Anthropology Exam 1 Study Guide
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Anthropology
The study of humans around the world and through time
Adaptation
The processes by which organisms cope with environmental forces and stresses
Culture
Traditions and customs transmitted through learning
Food production
An economy based on plant cultivation and/or animal domestication
Cultural anthropology
The comparative, cross-cultural study of human society and culture
Ethnography
Fieldwork in a particular cultural setting
Ethnology
The study of sociocultural differences and similarities
Biological anthropology
The study of human biological variation through time and as it exists today
Linguistics
The study of language and lingustic diversity in time, space, and society
Archeaology
The study of human behavior through material remains
Applied anthropology
The use of anthropology to solve contemporary problems
Science
A field of study that seeks reliable explanations, with reference to the material and physical world
Hypothesis
A suggested but as yet unverified explanation
Theory
A set of ideas formulated to explain something
Enculturation
The process by which culture is learned and transmitted across the generations
Symbol
Something, verbal or nonverbal, that stands for something else
Maladaptive culture
An inadequate adaptation that occurs when a group pursues an adaptive strategy that fails to provide the necessities of life or, in the long run, destroys the environment that nourishes it
Universal
Something that exists in every culture
Generality
Culture pattern or trait that exists in some but not all societies
Acculturation
An exchange of cultural features between groups in firsthand contact
Independent invention
The independent development of a cultural feature in different societies
Globalization
The accelerating interdependence of nations in the world system today
Particularity
Distinctive or unique culture trait, pattern, or integration
Ethnocentrism
Judging other cultures using one’s own cultural standards
Human rights
Rights based on justice and morality beyond and superior to particular countries, cultures, and religions
Cultural relativism
The idea that behavior should be evaluated not by outside standards but in the context of the culture in which it occurs
Diffusion
Borrowing of cultural traits between societies
Rapport
A good, friendly working relationship based on personal contact with hosts
Participant observation
Taking part in community life, participating in the events one is observing, describing, and analyzing
Emic
A research strategy focusing on local explanations and meanings
Etic
A research strategy emphasizing the ethnographer’s explanations and categories
Variables
Attributes that differ from one person or case to the next
Informed consent
An agreement to take part in research after having been informed about its purpose, nature, procedures, and possible impacts
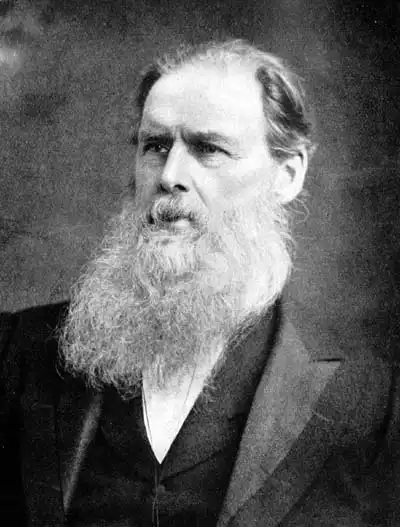
Edward Burnett Tylor
English founder of cultural anthropology who applied the theory of evolution to human societies (cultural evolutionism) and introduced the idea of animism
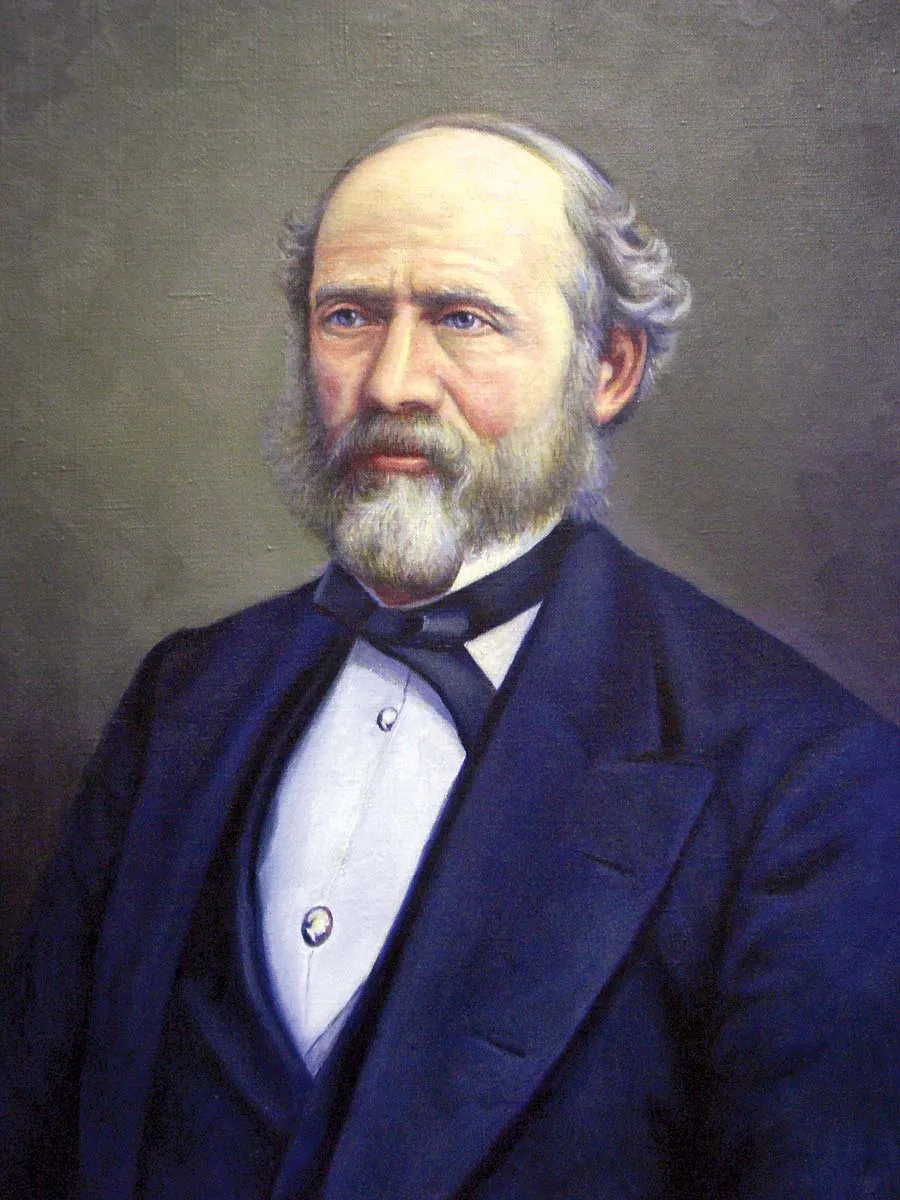

Lewis Henry Morgan
American ethnologist and principal founder of scientific anthropology, known for establishing and expanding the study of kinship systems and his theory of social evolution (savagery, barbarism, and civilization)
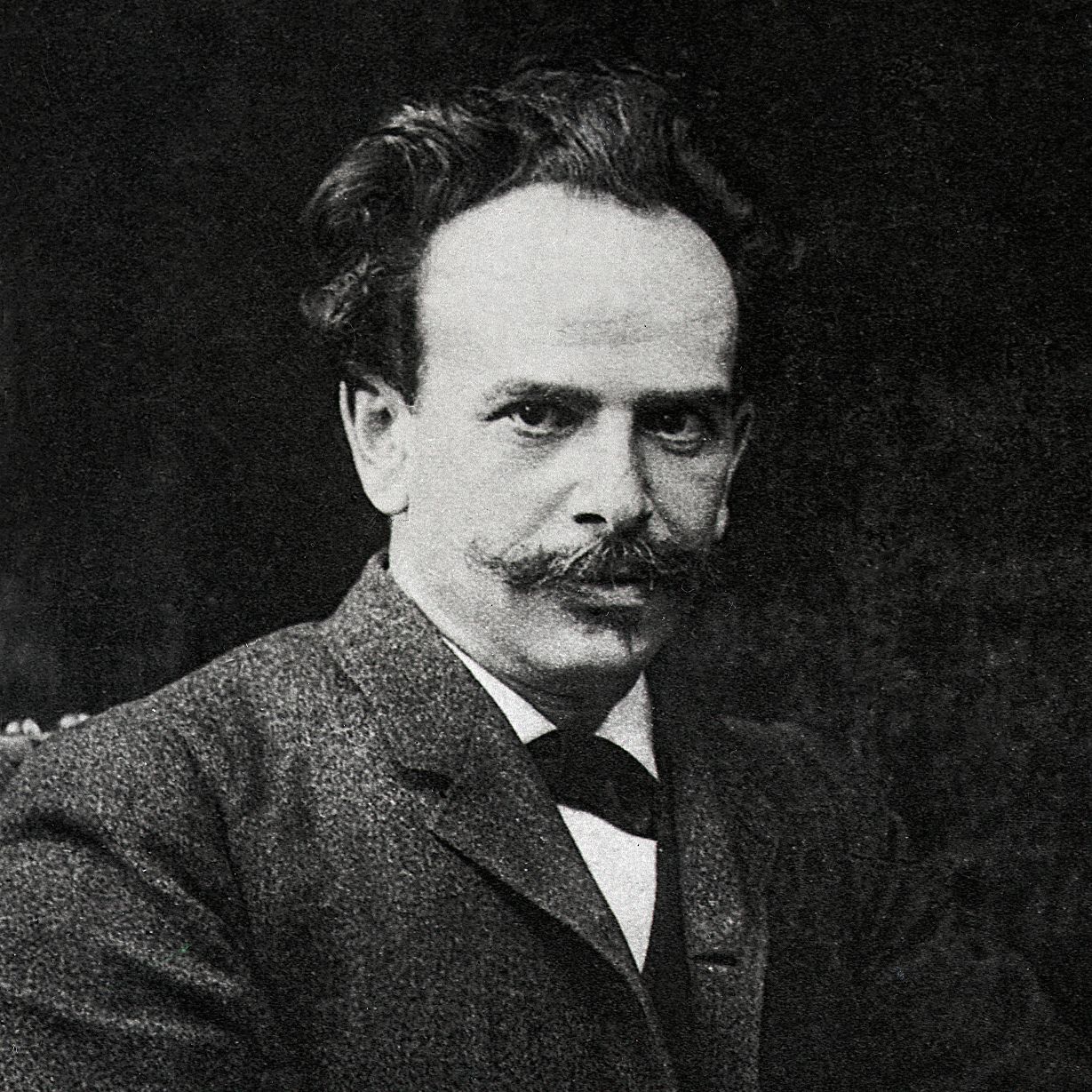
Boas
German-American anthropologist who is associated with historical particularism, cultural relativism, and the four-field anthropological approach

Malinowski
Polish-British anthropologist and ethnologist who helped found social anthropology, studied the people of Oceania, and created participant observation
Unilinear evolutionism
The 19th-century idea of single line or path of cultural development
Historical particularism
The idea that histories are not comparable and diverse paths can lead to the same cultural result
Functionalism
An approach that focuses on the role/function of sociocultural practices in social systems

Marvin Harris
American anthropologist who heavily influenced cultural materialism by popularizing the idea of emic perspectives
Cultural materialism
The idea that cultural infastructure determines structure and superstructure

Geertz
Primary advocate for interpretive anthropology who used Malinowski’s beliefs of grasping a native point of view
Interpretive anthropology
The study of a culture as a system of meaning
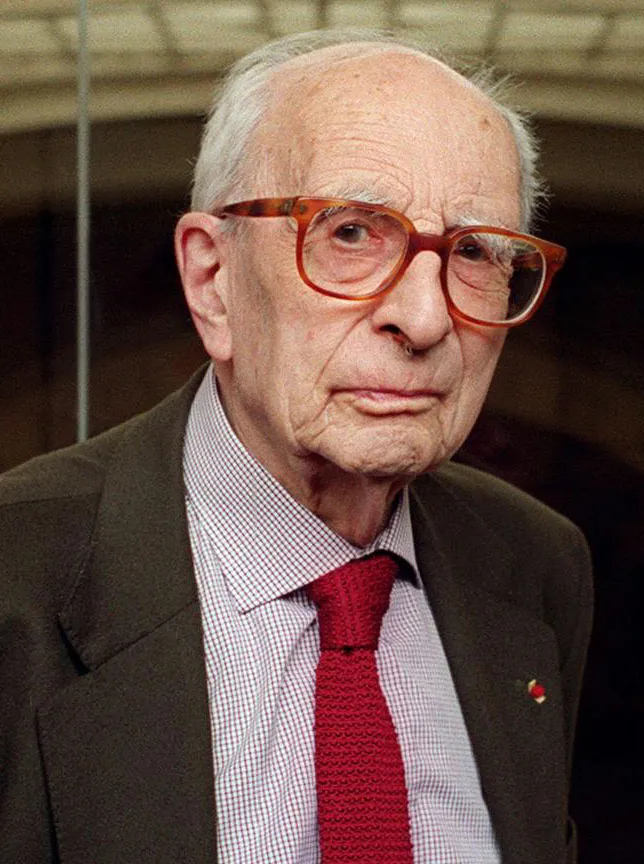

Levi-Strauss
French anthropologist most associated with structuralism and his idea that all human minds have universal characteristics due to being human
Structuralism
The belief that all minds have universal characteristics of needing to classify and impose order on aspects of nature, people’s relation to nature, and on interpersonal relations
Agency
The actions of individuals, alone and in groups, that create and transform culture
Practice theory
The approach to culture which recognizes that individuals in a society vary in motive and held power
World-system theory
The theory in which countries are placed in different economic classes to explain their economic relationships with each other
Political economy
The web of interrelated economic and power relations in society
Hegemony
The dominance of one culture over another’s culture due to enforcement from the dominating culture
Development anthropology
A field that examines the sociocultural dimensions of economic development
Increased equity
Reduction in absolute poverty, with a more even distribution of wealth
Overinnovation
Trying to achieve too much change
Underdifferentiation
Seeing less-developed countries as all the same; Ignoring cultural diversity
Urban anthropology
The anthropological study of cities and urban life
Medical anthropology
The comparative, biocultural study of disease, health problems, and health care systems
Public anthropology
Efforts to extend anthropology’s visibility beyond academia and to demonstrate its public policy relevance
Ethnicity
Indentification with, and feeling a part of, an ethnic group and exclusion from certain other groups because of this affiliation
Racial classification
Assigning humans to categories (purportedly) based on common ancestry
Phenotype
The expressed or evident biological characteristics of an organism
Hypodescent
Children of mixed unions assigned to the same group as their minority parent
Multiculturalism
The view of cultural diversity as valuable and worth maintaining
Prejudice
Devaluing a group because of its assumed attributes
Stereotypes
Fixed ideas—often unfavorable—about what members of a group are like
Discrimination
Policies and practices that harm a group and its members
Cultural colonialism
The internal domination by one group and its culture or ideology over others
Food production
An economy based on plant cultivation and/or animal domestication
Adaptive strategy
A society’s primary way of making a living, even though its people might engage in other economic activities
Foraging
An economy and a way of life based on hunting, gathering, and/or fishing
Economy
A system of resource production, distribution, and consumption
Mode of production
A specific set of social relations that organizes labor
Means (factors) of production
Major productive resources, e.g., land, labor, technology, capital
Market principle
Buying, selling, and valuation based on supply and demand