Physio Lab Exam 2
0.0(0)Studied by 0 people
Card Sorting
1/106
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:19 PM on 3/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
1
New cards
Where is the heart located?
between the 2nd and 5th intercostal spaces
2
New cards
Where is the heart located?
within the thoracic cavity in the mediastinum
3
New cards
Types of pericardium
fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium
4
New cards
Layers of the serous pericardium
parietal layer, pericardial cavity, and visceral layer (epicardium)
5
New cards
Layers of the heart
epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium
6
New cards
What is myocardium composed of?
cardiac muscle and forms the bulks of the heart
7
New cards
Pericarditis
inflammation of the pericardium
visceral and parietal pericardium stick together and impede heart activity
visceral and parietal pericardium stick together and impede heart activity
8
New cards
Cardiac tamponade
excess fluid compresses the heart and limits its ability to pump blood
9
New cards
Describe blood flow in the heart
SVC/IVC/coronary sinus > right atrium > tricuspid valve > right ventricle > pulmonary semilunar valve > pulmonary trunk > pulmonary arteries > lungs > pulmonary capillaries/veins > heart > left atrium > mitral valve > left ventricle > aortic semilunar valve > aorta > systemic capillaries > body
10
New cards
Semilunar valves
prevents backflow into the ventricles when ventricles relax
11
New cards
2 types of semilunar valves
pulmonary valve and aortic valve
12
New cards
Pulmonary valve
controls blood flow of deoxygenated blood from right side of heart into pulmonary trunk
13
New cards
Aortic valve
regulates the oxygenated blood flow from the left side of the heart into the aorta
14
New cards
In diastole (relaxation) phase, which valves are open and closed?
AV valve - open
SV valve - closed
SV valve - closed
15
New cards
In systole (contraction) phase, which valves are open and closed?
AV valve - closed
SV valve - open
SV valve - open
16
New cards
Atrioventricular valves (AV)
prevents backflow into the atria when ventricles contract
17
New cards
2 types of atrioventricular valves
tricuspid valve and bicuspid valve
18
New cards
Tricuspid valve
right side between right atrium and ventricle
19
New cards
Bicuspid valve
left side between left atrium and ventricle
20
New cards
Diastole
filling phase
21
New cards
Systole
ejection phase
22
New cards
Pulmonary circuit
bloods vessels that carry blood to and from the lungs.
receives oxygen poor blood from tissues and pumps this blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen and dispel carbon dioxide.
receives oxygen poor blood from tissues and pumps this blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen and dispel carbon dioxide.
23
New cards
Systemic circuit
blood vessels that transport blood to and from all body tissues.
receives oxygenated blood returning from the lungs and pumps this blood throughout the body
receives oxygenated blood returning from the lungs and pumps this blood throughout the body
24
New cards
S1 "Lub"
first sound
produced by turbulent blood flow through the AV valves
produced by turbulent blood flow through the AV valves
25
New cards
S2 "Dub"
second sound
produced by turbulent blood flow through the semilunar valves
produced by turbulent blood flow through the semilunar valves
26
New cards
5 areas of auscultation
tricuspid, bicuspid (mitral), primary pulmonic, secondary pulmonic, aortic
27
New cards
Systole
phase of ventricular contraction
0\.3 seconds
0\.3 seconds
28
New cards
Diastole
phase of ventricular relaxation
0\.5 seconds
0\.5 seconds
29
New cards
Cardiac output
amount of blood pumped out by each ventricle in one minute.
product of heart rate and stroke volume
product of heart rate and stroke volume
30
New cards
Heart rate
number of contractions per minute
31
New cards
Resting heart rate
60-100 bpm
32
New cards
Stroke volume
volume of blood ejected from the ventricles with each beat (70 mL)
33
New cards
End systolic volume
total volume of blood left in the ventricles at the end of systole (50 mL)
34
New cards
End diastolic volume
total volume of blood in the ventricles at the end of diastole (120 mL)
35
New cards
Systolic pressure
maximal arterial pressure following ejection
36
New cards
Diastolic pressure
minimal arterial pressure following ventricular relaxation
37
New cards
Aortic blood pressure is usually measured directly. True or False?
False. Aortic blood pressure is NOT usually measure directly but estimated by using a sphygmomanometer
38
New cards
Systolic pressure
the pressure at which first Korotkoff sound is heard
39
New cards
Diastolic pressure
the pressure at which the sound disappears
40
New cards
"Normal" blood pressure
less than 120 and less than 80
41
New cards
"Elevated" blood pressure
120-129 and less than 80
42
New cards
"High (hypertension) Stage 1" blood pressure
130-139 or 80-89
43
New cards
"High (hypertension) Stage 2" blood pressure
140 or higher or 90 or higher
44
New cards
"Hypertension Crisis"
higher than 180 and/or higher than 120
45
New cards
Conduction System
SA node > AV node > bundle of HIS > R + L bundle branches > Purkinje fibers
46
New cards
P wave
atrial depolarization/contraction
47
New cards
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization/contraction
48
New cards
T wave
ventricular repolarization
49
New cards
PR or PQ interval
amount of time for the signal to be transduced from atria to ventricle
50
New cards
QT interval
time ventricles depolarize/repolarize
51
New cards
RR interval
* 1 cardiac cycle
* used to calculate heart rate
* used to calculate heart rate
52
New cards
ST segment
plateau phase
leads to heart attack
leads to heart attack
53
New cards
Sinus Bradycardia
rhythm rate less than 60 beats per minutes
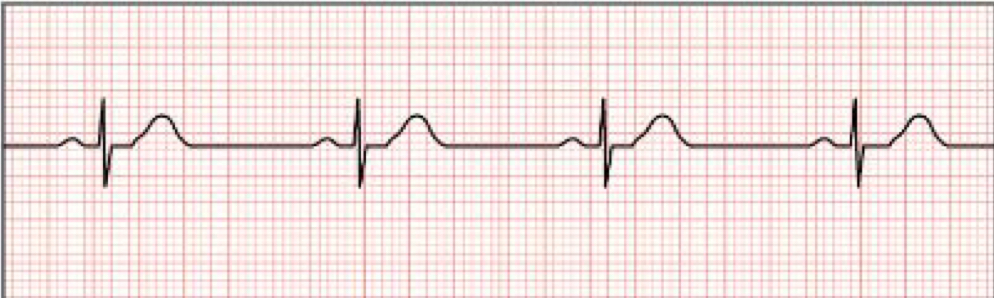
54
New cards
Sinus Tachycardia
rhythm rate greater than 100 beats per minute
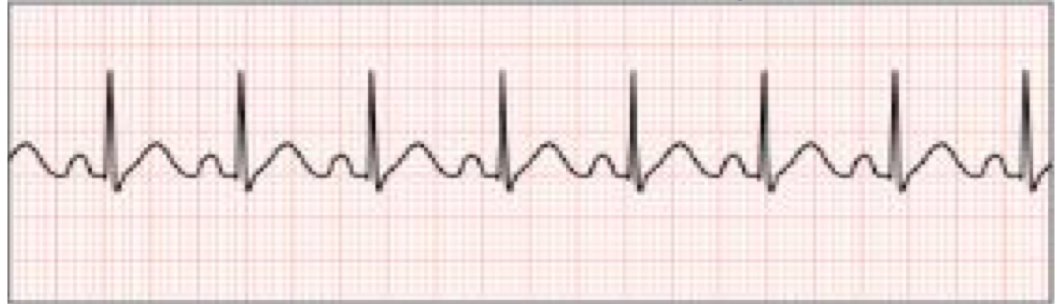
55
New cards
Atrial Flutter (A-flutter)
* atrial depolarization waves or "flutter" waves
* “saw tooth” appearance
* different ratios possible
* “saw tooth” appearance
* different ratios possible
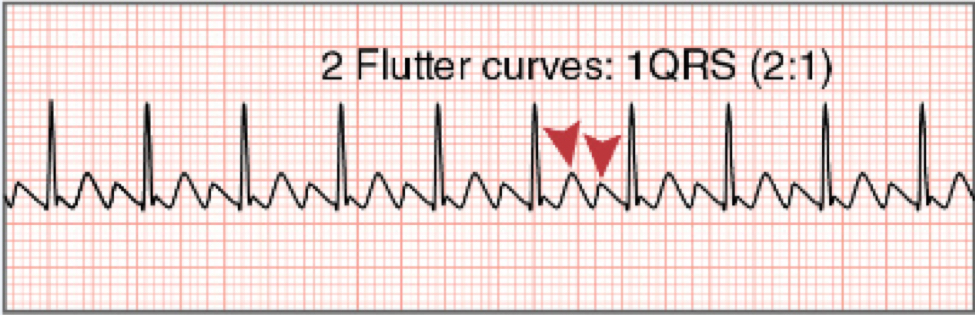
56
New cards
Atrial Fibrillation (A-Fib)
* caused by many ectopic atrial foci firing at rapid rates
* no distinguishable P waves because the atria are sending impulses erratically
* irregular QRS response/distances
* no distinguishable P waves because the atria are sending impulses erratically
* irregular QRS response/distances
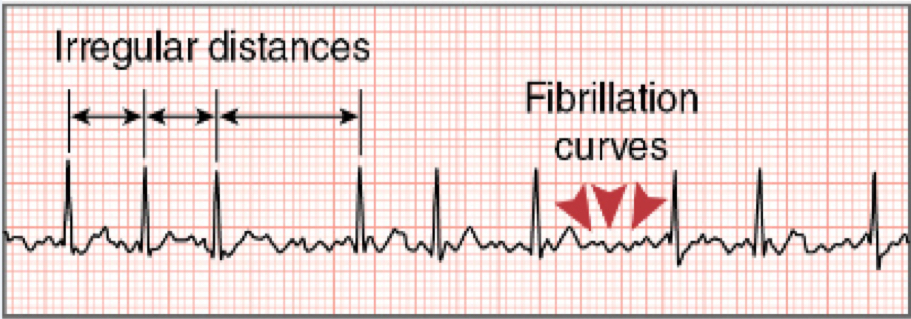
57
New cards
Ventricular Tachycardia (V-tach)
* wide QRS complexes
* P waves blends within the QRS
\
* P waves blends within the QRS
\
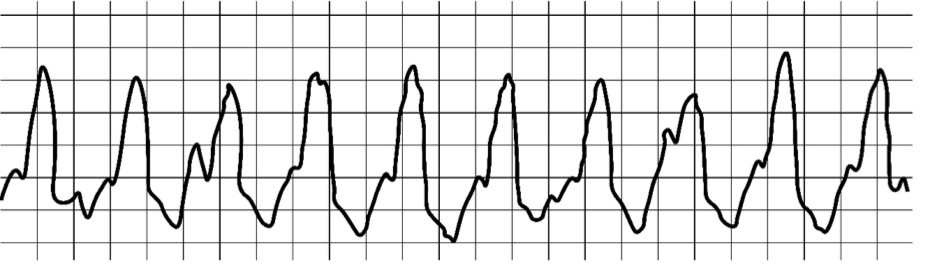
58
New cards
Ventricular Fibrillation (V-fib)
* cardiac arrest. no effective pumping action by the heart and thus there is no circulation
* lack of identifiable waves on EKG: appears erratic, rapid twitching of the ventricles
* requires immediate CPR and defribillation
* lack of identifiable waves on EKG: appears erratic, rapid twitching of the ventricles
* requires immediate CPR and defribillation
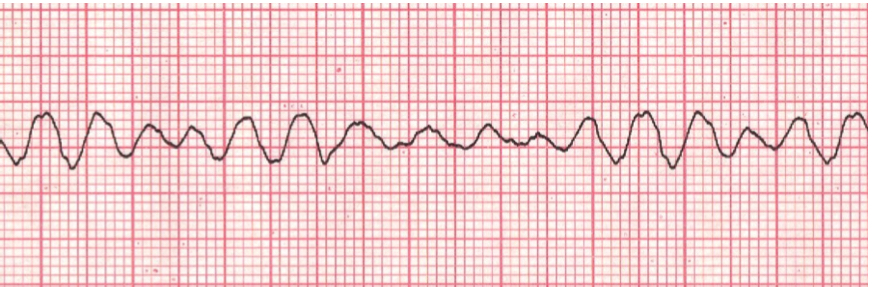
59
New cards
First degree AV block
* consistently prolonged PR interval
* PR interval greater than 0.2 seconds or one large square
* not a “block” but a “delay”
* PR interval greater than 0.2 seconds or one large square
* not a “block” but a “delay”
60
New cards
Second degree AV block
* allows some atrial depolarizations to conduct to the ventricles, while some are blocked, leaving lone P waves without QRS
* repeated P waves prior to the QRS complex or P waves that are missing their QRS complex
* repeated P waves prior to the QRS complex or P waves that are missing their QRS complex
61
New cards
Third degree AV block
* total block of conduction from the atria to the ventricles
* atria and ventricles have lost communication and are now functioning independently of one another
* no relationship between the P and the QRS waveforms
* atria and ventricles have lost communication and are now functioning independently of one another
* no relationship between the P and the QRS waveforms
62
New cards
Hematopoiesis
the process by which blood cells (connective tissue) are formed
63
New cards
Functions of blood
transportation
* respiration, nutrition, excretion, hormonal
regulation
* thermoregulation
Protection
* immune response
* respiration, nutrition, excretion, hormonal
regulation
* thermoregulation
Protection
* immune response
64
New cards
Plasma
* 55%
* water
* proteins
* electrolytes, blood gases, nutrients, enzymes, waste products, etc
* water
* proteins
* electrolytes, blood gases, nutrients, enzymes, waste products, etc
65
New cards
Formed elements
* 45%
* erythrocytes
* buffy coat (
* erythrocytes
* buffy coat (
66
New cards
Blood plasma
consists of 90% water, remaining 10% consists of proteins, electrolytes, gases, hormones, waste, etc
67
New cards
Plasma proteins
make up 7-9% of the plasma
* albumin
* globulin
* fibrinogen
* albumin
* globulin
* fibrinogen
68
New cards
Albumin
* maintains osmotic pressure, helps keep water from diffusing out of the bloodstream into the extracellular matrix of tissues
* maintain blood volume/pressure
* maintain blood volume/pressure
69
New cards
Globulin
* Alpha and Beta globulins transport lipids and fat soluble vitamins
* Gamma globulins are antibodies produced by lymphocytes
* Gamma globulins are antibodies produced by lymphocytes
70
New cards
Fibrinogen
* forms fibrin threads essential in blood hemostasis
* stops bleeding to form blood clot
* thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin, which forms fibrin threads
* active form of zymogen
* stops bleeding to form blood clot
* thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin, which forms fibrin threads
* active form of zymogen
71
New cards
Zymogen
inactive form of an enzyme, don’t need all thetime, but ready to use
72
New cards
Formed elements structure
* lack nuclei and organelles
* biconcave discs
* biconcave discs
73
New cards
How do these structural characteristics contribute to their ability to transport oxygen?
* increased surface area means oxygen exchange is more efficient
* no mitochondria = no aerobic respiration
* no mitochondria = no aerobic respiration
74
New cards
Life span of RBC
100-120 days
75
New cards
“Shear effect”
unaligned forces pushing 1 part of the body in 1 direction and another part of the body in the opposite direction
76
New cards
Hematocrit
proportion of blood that consists of red blood cells
* men: 46% +/- 5%
* women: 44% +/- 5%
* men: 46% +/- 5%
* women: 44% +/- 5%
77
New cards
Erythropoietin (EPO)
maintains the balance between production and destruction of RBC
78
New cards
WBC
* move in an amoeboid fashion via cytoplasmic extensions
* squeeze through the intracellular junctions between capillary walls via diapedesis or extravasation
* classified based on staining properties
* squeeze through the intracellular junctions between capillary walls via diapedesis or extravasation
* classified based on staining properties
79
New cards
Granulocytes
cells that have brightly stained granules
* basophils
* eosinophils
* neutrophils
* basophils
* eosinophils
* neutrophils
80
New cards
Agranulocytes
cell that don’t have brightly stained granules
* lymphocytes
* monocytes
* lymphocytes
* monocytes
81
New cards
neutrophils
* most abundant WBC
* multilobed nucleus
* lightest stained, able to see nucleus
* phagocytic, help respond to bacterial infections
* multilobed nucleus
* lightest stained, able to see nucleus
* phagocytic, help respond to bacterial infections
82
New cards
eosinophils
* more red than others
* bilobed nucleus
* phagocytic
* large quantities responding to parasitic invaders
* bilobed nucleus
* phagocytic
* large quantities responding to parasitic invaders
83
New cards
basophils
* darkest stain, sometimes cover nucleus
* release histamine
* release histamine
84
New cards
monocytes
* massive, twice the size of RBC
* lot of cytoplasm
* big nucleus (curved)
* called macrophages when migrate out of cell and enter tissues, engulf lots of pathogens
* lot of cytoplasm
* big nucleus (curved)
* called macrophages when migrate out of cell and enter tissues, engulf lots of pathogens
85
New cards
lymphocytes
* smalles
* round, dark-staining nucleus
* little room for cytoplasm
* T cells: attack virus-infected cells and tumor cells
* B cells: produce/secrete antibodies
* round, dark-staining nucleus
* little room for cytoplasm
* T cells: attack virus-infected cells and tumor cells
* B cells: produce/secrete antibodies
86
New cards
Antigens
found on the surface of cells to help the immune system recognize self cells
87
New cards
Antibodies
secreted by lymphocyte in response to foreign cells or antigens
88
New cards
Which blood type is the universal donor and why?
O- has no antigens
89
New cards
Which blood type is the universal recipient and why?
AB+ has no antibodies, so won’t attack
90
New cards
\+ blood type is determined by:
presence of Rh factor
91
New cards
\- blood type is determined by:
lack of Rh factor
92
New cards
Rh negative blood is given to:
Rh negative patients
93
New cards
Rh positive blood or Rh negative blood may be given to:
Rh positive patients
94
New cards
Anemia
* inability of erythrocytes to deliver the needed amount of oxygen to the cells of the body
* insufficient number of erythrocytes
* inability of the erythrocytes to bind the normal amount of oxygen
* insufficient number of erythrocytes
* inability of the erythrocytes to bind the normal amount of oxygen
95
New cards
pernicious anemia
vitamin B12 deficiency
96
New cards
iron-deficiency anemia
lacking iron
97
New cards
aplastic anemia
destruction of bone marrow
98
New cards
sickle cells anemia
RBC has crescent shape and affects hemoglobin
99
New cards
hemorrhagic anemia
acute or chronic blood loss
100
New cards
polycythemia
* “many blood cells”
* abnormal excess of erythrocytes in the blood
* abnormal excess of erythrocytes in the blood