Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis Overview
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Eukaryotic Cell Cycle
Life cycle of a typical eukaryotic cell.
Mitosis
Process producing two genetically identical daughter cells.
Meiosis
Process producing four genetically diverse gametes.
Interphase
Preparation phase for cell division.
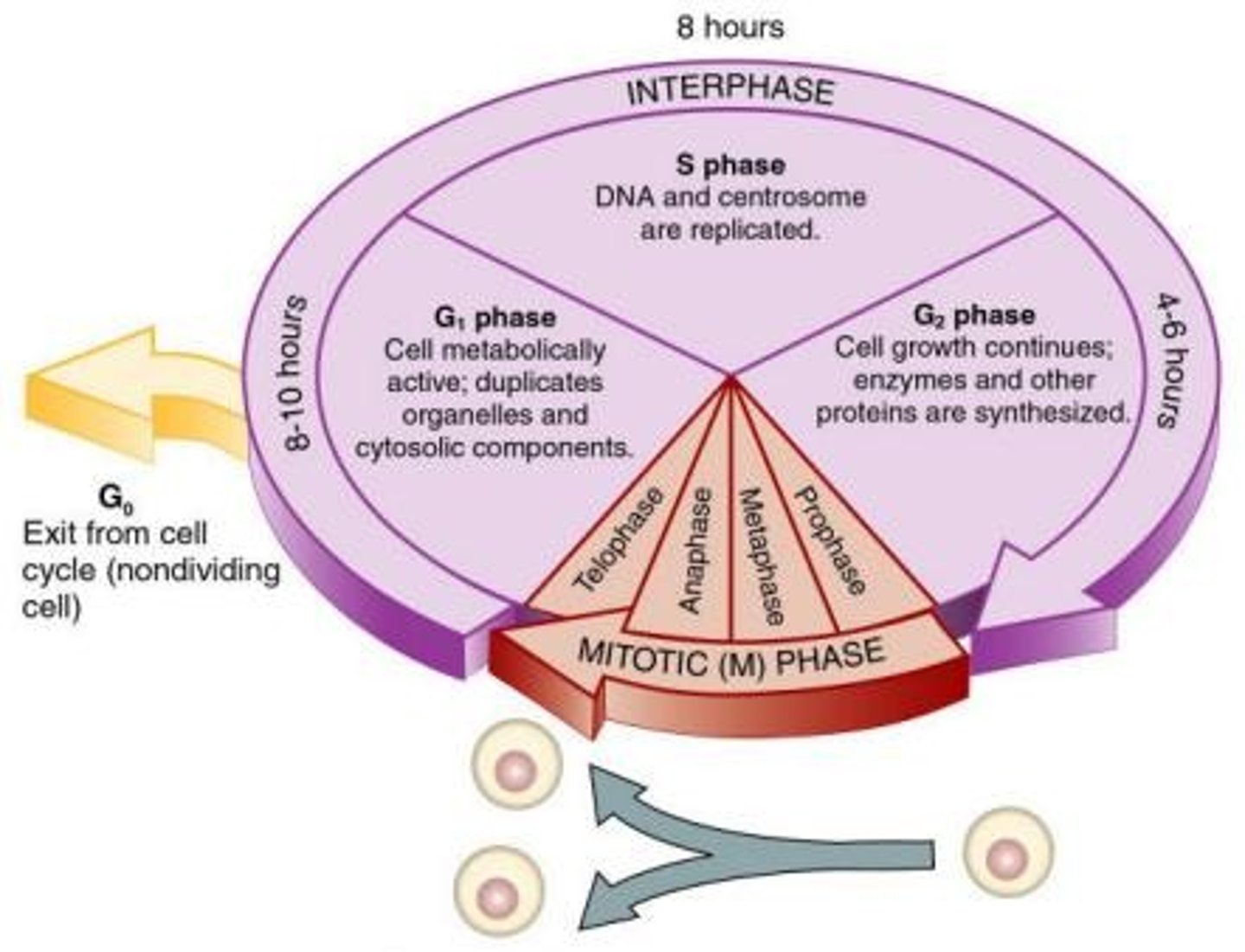
G1 Phase
Cell growth and organelle replication.
S Phase
DNA synthesis occurs, producing identical copies.
G2 Phase
Final preparations for mitosis, checks DNA synthesis.
Mitotic Phase
Division of the nucleus and cytoplasm.
Prophase
Chromatin condenses into chromosomes, spindle forms.
Metaphase
Chromosomes align at the metaphase plate.
Anaphase
Sister chromatids are pulled apart to poles.
Telophase
Chromosomes revert to chromatin, nuclear envelopes reform.
Cytokinesis
Division of cytoplasm, forming two complete cells.
Checkpoints
Regulatory points ensuring proper cell cycle progression.
G1 to S Checkpoint
Decides if the cell should divide.
G2 to M Checkpoint
Checks readiness to enter mitosis.
CDK
Cyclin-dependent kinase, regulates cell cycle progression.
Cyclin
Binds to CDK, activating it for mitosis.
MPF
Mitotic Promotion Factor, initiates mitosis.
Colchicine
Inhibits mitosis by blocking microtubule formation.
Meiosis I
Homologous chromosomes are separated.
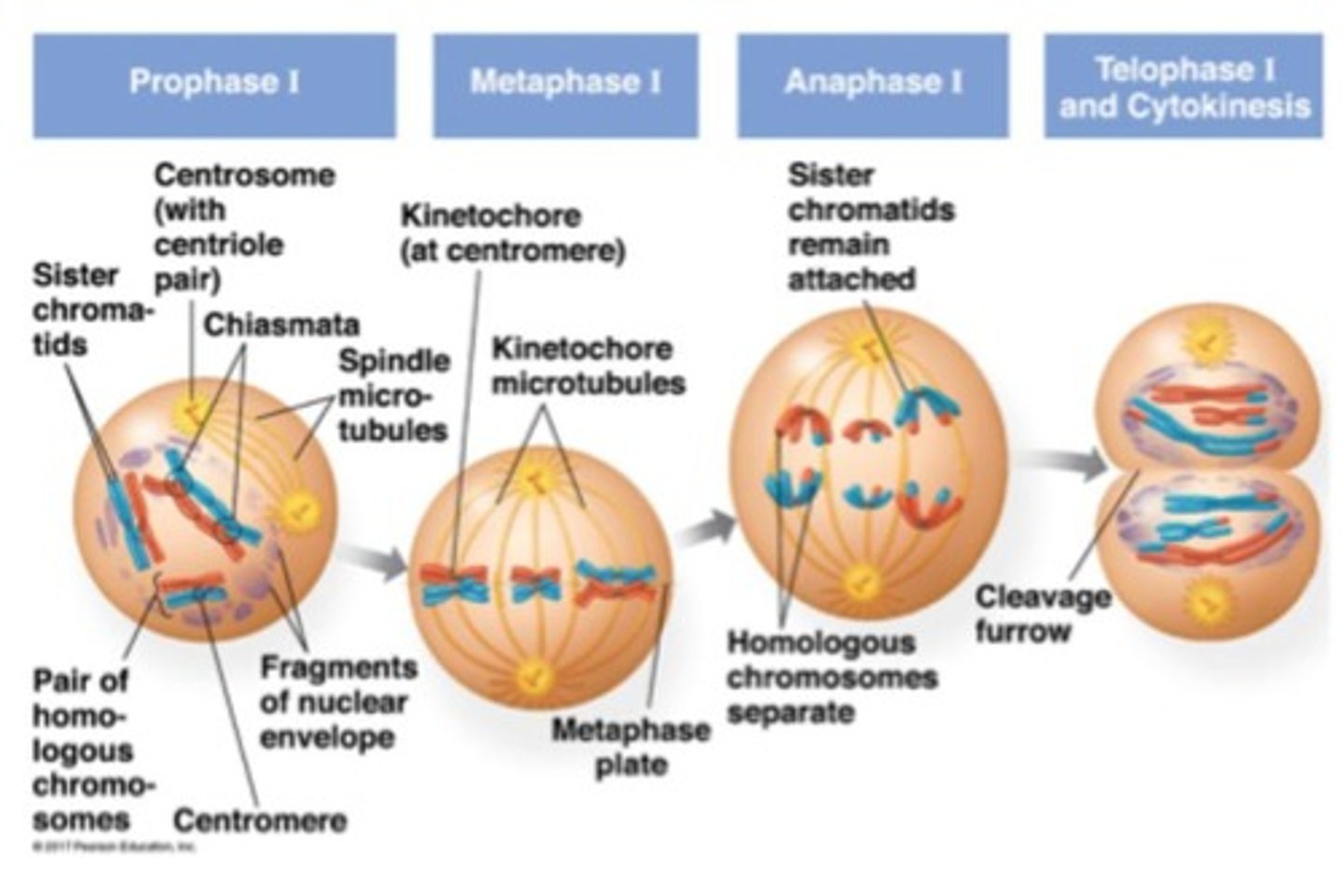
Prophase I
Chromosomes condense, homologous pairing and crossing over.
Metaphase I
Homologous chromosomes align at the equator.
Anaphase I
Homologous chromosomes pulled to opposite ends.
Telophase I
Two new cells form with one chromosome each.
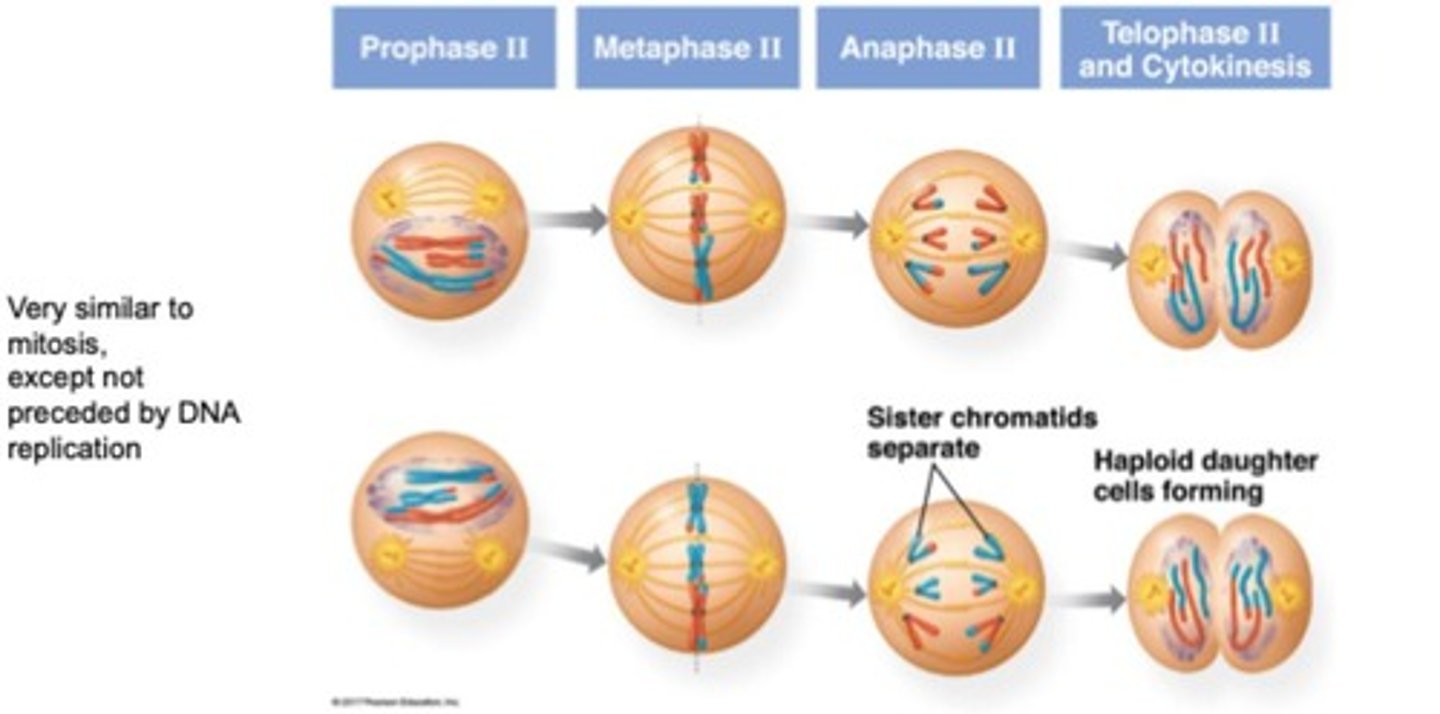
Meiosis II
Similar to mitosis, separates sister chromatids.
Genetic Variation
Occurs in meiosis through crossing over.
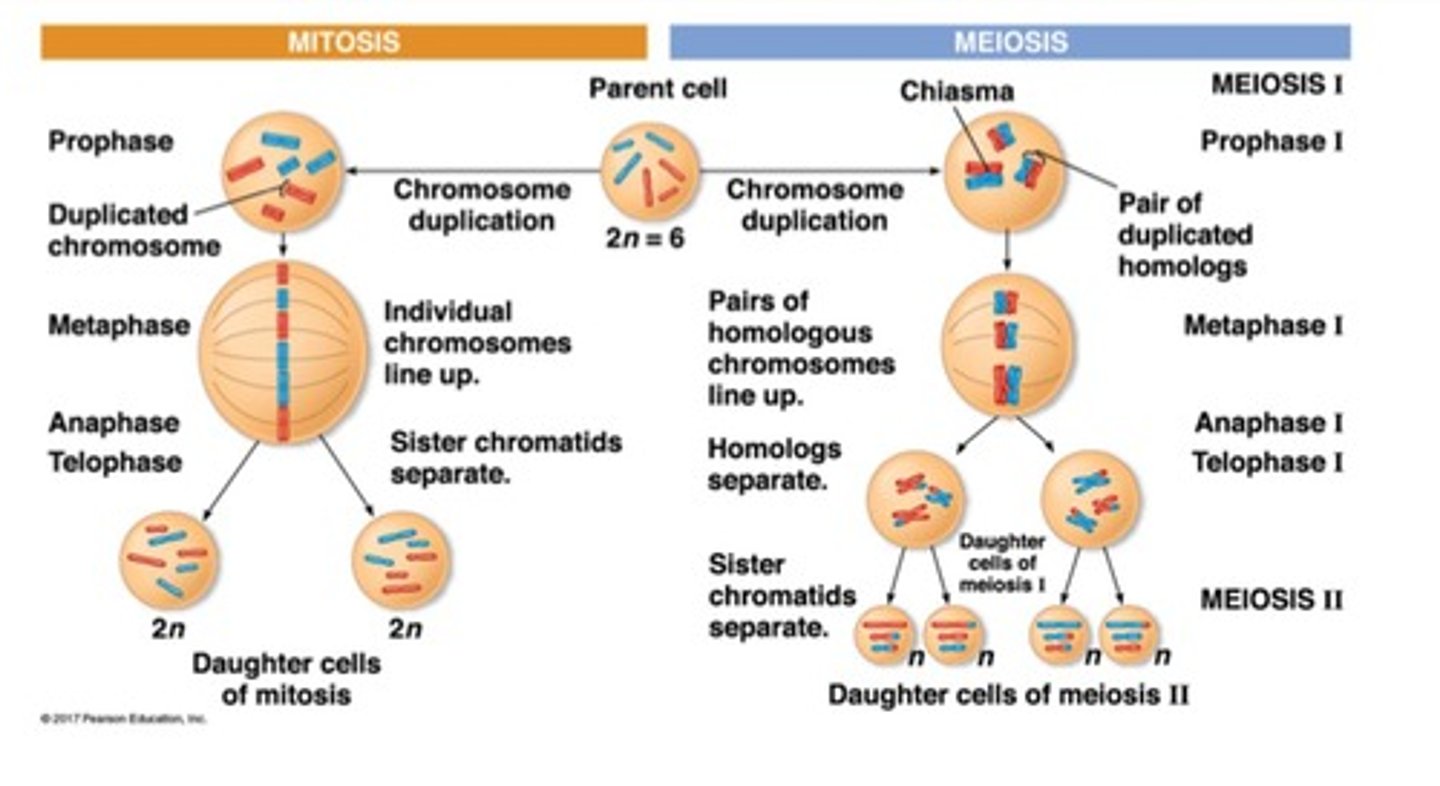
Diploid Cells
Cells with two sets of chromosomes (2n).
Haploid Cells
Cells with one set of chromosomes (1n).