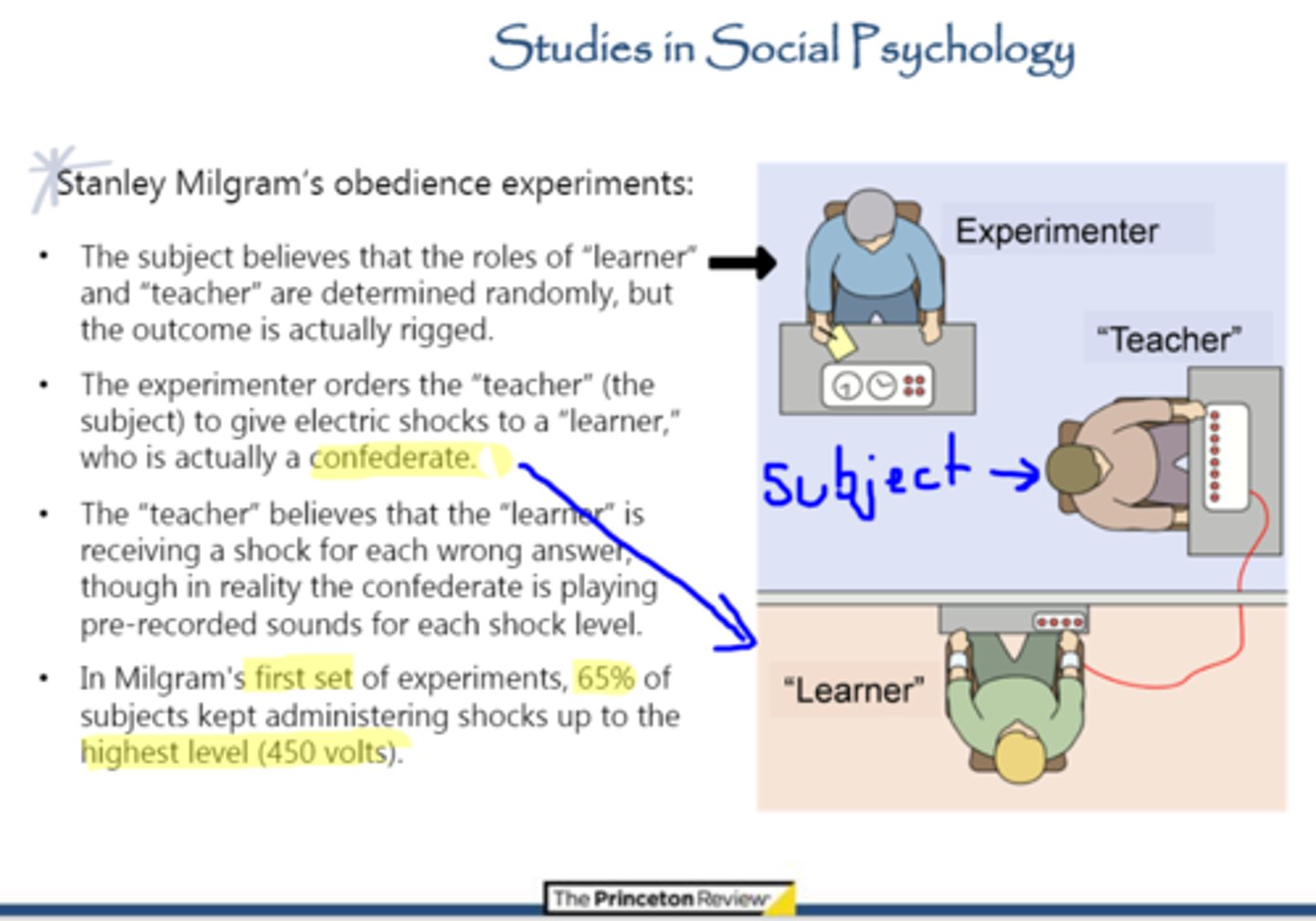
Stanley Milgram Obedience Experiment
aimed to investigate how far individuals would go in obeying authority, even when it involved potentially harming others
Individualism
emphasizes people's own goals over group goals and defines identity mainly in terms of unique personal attributes
Collectivism
prioritizes the goals of important groups(often one's extended family or work group)
Multiculturalism
the quality or condition of a society in which different ethnic and cultural groups have equal status and access but each maintains its own identity, characteristics and more.

Groupthink
the desire for harmony in a decision
-just agree with people just to keep the harmony
Group Polarization
refers to the tendency for a group to make decisions that are more extreme than the initial inclination of its members

Social Loafing
-tendency for people in a group to exert less effort when pooling their efforts toward attaining a common goal then when individually accountable
Diffusion of Responsibility
-created by presence of others
-people feel less responsibility for taking action in a given situation because there are also other people who are responsible
Deindividuation
the loss of self-awareness and self-restraint occurring in group situations that foster arousal and anonymity
-lessens inhibitions against engaging in harmful behavior
Social Facilitation
improved performance on simple or well-learned tasks in the presence of others
-what you do well, you are likely to do even better in front of a crowd
Social Inhibition
the mere presence of others can impair performance on tasks that one is not particularly good at

False Consensus Effect
people often overestimate the levels to which others agrees with them
Superordinate Goal
shared goals that override differences among people and require their cooperation
Social Traps
occur when individuals do not unite and act in their own self-interest to the detriment of the group
Industrial Organizational Psychologists
study best practices in management of work, relationships among people working together, or for a common company or program, and how people feel about work
Burn-out
to become extremely tired or sick by working hard for a long time
Altruism
unselfish regard for the welfare of others
Social Reciprocity Norm
an expectation that people will help those needing their help
Bystander Effect
the tendency for any given bystander to be less likely to give aid if other bystanders are present
Psychodynamic Theories
unconscious processes drive personality
Unconscious(Freud)
mostly unacceptable thoughts, wishes, feelings and memories
Unconscious(Modern Day)
Information processing of which we are unaware
-inaccessible to the conscious mind but which affects behavior and emotions
ID
-a reservoir of unconscious psychic energy that strives to satisfy basic sexual and aggressive drives; blind, impulsive, irrational
Ego
the largely conscious, "executive" part of personality that, according to Freud, mediates among the demands of the id, superego, and reality. The ego operates on the reality principle, satisfying the id's desires in ways that will realistically bring pleasure rather than pain.
Superego
-the part of personality that represents internalized ideas and provides standards of judgements (the conscience) and for future aspirations
Denial
-refusing to believe or even perceive painful realities
Displacement
shifting sexual or aggressive impulses toward a more acceptable or less threatening object of person
Projection
disguising one's own threatening impulses by attributing them to others
Rationalization
offering self-justifying explanations in place of the real, more threatening unconscious reasons for one's actions
Reaction Formation
switching unacceptable impulses into their opposite
Regression
reverting to the behavior or emotions of an earlier developmental stage
Sublimation
transferring of unacceptable impluses into socially valued motives
Repression
Basis defense that banishes from consciousness anxiety provoking arousing thoughts.
Projective Test
a personality test that provides ambiguous images designed to trigger projection of one's inner dynamics.
-projective tests lack validity and reliability
Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
a projective test in which people express their inner feelings and interests through the stories they make up about ambiguous scenes
Rorschach Inkblot Test
the most widely used projective test, a set of 10 inkblots, designed by Hermann Rorschach; seeks to identify people's inner feelings by analyzing their interpretations of the blots