PSYC EXAM 3: learning , intelligence, memory
1/137
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ac
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
reflex
motor/neural reaction to a stimulus in the environment
simpler than instincts, involving body systems
eg: knee jerk reflex, pupil dilating, sucking reflex
primitive centers of central nervous system (spinal cord and medulla)
instincts
innate behaviors triggered by a broader range of events
maturation, change of seasons
complex patters including the movement of the organism as a whole
involve higher brain centers
sexual activity, migration, hibernation
learning
permanent change in behavour or knowledge resulting from experince
involes acquriing knowledge
associative learning
minds have a natural tendancy to connect events closley together
occours when organism makes connections betweens stimuli or events that occour together in the enviroment
used in conditioning
classical conditioning
Ian pavlov (1849-1936): dogs salivating to the ring of a bell, assosiated with food
associate stimuli that are repeated together
a neutral stimulus is presented immediately before an unconditioned stimulus.
unconditioned stimulus
a stimulus that elicits a reflexive response in an organism
eg: the smell of food
unconditioned response
a natural unlearned reaction to a stimulus
eg: salivation
neutral stimulus (NS)
stimulus that does not naturally
eg: ringing a bell
when paired with and repeated with stimulus (becomes conditoned) , results in reponse
conditioned response
simulus that ilicits a response after being repeatdly paired with a unconditoned stimulus
eg: dogs associated the bell (CS), salivate (CR) in anticipation of food
higher-order conditioning (second order conditioning)
pairing a new stimulis with the condtioned stimulus
using the condtioned stimulus to condition another stimulus
hard to acheive anything above 2nd order conditioning
blowing a horn every time the bell rights for food, dog will not get excited hearing bell alone
acquisition
when an organism learns to connect a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus
timing is key: there should only be a brief interval between condtioned stimulus and uncondtioned stimulus
usally as little as 5 seconds sometimes up to hours
taste aversion:
interval of several hours between ingestion (conditioned stimulus) and unconditioned stimulus (nausea or illness)
can occur in a single instance due to evolutionary adaptation to avoid harmful foods
survive via natural selection
Extinction
decrease in conditioned response when unconditioned stimulus is no longer presented together with conditioned reponse
gradual wekening and disapperance of the conditoned reponse
eg: ring bell no food provided
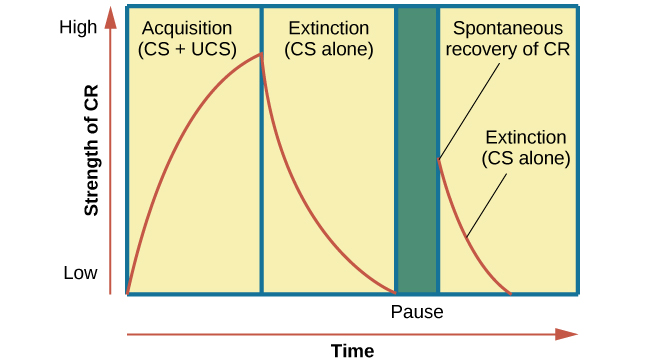
spontaneous recovery
the return of a prevously extinguished conditoned repsonse following a rest period
stimulus discrimination
need to distinguish between stimuli to respond appropriately when an organism learns to respond different to various stimuli that are similar
involved in determining which stimuli will trigger learned responses
eg: salivating at bell and not a doorbell
Behavoirism
John B watson founder of behavoirism
focus on outword observable behavoir that can be measured contrasting freuds theories on unconcious
influenced by pavlov
little albert: exposed to loud noises when playinf with animals conditoning a phobia
operant conditioning
organisms learn to associate a behavior and its consequence
punsihment vs reward stimulus
occours soon after response
law of effect
BF. Skinner
consequences that are satisfying to the organism are more likely to be repeated, and behaviors that are followed by unpleasant consequences are less likely to be repeated
eg: showing up to work because of pay
skinner box
animal press for food reward
counts respones made by animal
positive reinforcment
Something is added to increase the likelihood of a behavior
eg: giving treat to a dog who sits to continue such behavoior
negative reinforcement
something is removed to increase the liklehood of a behavior
eg: plugging in seatbelt to remove annoying beep sound
Positive punishment
Something is added to decrease the likelihood of a behavior.
eg: spanking a kid to decrease stealing
Negative Punishment
Something is removed to decrease the likelihood of a behavior.
taking away a toy if kid misbehaves
pros and cons of punishment
pros
effective, person is less likley to do
con
instills fear towards person who delivered punsihment
can mkae child more agressive, antisocial and use the same behavoir on others
shaping
skinner used in his operant condiutioning experirments
reward successive approximants of a target behavoir
reifnrces any response that resembles the desired behavoir
reinforce closer and closer approximations of the desired behavoir, until only reinfocing the desired behavoir
skinner used to teach pigeons behaovirs such as turning in circles, playing ping pong etc
primary reinforcer.
are reinforcers that have innate reinforcing qualities.
These kinds of reinforcers are not learneed
Water, food, sleep, shelter, sex, and touch, plrasureamong others, are primary reinforcers.
secondary reinforcer
has no inherent value and only has reinforcing qualities when linked with a primary reinforcer.
praise is linked to affection
money is linked to buy needs
continuous reinforcement
When an organism receives a reinforcer each time it displays a behavior
the quickest way to teach someone a behavior
effective in teaching new behavoir
eg: each time rat presses button it gets food
partial reinforcement
intermittent reinforcement
does not get reinforced every time they perform the desired behavior
diffrent schedules: fixed, variable, interval, ratio
Fixed interval
Reinforcement is delivered at predictable time intervals
higher qualirt of output
results in moderate response rate with signficant pauses after reinfocement
eg: patient presses button for morphine which is docter timed
Variable interval
Reinforcement is delivered at unpredictable time intervals
moderate yet steady response rate
eg: checking social media, not knowing when manager will come
Fixed ratio
Reinforcement is delivered after a predictable number of responses
high response rate with pauses after reinforcments
quantity based
worker getting paid for every x number of items manufactured
Variable ratio
Reinforcement is delivered after an unpredictable number of responses
high and steady response rate
eg: gambling
radical behavoirism
Skinner was such a staunch believer that cognition didn't matter
considered the mind a "black box"—something completely unknowable— not to be stuided
cognitive map
As the unreinforced rats explored the maze, they developed a cognitive map: a mental picture of the layout of the maze
latent learning:
learning that occurs but is not observable in behavior until there is a reason to demonstrate it.
exiting the maze onlydue to food (shupid rat),
observational learning
learn by watching others and then imitating, or modeling, what they do or say
eg: chimpanizes, humans
models
The individuals performing the imitated behavior
Albert Bandura
the scientists behind:
pure behaviorism could not explain why learning can take place in the absence of external reinforcement.
internal mental states must also have a role in learning and that observational learning
3 kinds of models
live: behaovir inperson
verbal: explains behaovir such as a coach
symbolic: books, movies etc
vicarious reinforcement
occurs when learners observe role models receiving either positive or negative reinforcement
behavior, you will be more motivated to copy them.
vicarious punishment
hand, if you observed the model being punished, you would be less motivated to copy them.
Bobo doll
When the teacher was praised or ignored (and not punished for her behavior), the children imitated what she did, and even what she said.
when the teacher was punished for this behavoir they were less likley to
whem teacher was praised, They punched, kicked, and yelled at the doll too
conclusion: Bandura concluded that we watch and learn, and that this learning can have both prosocial and antisocial effects.
cognition
thinking
encompasses the processes associated with perception, knowledge, problem solving, judgment, language, and memory.
Cognitive psychology
field of psychology dedicated to examining how people think.
explain how and why we think the way we do by studying the interactions among human thinking, emotion, creativity, language, and problem solving,
Concepts
are categories or groupings of linguistic information, images, ideas, or memories, such as life experiences.
big ideas generated by observing details
informed by our semantic memory
can be abstract or concrete
prototype
an ideal example of a concept
eg: what comes to mind when hearing “dog” is a golden retriver, that is someones prototype
Natural concepts
created “naturally” through your experiences and can be developed from either direct or indirect experiences
eg: living in canada, having a natural understanding of snow vs someone in Guyana
can construct an understanding of it through direct observations, experiences with snow, or indirect knowledge (such as from films or books)
artificial concept
a concept that is defined by a specific set of characteristics
artificial concepts can be built off of another
eg: understanding the properties of a square or triangle
schema
a mental construct consisting of a cluster or collection of related concepts
a method of organizing information that allows the brain to work more efficiently.
examples: sterotypes, social roles, worldviews, archetypes, mental models
role schema
makes assumptions about how individuals in certain roles will behave
pre-exisitng belifs of someones personality due to some information
u hear they are a firefighter and assume they are brave and community oriented
event schema
also known as a cognitive script
set of behaviors that can feel like a routine
behaviors you do when walking into an elevator
eg: when u geeking and u go on autopilot
can vary in different cultures (tibet greeting by ticking tounge out vs America hand shake)
Language
is a communication system that involves using words and rules to organize and transmit information from one individual to another
not all communication is language
some species use movments, odors, vocalizations
langauge makes human unique
Lexicon
refers to the words of a given language
is a language’s vocabulary
Grammar
refers to the set of rules that are used to convey meaning through the use of the lexicon
phoneme
(e.g., the sounds “ah” vs. “eh”)
is a basic sound unit of a given language, and different languages have different sets of phonemes.
morphemes
phonems are combined to form morphemes
smallest unit of language that convey meaning that cannot be further dividedrefers to the process by which we derive meaning from morphemes and words.
eg: ing
Semantics
refers to the process by which we derive meaning from morphemes and words
Syntax
refers to the way words are organized into sentences
B. F. Skinner
(1957)
proposed that language is learned through reinforcement
Noam Chomsky- Langauge
(1965)
criticized this Skinners behaviorist approach
said that mechanisms underlying language acquisition are biologically determined
Stages of Language and Communication Development: Stage 1
Age | Developmental Language and Communication |
0–3 months | Reflexive communication |
Stages of Language and Communication Development: Stage 2
Age | Developmental Language and Communication |
3–8 months | Reflexive communication; interest in others |
Developmental Language and Communication: Stage 3
Age | Developmental Language and Communication |
8–13 months | Intentional communication; sociability |
Stages of Language and Communication Development: 4
Age | Developmental Language and Communication |
12–18 months | First words |
Stages of Language and Communication Development: 5
Age | Developmental Language and Communication |
18–24 months | Simple sentences of two words |
Stages of Language and Communication Development: 6
Age | Developmental Language and Communication |
2-3 years | Sentences of three or more words |
Stages of Language and Communication Development: 6
Age | Developmental Language and Communication |
3-5 years | Complex sentences; has conversations |
overgeneralization- language
to an extension of a language rule to an exception to the rule
eg: children will “add an s to the end of the word” rule and say things like “those two gooses” or “three mouses.”
problem-solving strategy
is a plan of action used to find a solution
trial and error
Continue trying different solutions until problem is solved
eg: restarting phone or turning off wifi to see why phone tweakingqStep-by-step problem-solving formula
Algorithm
Step-by-step problem-solving formula
eg: Instructional video for installing new software on your computer
Heuristic
General problem-solving framework
eg: Working backwards; breaking a task into steps
planning time from when u gotta be there to when u need to start getting ready
mental set
where you persist in approaching a problem in a way that has worked in the past but is clearly not working now.
Functional fixedness
type of mental set where you cannot perceive an object being used for something other than what it was designed for
anchoring bias
when you focus on one piece of information when making a decision or solving a problem.
eg: if you see a shirt that is 1k and then one that is 10ur more likey to see the 2nd as cheap
The confirmation bias
tendency to focus on information that confirms your existing beliefs.
example, if you think that your professor is not very nice, you notice all of the instances of rude behavior exhibited by
Hindsight bias
leads you to believe that the event you just experienced was predictable, even though it really wasn’t.
Representative bias
which you unintentionally stereotype someone or something
for example, you may assume that your professors spend their free time reading books
availability heuristic
Decision is based upon either an available precedent or an example that may be faulty
Crystallized intelligence
characterized as acquired knowledge and the ability to retrieve it
When you learn, remember, and recall information, you are using crystallized intelligence
Fluid intelligence
encompasses the ability to see complex relationships and solve problems.
Navigating your way home after being detoured onto an unfamiliar route because of road construction would
triarchic theory of intelligence
Robert Sternberg developed
practical, creative, and analytical intelligence
Practical intelligence
“street smarts.”
Being practical means you find solutions that work in your everyday life by applying knowledge based on your experiences
Analytical intelligence
academic problem solving and computations.
ability to analyze, evaluate, judge, compare, and contrast.
Creative intelligence
is marked by inventing or imagining a solution to a problem or situation
Multiple Intelligences Theory
developed by Howard Gardnereight
linguistic intelligence,
logical-mathemcatiical
musical
bodily kniesthetic
spatial
interpersonal
naturalsitic
linguistic intelligence,
the ability to understand the emotions of yourself and others, show empathy, understand social relationships and cues, and regulate your own emotions and respond
Creativity
the ability to generate, create, or discover new ideas, solutions, and possibilities.
divergent thinking.
thinking “outside the box;”
allows an individual to arrive at unique, multiple solutions to a given problem
convergent thinking
describes the ability to provide a correct or well-established answer or solution to a problem
intelligence quotient
IQ
describes a score earned on a test designed to measure intelligence
only professionals trained in psychology can administer IQ tests
Standardization
means that the manner of administration, scoring, and interpretation of results is consistent.
Norming
giving a test to a large population so data can be collected comparing groups, such as age groups
the resulting data provides norms of what the group does know
ensures the test are reliable
Flynn effect
refers to the observation that each generation has a significantly higher IQ than the last
representative sample is
subset of the population that accurately represents the general population.
example, you measured the height of the women in your classroom only, you might not actually have a representative sample.
Standard deviations
describe how data are dispersed in a population and give context to large data sets.
The bell curve uses the standard deviation to show how all scores are dispersed from the average score
Range of Reaction
theory that each person responds to the environment in a unique way based on their genetic makeup.
genetics are fixed but reaching full intellectual potential is dependent upon environmental stimulation
dysgraphia
have a learning disability that results in a struggle to write legibly.
physically writing is challenging
Dyslexia
most common learning disability in children
exhibits an inability to correctly process letters