PLB105 Final Study Guide
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Determinate
= growth of limited duration.
-Ex: Leaf, flower
Indeterminate
= unrestricted growth in which an apical meristem will remain active during growing seasons over many years.
-Ex: Shoot, roots
Competence
= ability to respond to a signal with the appropriate pathway.
= ability create new structures due to certain pathways being expressed
-Ex: responding to floral stimulus
Flowering
= the process of producing conspicuous flowers.
- Important evolutionary tactic of angiosperms that allowed for successful, sexual reproduction
External flowering requirements
i) Photoperiod: How long is the day?
ii) Temperature: When to germinate
Internal flowering requirements
i) Juvenility: is it sexually active?
ii) Competency: is a new set of structures being expressed?
iii) Floral transitions: How long does it live + flower for?
Juvenility
= is not yet sexually mature.
Gynoecium
= pistil, carp female reproductive parts of a flower.
- Stigma + Style + Ovary
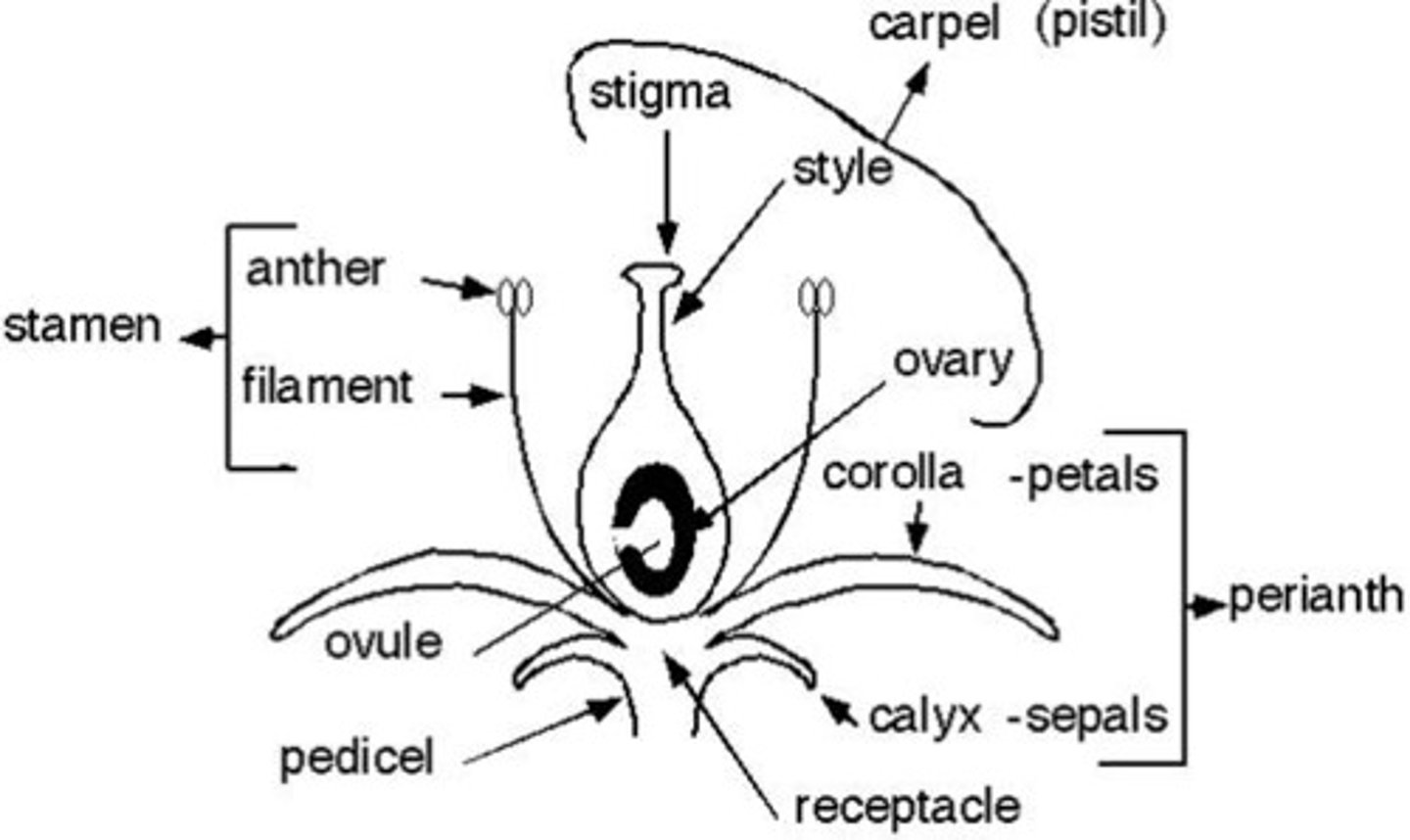
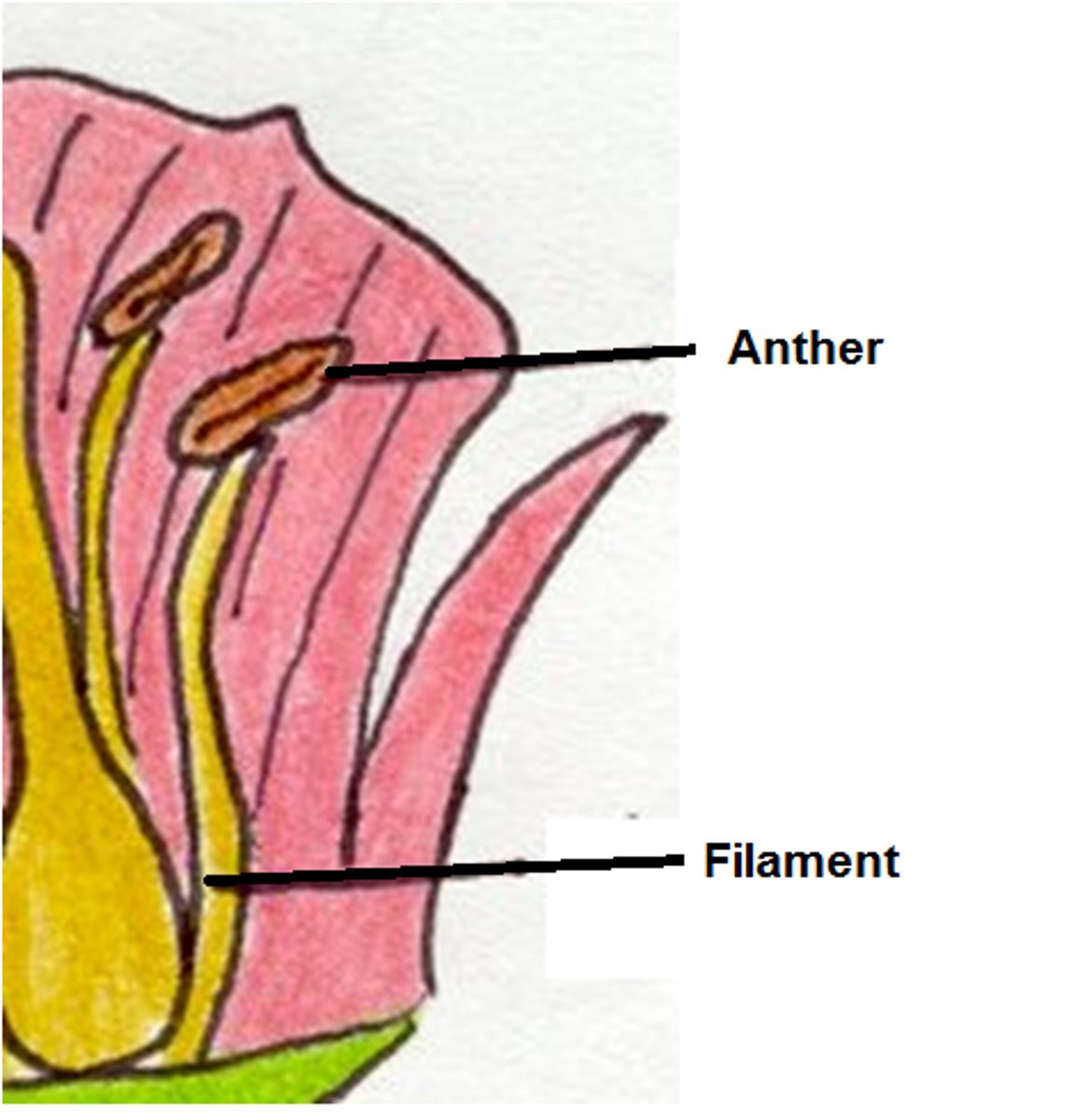
Androecium
= stamen, male reproductive parts of a flower.
= Anther + filament
Pollen grain
= male gametophyte in seed plants
= plant sperm
Transmitting tissue
= tissue in the style of a flower through which the pollen tube grows.
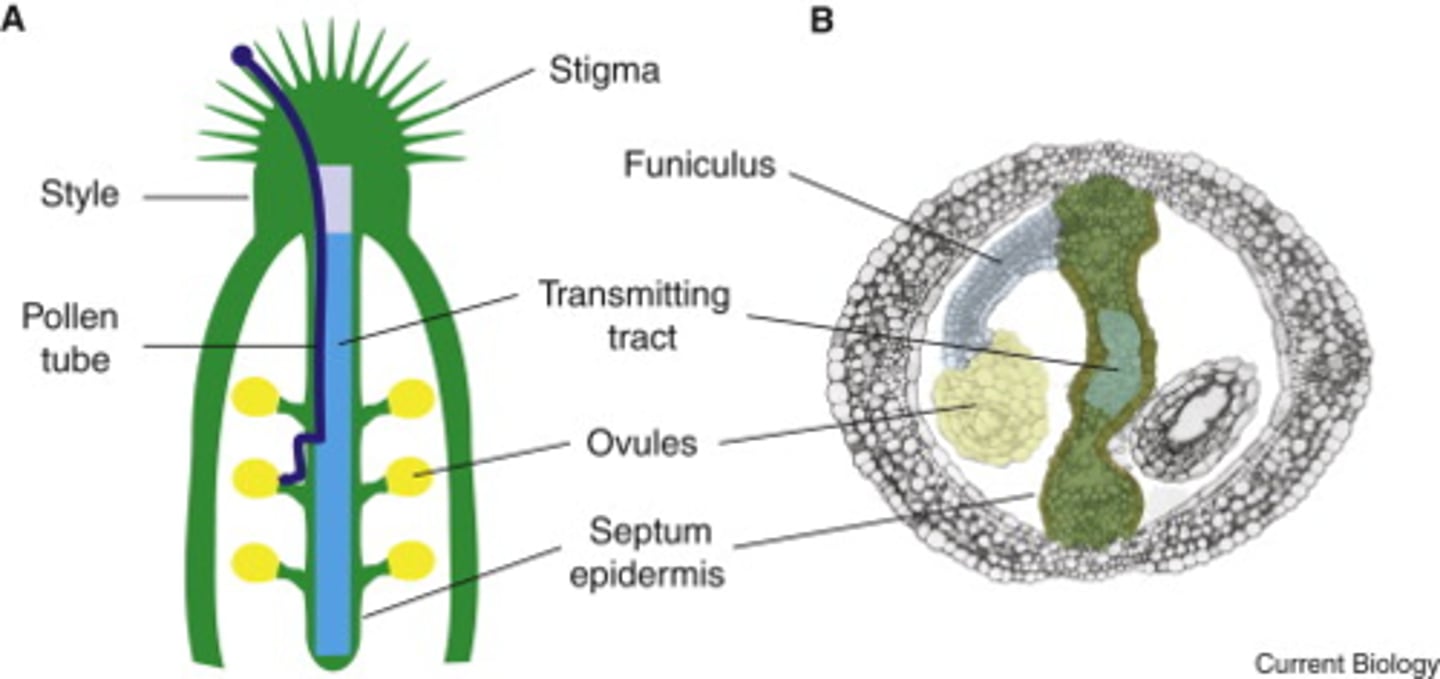
Endosperm
=a nutrient-rich tissue formed of sperm + two polar nuclei
-Provides nourishment to developing embryo
-Angiosperms
FLC gene
= Flowring Locus C gene, it reperesses flowering in barley.
-High temp --> Increase FLC --> vegetative
-Low temp--> Decrease FLC --> flowering
Annual
= plant with 1 year life span + 1 flowering season
Biennial
= plant with 2 year lifespan + 2 flowering seasons
Perennial
= plant with with multiple years + multiple seasons
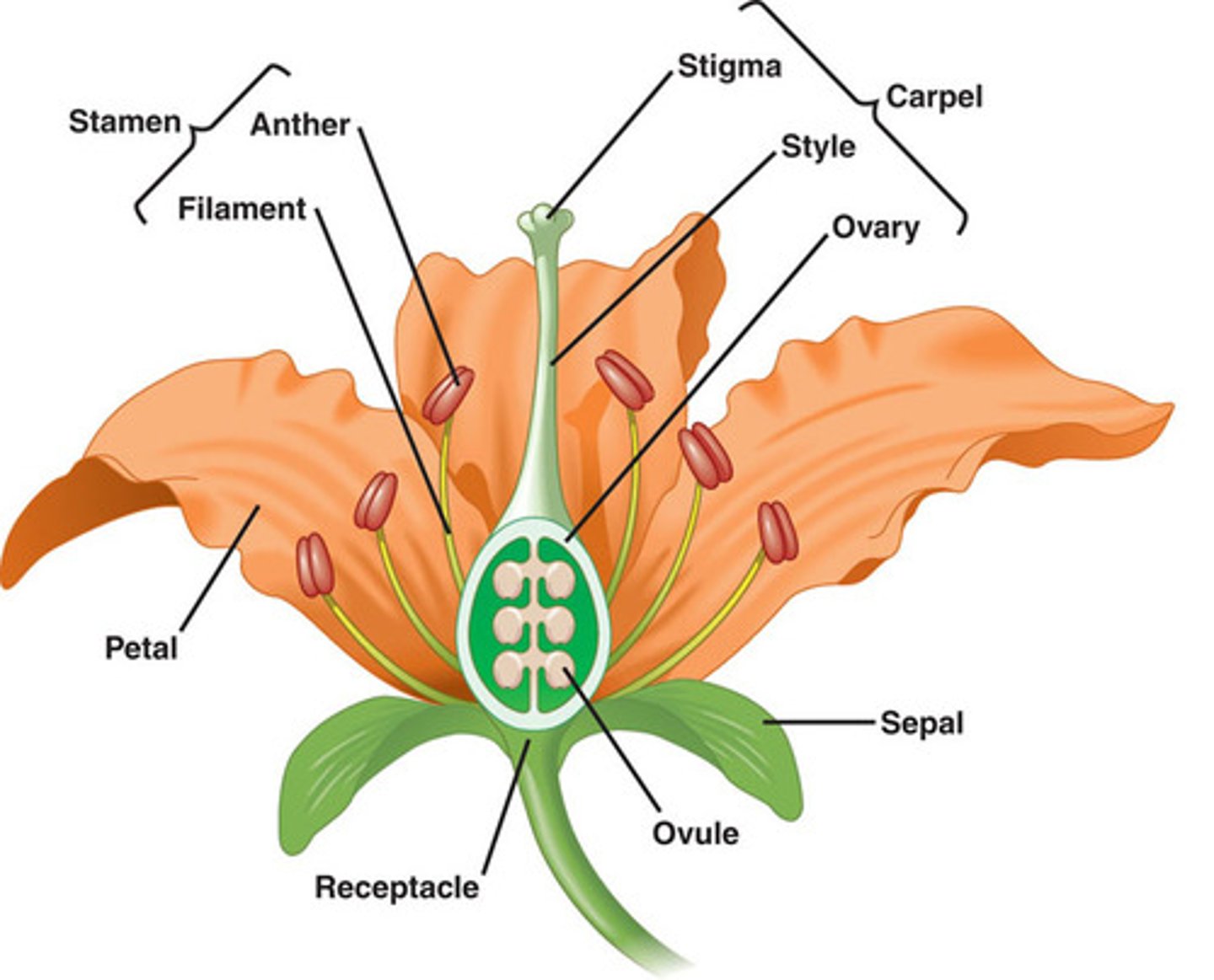
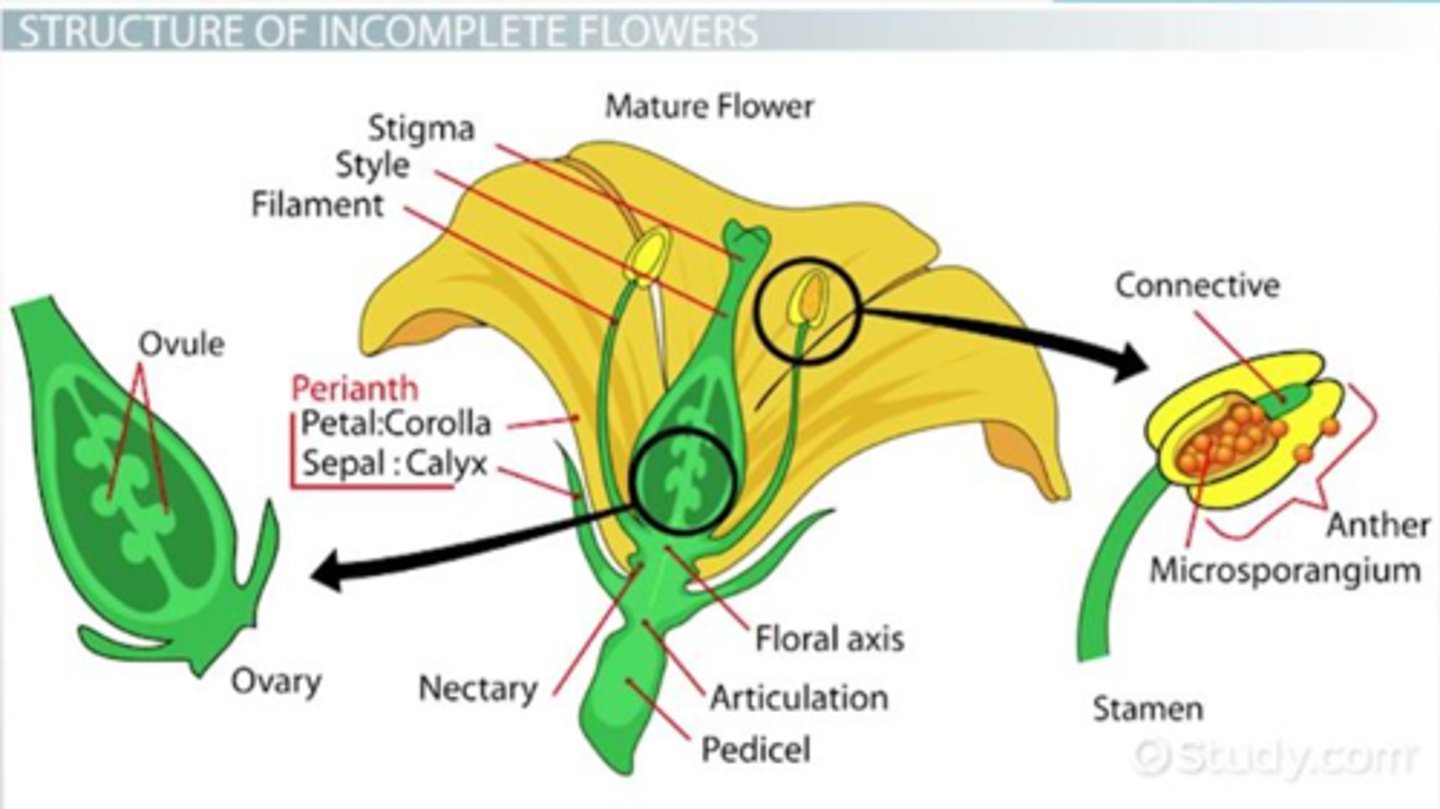
Flower parts
i) Petal
ii) Pedicel
iii) Sepal
iv) Receptacle
v) Ovary
vi) Ovules
vi) Style
vii) Stigma
iix) Anther
ix) Filament
Tepals
= petals + sepals that are indistinguishable from each other.

Anther
= end part of stamen with pollen
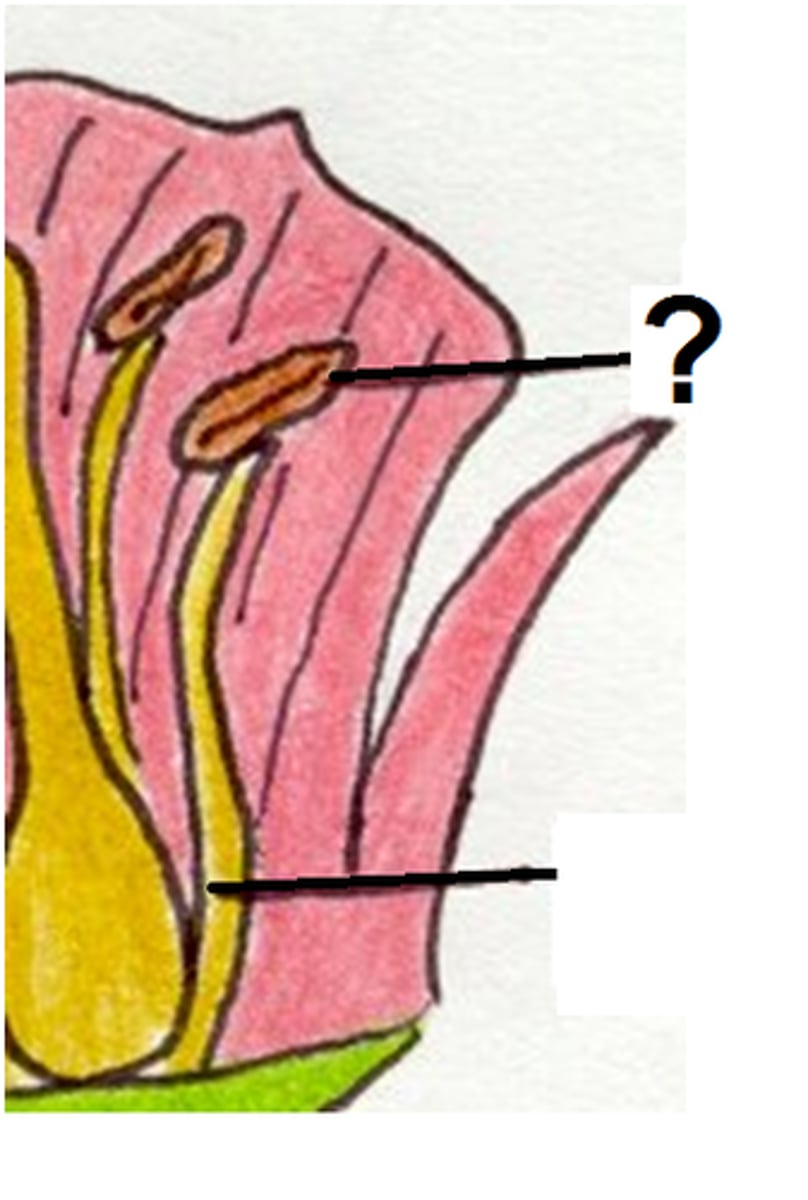
Filament
= part of stamen that holds anther

OVary
= female reproductive organ of a plant which contains ovules.
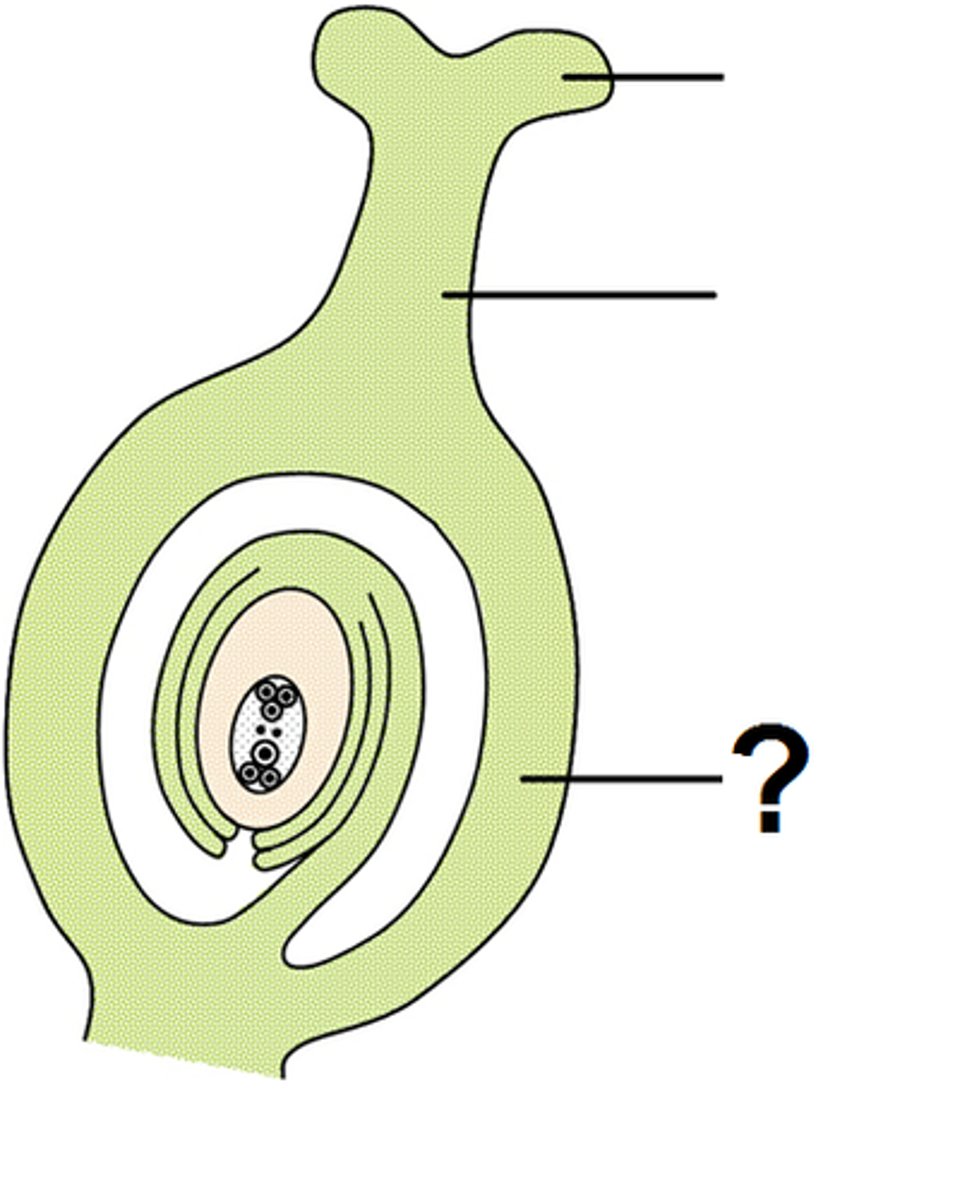
Stigma
= part of pistil that is modified for pollen reception
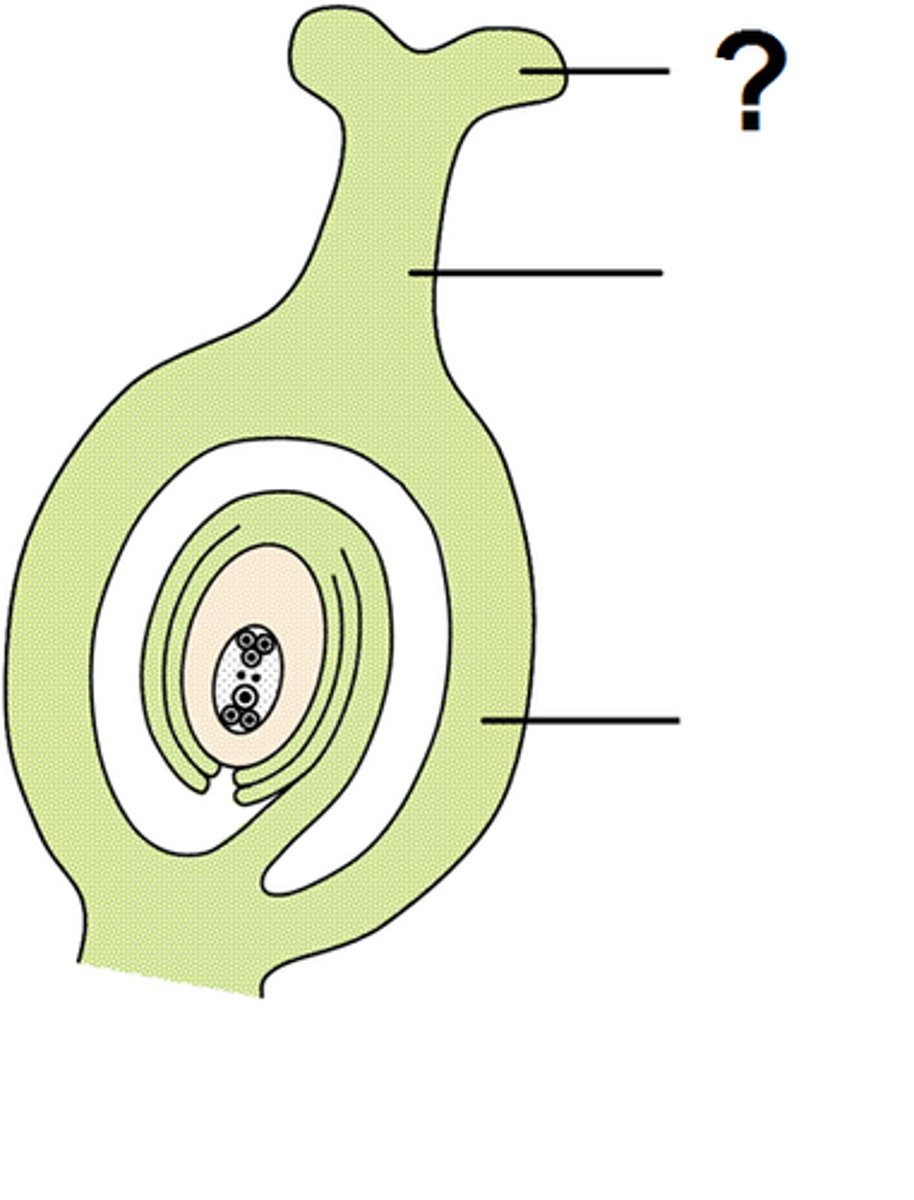
Style
= slender stalk that connects stigma to ovary.
-Allows sperm to get to ovaries.
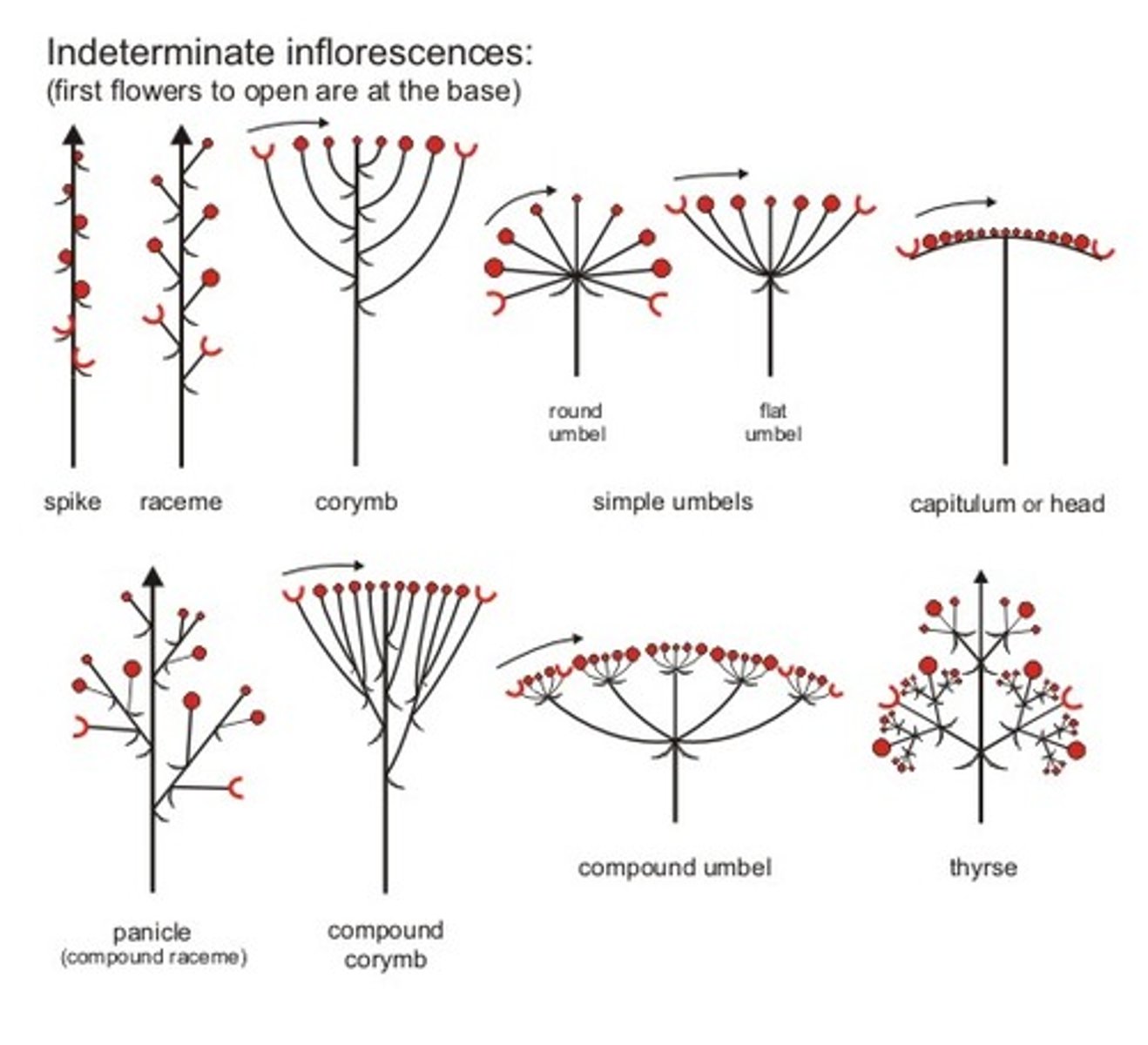
Inflorescence
= A group of flowers tightly clustered together.
Complete
= flower with all types of floral parts.
= Sepals + Petals + Stamens + Carpels
- 2 sex flower
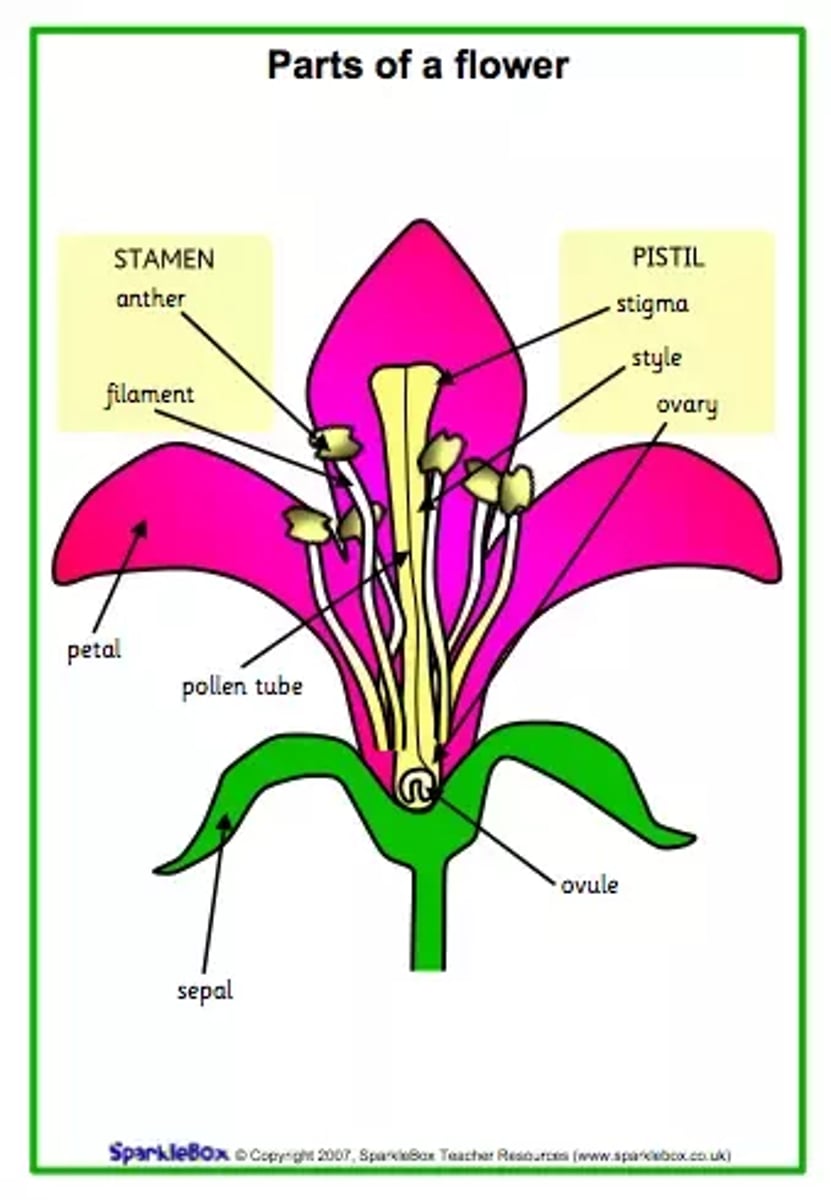
Incomplete
= any flower missing any of its parts in its natural form.
- Usually lacking stamens or pistils
- 1 sex flower
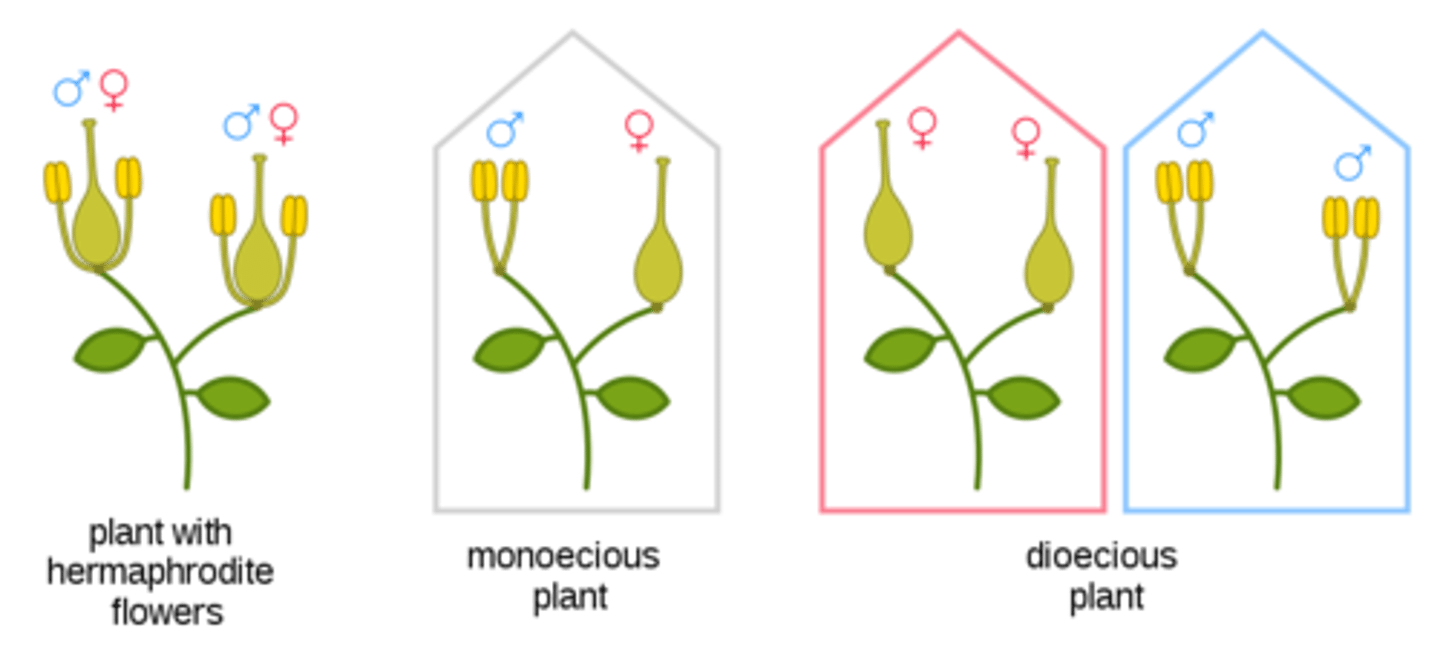
Monoecious
= plant with both male and female flowers
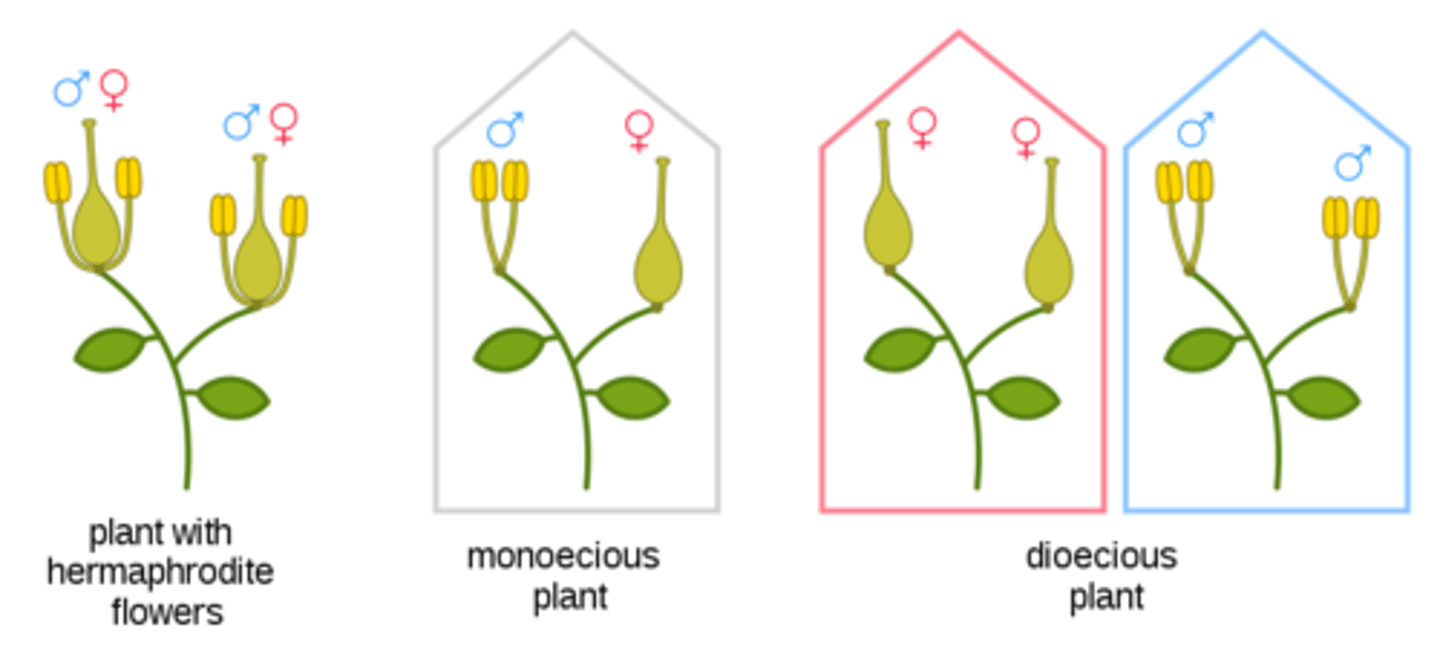
Dioecious
= plant that has only male or female flowers.
ABC model
= 3 classes of genes, A + B + C, that code for different parts of the flower.
-Class A for Sepals + Petals
-Class B for Petals + Stamens
-Class C for Stamens + Carpels
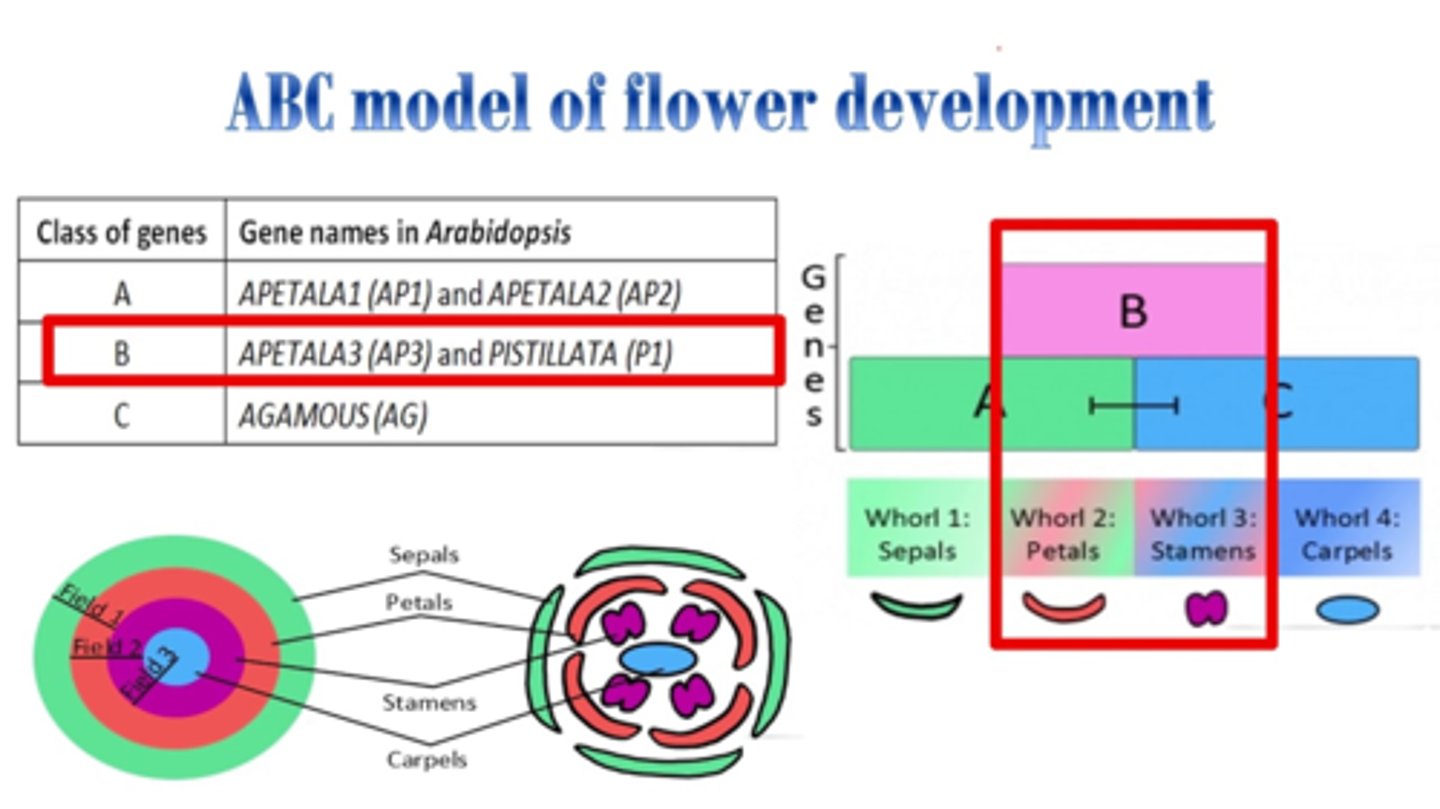
Whorl
= leaves or flower parts arranged in a circle on an axis.
- Change in ABC genes --> change in expression of affected parts --> Changes in whorls

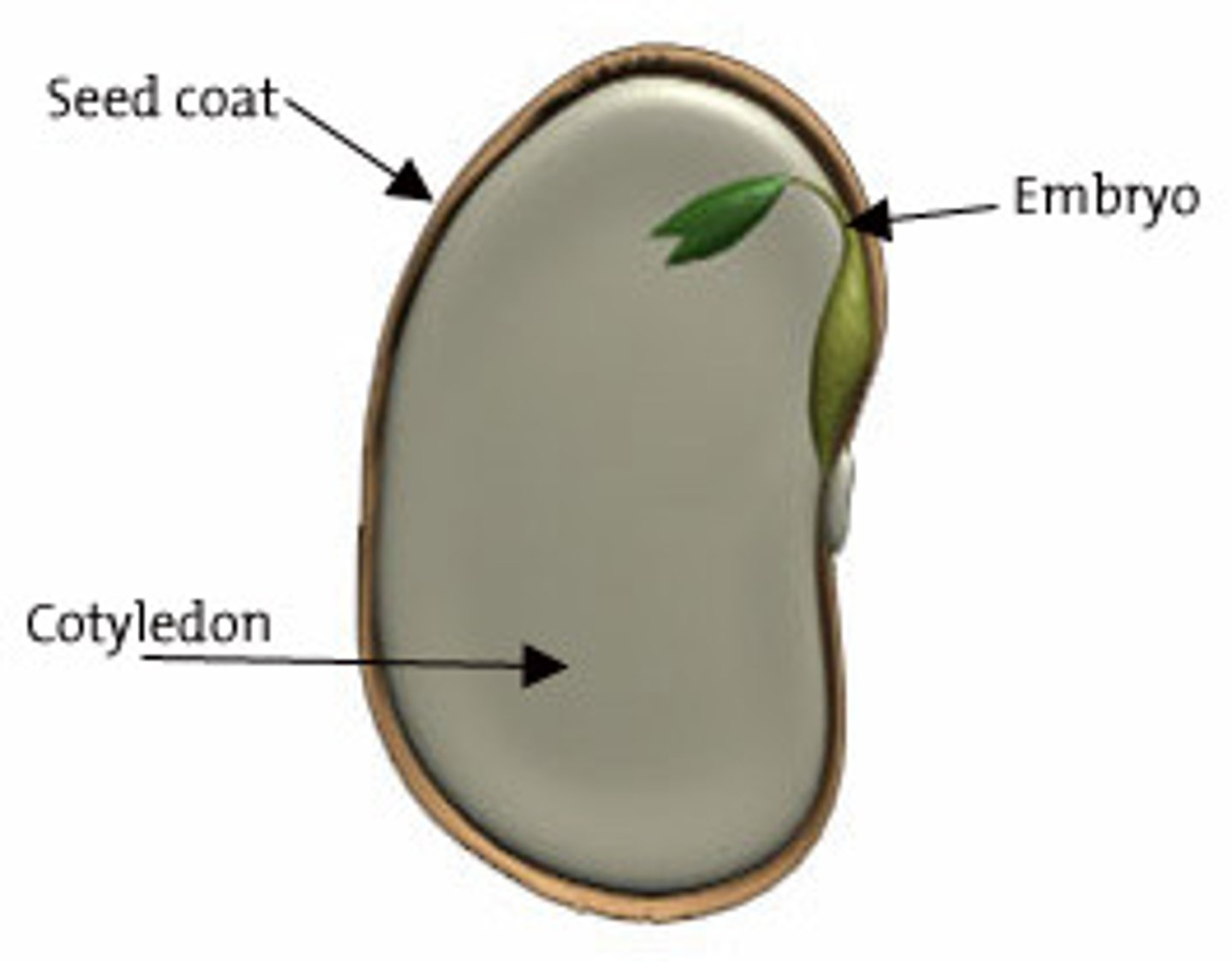
Seed
= plant embryo enclosed in a seed coat.
-Important evolutionary advantage over non-seed plants --> Domination
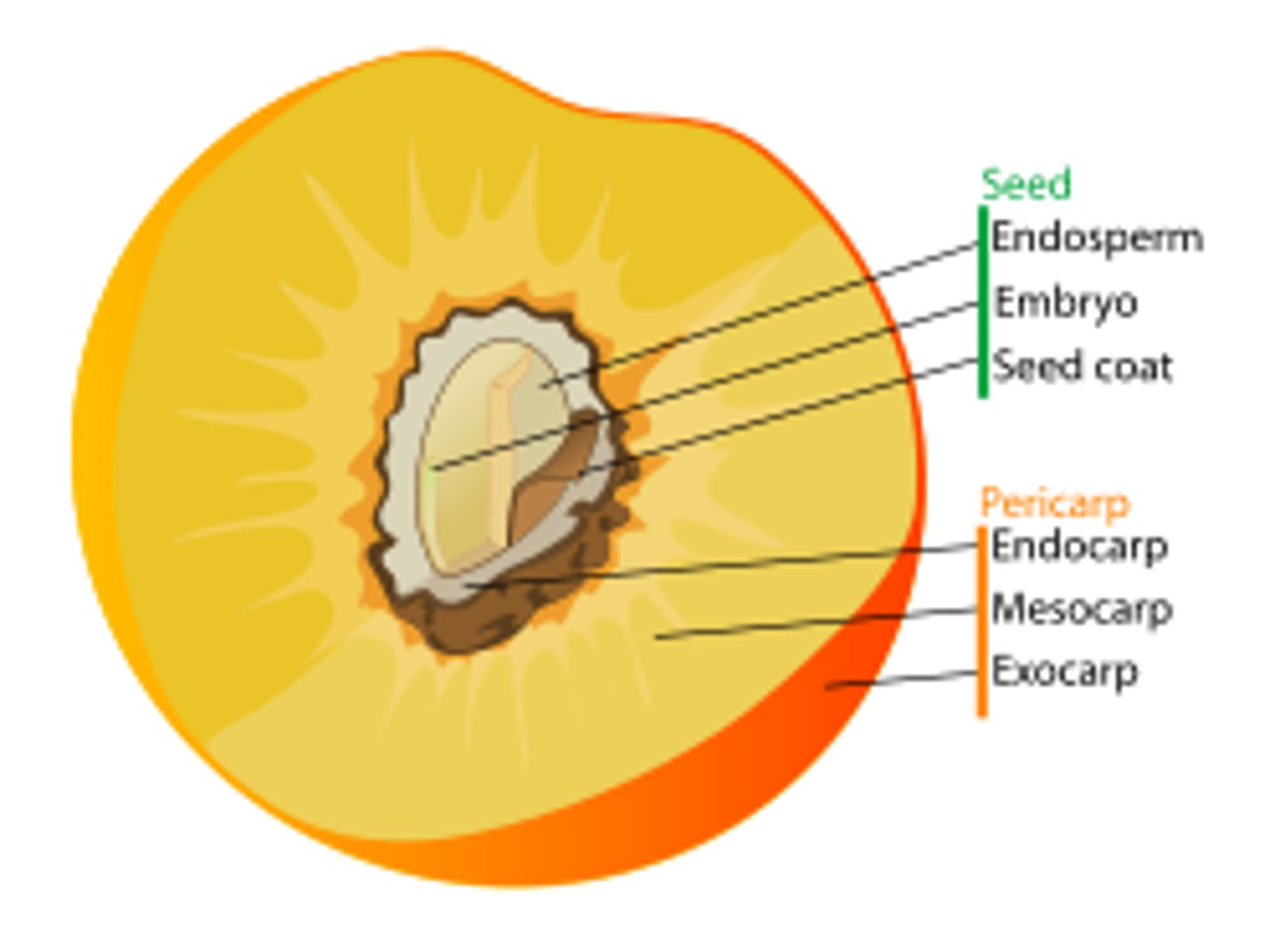
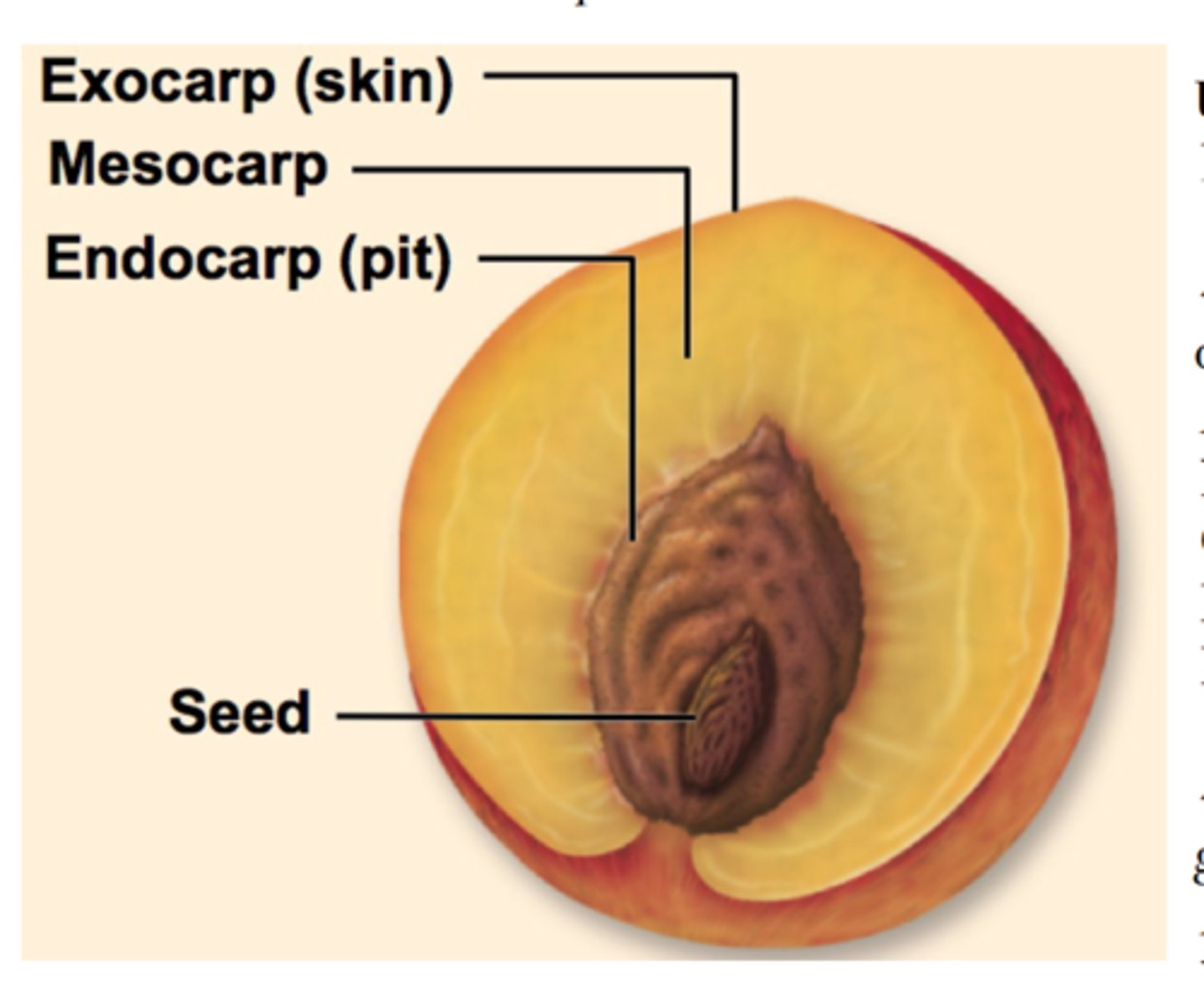
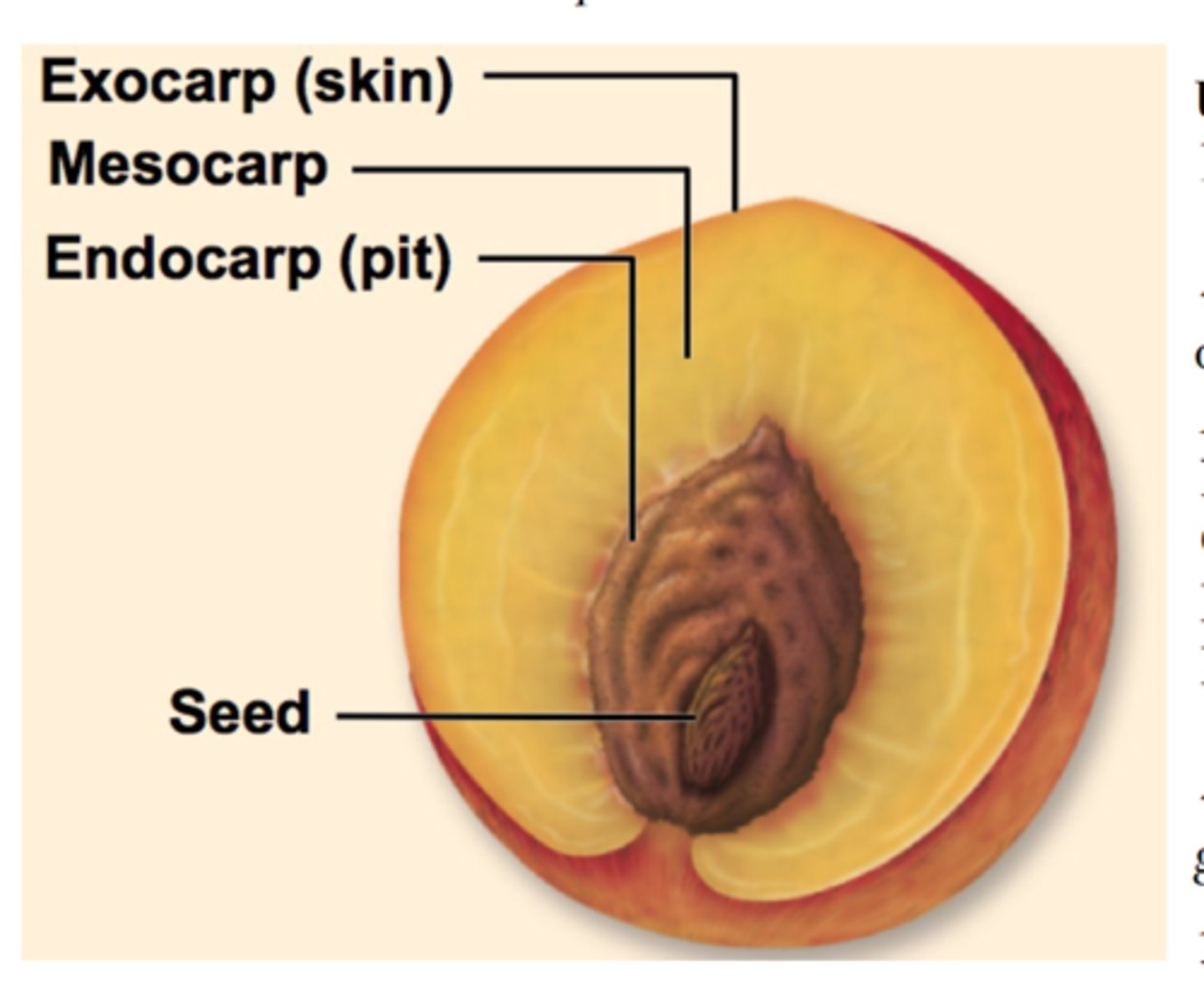
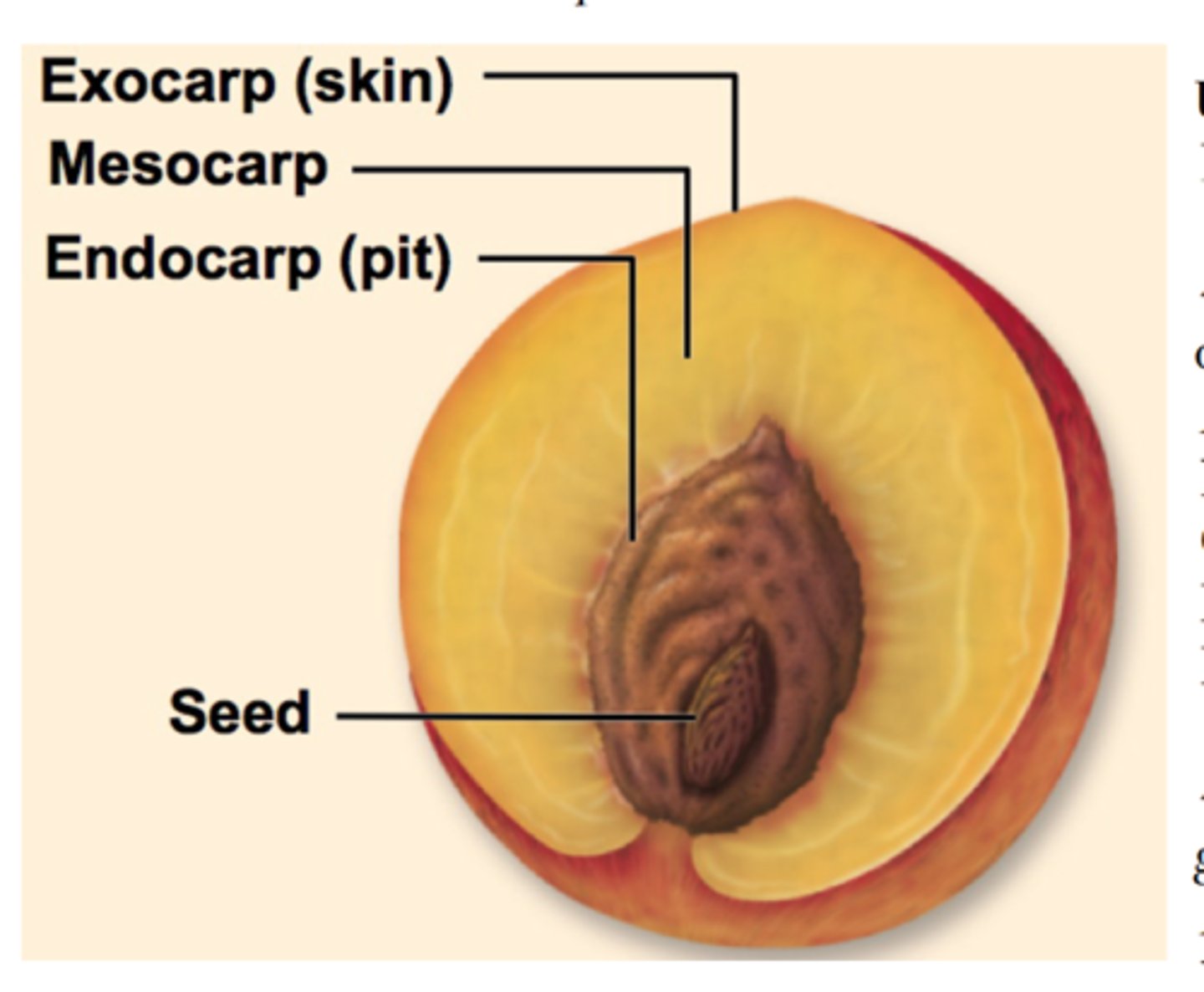
Pericarp
= ovary wall with 3 layers:
i) Exocarp
ii) Mesocarp
iii) Endocarp
Exocarp
= outer skin-like layer of fruit
Mesocarp
= middle layer of fruit that is usually soft + fleshy
Endocarp
= innermost layer of pericarp that surrounds the seed/seeds.
- Not present in most fleshy fruits
Main fruit types
i) Simple fruit
ii) Compound fruit
Simple fruit
= A fruit derived from a single carpel or several fused carpels.

Compound fruit
= a fruit composed from a multiple carpel ovary.

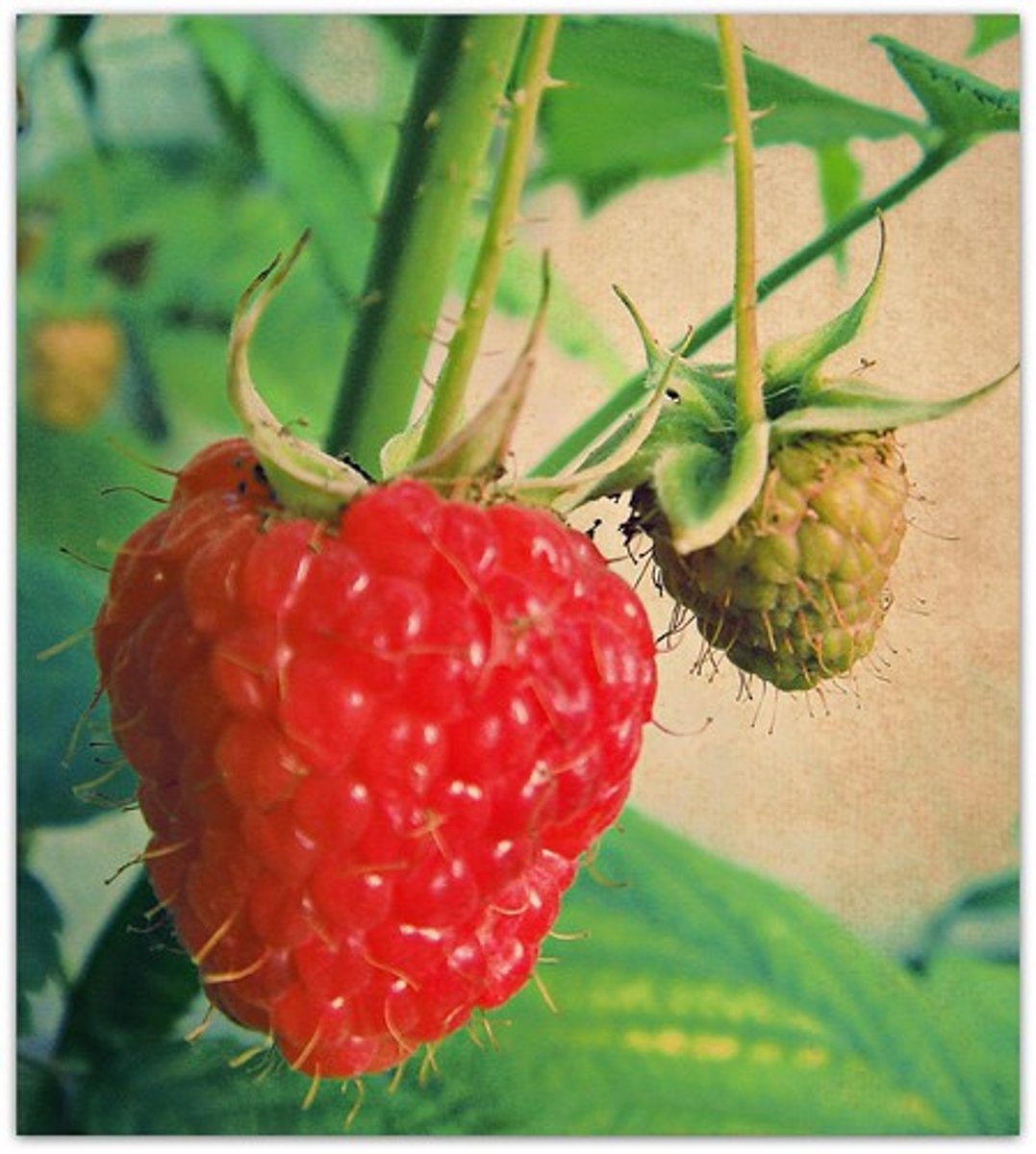
Aggregate fruit
= fruit developing from single flower with multiple carpels.
-Ex: Strawberry, raspberry

Multiple fruit
= a fruit composed of multiple mature ovaries each produced in a separate flower.
-Ex: Pineapple

Indehiscent
= fruit in which the seeds remain in the pericarp.
Dehiscent
= fruit that splits open to release its seeds.
Fleshy pericarp
= edible layer of fruit.
-Ex: Tomato, apple
Fruit
= mature ovary
-Means by which angiosperms disseminate seeds.
- Allows for symbiotic relationship between animals + plants
Secondary growth
= Growth produced by lateral meristems, which thickens the roots and shoots of woody plants.
-THICKEN
-DICOTS
-Monocots do not perform secondary growth because of their vascular tissue design.
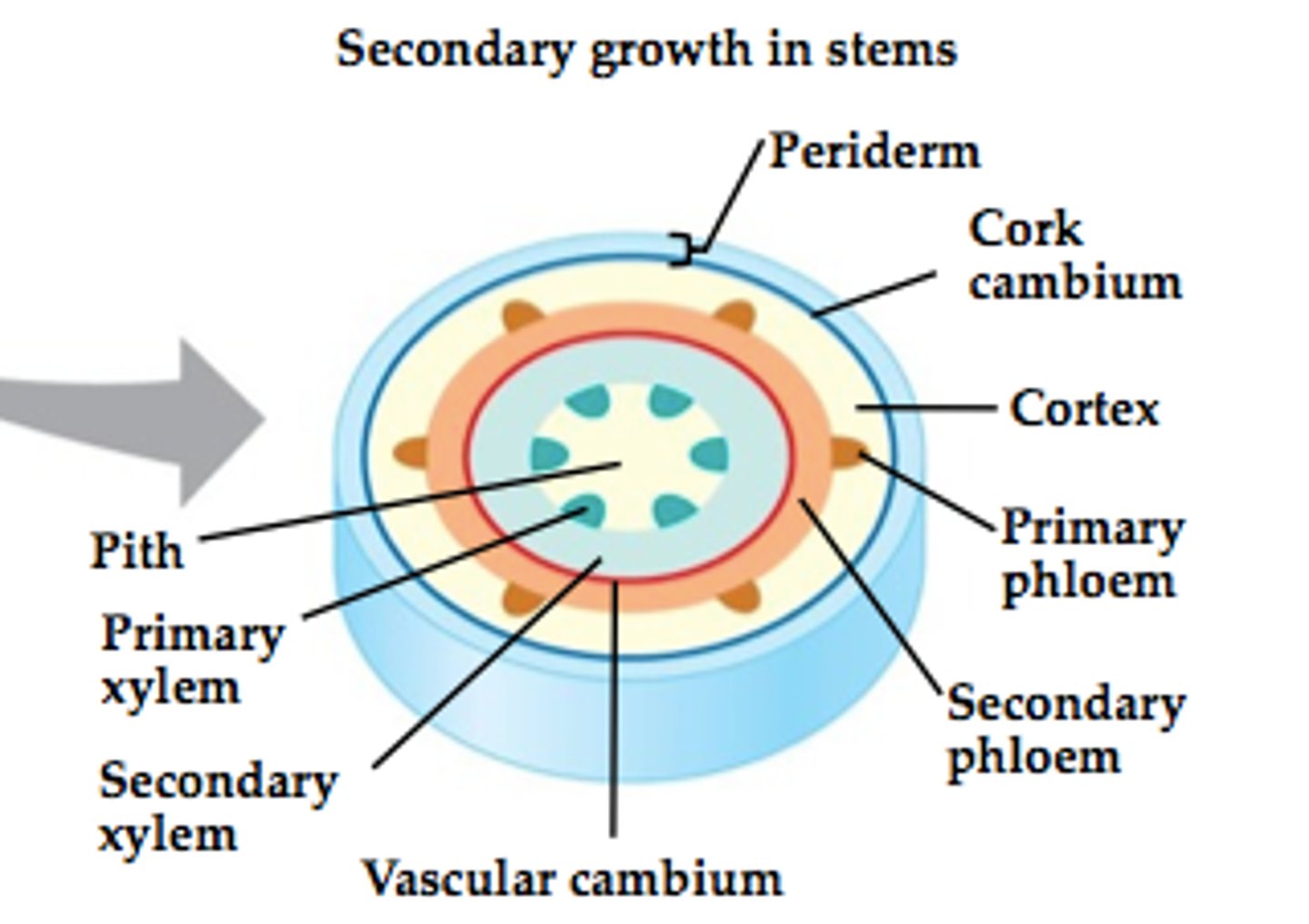
Vascular cambium
= A cylinder of meristematic tissue in woody plants that adds layers of secondary vascular tissue called secondary xylem (wood) and secondary phloem.
= Fusiform initials + Ray initials
-Roots: Pericycle
-Shoots: Procambium
Initial
= cell in a meristem that by division gives rises to 2 cells; one cell remains in meristem + other cell differentiates.
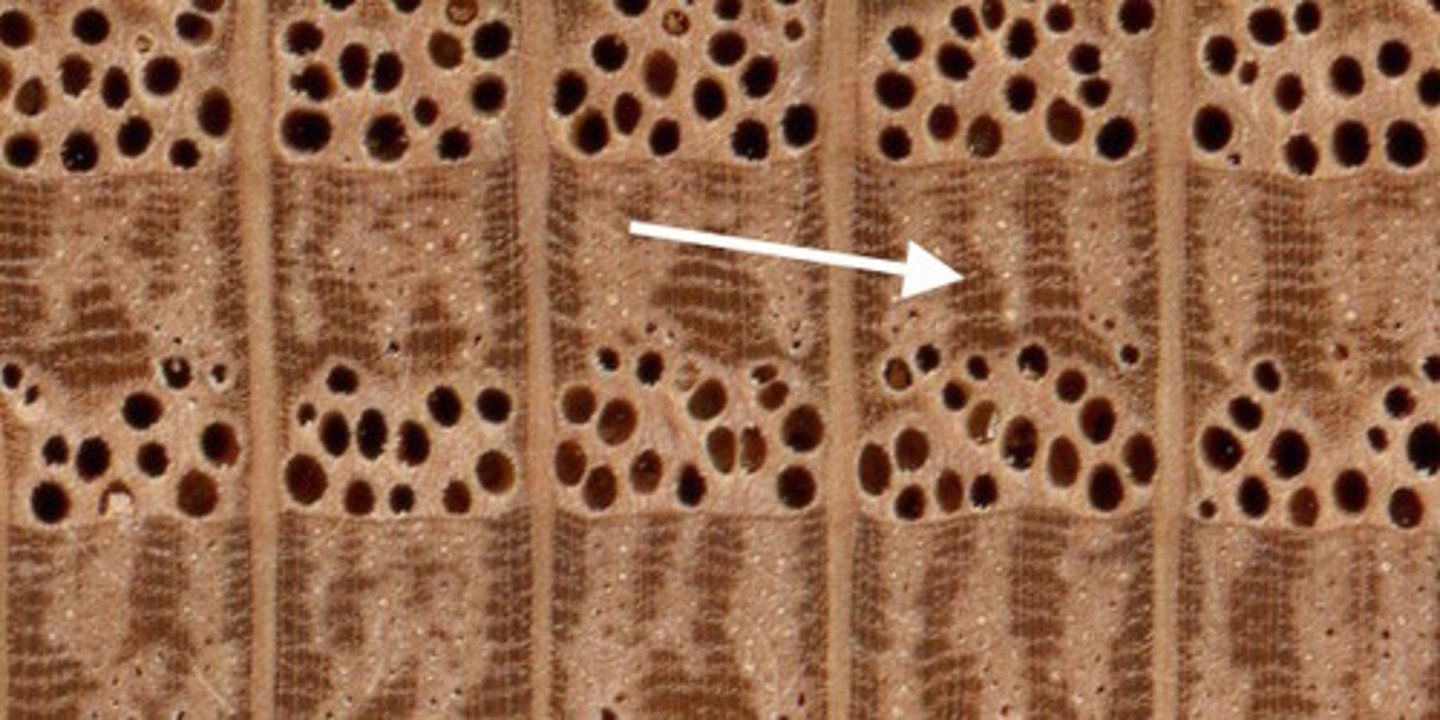
Earlywood
= springwood, lighter colored wood formed during the spring that is:
i) Less dense
ii) Grow more
-Has more water available
Latewood
= summerwood, darker colored wood formed during summer that is
i) More dense
ii) Grows less
-Has less water available
Heartwood
= Older xylem near the center of a woody stem that no longer conducts water but provides structure
- Darker
- Less wet --> Less prone to rot
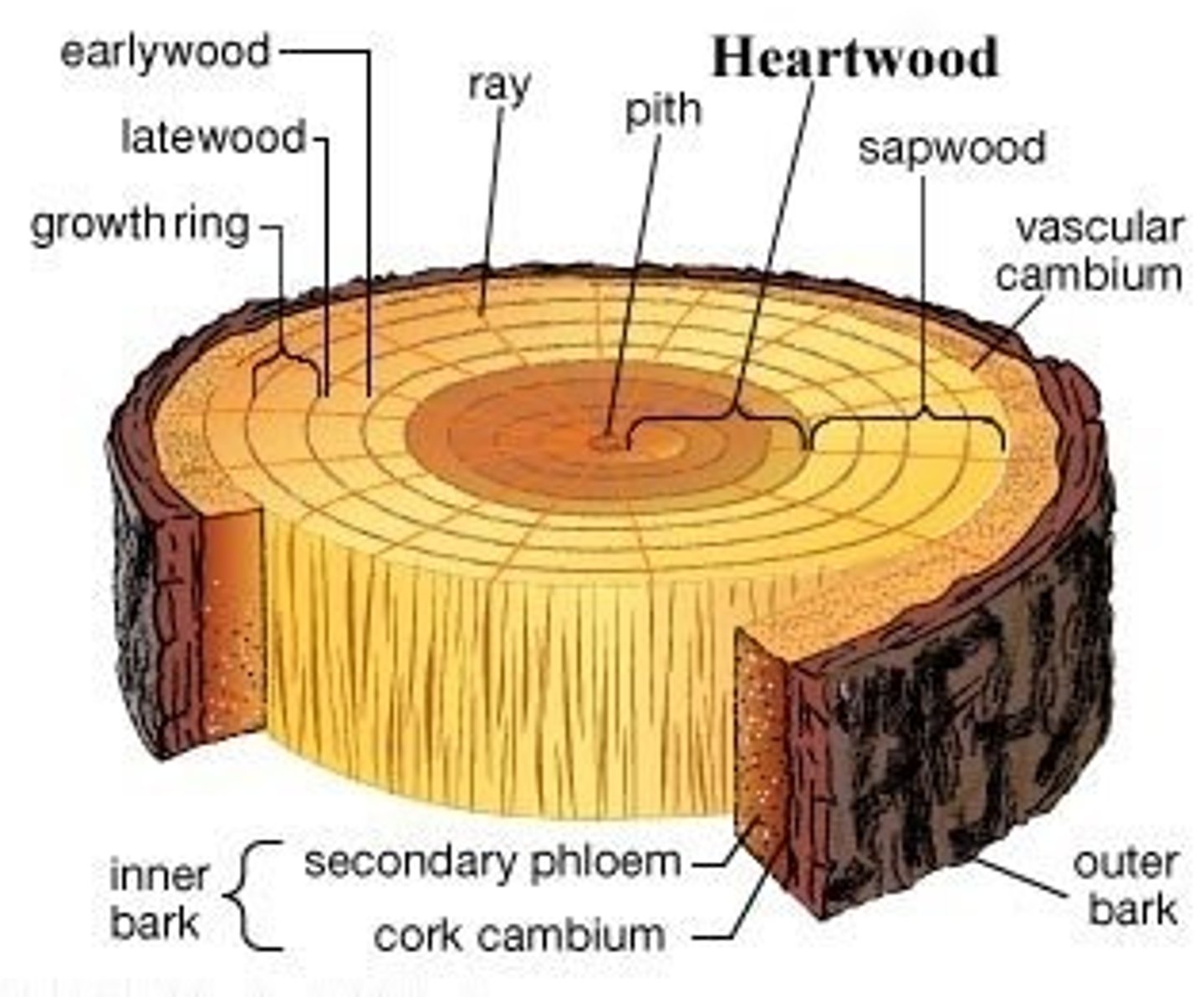
Sapwood
= younger xylem near outside of woody stem that conducts water + minerals.
-Lighter
-More wet --> More prone to rot
Periderm
= The protective coat that replaces the epidermis in plants during secondary growth
= Cork and Cork cambium.
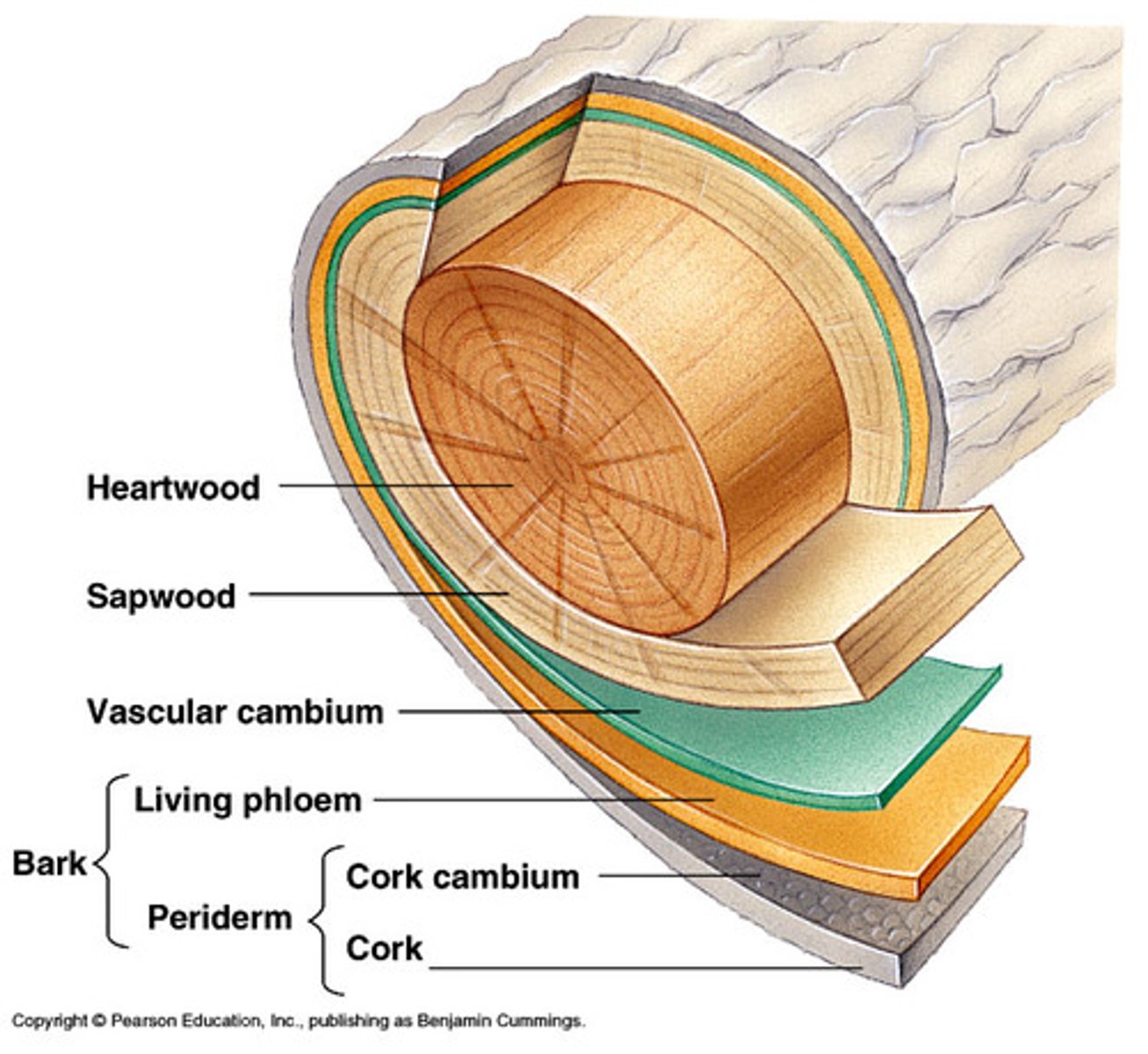
Phellem
= cork, tissue produced by phellogen that is external to phellogen.
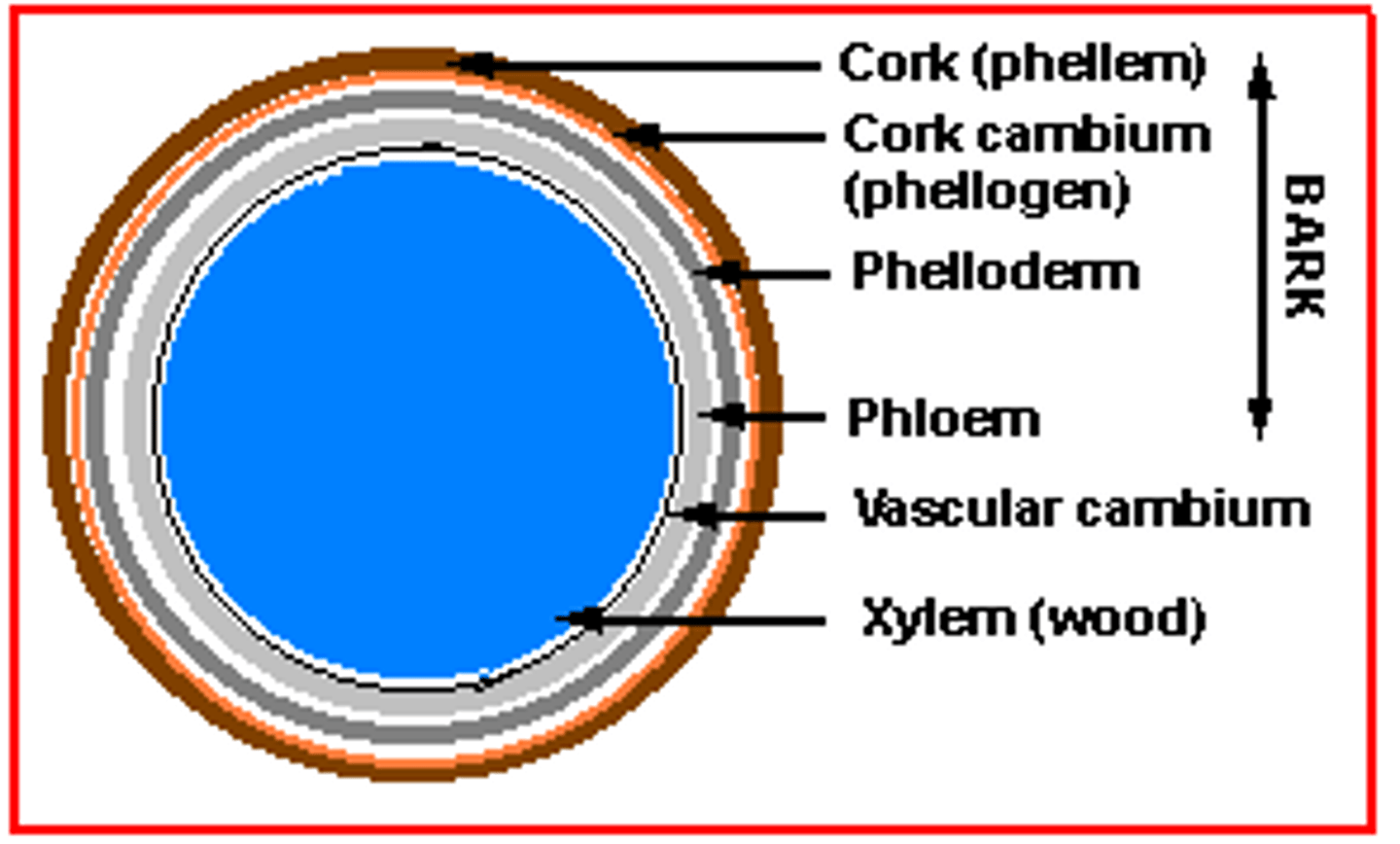
Phellogen
= cork cambium, produces phellem + phelloderm
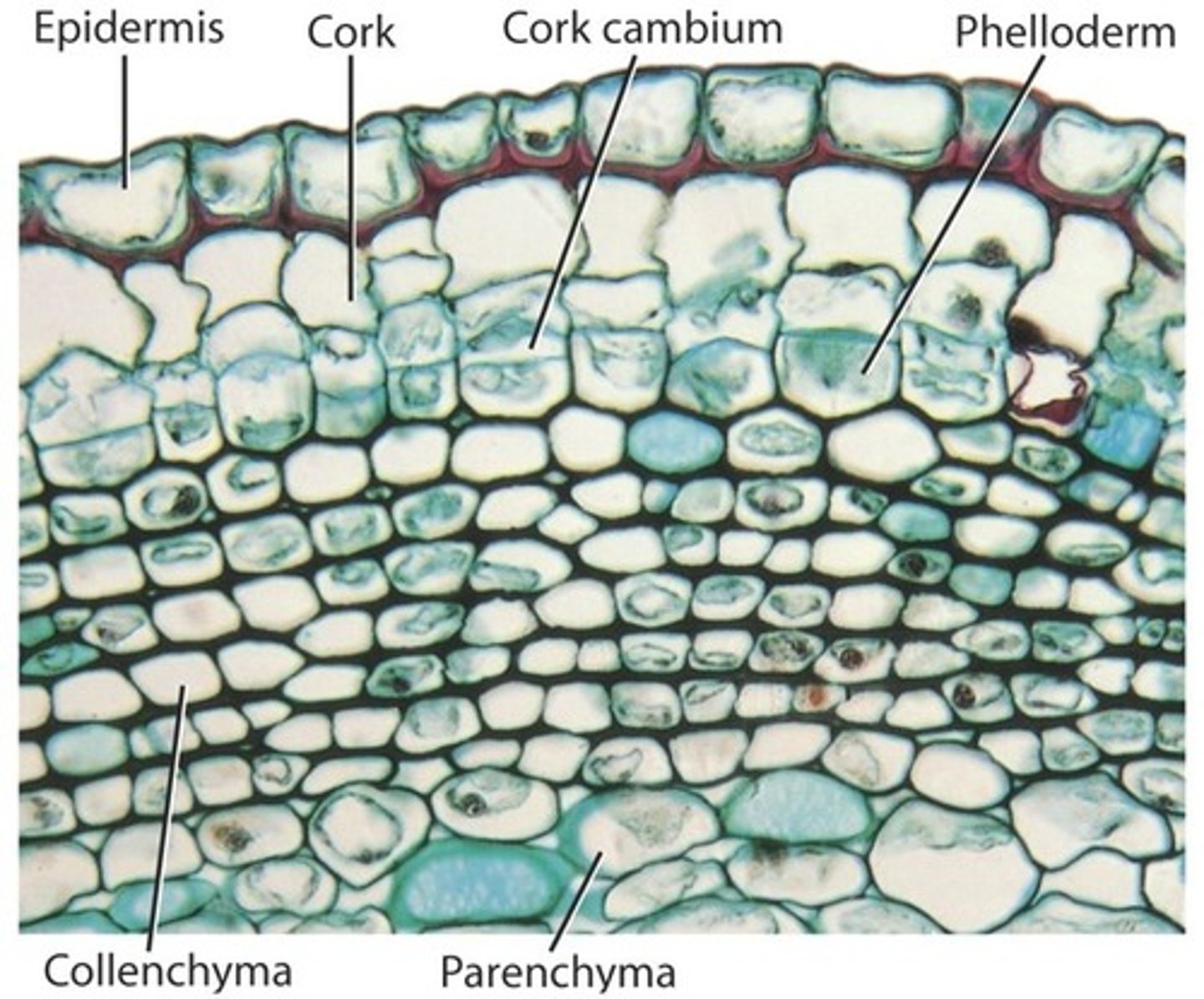
Phelloderm
= phellogen produced tissue that is internal to phellogen.
Lenticel
= specialized region in periderm containing intercellular spaces which allows for gas exchange.

Anomalous secondary growth
= Any form of secondary growth that does not conform.
-Gymnosperms + Dicots
-Climbing species
Anomalous secondary growth types
i) Abnormal activity of Normal Cambium
ii) Abnormally situated cambium that forms normal secondary vascular tissues.
iii) Formation of secondary tissue by accessory cambium
iv) Formation of inter-xylary phloem = Phloem between xylem
v) Formation of intra-xylary phloem = Phloem in xylem
Secondary growth in roots
= occurs as thickening of root via addition of vascular tissue.
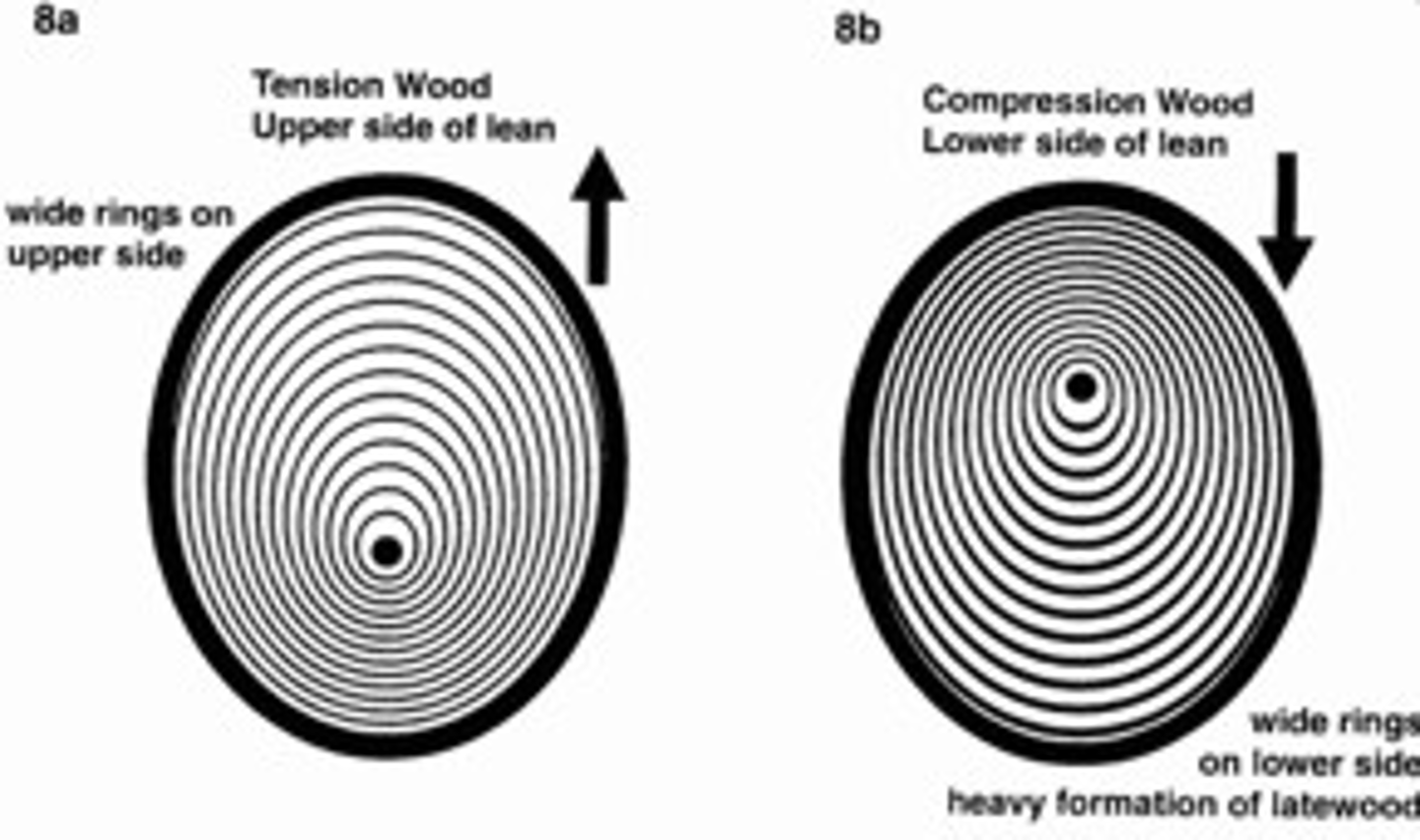
Reaction wood
= wood formed in place of normal wood as gravity response.
i) Compression wood
ii) Tension wood
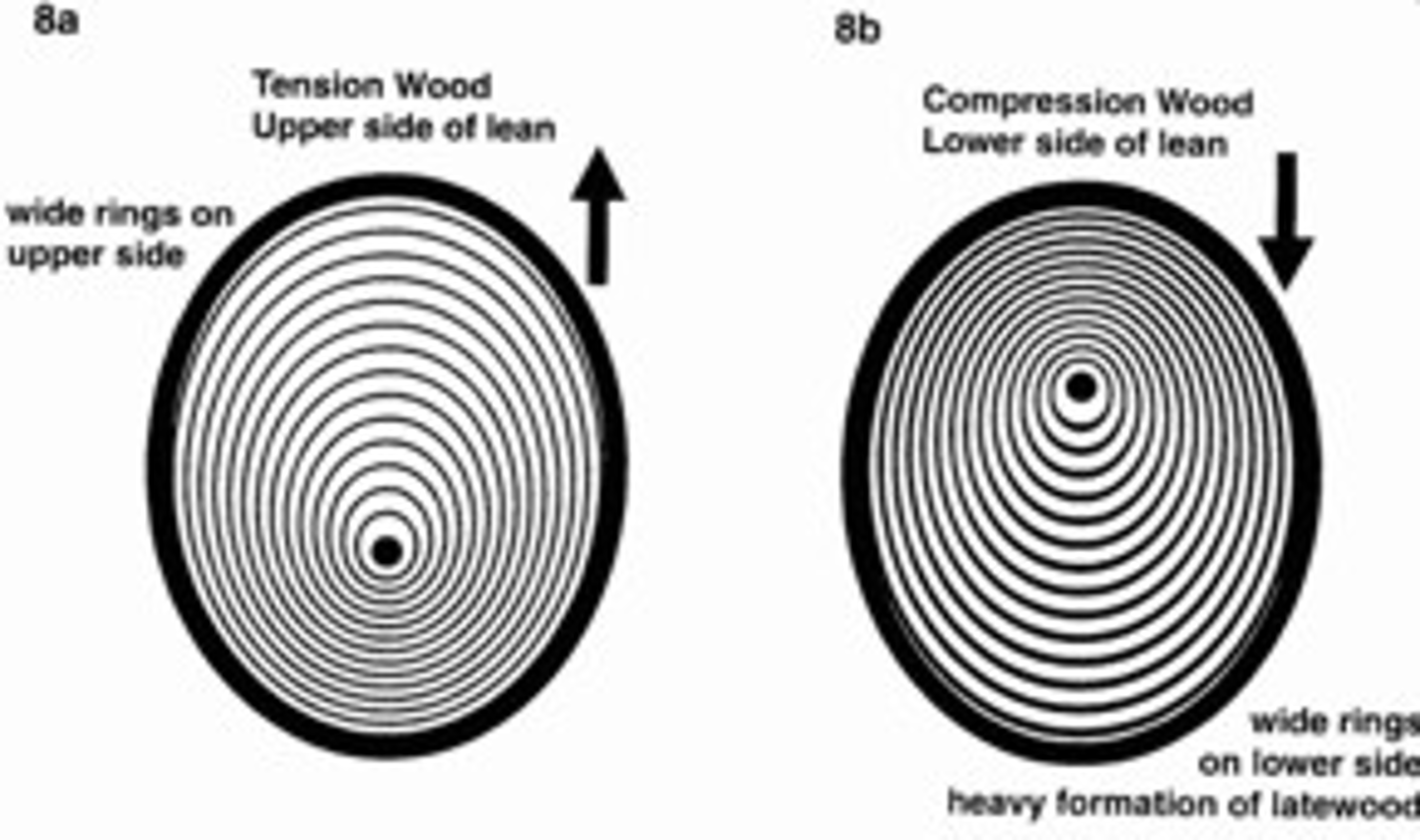
Compression wood
= the reaction wood of gymnosperms that grows in direction of weight to prop itself up.
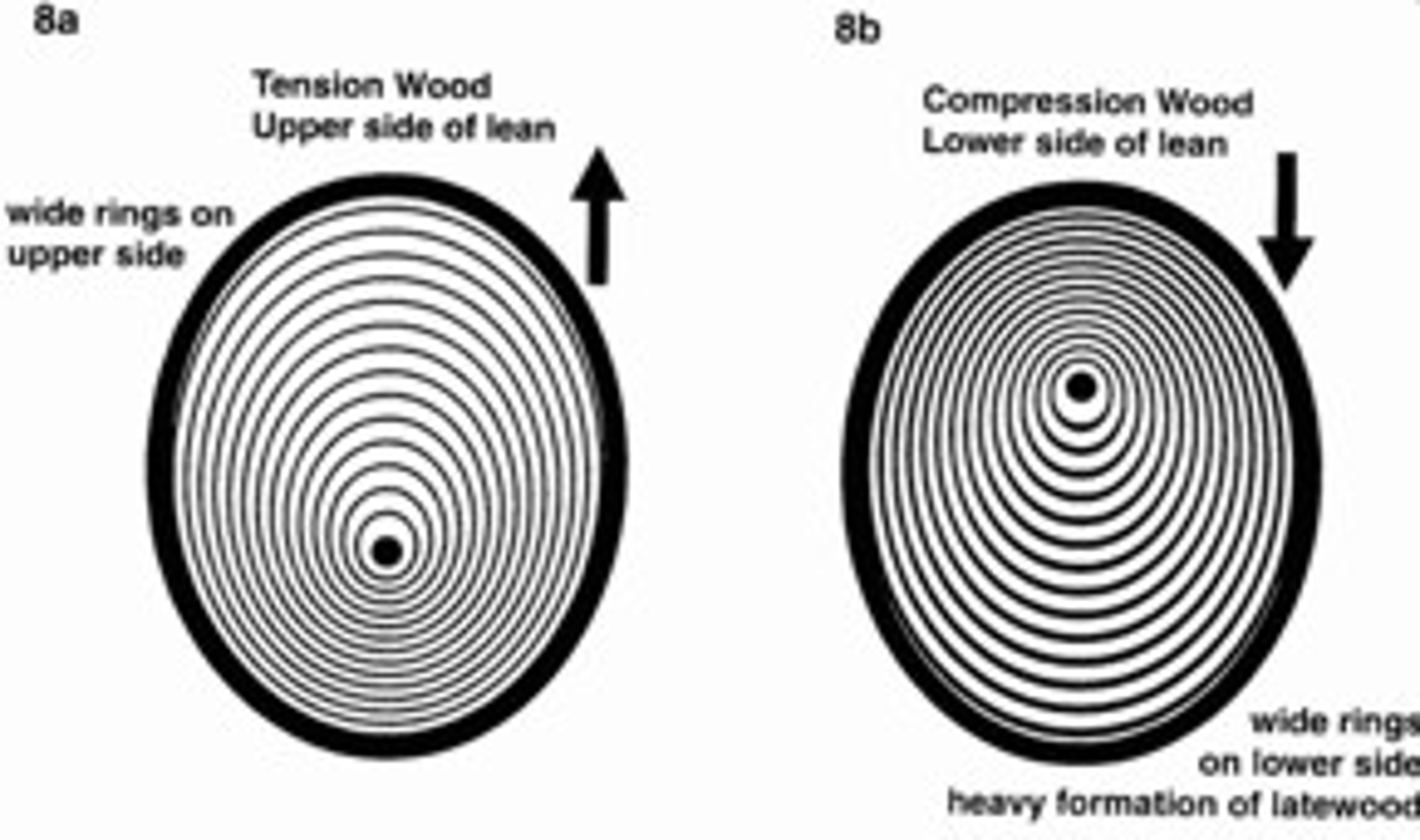
Tension wood
= reaction wood of angiosperms that grows in direction opposite of weight.
-Tries to pull itself up