Special Pops Lectures 15 and 16: Geriatrics | Quizlet
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What is the mean prevalence of ADRs in the elderly?
11%
Polypharmacy
regular use of 5 or more medications (Rx, OTC, or herbal) on a daily basis
Why is polypharmacy an issue in the elderly?
higher prevalence of chronic diseases and comorbidities that place them at higher risk of ADRs
What medications pose higher risk of ADRs in the elderly?
Antithrombotics/ Anticoagulants
Antidiabetic medications (insulin, sulfonylureas)
Opioids
How does absorption and first-pass metabolism change in the elderly?
Unchanged absorption
Reduced FPM
How does volume of distribution metabolism change in the elderly?
increased body fat and decreased body water
How does protein binding metabolism change in the elderly?
lower serum albumin - increased free concentraions of protein bound drugs
How does metabolism metabolism change in the elderly?
reduced oxidative metabolism and unchanged conjugative metabolism
How does excretion metabolism change in the elderly?
reduced with decreased GFR and tubular excretion
Most medications are absorbed by passive diffusion ________________ significant age-related changes.
without
Lipid soluble medications have an __________ half-life in older adults.
increased
Highly-albumin-bound drugs have __________ fraction of free drug.
increased
What benzodiazepines can be used in elderly patients? Why?
Lorazepam
Oxazepam
Temazepam
dependent on Phase 2 metabolism that is not affected by age changes
Older adults have decreased sensitivity to what medications?
Beta-blockers
Beta-agonists
___ of ADRs in older adults are due to inappropriate prescribing.
50%
What are the principles of appropriate prescribing in the elderly?
Start low and go slow
Start one at a time
Use old meds rather than new
Quality of life vs mortality benefit
Medications monitoring
What is the prescribing cascade?
starts when an ADR is misinterpreted as a new medical condition where a new medication is prescribed and repeats
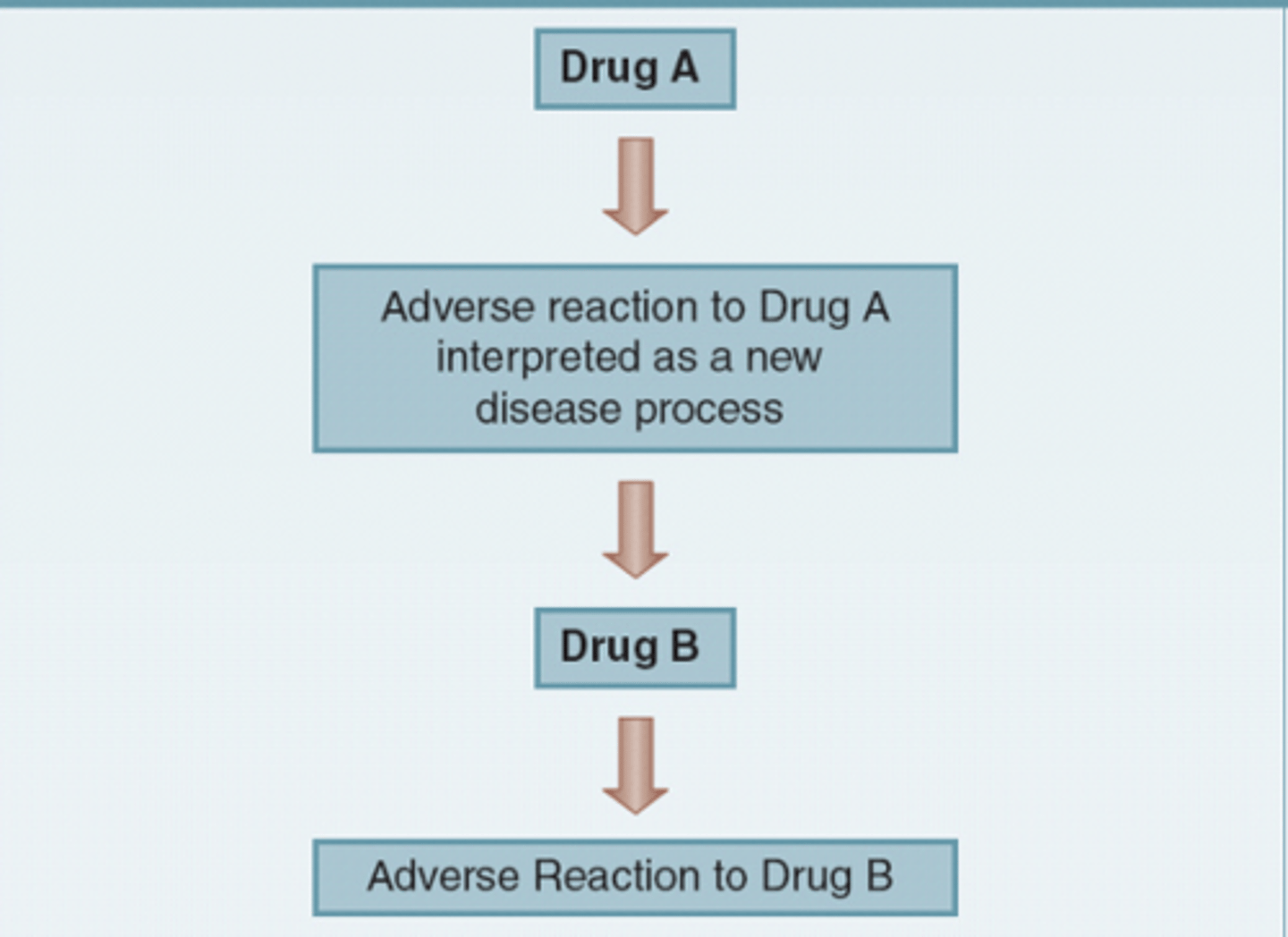
What are some strategies to minimize the prescribing cascade?
Prevention
Detection
Reverse
Deprescribing
process of identifying and D/C-ing drugs in instances which existing or potential harms outweigh existing or potential benefits within the context of a patient's care goals
What are the goals of deprescribing?
improve health outcomes
Reduce medication burden
Reduce falls
Decrease hospitalizations and death
Decrease costs
Improve QoL
What are the steps of deprescribing?
1. Review all of the patients medications
2. Talk to the patient about the process
3. Deprescribe medications (one at a time)
4. Create a follow-up plan
Who is the target for deprescribing?
Polypharmacy
Multimorbidity
Renal impairment
Dementia
Nonadherence
Multiple prescribers
What medications should we consider deprescribing in the eldery?
Anticholinergics
BZDs
Sulfonylreas (long acting)
Insulins
PPIs
NSAIDs
Beer's Criteria
used to assist in preventing ADEs in older adults in the inpatient/outpatient setting
Starting and stopping medications in the elderly should be done how?
one at a time
What does START stand for?
Screening Tool to Alert Doctors to Right Treatment
What does STOPP stand for?
Screening Tool of Older Person's potentially inappropriate Prescriptions
What are the barriers to deprescribing?
Patient/family reluctance
Limited time
Lack of evidence
Multiple providers
Clinical inertia
What are the medication related risk factors for falls?
Polypharmacy
Low BP
UTIs
Low sodium and glucose levels
What medication should be used for glucose control in older adults?
Metformin