1.1 Motion 💨
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GCSE CCEA Specification GCSE Physics Double Award Science, Triple Award Science Unit 1: Motion, Force, Moments, Energy, Density, Kinetic Theory and Radioactivity
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
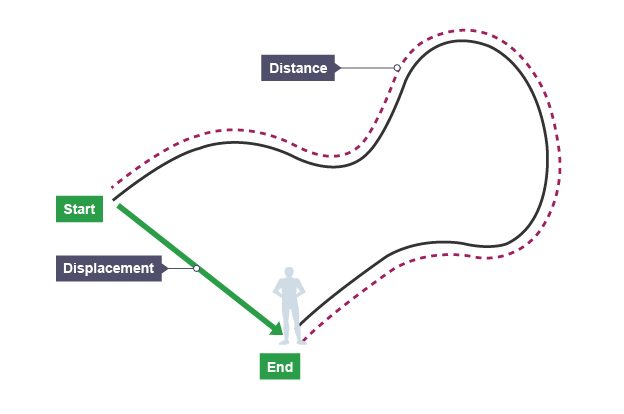
Distance
how far an object moves along its path
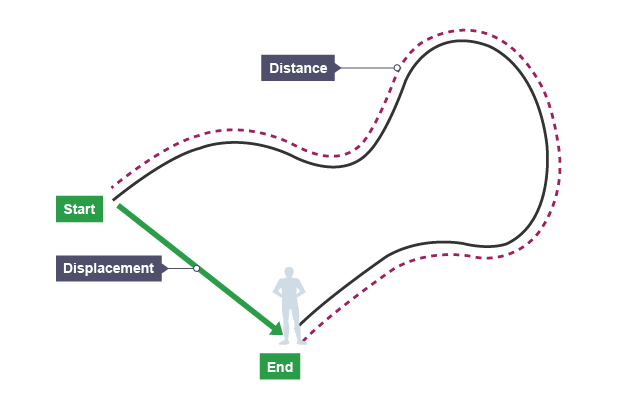
Displacement
how far an object has travelled from its starting point
Speed
the rate of change of distance
The equation linking average speed, distance travelled and time taken
Average speed = distance travelled ÷ time taken
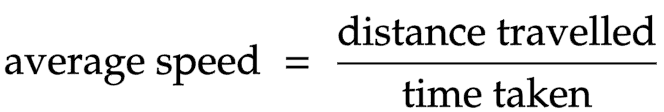
The equation linking uniform average speed, initial speed and final speed
uniform average speed = (initial speed + final speed) ÷ 2
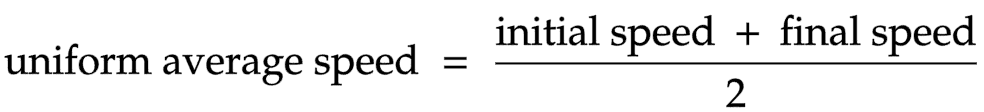
The equation linking rate of change of speed, final speed, initial speed and time taken
rate of change of speed = (final speed – initial speed) ÷ time taken
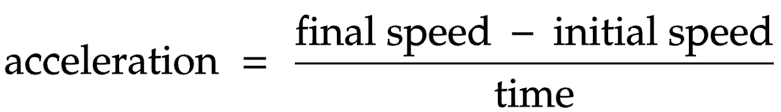
Unit for speed and velocity
Metres per second (m/s)
Unit for distance and displacement
Metres (m)
Unit for time
Seconds (s)
Unit for acceleration/ rate of change of speed
Metres per second squared (m/s²)
Why is average velocity 0
If start and finish are the same, total displacement is 0 so average velocity is also 0
Distance-time graph
graph with distance on the y-axis and time on the x-axis
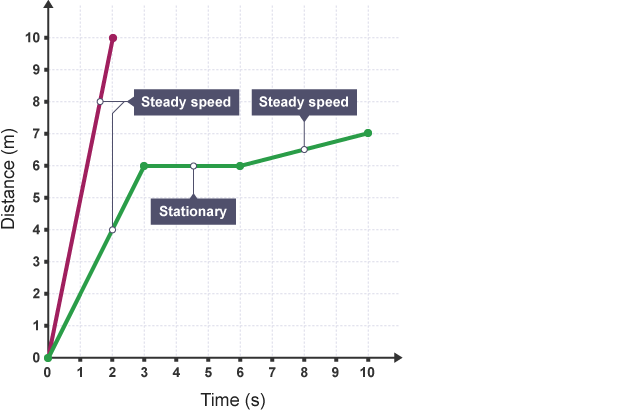
Horizontal line on a distance-time graph
Represents a stationary object
Inclined line on a distance-time graph
Represents an object moving at a constant speed
Curved line on a distance-time graph
Represents an object that is accelerating/ decelerating
How to calculate the speed of an object from a graph
Gradient of a distance-time graph
How to calculate the distance/ displacment from a graph
Area under graph
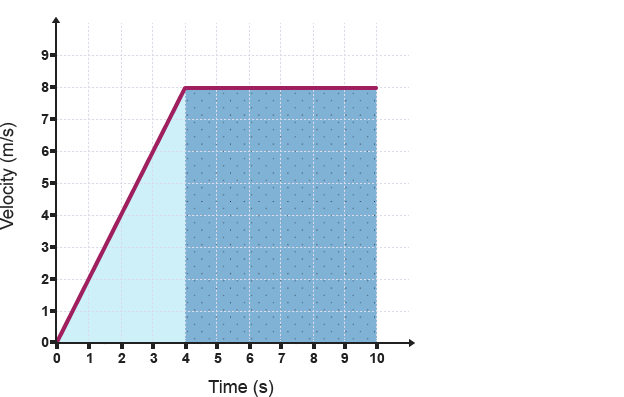
Velocity-time graph
Velocity on the y-axis and time on the x-axis
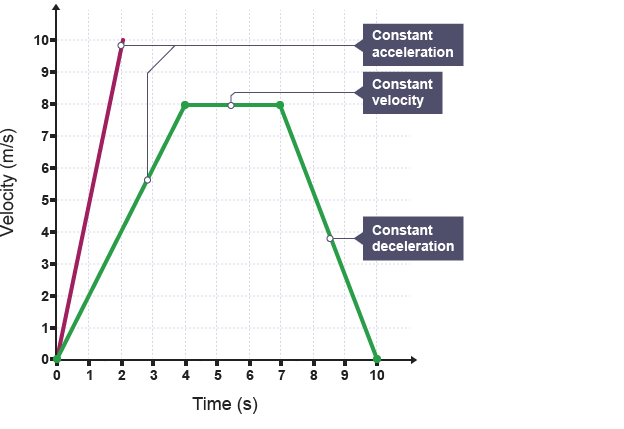
Horizontal line on a velocity-time graph
Represents an object moving at a constant speed
Inclined line on a velocity-time graph
Represents an object accelerating at a constant rate
How to calculate the acceleration of an object from graph
Gradient of a velocity-time graph
Velocity
rate of change of displacement
The equation linking average velocity, displacement and time
Average velocity = displacement ÷ time
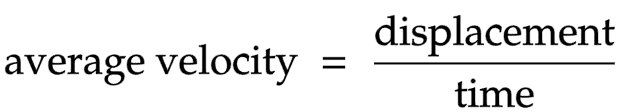
The equation linking uniform average velocity, initial velocity and final velocity
Uniform average velocity = (initial velocity + final velocity) ÷ 2
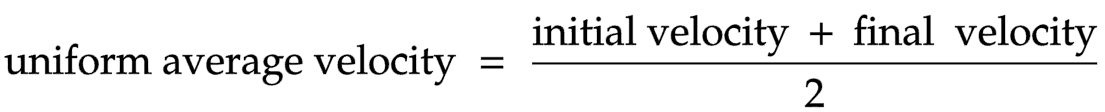
Acceleration
rate of change of velocity over a specific time
The equation linking acceleration, final velocity, initial velocity and time
Acceleration = (final velocity – initial velocity) ÷ time
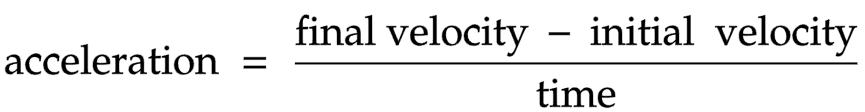
Retardation
When an object is slowing down and its acceleration has a negative value