Cell Division and Meiosis: Key Concepts and Processes
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is the definition of cell division?
Cell division is nuclear division (karyokinesis) followed by cytoplasmic division (cytokinesis).
What are the two main phases of the cell cycle?
The cell cycle is divided into interphase (G1, S, and G2) and the mitotic phase (mitosis and cytokinesis).
What occurs during the G1 phase of the cell cycle?
In the G1 phase, the cell increases in size, produces proteins, ribosomes, and mitochondria, and replicates organelles.
What is the significance of the spindle apparatus in cell division?
The spindle apparatus is crucial during the mitotic phase for separating sister chromatids.
What happens during the S phase of the cell cycle?
During the S phase, DNA is replicated, resulting in sister chromatids.
What is the role of centrioles in cell division?
Centrioles produce spindle fibers that separate sister chromatids during anaphase.
What is the inactive state of cells not actively growing or dividing called?
The inactive state is called G0.
What are the stages of mitosis?
The stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
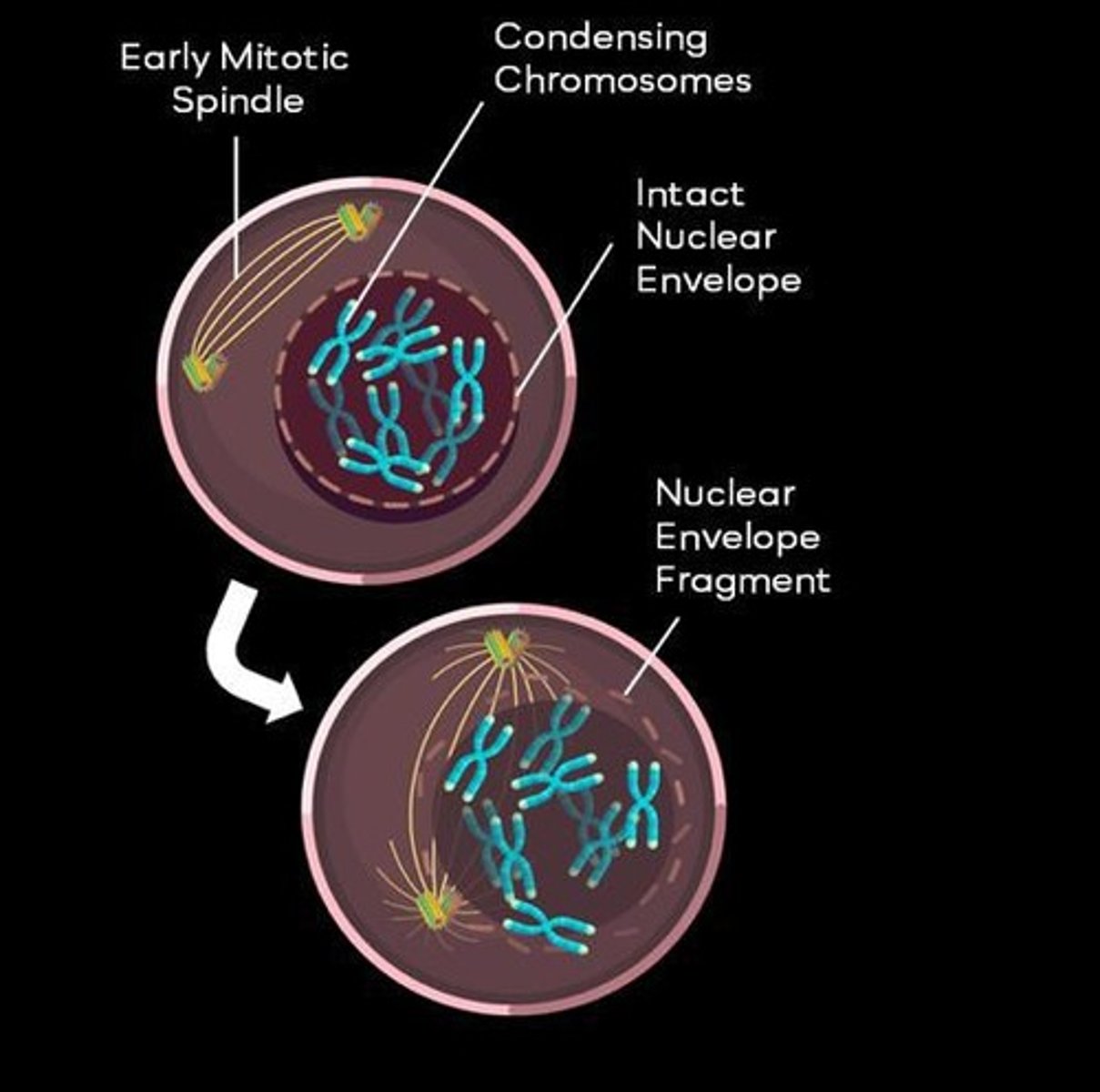
What occurs during prophase of mitosis?
During prophase, the nucleus disassembles, chromatin condenses into chromosomes, and the spindle apparatus begins to form.
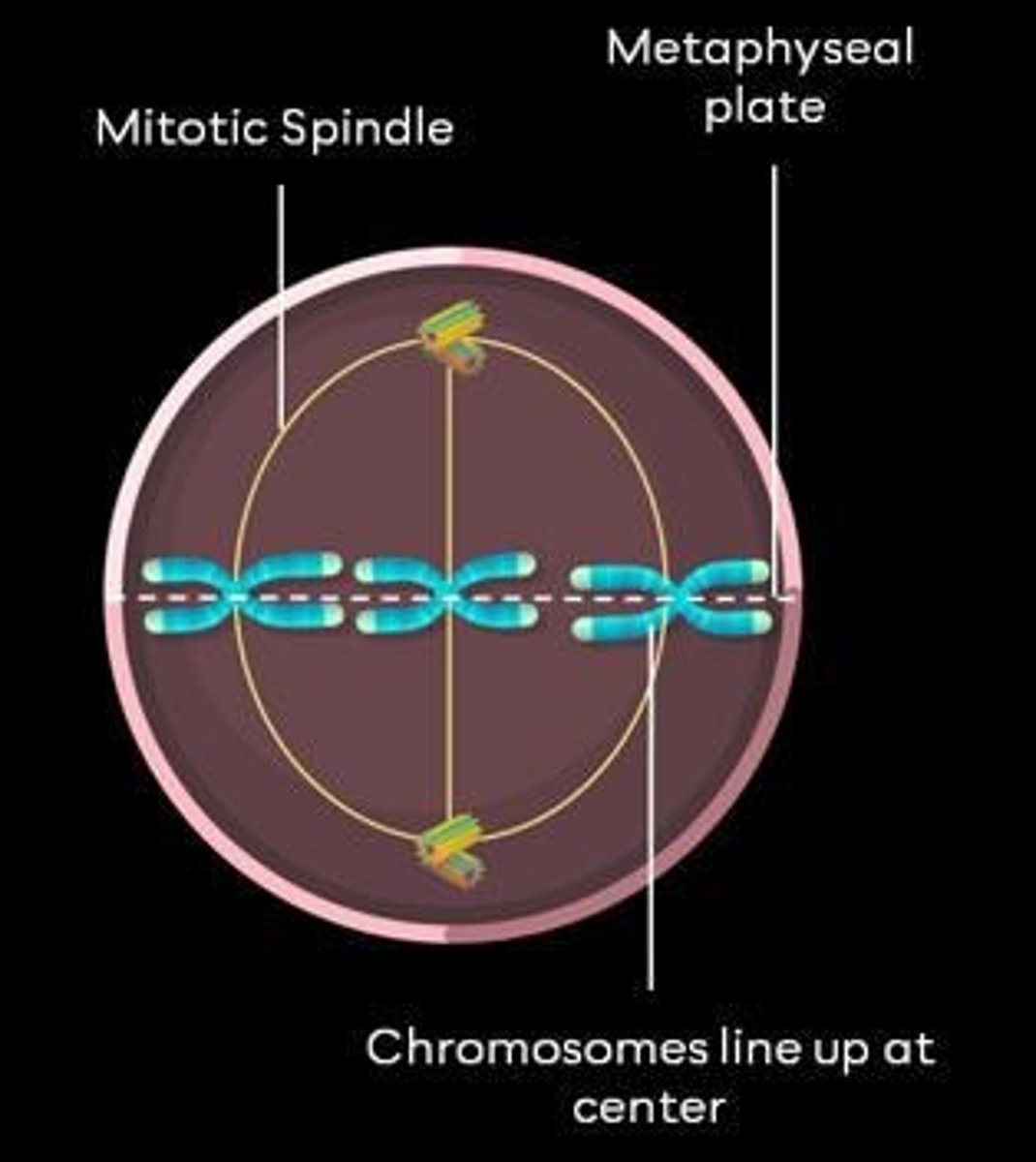
How many chromosomes and chromatids are present during metaphase?
During metaphase, there are 46 chromosomes and 92 chromatids.
What is the outcome of anaphase in mitosis?
In anaphase, sister chromatids are pulled apart, resulting in 92 chromosomes at the end of the phase.
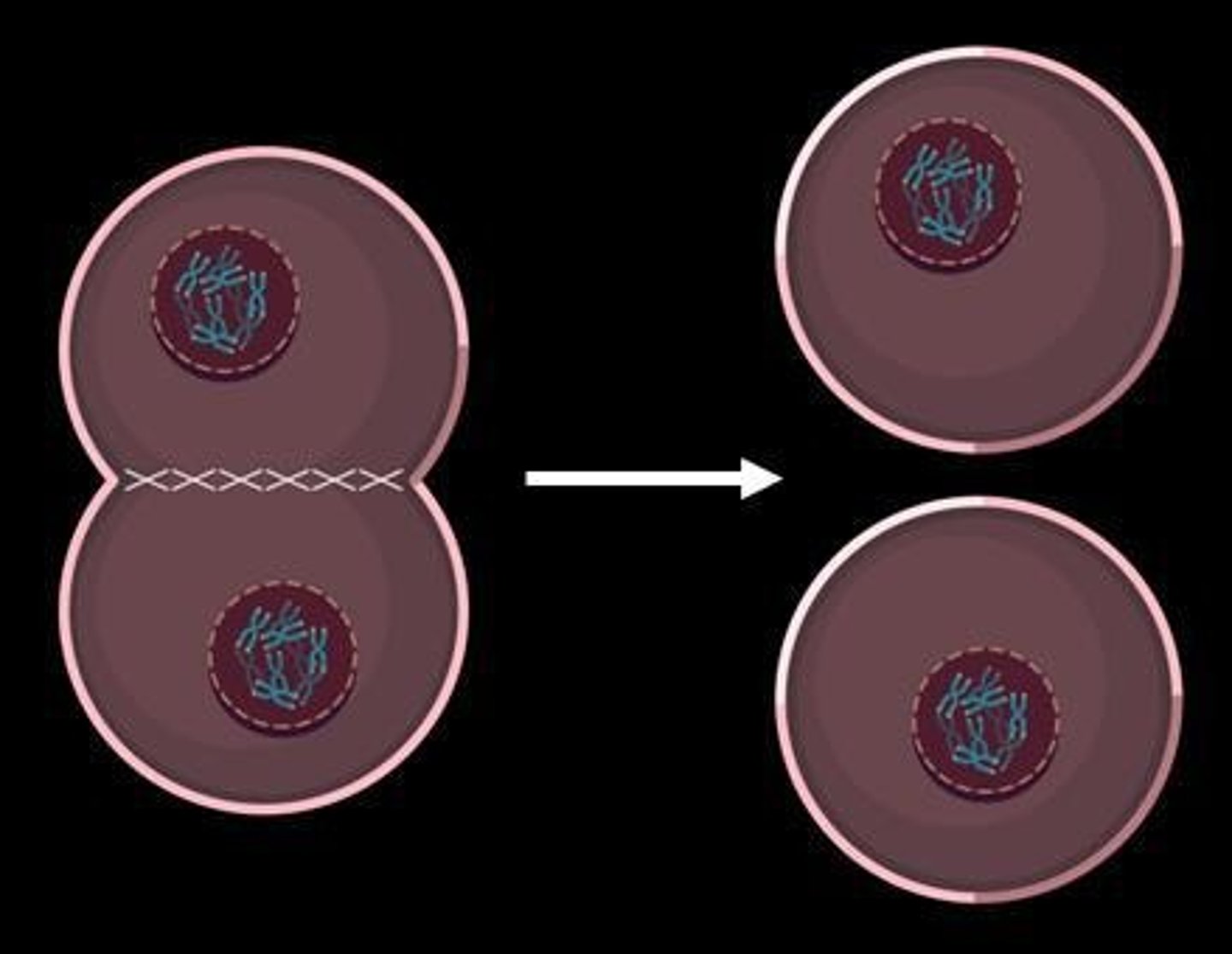
What happens during telophase and cytokinesis?
During telophase, the nuclear envelope re-forms, chromosomes decondense, and cytokinesis results in two cells, each with 46 chromosomes.
What is meiosis and how does it differ from mitosis?
Meiosis produces four non-identical haploid daughter cells from one diploid parent cell, while mitosis produces two identical diploid cells.
What are the two main stages of meiosis?
Meiosis is divided into meiosis I (where homologous chromosomes separate) and meiosis II (where sister chromatids separate).
What is crossing over and when does it occur?
Crossing over is the exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes, occurring during prophase I.
What is independent assortment in meiosis?
Independent assortment occurs during metaphase I, where the random orientation of homologous chromosomes leads to varied allele combinations in gametes.
What is the result of telophase I and cytokinesis in meiosis?
Telophase I and cytokinesis result in two haploid daughter cells, each containing one chromosome from every homologous pair.
What is the significance of genetic linkage?
Genetic linkage refers to genes that are physically closer together on a chromosome being more likely to be inherited together.
How many rounds of cell division occur in meiosis?
Meiosis involves two rounds of cell division.
What is the chromosome number in the daughter cells produced by meiosis?
The daughter cells produced by meiosis have half the chromosome number of the parent cell, resulting in haploid cells.
What is the outcome of anaphase II in meiosis?
In anaphase II, sister chromatids separate, resulting in 46 chromosomes in total.
What happens during metaphase II of meiosis?
During metaphase II, chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate, and sister chromatids are no longer genetically identical due to crossing over.
What is the final result of meiosis II?
Meiosis II results in four genetically distinct haploid daughter cells.
What is the role of microtubules during cell division?
Microtubules attach to kinetochores and help move chromosomes towards the metaphase plate and separate them during anaphase.
What is the significance of the genome to volume ratio (G/V) in cells?
As the G/V ratio decreases, the cell exceeds its genome's ability to produce proteins needed for regulation, leading to cell division.
What is the surface to volume ratio (S/V) and its importance in cell size?
A small S/V ratio makes cellular exchange difficult, leading to cell death or the necessity for cell division to increase surface area.