Axonal Specificity
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Growth cone
o Only present at tip of developing neuron
o Later urns into synapse
o Sensory and motor structure that allows neuron/axon to find it way to its target by responding to cues in their environment.
axon growth cone 2 major cytoskeletal components
actin
tubulin
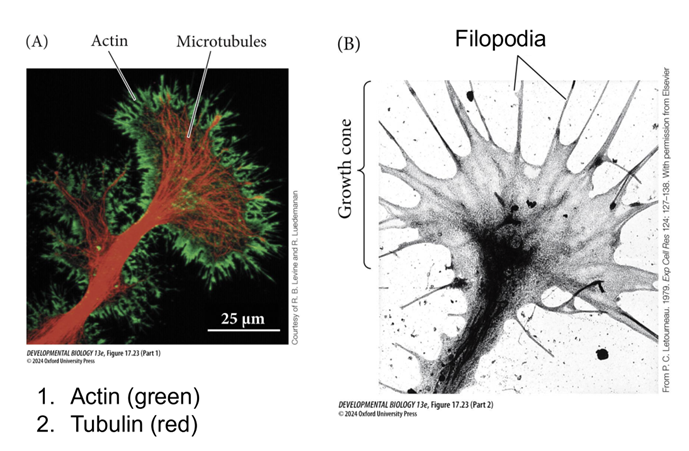
Actin
§ Present in finger like extensions called filopodia
· Filopodia have receptors for guidance cues to know where to go to get to their targets
Tubulin
§ Makes up cytoskeleton on axon
§ When tubulin comes together in long chains it gives us tubules
· Microtubules are present throughout the growth cone
Central domain
o Central region where a lot of microtubules are coming up
Growth cones can encounter two different types of signals
attractive or repulsive
this initiate signaling causing the growth cone to turn
What needs to happen in order for the growth cone to turn?
disassemble the cytoskeleton
Axon elongation
Disassemble the cytoskeleton
· Remove cytoskeleton on repulsive side and build up cytoskeleton on attractive side
Axon needs to be elongated
· Growth cone moves forward by building up microtubules behind it allowing it to move forward
Guidance cues
- Affect cytoskeleton
- Can be attractive or repulsive
- Can be
-Contact meditated
Juxtracrine
o Diffusible
Paracrine
Rho GTPases
- Interpret and relay external guidance signals to the actin cytoskeleton
- Intermediate step between guidance cues binding to receptors and cytoskeleton changes- Interpret and relay external guidance signals to the actin cytoskeleton
Guidance cues binds to receptors which either turns on or turns off Rho GTPases which leads to cytoskeleton changes by either assembling or disassembling actin.
Common Guidance Cues
Ephrins
Netrins
Slit
Semaphorins
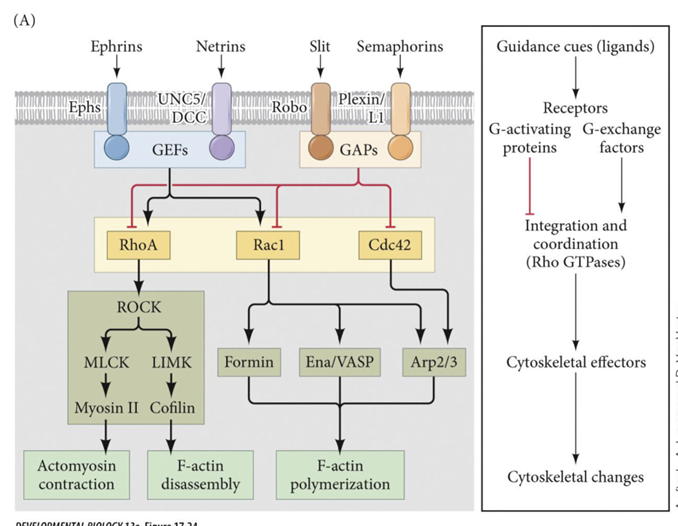
Ephrins
bind to receptor Eph
Netrins
binds to receptors UNC5/ DCC
Slit
binds to receptor Robo
Semaphorins
bind to receptor Plexin
Local translation
- Some mRNA present within the growth cone that can be translated locally in the growth cone to gives the growth cone the proteins it needs
- This allows the growth cone to not have to send a signal all the way back to the cell body and wait for the cell body to send the protein needed
Local translation accomplished by
- tubulin mRNA
o When growth cone receives attractive guidance cue it signals the tubulin mRNA to make proteins
How are Axonal Connections Made?
1. Axon guidance
2. Synaptogenesis
3. Synaptic refinement
Axon guidance
route to target
pioneer and follower growth cones
Synaptogenesis
recognize and bind to target
Synaptic refinement
refinement of target connectivity
Example of Axon Guidance: motor neurons
- Ephrins important guidance cue
- Contact-mediated Axon Guidance – Repulsive
Ephs (receptor) expressed by motor neuron growth cones
Ephrin’s expressed by cells in posterior part of the sclerotome
Ephrins binding to Ephs is repulsive
axons only grow through anterior part not posterior part because posterior region expresses ephrins
What assay was used to determine attractive or repulsive
- Used strip assay where + have ephrins and – do not have ephrins
o Axons only grow in medium without ephrins (-)
Example of Axon Guidance: Commissural axons
- Sit at top of developing neural tube / spinal cord
- Cell body at the top of the spinal cord and they put out axons that are guided down to bottom of spinal cord cross the midline and then go through the spinal cord up towards the brain.
- Netrin 1
Netrin 1
o Attractive cue that guides the axon down to the midline
o DCC present in the growth cone
Robo/Slit regulation of midline crossing by axons of commissural neurons
- Repulsive Axon Guidance
o Slit expressed by midline glial cells
o Robo (receptor for slit) expressed by commissural neuron growth cone
o Commissural neurons upregulate Robo after crossing.
Once growth cone reaches midline it activates a
different signaling pathway that removes DCC and puts Robos into its place.
Topographic map
o There is a spatial arrangement of neurons where adjacent areas of the body or sensory surface are represented by adjacent areas in the brain.
o Ex
§ Receptors in finger
Retinotopic map
o Type of topographic map
o Neighboring points on the retina connect to retinal connect to neighboring neurons in the brain
- Neighboring areas of the visual field connect to neighboring neurons in the brain
Retinal Ganglion Cells
- Multiple guidance cues direct the movement of retinal ganglion cell axon to the optic tectum
- Projections from left eye go to
right tectum and projections from right eye go to left tectum
- When image gets projected to the retina it is flipped
- Ventral RGC send axons to the
- Dorsal RGC send axons and connect to the
medial part of the tectum
lateral part of the tectum
Temporal RGC send to
Nasal RGC send to
caudal/posterior part of tectum
rostral/anterior part of tectum
- Eph receptors produced by
RGCs region of retina and have Eph receptors
in gradient
High temporal and low nasal

- Eph ligands are in the
tecta
o Low rostral and high caudal
- RGC in the nasal regions has
- RGC in the temporal region
low levels of Eph receptors
high levels of Eph receptors
Ephrin ligands are
low anterior and high posterior
- Less eph receptors means it can
grow further to more posterior region of tectum where ephrin ligands are high.
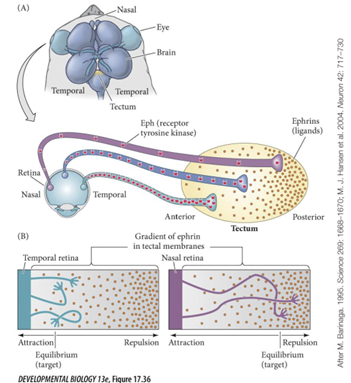
o Low levels of receptor is not enough to
stop / repel them so they have to go to region where there are more ligands
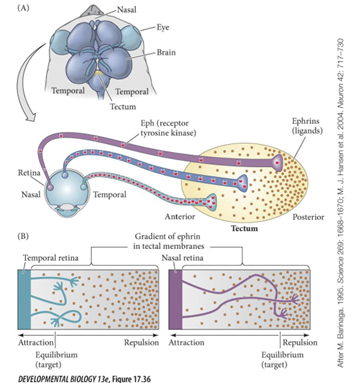
- More Eph receptors stop at
o They stop immediately
more anterior region of tectum because they have so many receptors, they do not need a lot of ligands to cause them to stop
they stop immediately
this gradient results in
orderly connections
Chemo affinity hypothesis
- Complicated nerve fiber circuits of the brain grow, assemble, and organize themselves through the use of intricate chemical codes under genetic control
Synaptogenesis
1. Growth cone comes into contact with myotube (muscle)
2. Growth cone then releases factor Agrin
3. Get formation of synaptic basal lamina
4. Transient polyneuraonal innervation
Axon that stays branches and makes multiple synapses that cluster tougher on fiber
Sheathing by schwann cells
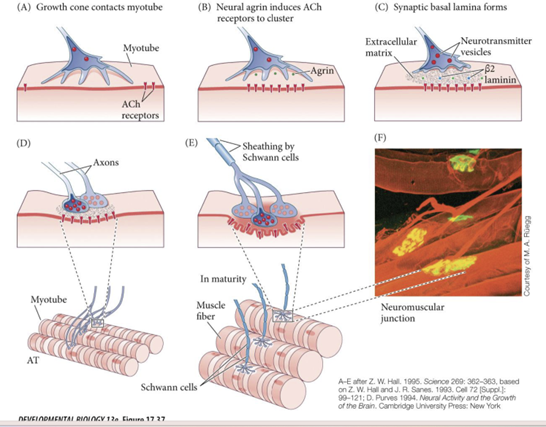
2. Growth cone then releases factor Agrin
a. Activates signaling pathway within the muscle that tells Ach receptors to cluster
Ach NT that makes our muscles contract
3. Get formation of synaptic basal lamina
a. Synaptic basal lamia: Dense ECM matrix between growth cone and muscle
Transient polyneuraonal innervation
a. Temporally multiple motor neurons will innervate the muscle
b. In maturity only one motor neuron innervates one muscle fiber
One wins and one prunes itself
Sheathing by Schwann cells
a. Myelinates the axon
The growth cone is the
sensory and motor structure of the developing neuron and rearranges its
cytoskeletal architecture (actin and tubulin) in response to environmental guidance cues.
Guidance cues can be
contact-mediated or diffusible.
Each of those categories can be further
divided into attractive or repulsive to the growth cone
Guidance cues bind to
receptors in the growth cone, which activates an intracellular pathway that
changes the cytoskeleton and guides the axon to its target.
_____ and signaling through _____ are two important intracellular mechanisms that are activated by
Local translation Rho GTPases
guidance cues and regulate axon guidance.
Motor neurons respond to
ephrins during axon guidance
Changes in growth cone responsiveness to the secreted attractive and repulsive cues secreted from the midline enable
commissural axons to cross the midline and connect the two sides of the central nervous system.
Retinal ganglion cells in frogs and chicks send axons that synapse in specific regions of the optic tectum. This process is mediated by
numerous guidance cues, and target selection appears to be mediated through ephrins
The chemoaffinity hypothesis explains how
neurons can make appropriate connections even
when moved from their original locations.
9. Synaptogenesis requires a series of steps including
contact
receptor clustering
formation of the basal lamina
transient polyneuronal innervation
sheathing by Schwann cells