Female sexual cycle (incl hormonal changes and menopause)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Monthly endometrial cycle is associated with and the cycle phases?
Associated with monthly estrogen/progesterone production by ovaries is endometrial cycle lining of uterus
Proliferation uterine endometrium
Secretory changes develop in endometrium
Desquamation of endometrium (menstruation)
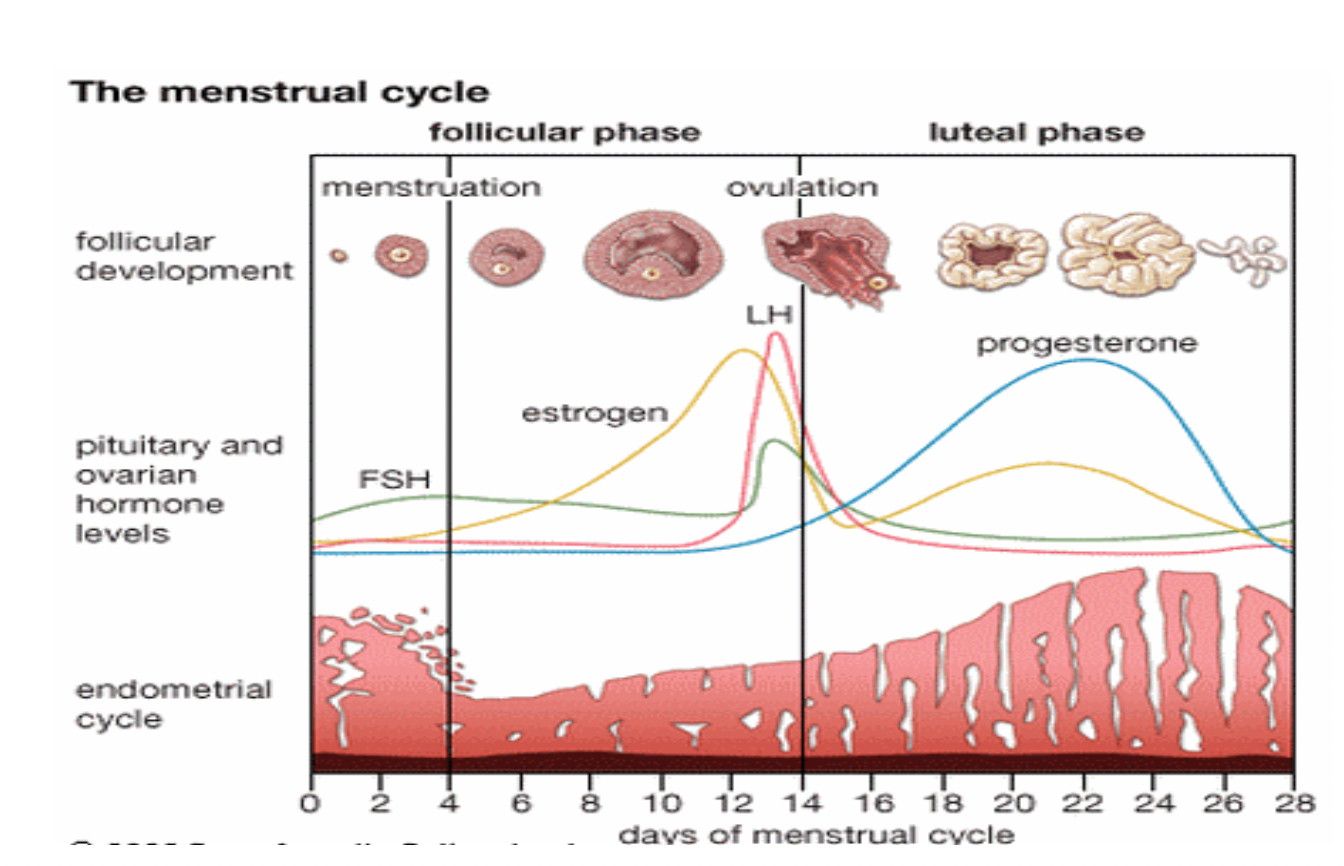
Endometrial cycle: Proliferative phase (Estrogen phase) occurs when and process
Occurs : Before ovulation (with follicular phase)
↑estrogens secretion by ovary during 1st part of monthly ovarian cycle so stromal cells & epithelial cells proliferate rapidly.
Endometrial surface re-epitahlized within 4 to 7 days after menstruation starts
Next wk and ½ before ovulation occurs → ↑ endometrium thickness (greatly) as ↑stroma cells and progressive growth of endometrial glands & new blood vessels into the endometrium
Endometrial cycle: Secretory phase (Progestational phase) occurs when , process and purpose
Occurs: After ovulation (with luteal phase)
Process
After ovulation progesterone and estrogen secreted in large amount by corpus luteum
Estrogen cause slight more cellular prolliferation of endometrium
Progesterone causes marked swelling and secretory development of endometrium
↑ tortuosity of Glands and excess secretory subst accumulates in glandular epithelial cells. Blood vessel becomes highly tortuous,
Purpose: Produce highly secretory endometrium contians large amount of stored nutrients to provide appropriate implantation condition for fertilized ovum during later half of monthly cycle
Endometrial cycle: Menstruation
If ovum not fertilised about 2 days before end of monthly cycle → corpus luteum in ovary involutes and ovarian hormones (estrogens and progesterone) ↓ to low levels of secretion
Menstruation caused by ↓estrogen and especially ↓progesterone at end of monthly ovarian cycle
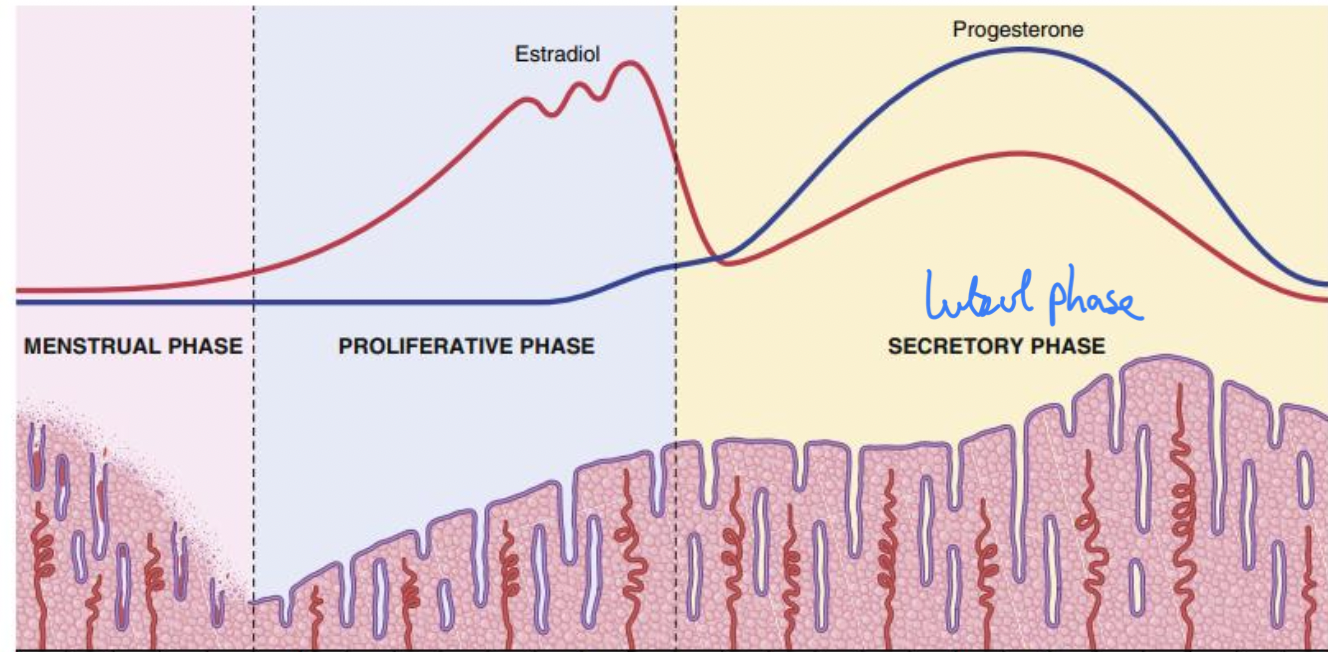
Estradiol during female sexual cycle
Estradiol
Preovulatory phase : Secreted large amounts by growing follicles under FSH influence
2 days before ovulation: ↑Estrogen secretion by graafian follicle
Postovulatory phase: Plasma estrogen level initially low due to Graafian follicle rupture
After corpus luteum forms: ↑Estrogen secretion but ↓ 2 days before end of cycle due to corpus luteum degeneration)
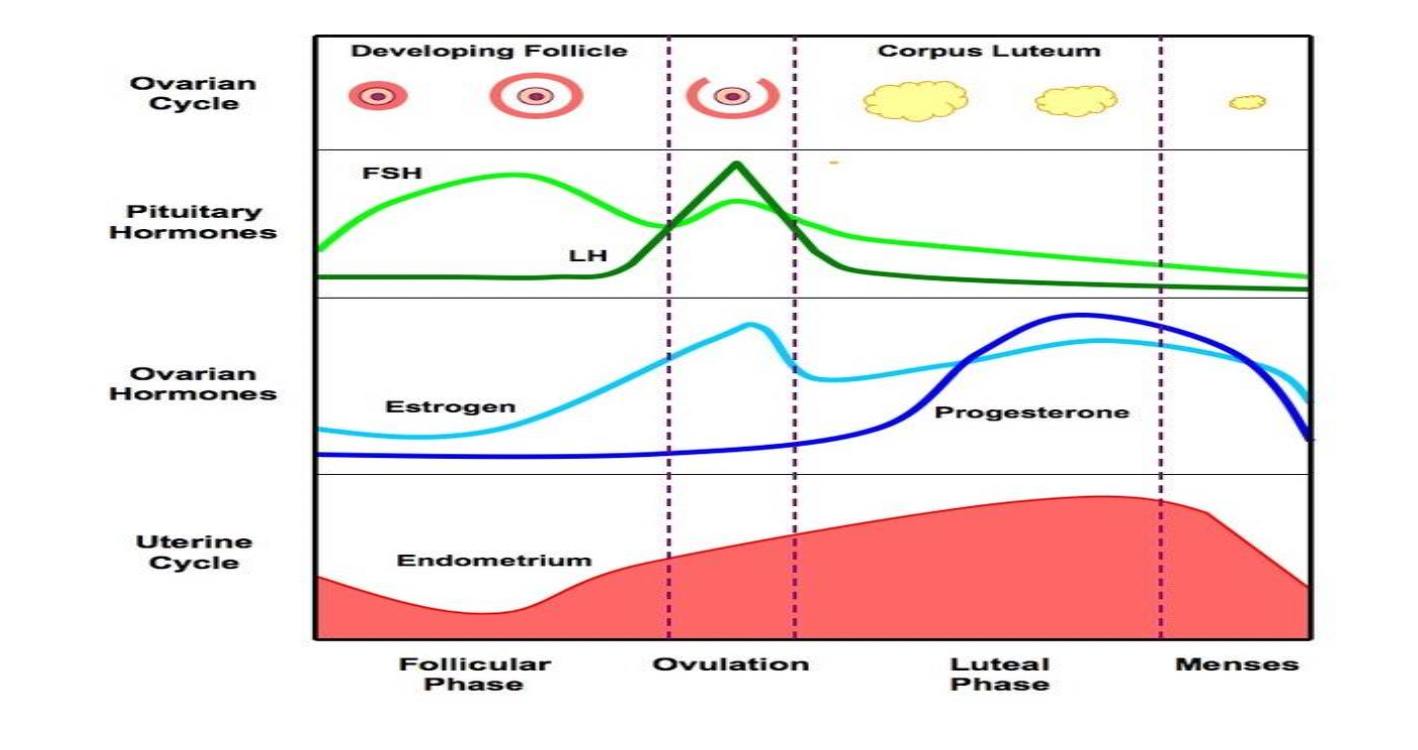
Progesterone during female sexual cycle
In preovulatory phase: Small amounts of progesterone secreted by ovarian follicles (mainly estrogen secretion)
In postovulatory phase: ↑ progresterone secreted by corpus luteum reaching peak on Day 22. 2 days before next cycle ↓ secretion rate due to corpus luteum degeneration
FSH during female sexual cycle and FSH functions
Preovulatory phase: High rate of FSH secretion as low plasma estrogen. When high plasma estrogen level cause - feedback ↓FSH level
2 days before ovulation: ↑FSH secretion by 2-3 folds due to + feedback effect of high estrogen level on anterior pituitary
Postovulatory phase: ↓FSH secretion cuz of high estrogen level secreted by corpus luteum
Functions:
Early growth of ovarian follicles during follicular phase of ovarian cycle
FSH with LH responsible for Graafian follicle maturation.
Stimulate estrogen secretion by granulosa cells of growing ovarian follicles
LH during female sexual cycle and LH functions
Preovulatory phase: LH secretion from anterior pituitary constant (basal)
2 days before ovulation: ↑ LH by 6-10 folds (LH) due to + feedback effect of high estrogen level on anterior pituitary
Postovulatory phase: LH secretion inhibited by - feedback of high progesterone level secreted by corpus luteum
Functions:
Regulates estrogen secretion from theca interna and granulosa cells of ovarian follicles
LH surge needed for ovulation and LH needed for corpus luteum formation
Stimulates estrogen and progesterone secretion from corpus luteum
GnRH during female sexual cycle (How is it secreted , Pulsatile nature , GnRH changes in the Phases)
How is GnRH secreted?
Intermittent pulsatile secretion of GnRH by hypothalamus → pulsatile release of LH from anterior pituitary gland about every 90 mins
Pulsatile nature of GnRH
The hypothalamus secrete GnRH in pulses (not continuous) lasting 5 to 25 mins occurring every 1-2 hrs
If GnRH is infused continuously so available all time rather than in pulses,its ability to release LH and FSH by anterior pituitary gland is lost.
Phases
Preovulatory phase : ↑ Frequency
Midcycle (LH surge): Gonadotropes more sensitive to GnRH cuz of exposure to GnRH pulses of high freq
Postovulatory: ↓ Frequency cuz of progesterone
Menopause (Def, Mechanisms, Manifestations)
Def: Menopause means end of menstruation due to ageing. Normal age between 40-50 yrs.
Mechanism of menopause
Burning out of ovaries
Puberty = 300,000 primordial follicles present in 2 ovaries
Thought reproductive life 400 primordial follicle grow to mature follicles and ovulate and rest degenerate.
About 45 years only few primordial follicles to be stimulated by FSH and LH so ↓estrogen production by ovaries.removes - feedback on pituitary. Increase of FSH and LH.
2. Aging of remaining follicles so cant’ respond to pituitary gonadotropes and fail to ovulate
Manifestations of Menopause
Loss of estrogen causes physiological changes in body function including…
Hot flushes due to vasomotor instability
Anxiety , irritability and fatigue
Atrophy and fibrosis of ovaries
Atrophy of 2ry sex organs except clitoris as it is androgen dependent
↓ bone strengths and calcification throughout body (osteoprosis) and muscle wasting due to loss of anabolic effects of estrogen