Aphasia Test 1
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
1
New cards
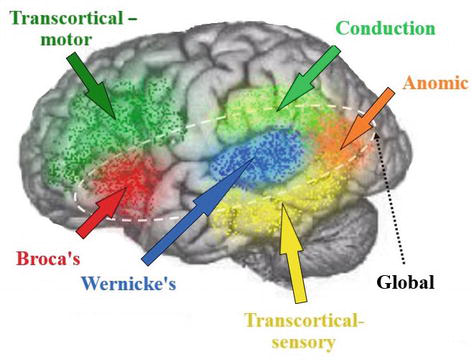
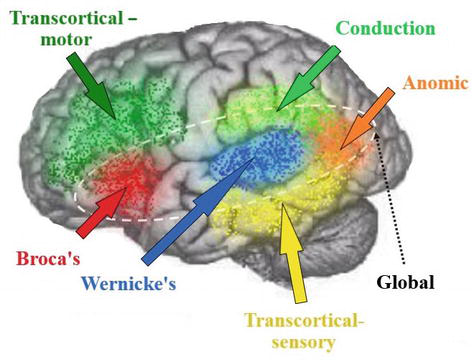
fluent types of aphasia
wernicke's
conduction
transcortical sensory
anomia
conduction
transcortical sensory
anomia
2
New cards
non-fluent types of aphasia
broca's
transcorical motor
transcortical mixed
global
transcorical motor
transcortical mixed
global
3
New cards
types of stroke
ischemic
hemorrhagic
hemorrhagic
4
New cards
symptoms of stroke (sudden onset)
weakness
numbness
aphasia
vision loss
double vision
vertigo
imbalance
incoordination
numbness
aphasia
vision loss
double vision
vertigo
imbalance
incoordination
5
New cards
types of paraphasia
global
semantic
neologism
phonetic
jargon
circumlocution
semantic
neologism
phonetic
jargon
circumlocution
6
New cards
global (verbal) paraphasia
entire word is substituted for intended word (unrelated word)
7
New cards
semantic paraphasia
word belongs to the same semantic field
8
New cards
neologism paraphasia
a novel or newly coined word
9
New cards
phonetic (literal) paraphasia
phoneme is added or substituted for the correct phoneme
10
New cards
jargon paraphasia
long stream of verbal output that is incomprehensible
11
New cards
circumlocution paraphasia
describing the intended word
12
New cards
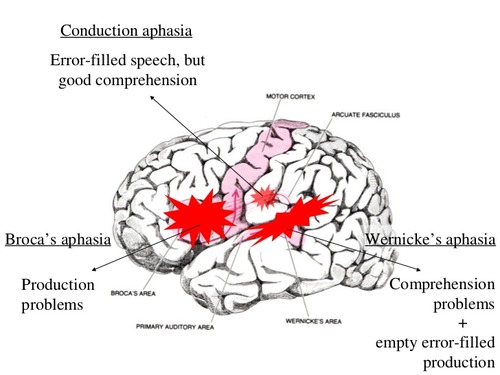
wernicke's aphasia
- poor auditory and reading comprehension
- poor repetition
- poor naming
- poor writing
- poor monitoring
- logorrhea (overload of verbal output)
paraphasias:
- neologism
- jargon
- semantic
- phonemic (literal)
- poor repetition
- poor naming
- poor writing
- poor monitoring
- logorrhea (overload of verbal output)
paraphasias:
- neologism
- jargon
- semantic
- phonemic (literal)
13
New cards
conduction aphasia
+ intact comprehension
- impaired repetition
- impaired naming
- impaired writing
paraphasias:
- literal/phonemic
- impaired repetition
- impaired naming
- impaired writing
paraphasias:
- literal/phonemic
14
New cards
transcortical sensory aphasia
- poor auditory comprehension
- poor confrontation naming
+ good repetition
paraphasias:
- global
- neologism
- poor confrontation naming
+ good repetition
paraphasias:
- global
- neologism
15
New cards
anomic apahasia
+ good auditory and reading comprehension
+ good repetition
- poor naming/word retrieval
paraphasias:
- circumlocution
+ good repetition
- poor naming/word retrieval
paraphasias:
- circumlocution
16
New cards
broca's aphasia
+ good auditory and reading comprehension
- poor repetition
-poor naming
- poor writing and reading aloud
- limited vocabulary
- right hemiparesis
- telegraphic speech (agrammatism)
- self aware of errors --> depression, frustration
paraphasias:
- phonemic/literal
- poor repetition
-poor naming
- poor writing and reading aloud
- limited vocabulary
- right hemiparesis
- telegraphic speech (agrammatism)
- self aware of errors --> depression, frustration
paraphasias:
- phonemic/literal
17
New cards
transcortical motor aphasia
+ good auditory and reading comprehension
+ good repetition
+ good naming
- may perseverate
- impaired writing and reading aloud
- syntactic errors
- mild dysarthria
paraphasias:
- phonemic/literal
+ good repetition
+ good naming
- may perseverate
- impaired writing and reading aloud
- syntactic errors
- mild dysarthria
paraphasias:
- phonemic/literal
18
New cards
transcortical mixed aphasia
- poor auditory and reading comprehension
+ good repetition
- poor naming
- may perseverate
* rare type of aphasia *
+ good repetition
- poor naming
- may perseverate
* rare type of aphasia *
19
New cards
global aphasia
- poor auditory and reading comprehension
- poor repetition
- poor naming
- restricted vocabulary
- limited understandable communication/output
- stereotypic utterances
* some people may start out with a diagnosis of global but develop into a different type over time *
- poor repetition
- poor naming
- restricted vocabulary
- limited understandable communication/output
- stereotypic utterances
* some people may start out with a diagnosis of global but develop into a different type over time *
20
New cards
exceptional aphasias
basal ganglia (subcortical)
thalamic (subcortical)
crossed
primary progressive
thalamic (subcortical)
crossed
primary progressive
21
New cards
basal ganglia aphasia
- comprehension deficits
- dysarthria
- motor impairments
- dysarthria
- motor impairments
22
New cards
thalamic aphasia
- non fluent
- good comprehension
- semantic paraphasia
- good comprehension
- semantic paraphasia
23
New cards
crossed aphasia
- right-handed individuals with right hemisphere lesions
- similar to other aphasias but with right hemisphere deficits
- visual neglect on left side
- trouble understanding jokes
- similar to other aphasias but with right hemisphere deficits
- visual neglect on left side
- trouble understanding jokes
24
New cards
primary progressive aphasia
- gradual progression without evidence of non-language impairments
- involves left hemisphere perisylvian region
- involves left hemisphere perisylvian region
25
New cards
general definition of aphasia
an acquired language disorder that is neurological in origin and not a problem of intellect or sensation
26
New cards
Fredric Darley's definition of aphasia
aphasia is an impairment (caused by brain damage) of the person's capacity for interpretation and formation of language symbols; results in a reduction in efficiency of interpreting and forming language symbols but it is not a problem of loss
27
New cards
Papathanasiou's definition of aphasia
results from a focal brain lesion in the language dominant hemisphere and affects the person's communicative and social functioning as well as the quality of life of the relatives and care persons
28
New cards
localizationism
belief that the brain relies on centers and pathways
29
New cards
holism
belief that the brain is a unitary function and that everything is connected; if something is not working properly it will affect the function of the brain
30
New cards
people who believed in localizationism
- Bouillaud located speech as a part of the frontal lobe
- Broca located where speech and language occur in the brain (BA 44, 45)
- Wernicke located the posterior area of the perisylvian region as where auditory reception/processing of language occurs (BA 22)
- Geschwind created the Boston classification of aphasia
- Broca located where speech and language occur in the brain (BA 44, 45)
- Wernicke located the posterior area of the perisylvian region as where auditory reception/processing of language occurs (BA 22)
- Geschwind created the Boston classification of aphasia
31
New cards
people who believed in holism
- Jackson believed language faculty was intertwined with memory and discussed hemispheric asymmetry
- Head discussed aphasia regarding assessments
- Head discussed aphasia regarding assessments
32
New cards
objections to localizationism
- assumes that if the lesion site is different, the symptoms will always be different although there could be variability in symptoms across patients with the same lesion site
- pure localization does not explain some phenomena like the variability in loss/ability, pure localization would mean total loss of ability
- pure localization does not explain some phenomena like the variability in loss/ability, pure localization would mean total loss of ability
33
New cards
definition of neuroplasticity
the brain's capacity to change at the micro level (neural plasticity) and the macro level (behavioral plasticity) in response to environmental changes or changes in the organism itself
34
New cards
adaptive vs maladaptive plasticity
adaptive = efficient rerouting
maladaptive = inefficient rewiring resulting in the persistence of aphasic symptoms and poor recovery
maladaptive = inefficient rewiring resulting in the persistence of aphasic symptoms and poor recovery
35
New cards
Wernicke's aphasia lesion site
posterior half of first temporal gyrus
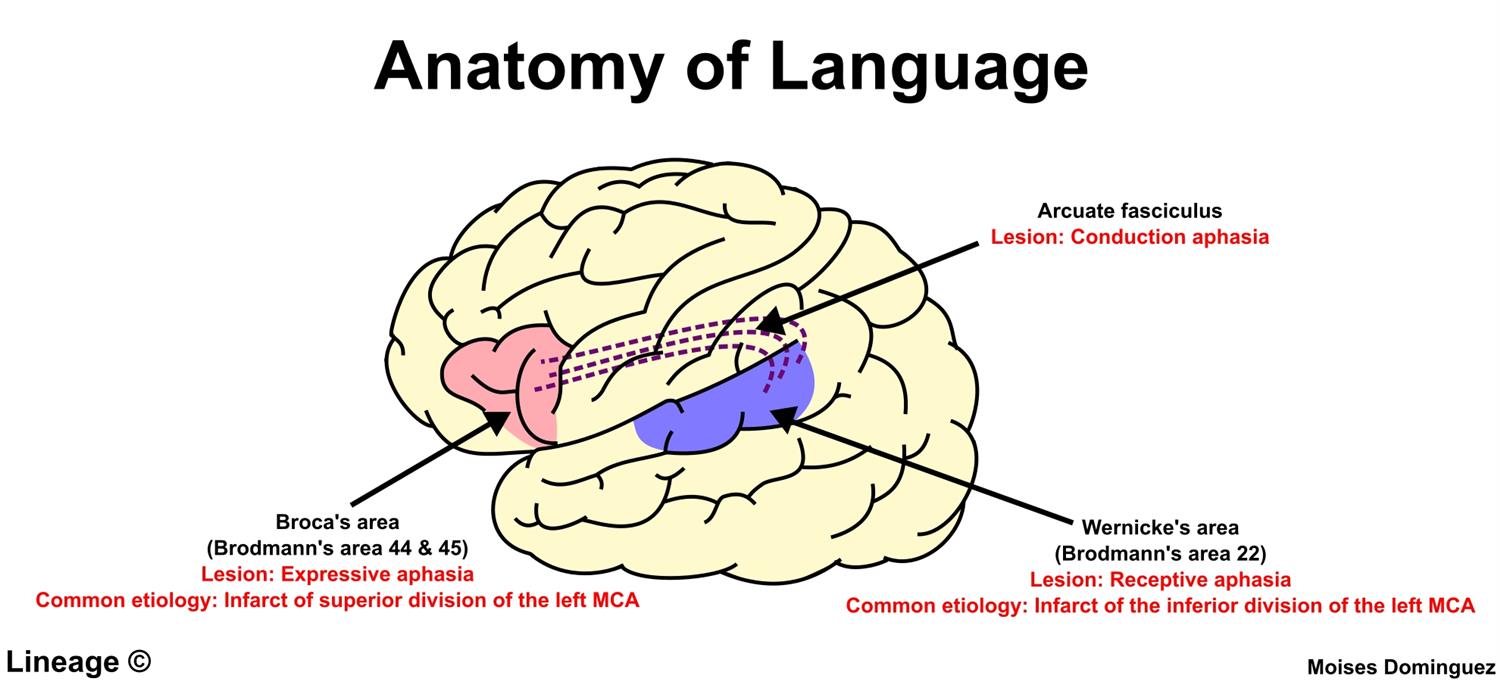
36
New cards
conduction aphasia lesion site
left supra marginal gyrus
37
New cards
transcortical sensory aphasia lesion site
angular and posterior middle temporal gyrus
38
New cards
anomia aphasia lesion site
no specific site; typically inferior parietal lobe
39
New cards
Broca's aphasia lesion site
left inferior frontal gyrus
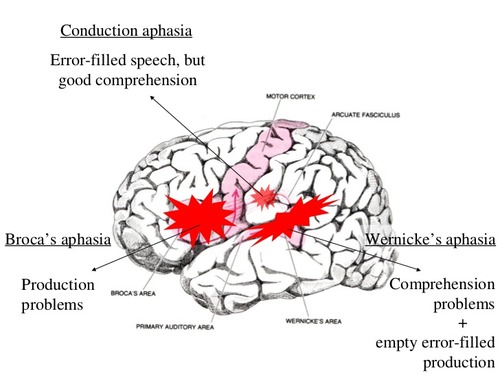
40
New cards
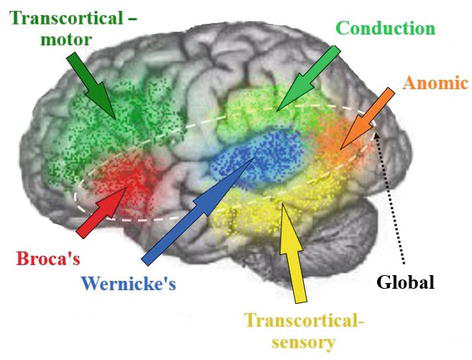
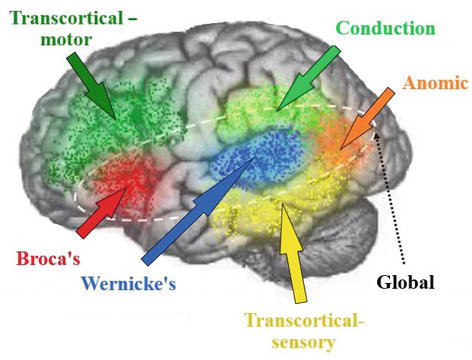
transcortical motor aphasia lesion site
Connection of supplementary motor area and frontal perisylvian areas
41
New cards
transcortical mixed aphasia lesion site
Broca’s & Wernicke’s intact, but “isolated” by damage of perisylvian association cortex
42
New cards
global aphasia lesion site
Perisylvian association cortex
43
New cards
subtypes of ischemic stroke
- cardioembolic
- atherothrombotic cerebrovascular disease
- lacunar
- cryptogenic
- atherothrombotic cerebrovascular disease
- lacunar
- cryptogenic
44
New cards
subtypes of hemorrhagic stroke
- intracerebral (bleeding inside brain)
- subarachnoid (bleeding around brain)
- subarachnoid (bleeding around brain)
45
New cards
10 principles of experience based neuroplasticity
1. use it or lose it
2. use it and improve it
3. specificity (nature of training experience dictates nature of plasticity)
4. repetition
5. intensity
6. time
7. salience (experience must be important)
8. age
9. transference (one training experience can enhance acquisition of similar behaviors)
10. interference
2. use it and improve it
3. specificity (nature of training experience dictates nature of plasticity)
4. repetition
5. intensity
6. time
7. salience (experience must be important)
8. age
9. transference (one training experience can enhance acquisition of similar behaviors)
10. interference
46
New cards
definition of stroke
sudden onset of focal brain dysfunction caused by a disruption in blood flow and oxygen to the brain
47
New cards
TIA
transient ischemic attack
- mini stroke
- symptoms last less than 24 hours
- mini stroke
- symptoms last less than 24 hours
48
New cards
common stroke syndromes
- left MCA stroke (middle cerebral artery)
- right MCA stroke
- right MCA stroke
49
New cards
left MCA stroke
- aphasia
- left gaze deviation
- right side numbness/weakness
- right visual field loss
- left gaze deviation
- right side numbness/weakness
- right visual field loss
50
New cards
right MCA stroke
- contralateral neglect (inability to attend to stimuli on one side of space)
- denial of weakness/impairment
- right gaze deviation
- left visual field loss
- left side numbness/weakness
- denial of weakness/impairment
- right gaze deviation
- left visual field loss
- left side numbness/weakness
51
New cards
cardioembolic ischemic stroke
results from blood clot forming in another area of the body and being carried through the bloodstream, lodging in an artery supply blood to the brain and blocking blood flow
52
New cards
atherothrombotic cerebrovascular disease (ischemic stroke)
can cause stroke when normal blood flow is disrupted by severe arterial blockage from plaque buildup in arteries and clotting occurs
53
New cards
lacunar ischemic stroke
results from occlusive disease of small penetrating arteries of the brain
54
New cards
cryptogenic ischemic stroke
underlying etiology of stroke remains obscure
55
New cards
intracerebral hemorrhagic stroke
occurs when a defective artery in the brain ruptures the surrounding area fills up with blood
56
New cards
subarachnoid hemorrhagic stroke
occurs when a blood vessel on the surface of the brain ruptures and causes bleeding around the brain