Mayo - Mitral Regurgitation
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
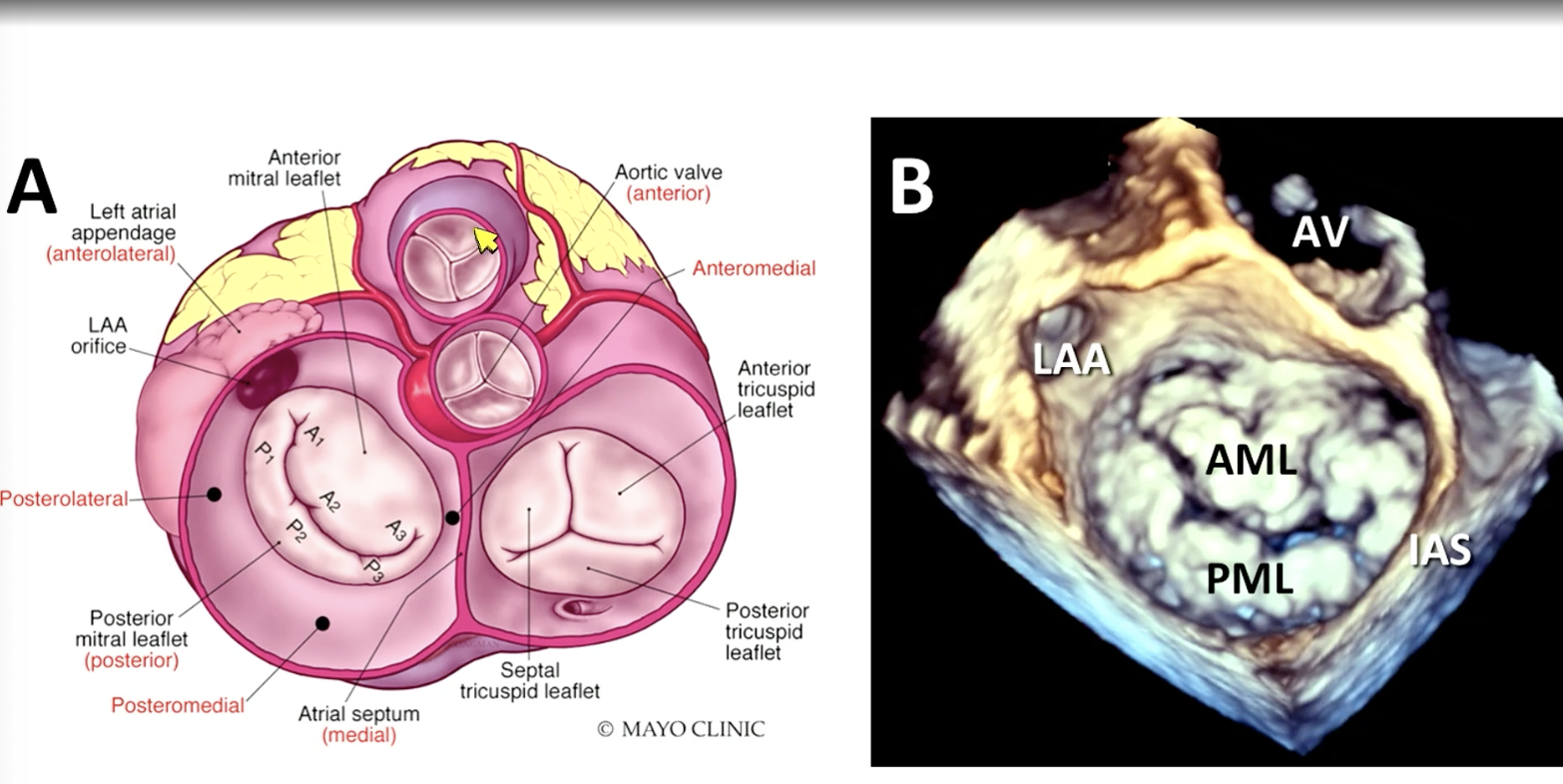
FYI mitral valve anatomy
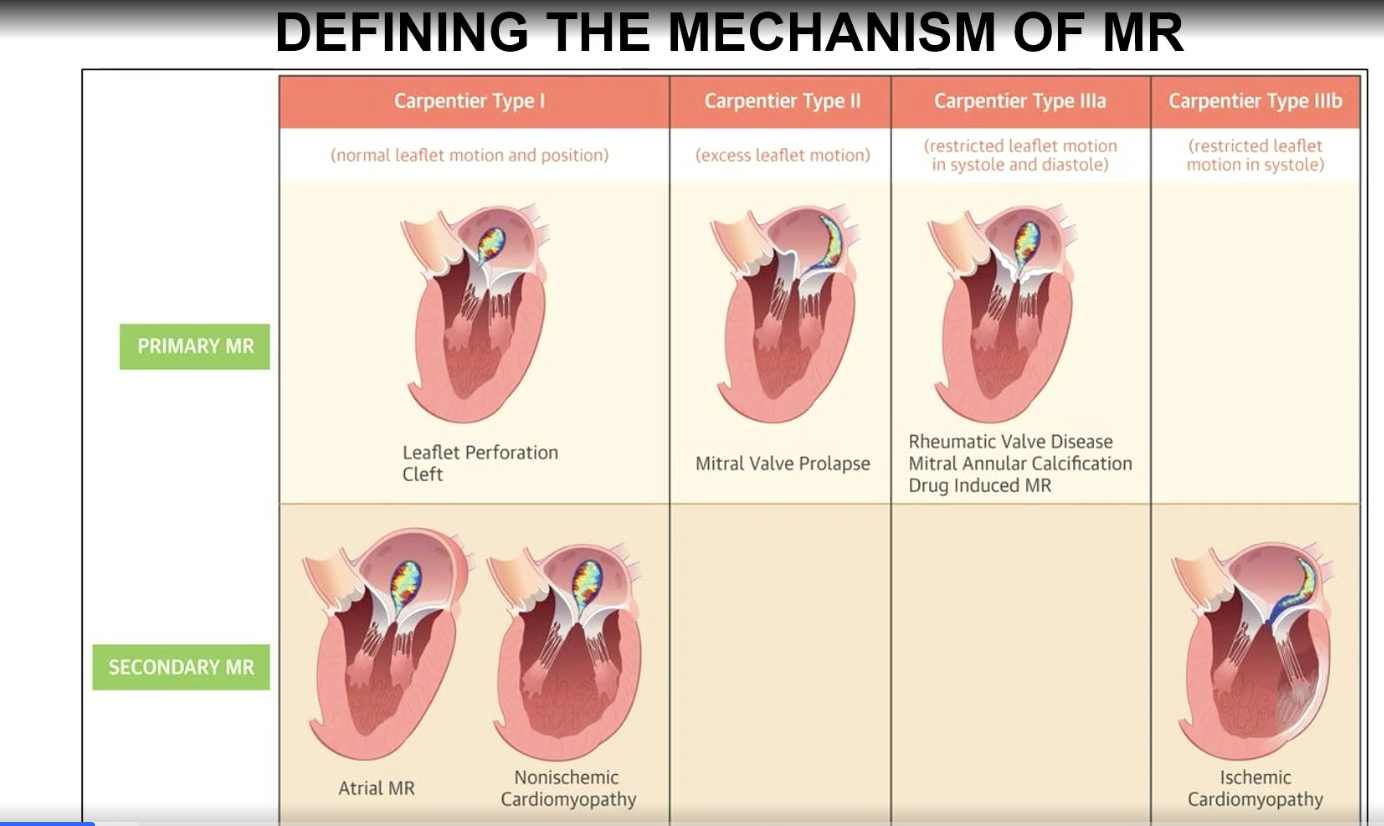
Carpentier Type I mechanism of MR
Normal leaflet motion and position
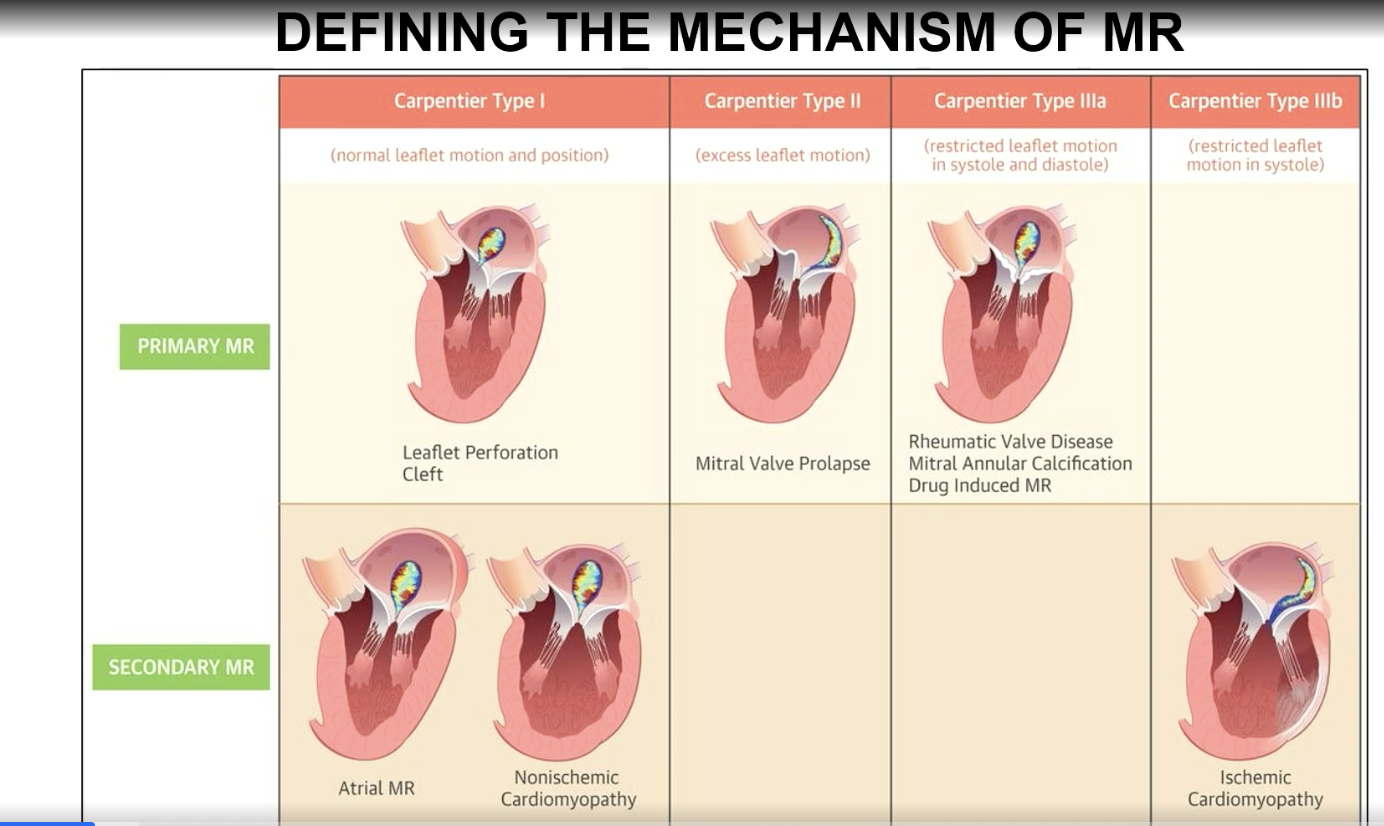
Carpentier Type II mechanism of MR
excess leaflet motion
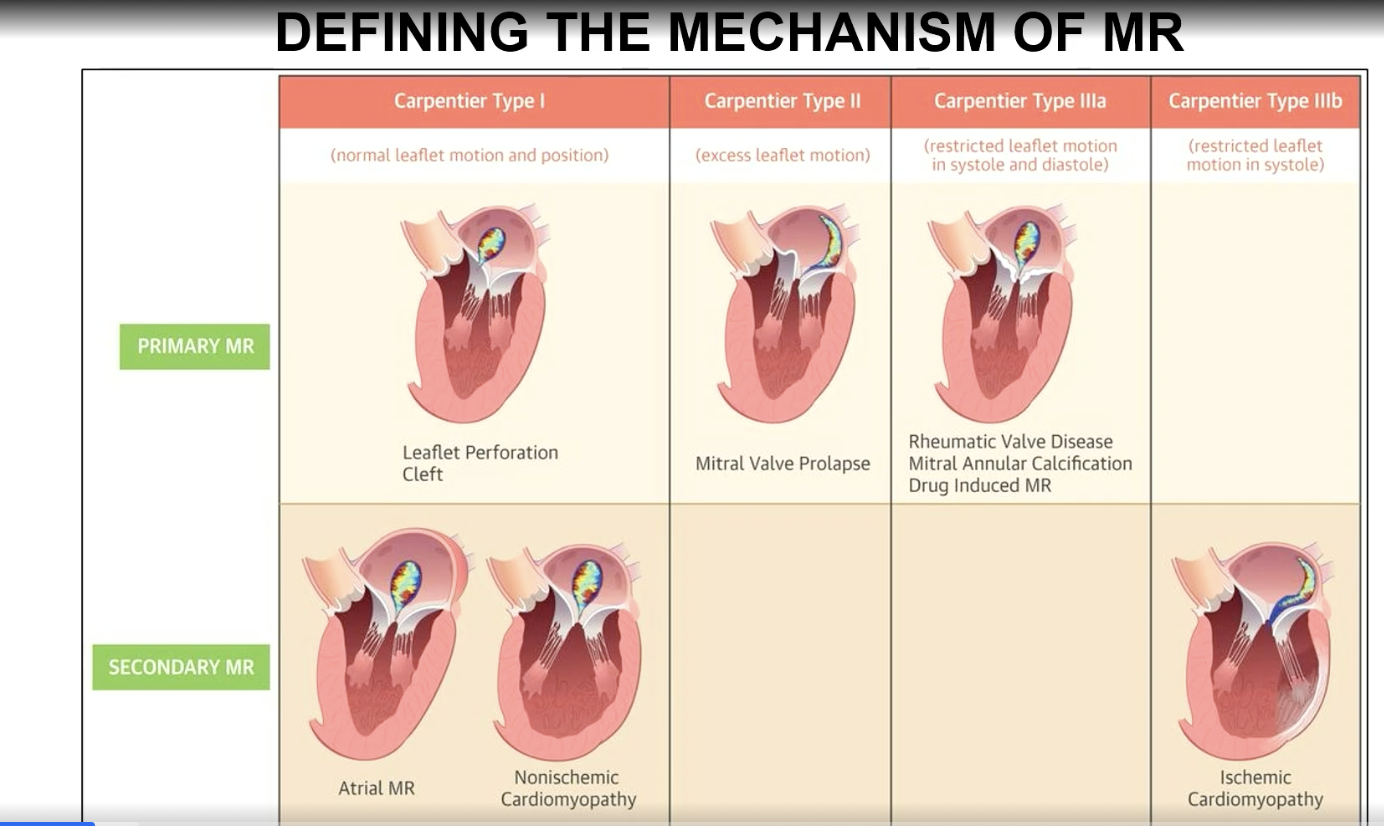
Carpentier type IIIa classification
Restricted leaflet motion in systole and diastole
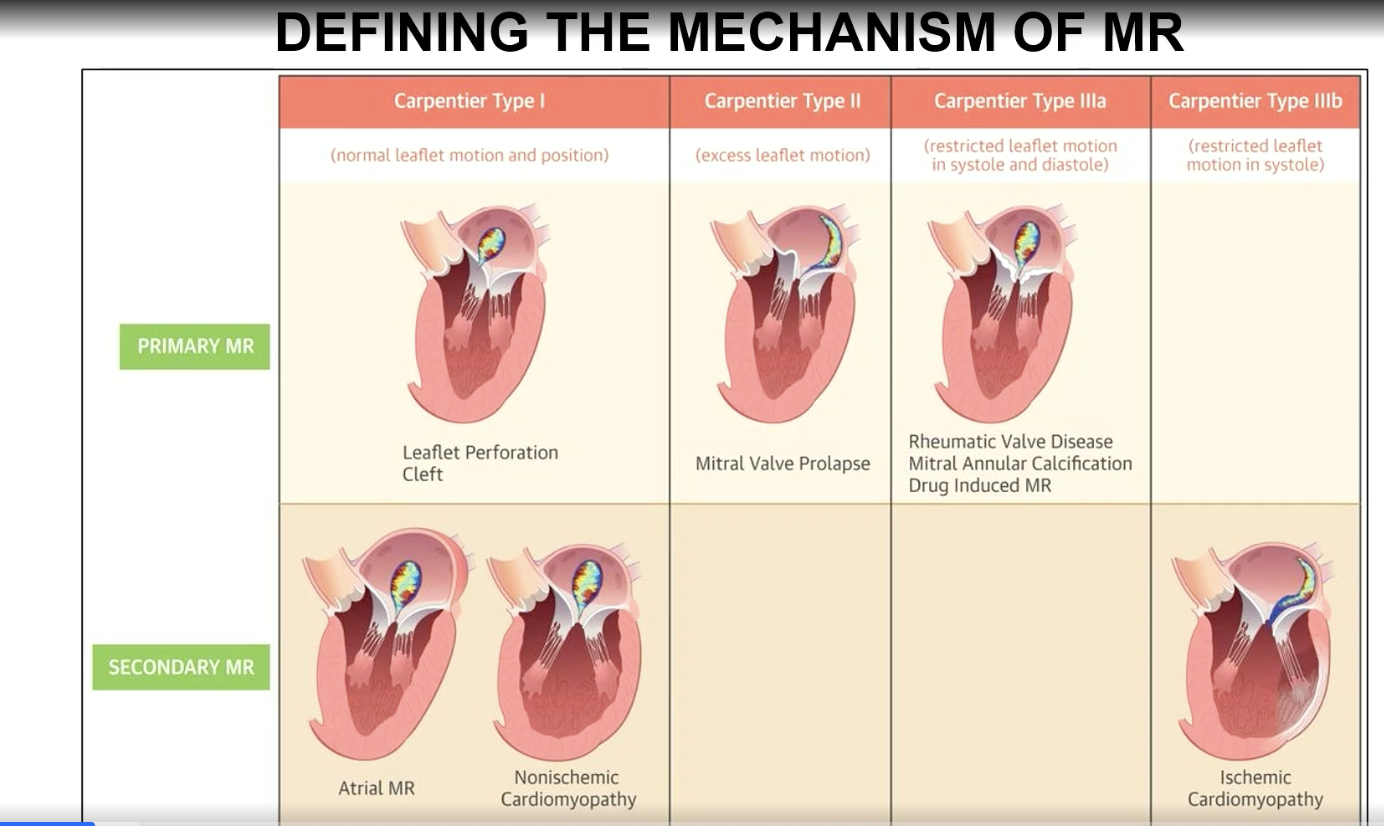
Carpentier type IIIb mechanism
restricted leaflet motion in systole (think ischemic CM which is a a secondary MR)
What is the timing of SAM-mediated MR?
FYI this is a type of MR that doesn’t fall into the Carpentier’s classification
Mid or late systolic timing (matches obstruction)
FYI typically this will go away if we eliminate the obstruction as it is dynamic
MR type I (normal leaflet motion) — treatment?
Potentially repairable
MR type II (increased leaflet mobility) — management?
Highly repairable
Type IIIA MR (decreased leaflet mobility; both systolic and diastolic) — do your repair or replace?
Not repairable, requires replacement
FYI often they are associated with mitral stenosis, that’s why
Type IIIb MR (decreased mobility — systolic only) — management?
Medical therapy FIRST, then repair/replacement is second line
In ASYMPTOMATIC severe PRIMARY mitral regurgitation, which patient’s is surgery indicated? (4)
LVEF < 60%
LV end systolic diameter > 40 mm
New atrial fibrillation
PASP > 50 mmHg
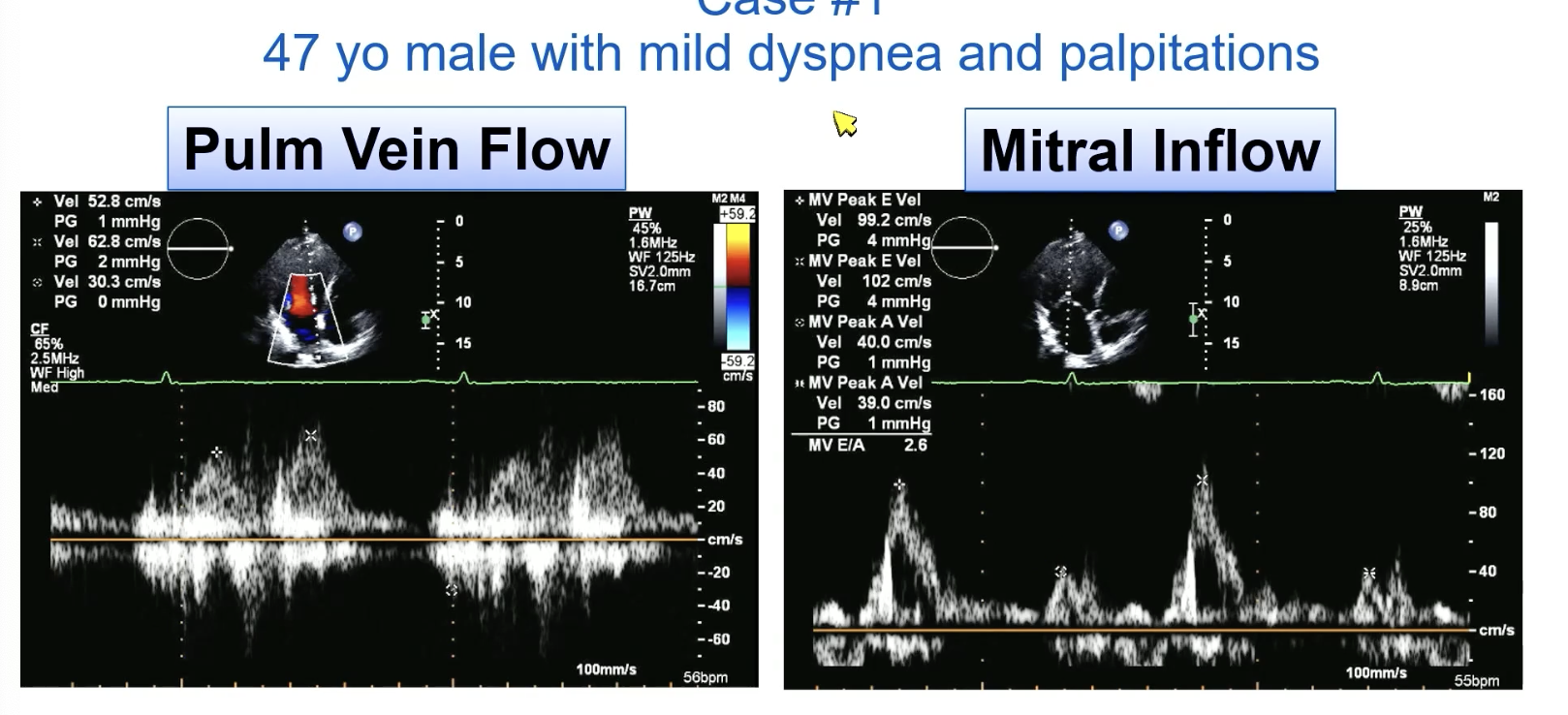
FYI this is systolic blunting of the pulmonary veins
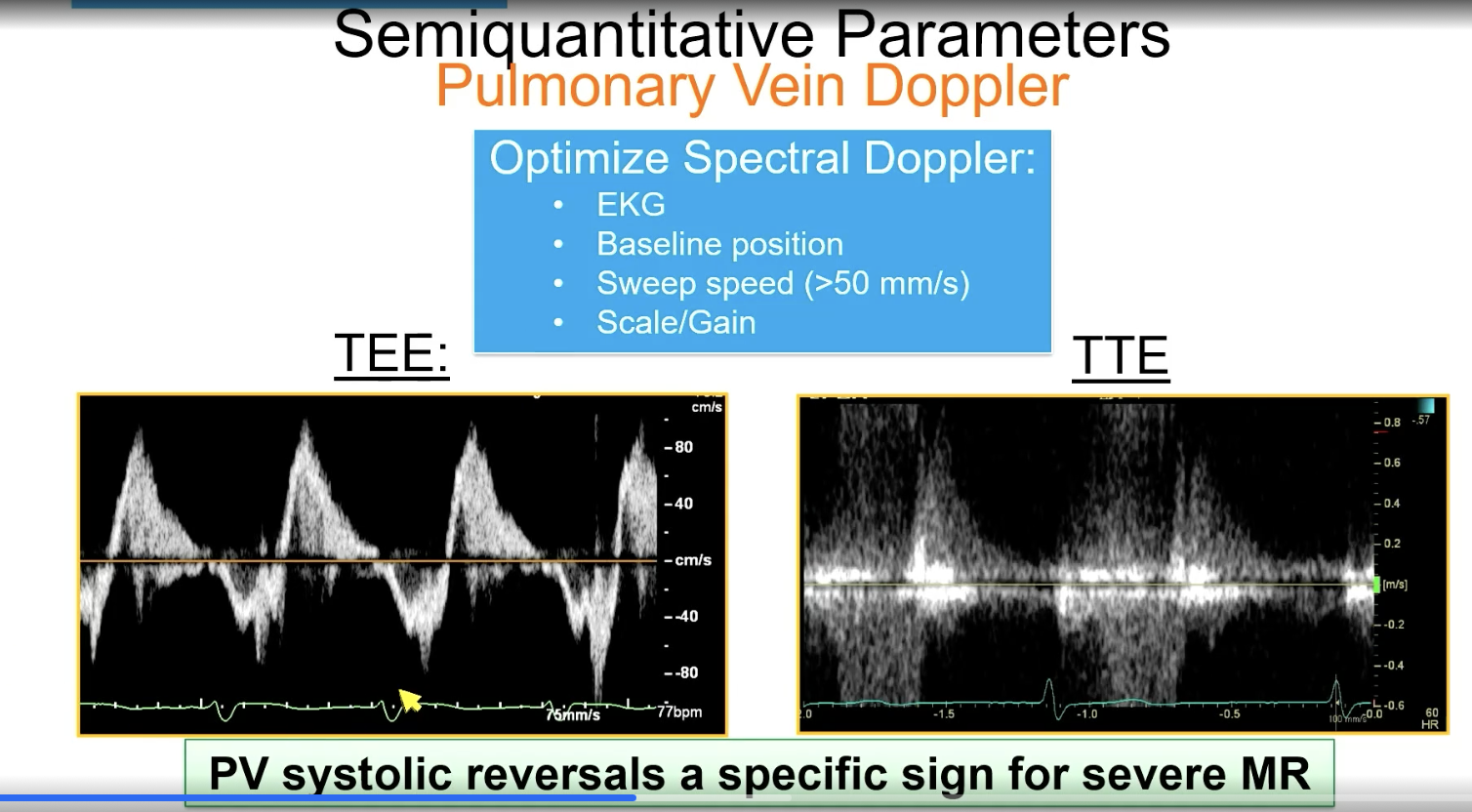
FYI this is PV systolic reversal
FYI
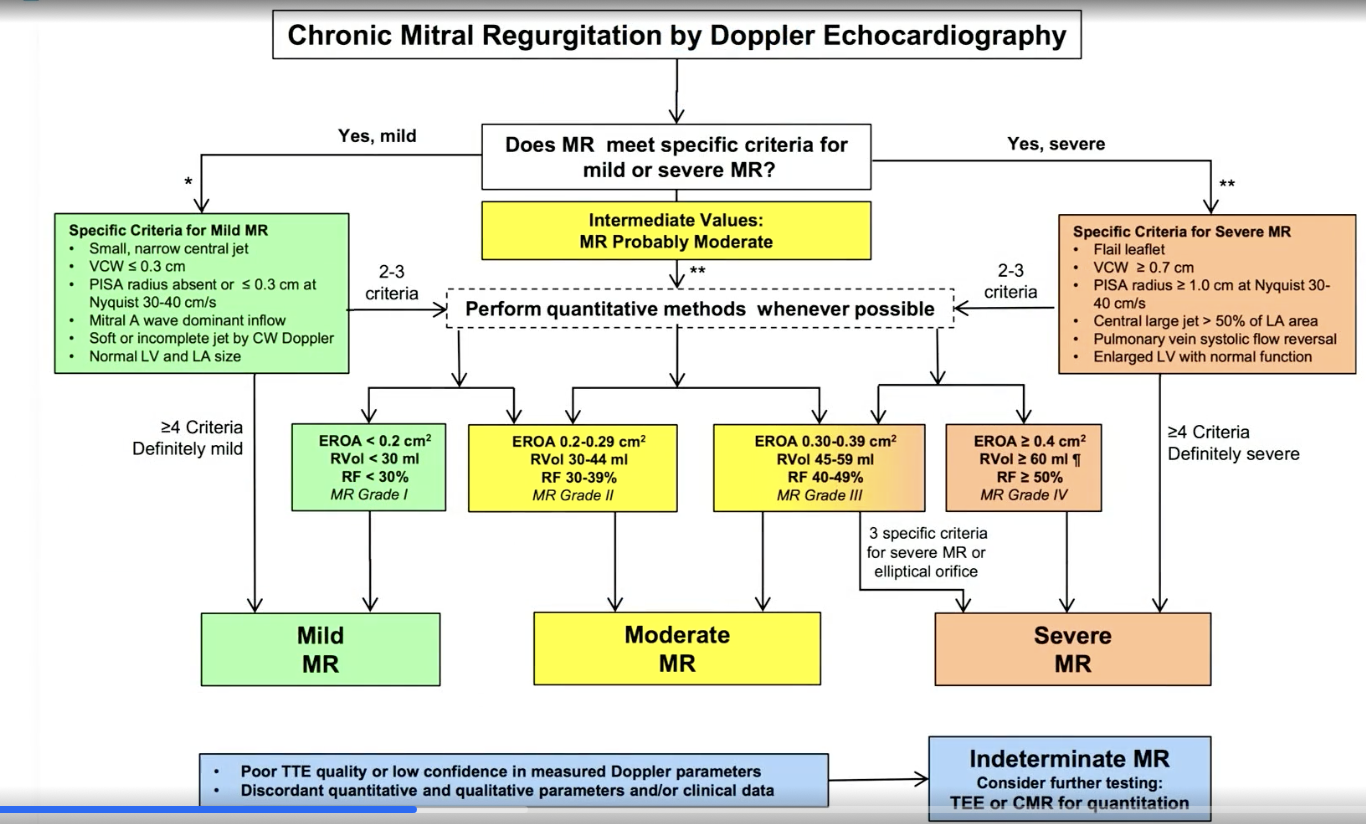
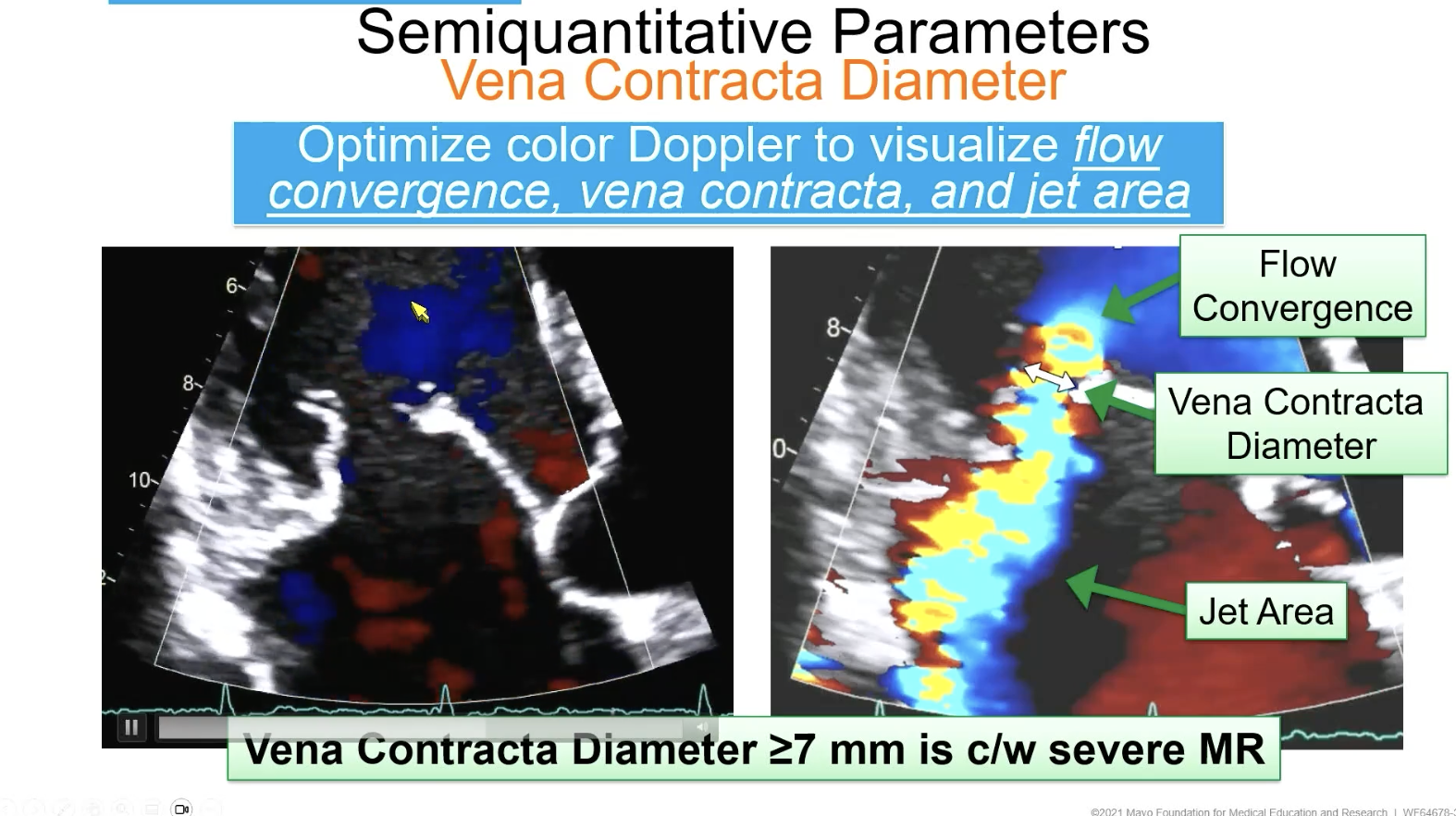
To measure MR vena contracta, what VC diameter is consistent with severe MR
> 7 mm
For pulmonary vein doppler, you want the baseline to be in the center and the sweep speed to be…
> 50 mm/s
The early driving pressure from systole to diastole of the left atrium from MR is what causes the
V wave to change
E wave > 1.2 m/s (high E/A ratio) suggests
severe MR or restrictive filling
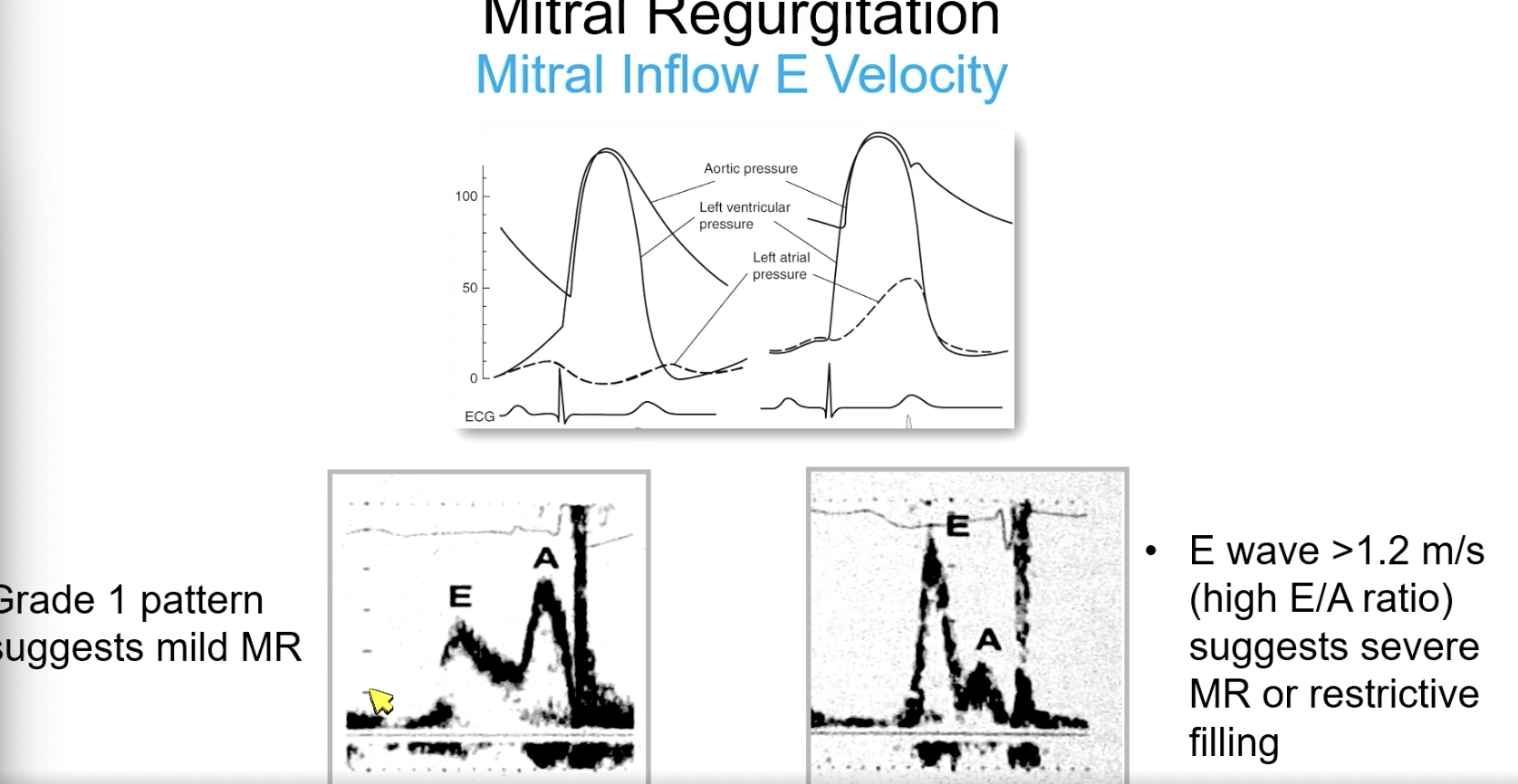
Low E velocity is indicative of
mild MR
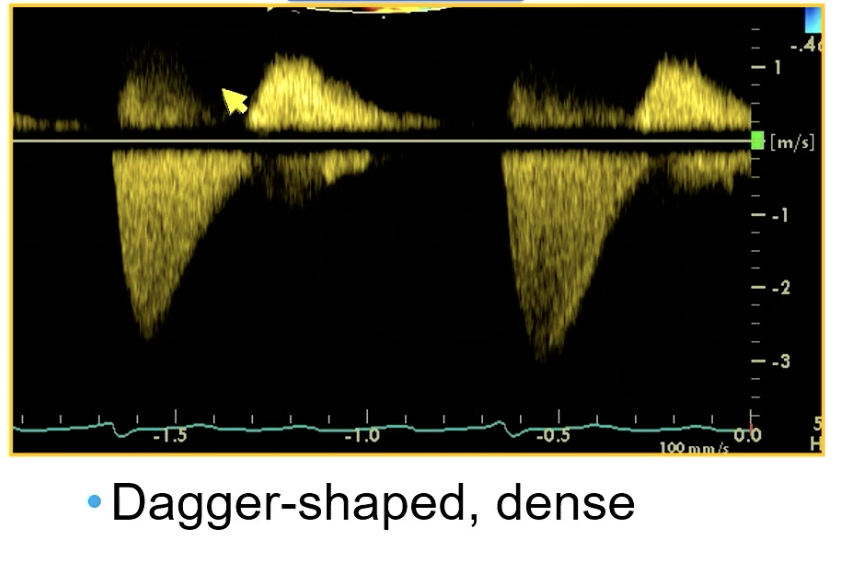
CW through mitral showing
severe MR
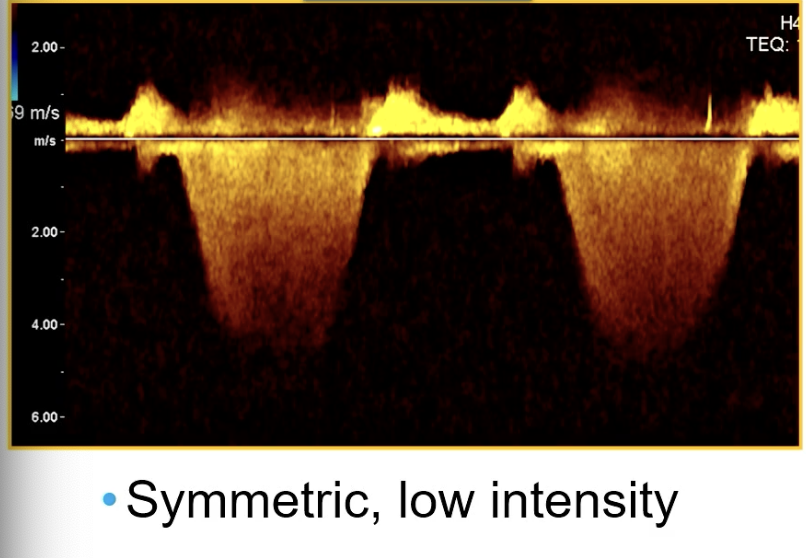
CW through mitral valve
Mild MR
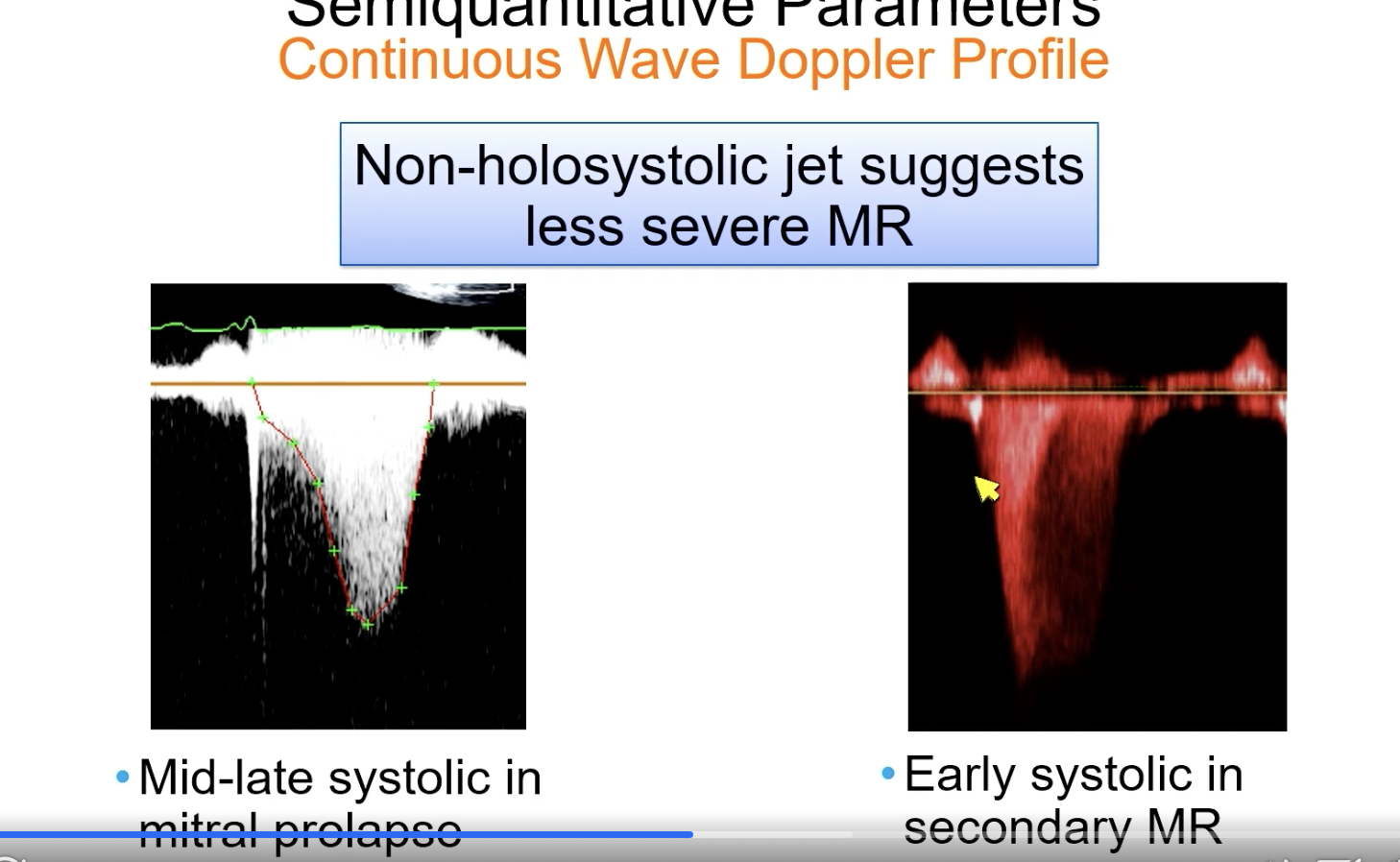
Non-holosystolic. CW doppler jet for MR suggests…
less severe MR
In asymptomatic MR, as ERO increases….
they do worse and survival decreases
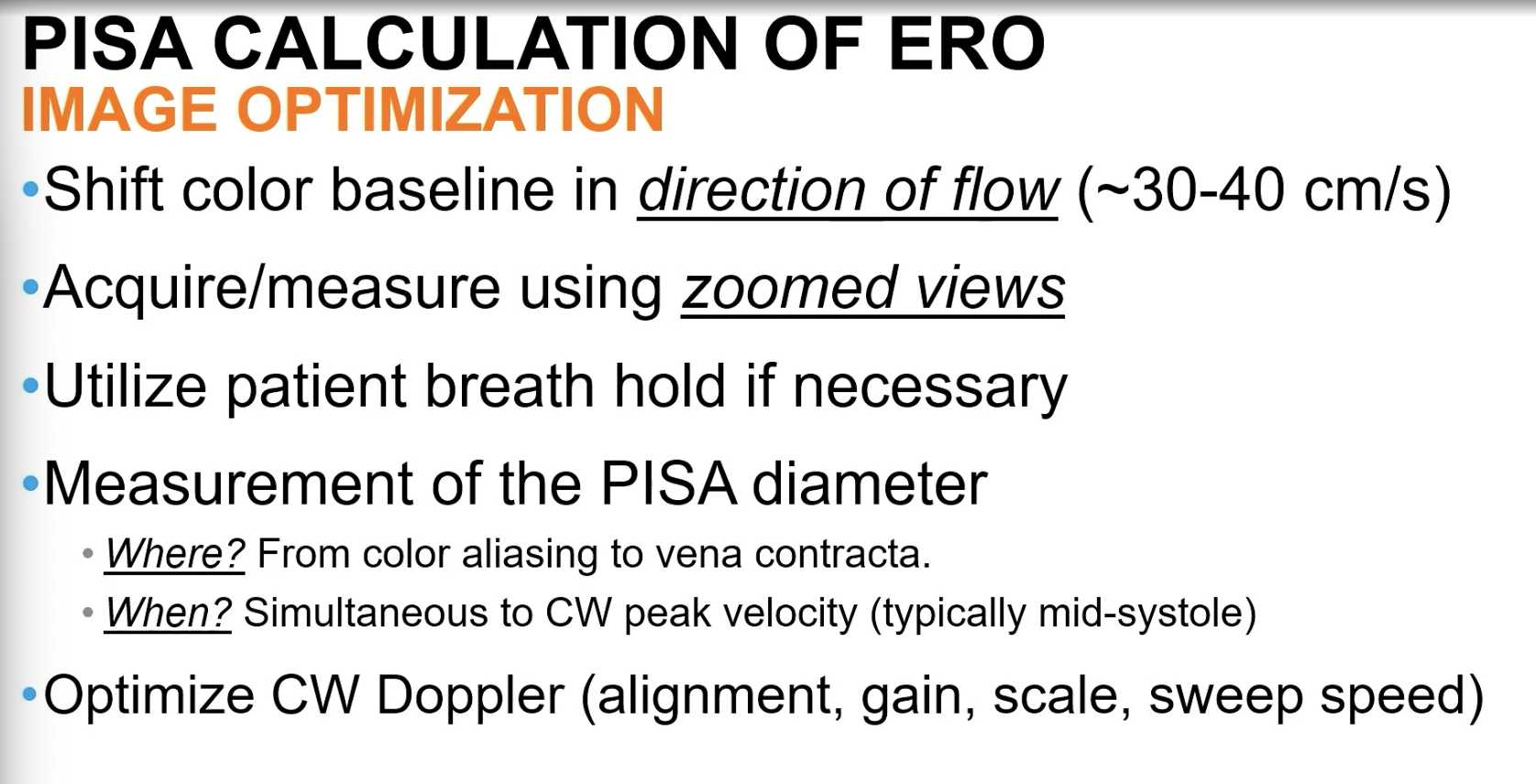
Remember that flow at regurgitant orifice equals flow at the PISA shell. So what is the equation for ERO with PISA for MR?
ERO = [ Pisa surface area x aliasing velocity ] / MR velocity
FYI PISA surface = 2𝝿R2
![<p>ERO = [ Pisa surface area x aliasing velocity ] / MR velocity</p><p></p><p>FYI PISA surface = 2<span>𝝿R<sup>2</sup></span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a09dbd1e-6fcd-43e6-bc23-421d25de4eaa.png)
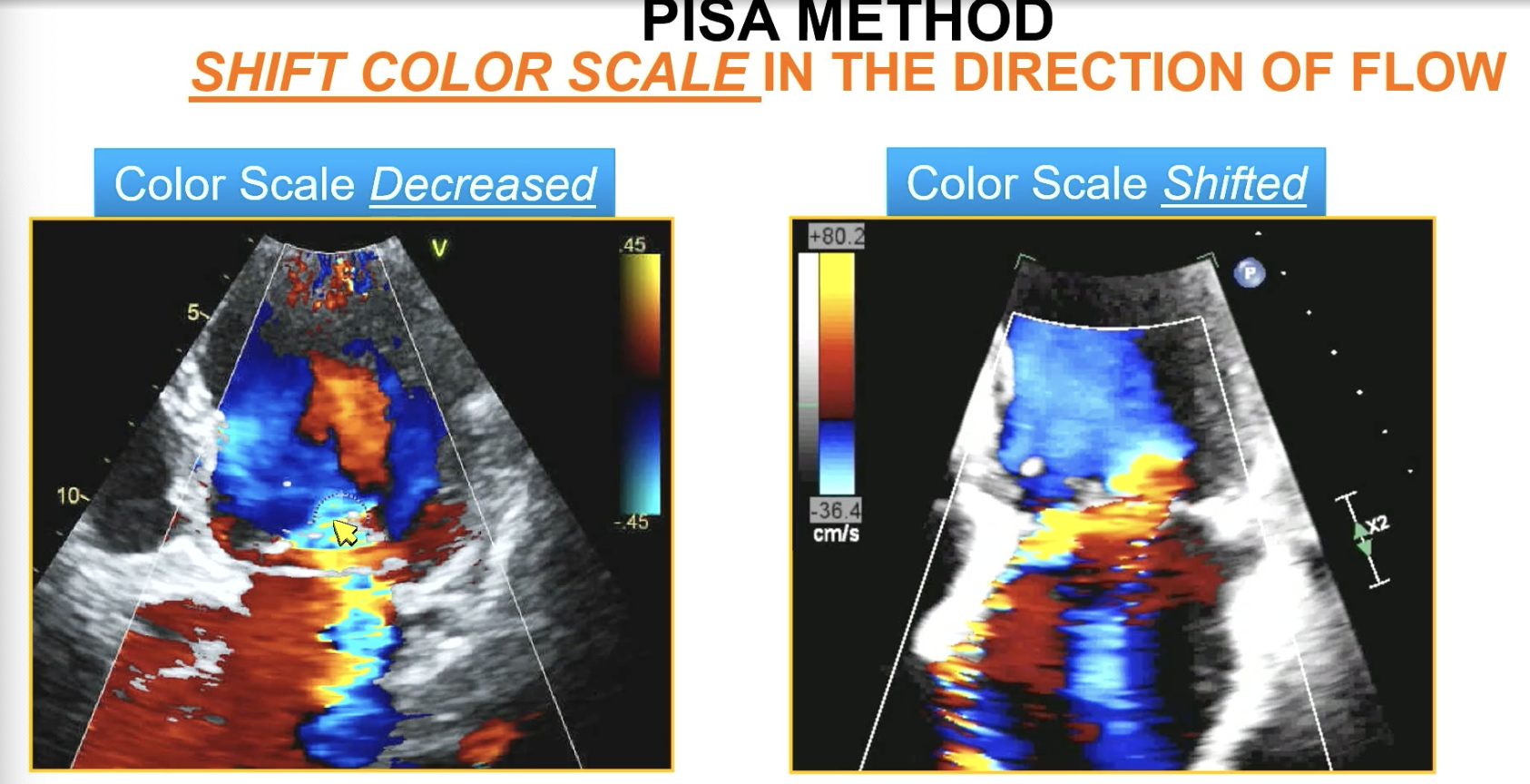
Shift the color baseline to get a Pisa toward…
the direction of flow (should be ~ 30-40 cm/s)
FYI used to “decrease” the color scale which is different. Not as good and end up with way more aliasing.
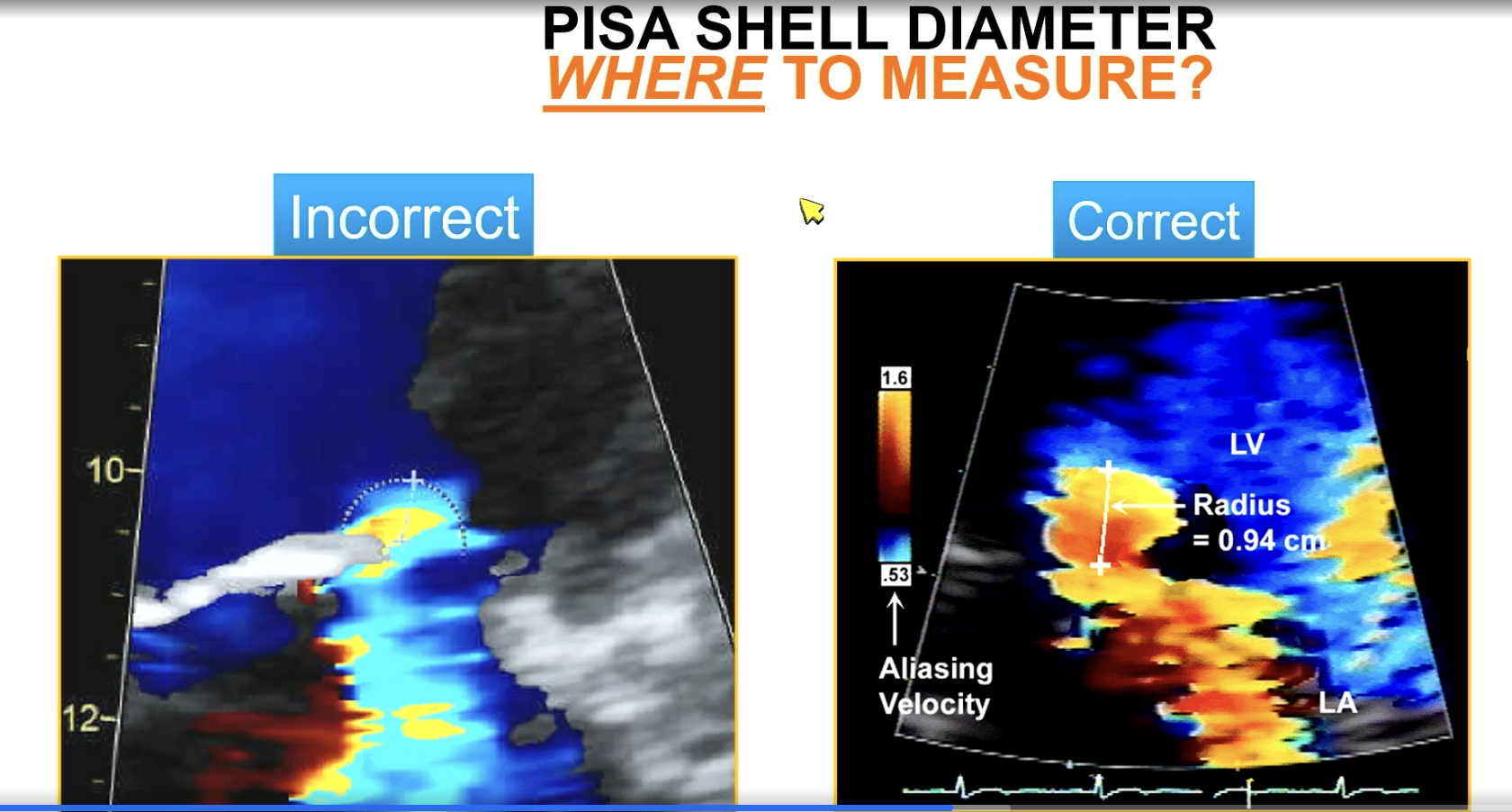
Measure the PISA diameter from the color aliasing to…
vena contracta
For MR, which side (LA or LV) do you measure PISA from?
You measure it on the side the flow is converging aka the LV side for MR!!! Because flow is converging and going back in the LA
Mitral valve prolapse (primary MR) without flail: the highest velocity tends to be in…
Mid to late systole (which tends to correlate with the largest ERO)
FYI this is versus prolapse with flail
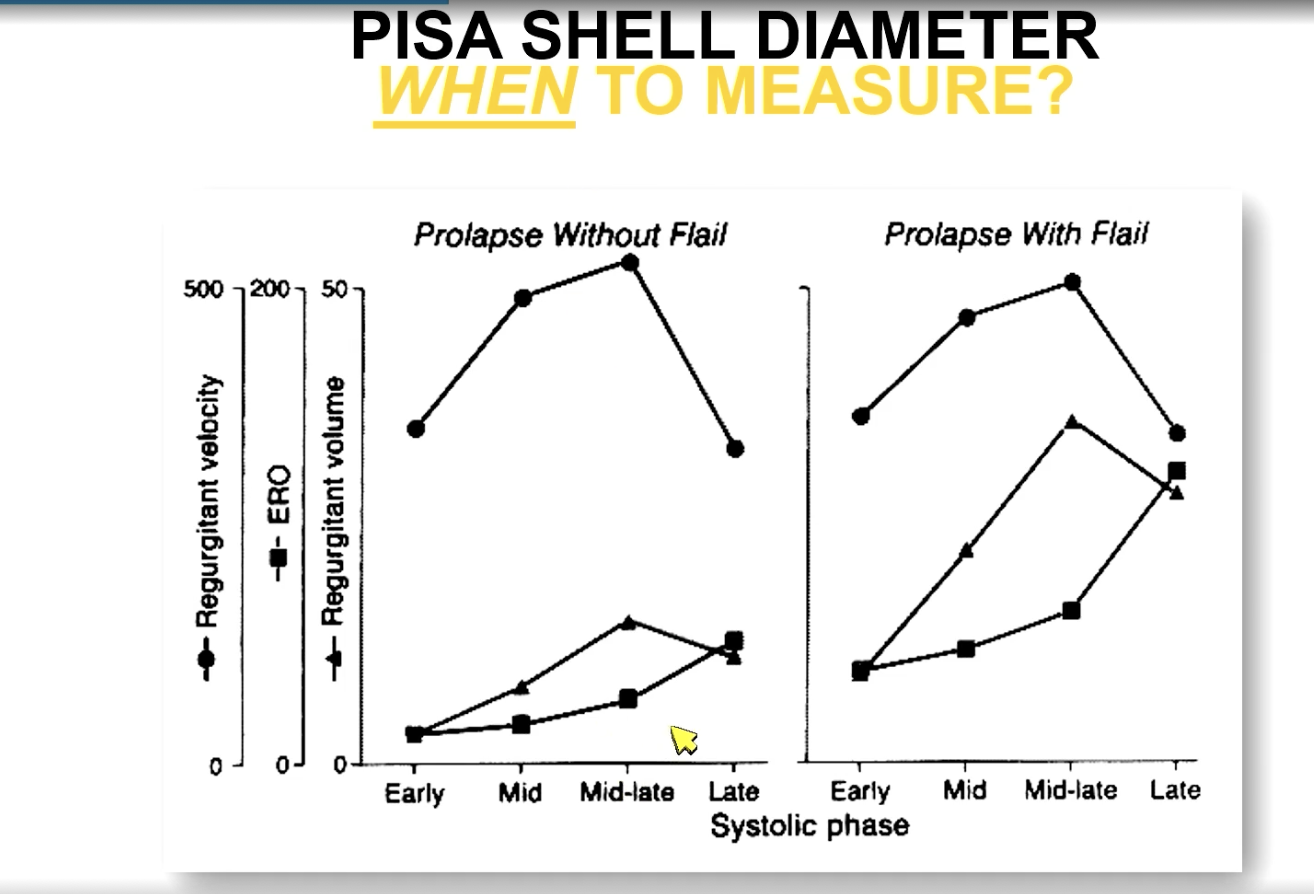
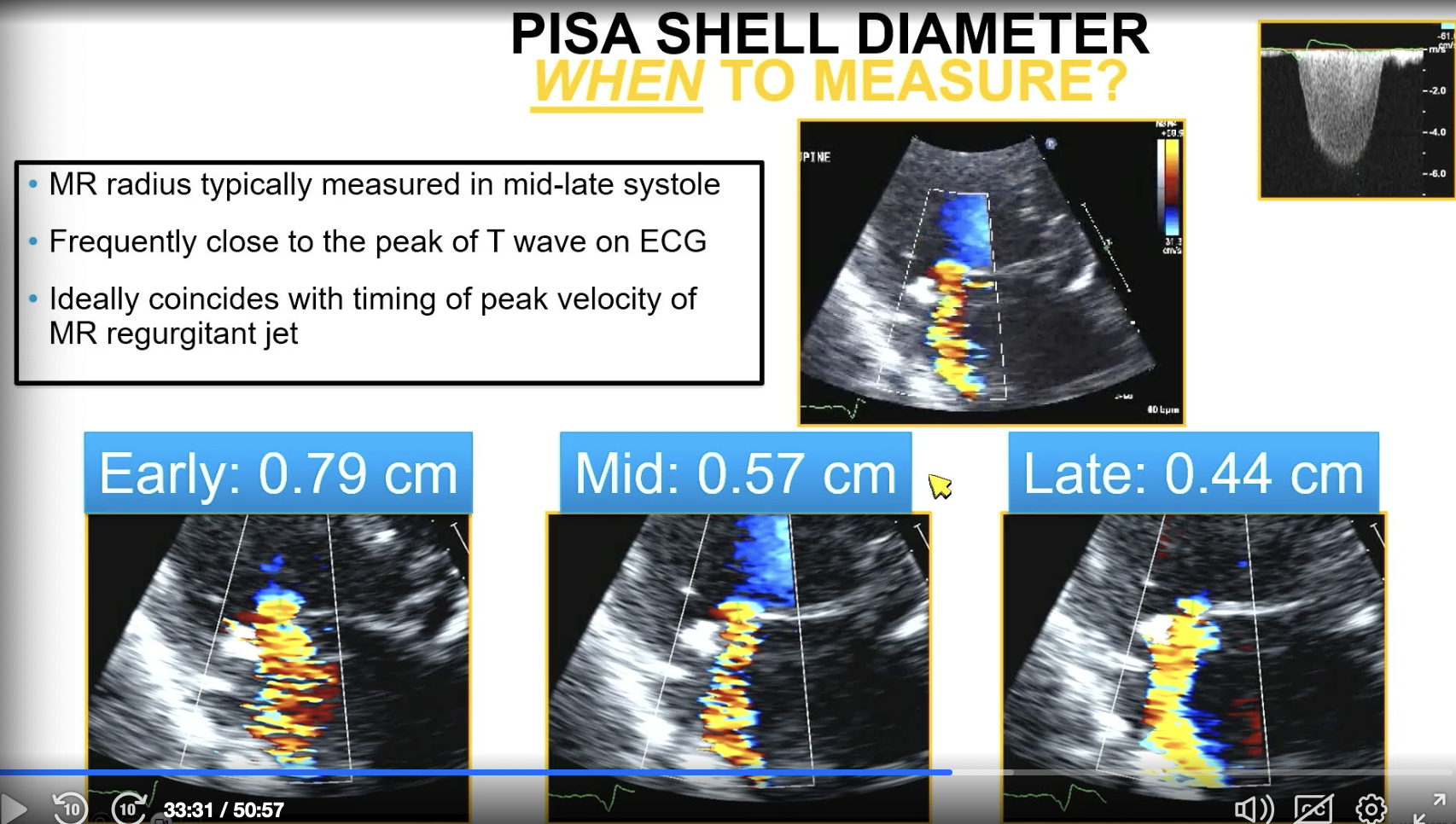
In primary MR such as prolapse without flail, when do you measure the PISA diameter?
You measure it in mid to late systole (close to the peak of the T wave)
FYI the image shows what happens if you don’t measure at the right time
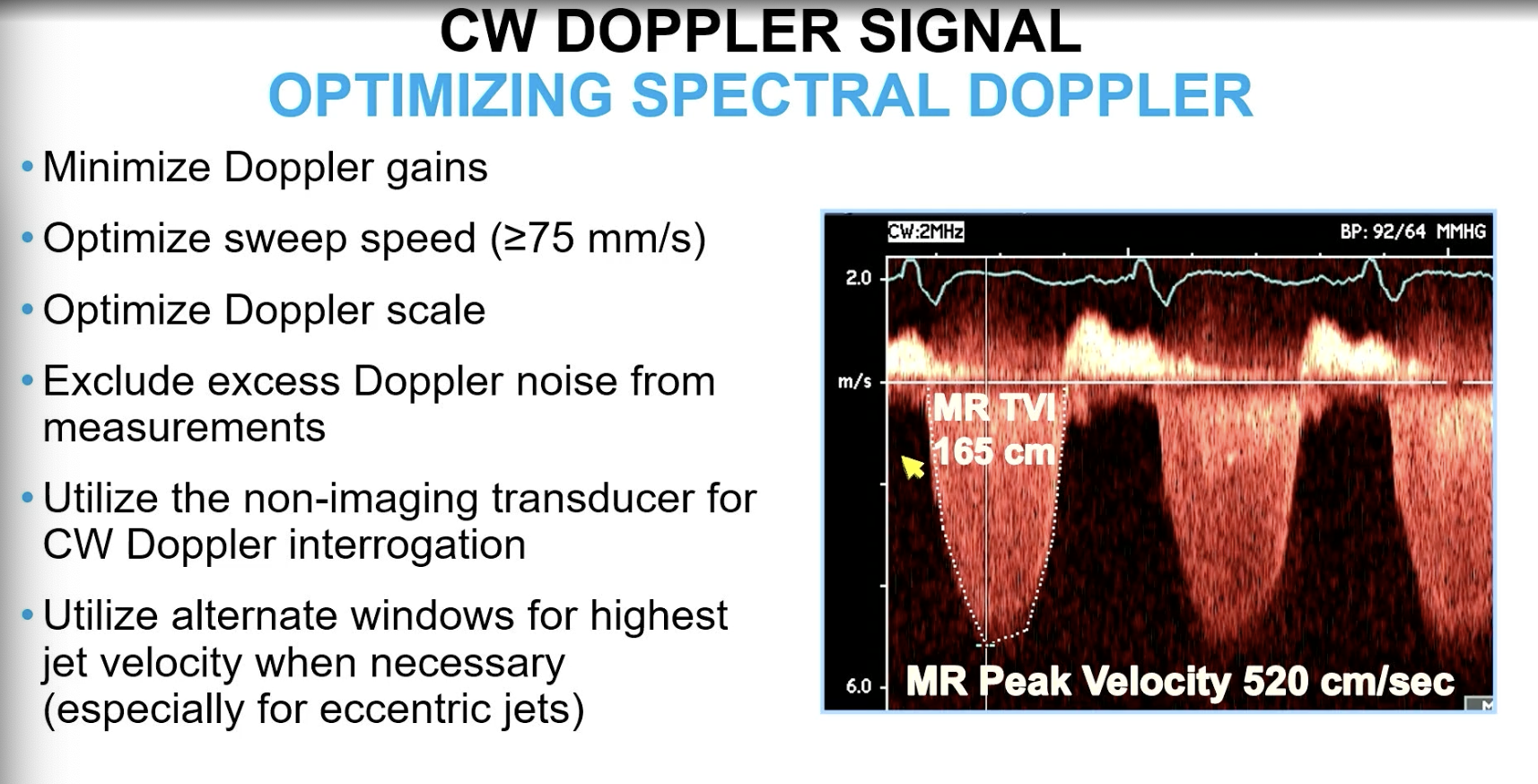
For MR VTI, you want to get a CW doppler and optimize sweep speed to be about…
>/= 75 mm/s
FYI if eccentric jet, can get CW doppler in other views

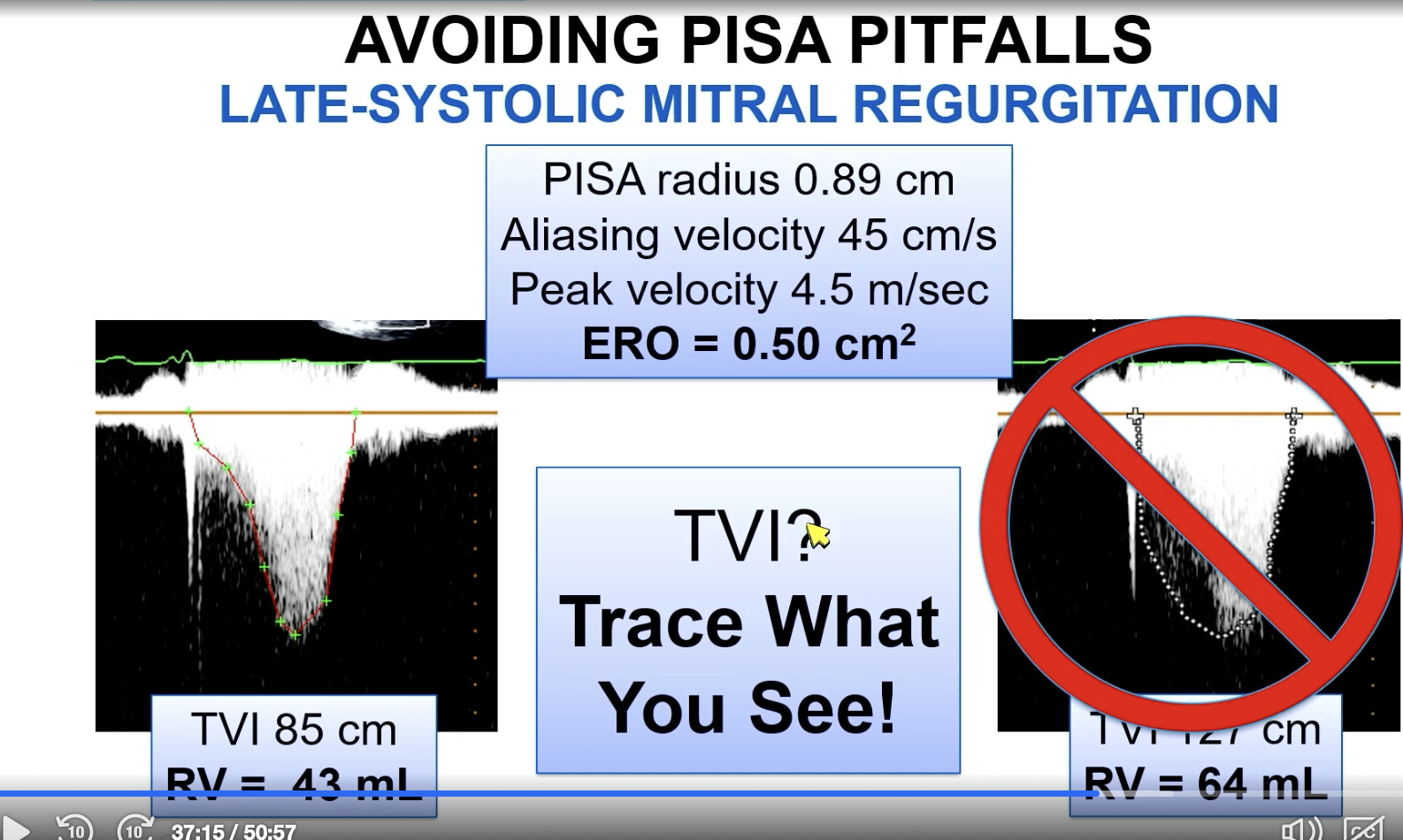
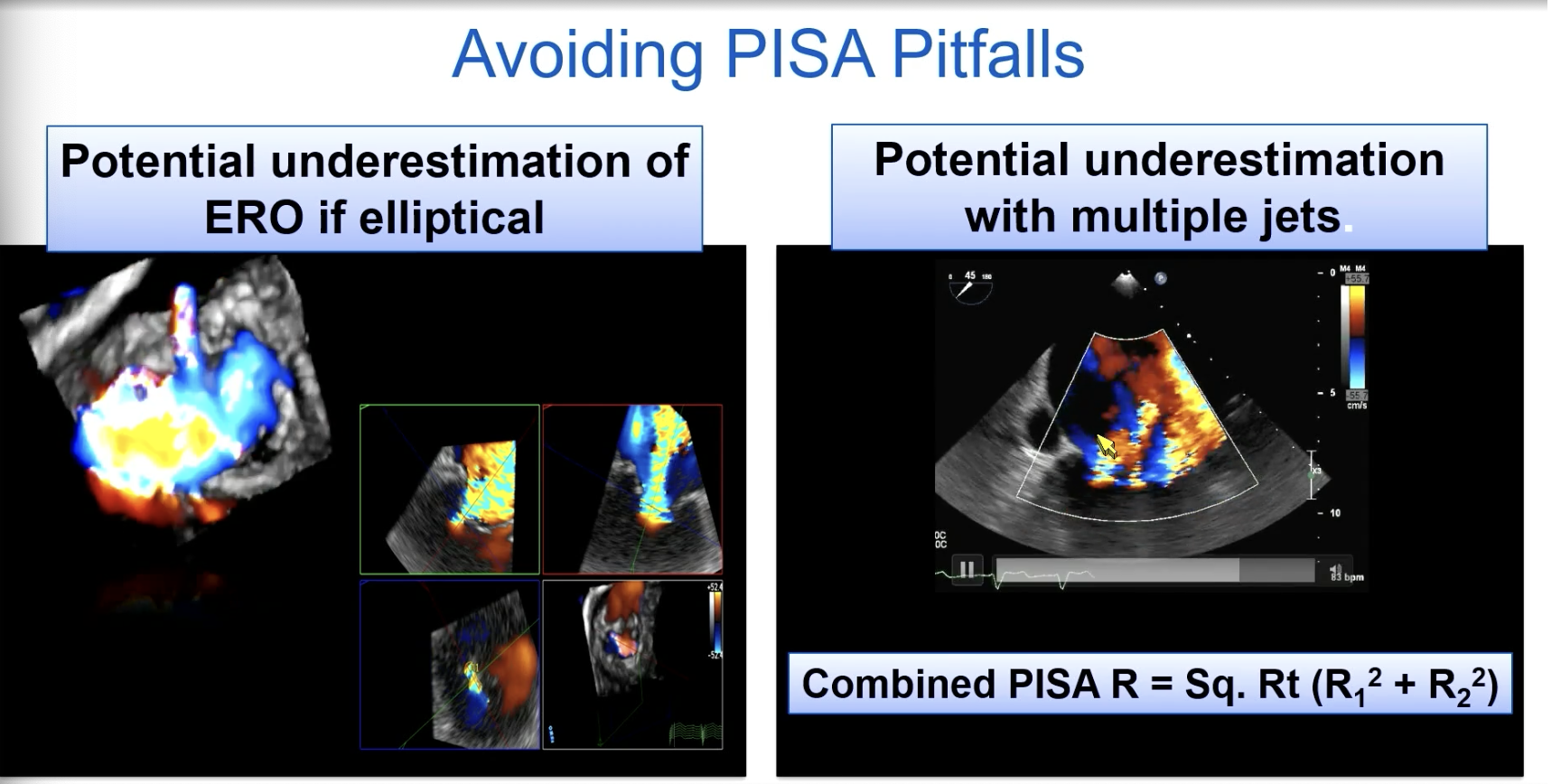
Pitfalls of PISA quantification of MR.
One of which is if there is late systolic MR where you have a large jet on color doppler.
Which of the pictures more accurately outlines the jet for an appropriate VTI?
The left image
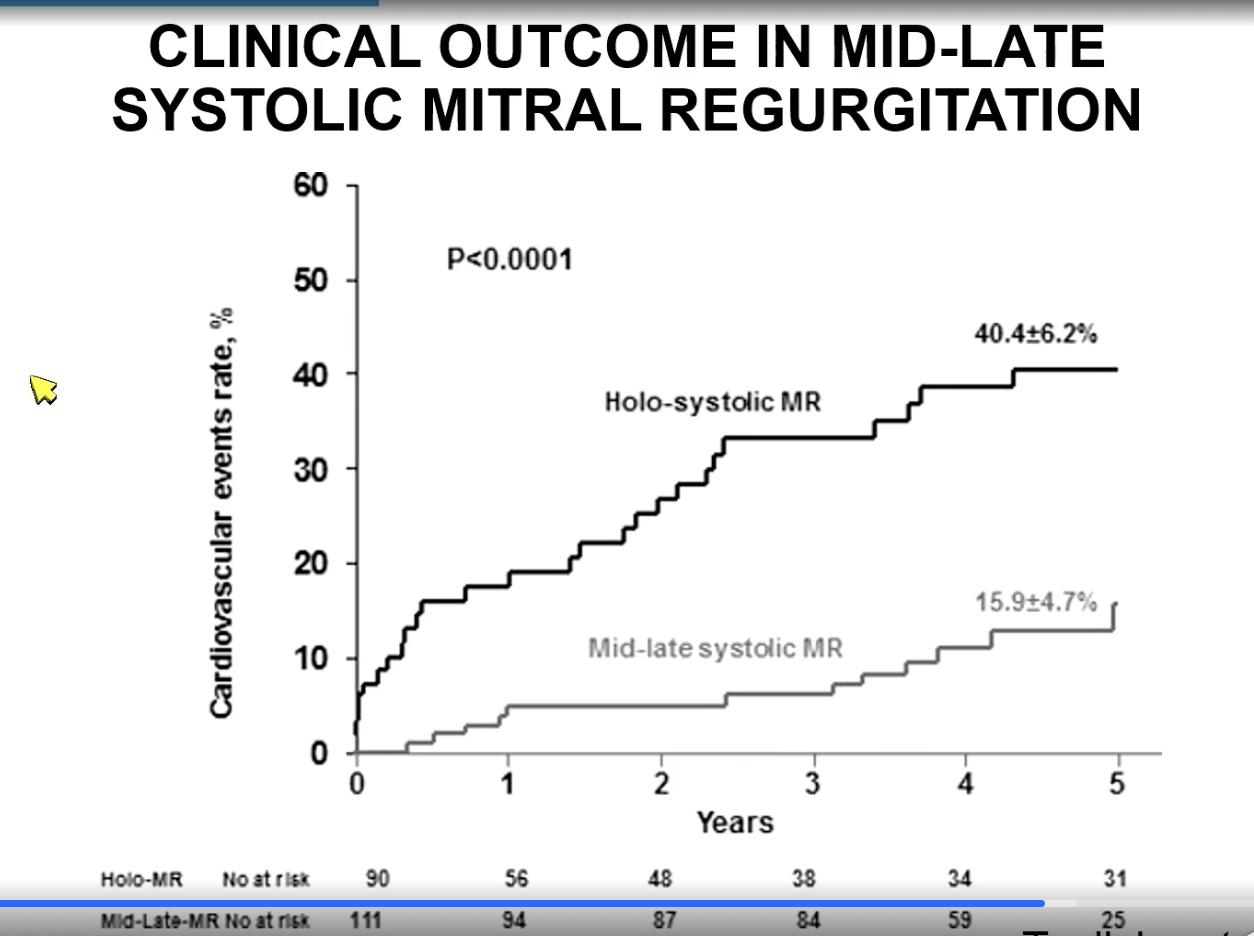
Which is worse — holosystolic MR or mid to late systolic MR?
Holosystolic MR as they tend to have more regurgitant volume.
FYI another PISA pitfall.
If you have a broad jet or multiple jets may be difficult to measure and we tend to [over/underestimate] the ERO
underestimate!
FYI with multiple jets, you combine the Pisa. So PISA R = square root (R12 + R22)
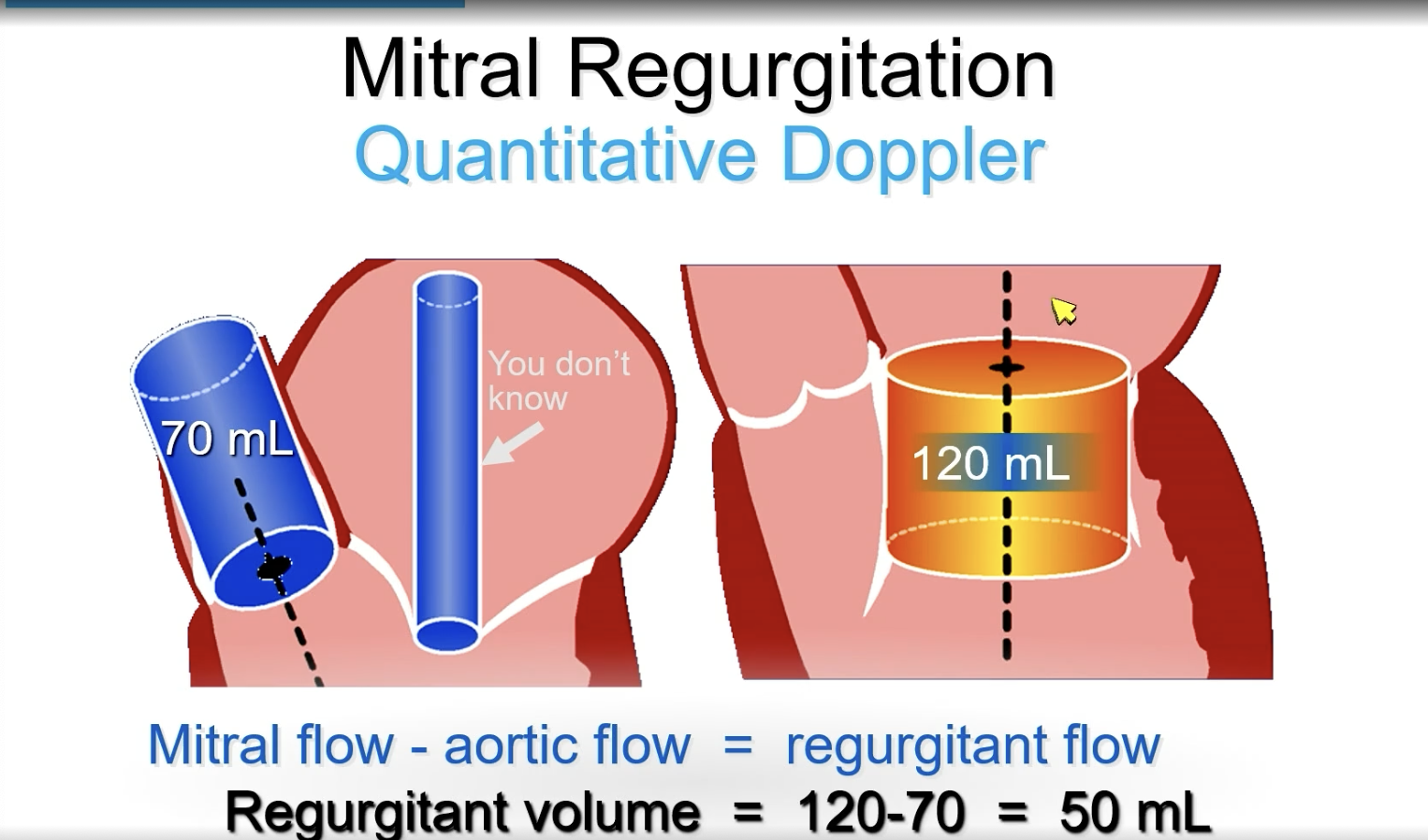
FYI Continuity Equation
SV = Area x VTI
Calculate at each orifice then subtract for regurgitant flow.
Mitral flow - aortic flow = regurgitant flow
FYI when obtaining the PW for the SV measurement of the aortic valve, you measure the outline of the pulse wave. For the mitral valve, you kind of measure more inward on the line of the entire “M” shape.
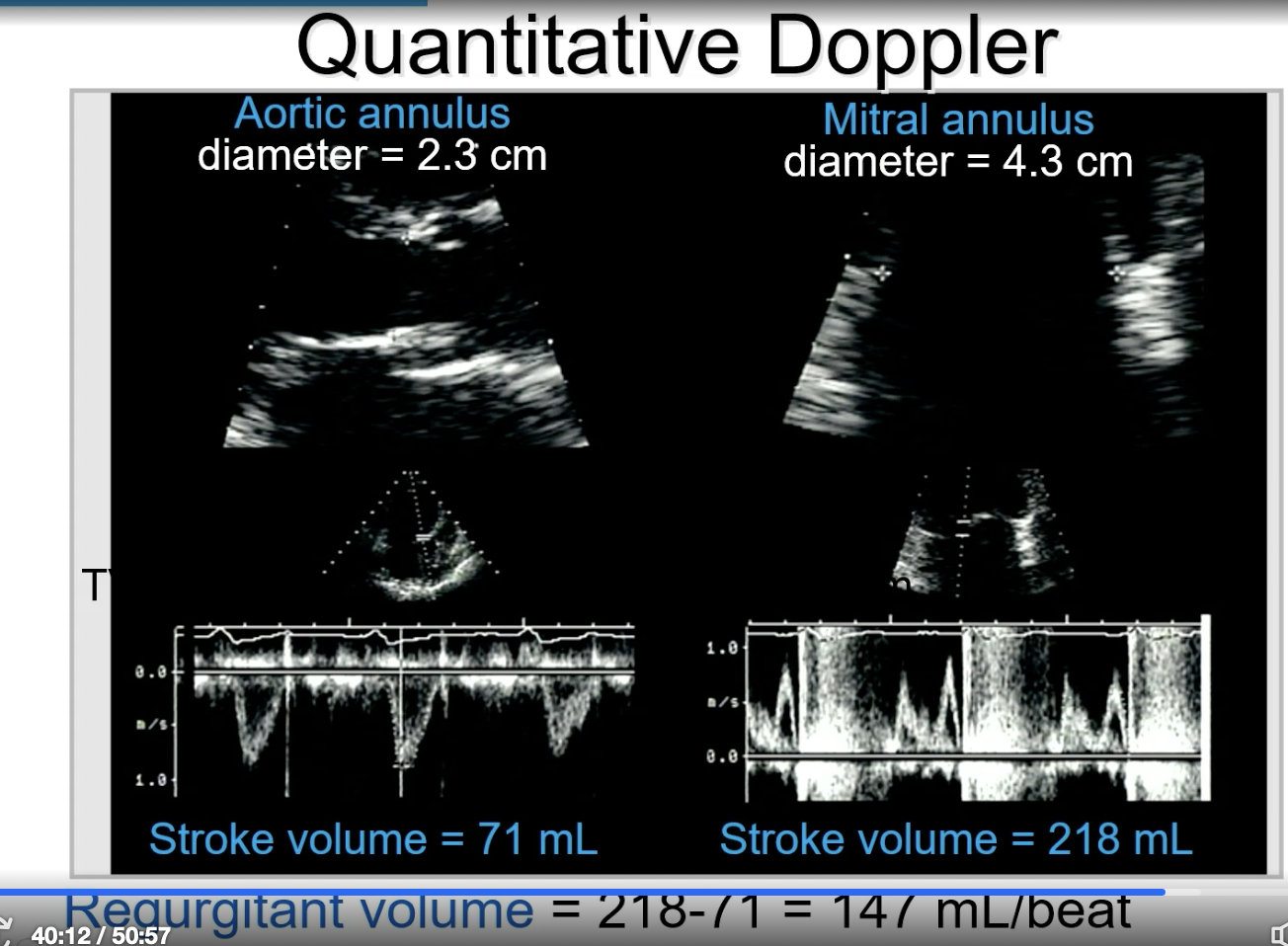
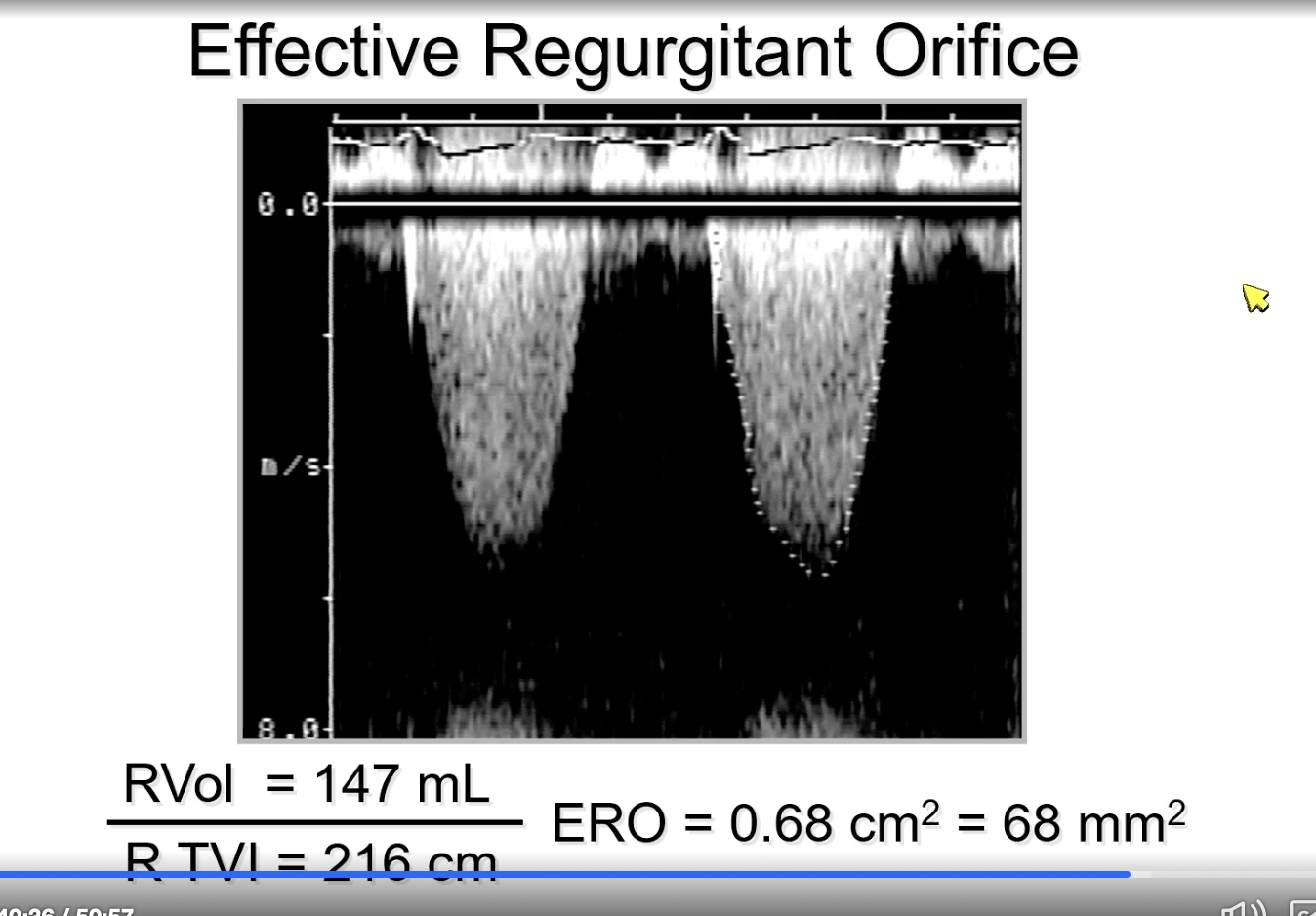
MR ERO equation via regurgitant volume
ERO = regurgitant volume / regurgitant VTI
FYI picture is an example of this
While PISA may underestimate a broad jet of MR, ______ may be be better
3D vena contracta area
Vena contracta >/= ____ is severe MR
7
If early peak CW of mitral valve think…
severe MR
FYI quantitative doppler differentiates moderate versus severe MR when specific semiquantitative parameters are note present