AP Chem T9
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
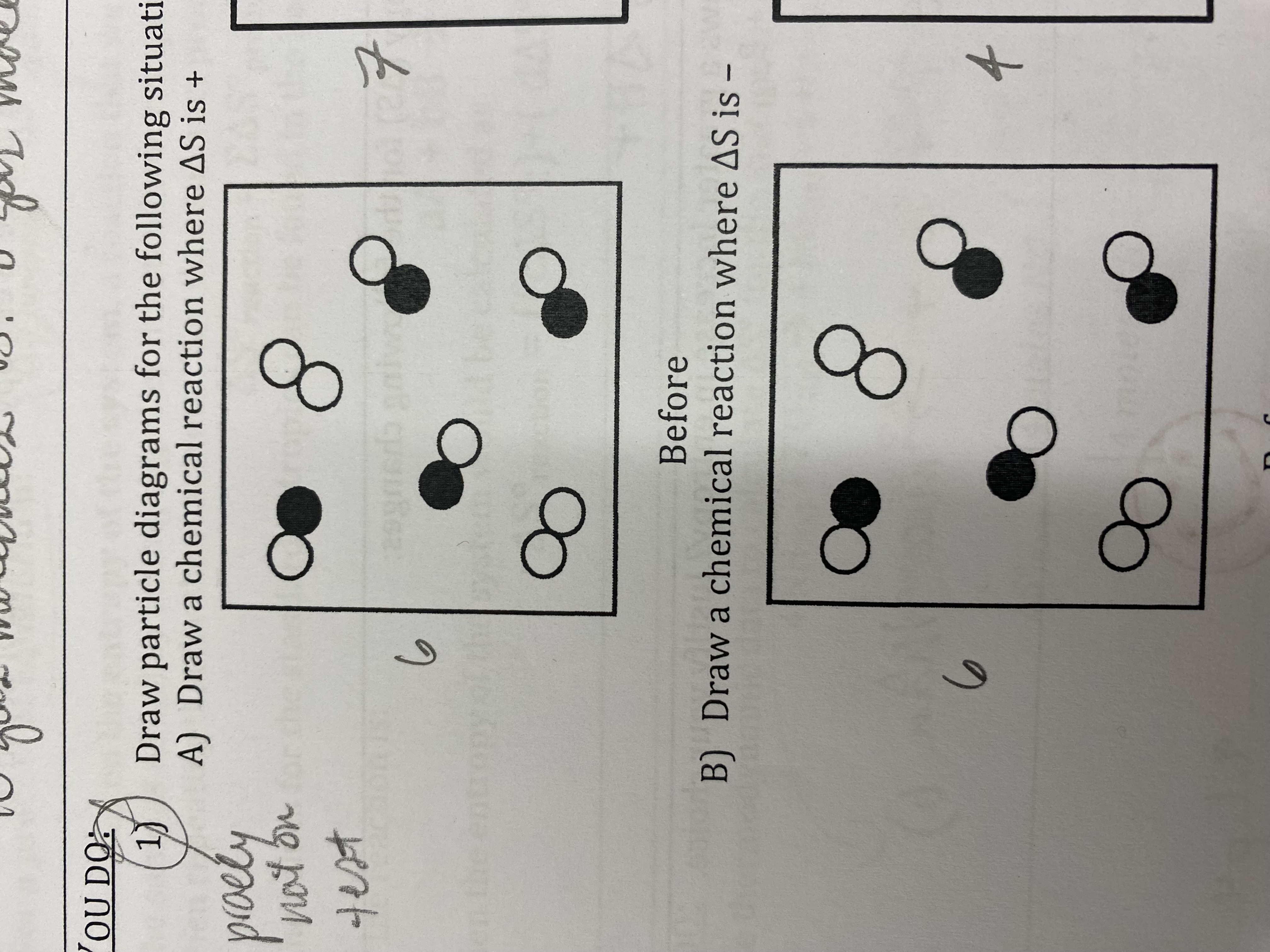
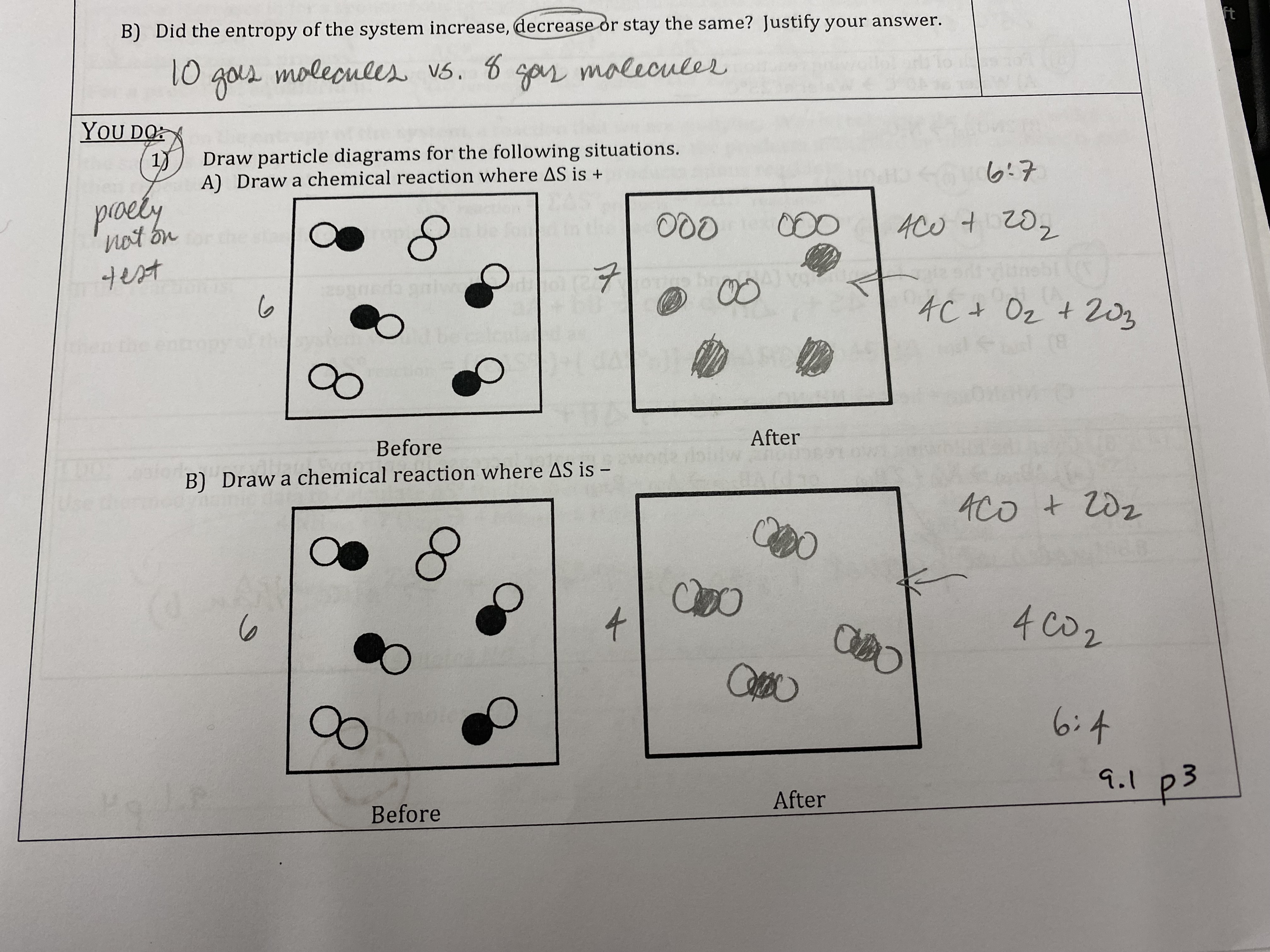
Would you expect the entropy of C2H7OH(l) to be greater than, less than, or equal to the entropy of C2H7OH(g)? Explain your reasoning.
It would be less than because gases have more distribution into microstates.



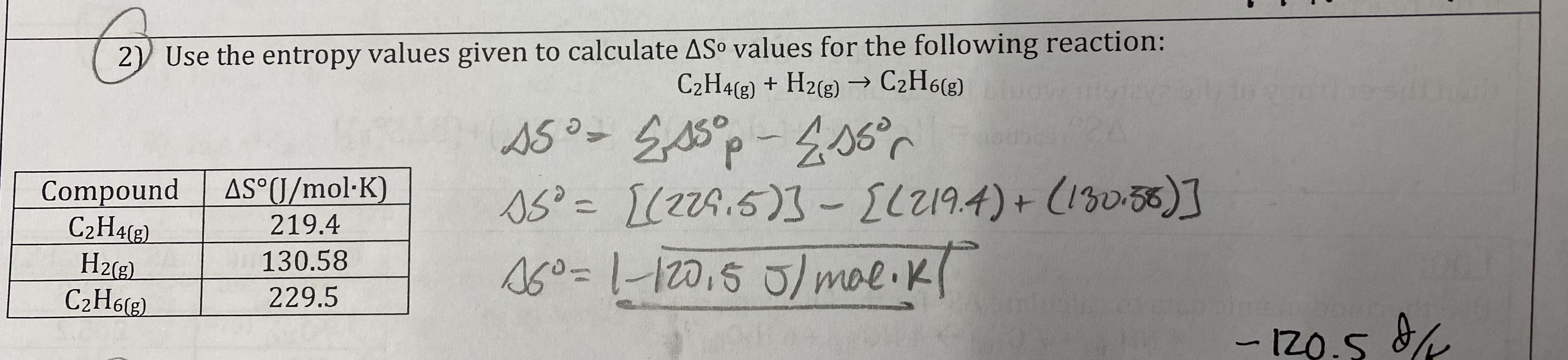
Given the following reaction occurs at 298 K:
A(s) + B(aq) —> C(s) + D(aq)
ΔH = -24.1 kJ/mol and ΔS = -4.2 J/K*mol
Is this reaction thermodynamically favorable? If so, is the reaction driven by enthalpy, entropy, or both, explain your choice.
ΔG = (-24.1) - (298)(-0.0042) = -22.8 kJ/mol
Yes, its driven by enthalpy because it is exothermic.
When calcium chloride is added to water at 298 K, it dissolves and the temperature of the wager increases.
A) Write the net ionic equation that describes this change.
B) Predict the sign for ΔH, justify your selection.
C) Predict the sign for ΔS, justify your selection.
D) Predict the sign for ΔG, justify your selection.
A) CaCl2 —> Ca^2+ + 2Cl-
B) Temperature increase = ΔH -
C) Temperature increase = ΔS +
D) ΔH - and ΔS + = ΔG - (spontaneous)
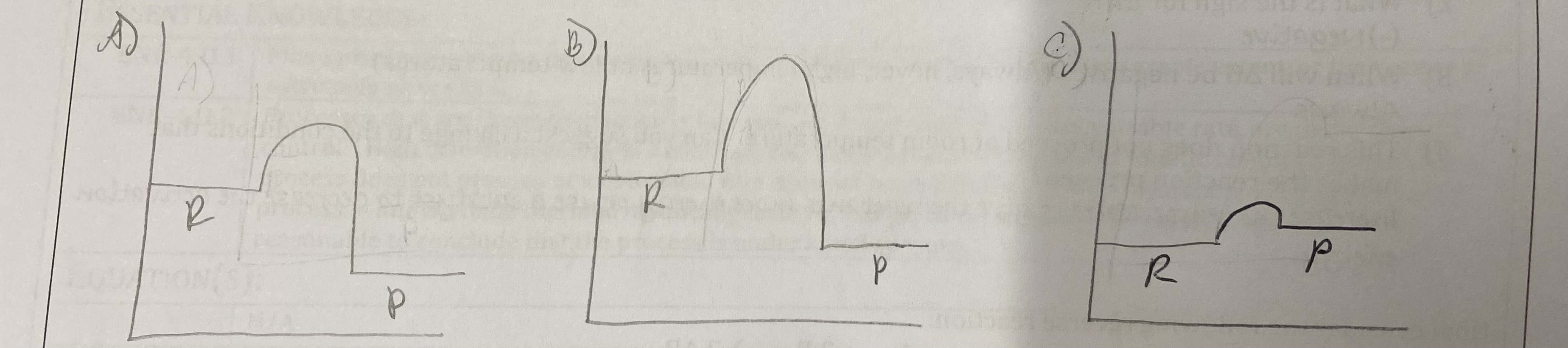
Sketch an energy diagram that would show the following:
A) An exothermic reaction that is thermodynamically favorable and would occur quickly.
B) An exothermic reaction that is thermodynamically favorable and would not occur at a measureable rate.
C) An endothermic reaction that is thermodynamically favorable and would occur quickly.
Explain why the addition of a catalyst can make a reaction occur that doesn't normally occur at room temperature even when ΔG < 0.
Catalysts provide an alternate reaction pathway with lower activation energy.




For each of the following choose the variable that will be more favorable in solution formation.
A) Weak or Strong Solvent intermolecular forces
B) Weak or Strong Solute intermolecular forces
C) Weak or Strong Solvent-Solute intermolecular forces
D) Increase or Decrease in Entropy
E) Increase or Decrease in Enthalpy
A) Weak
B) Weak
C) Strong
D) Increase
E) Decrease
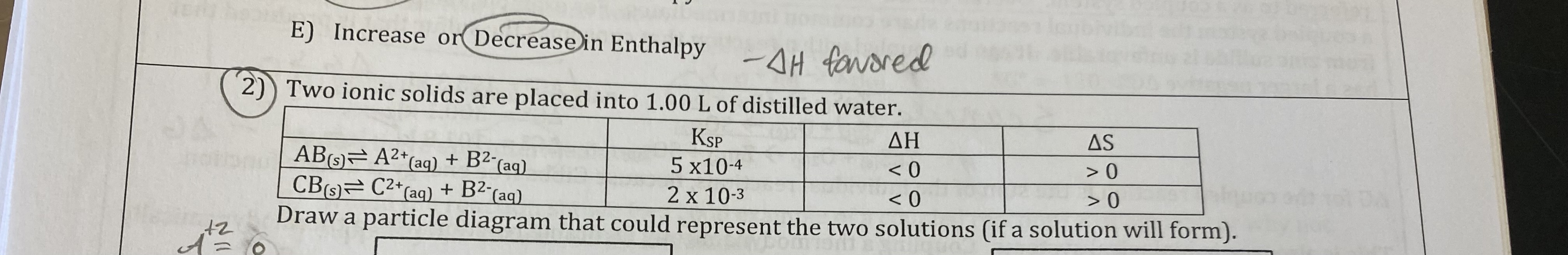
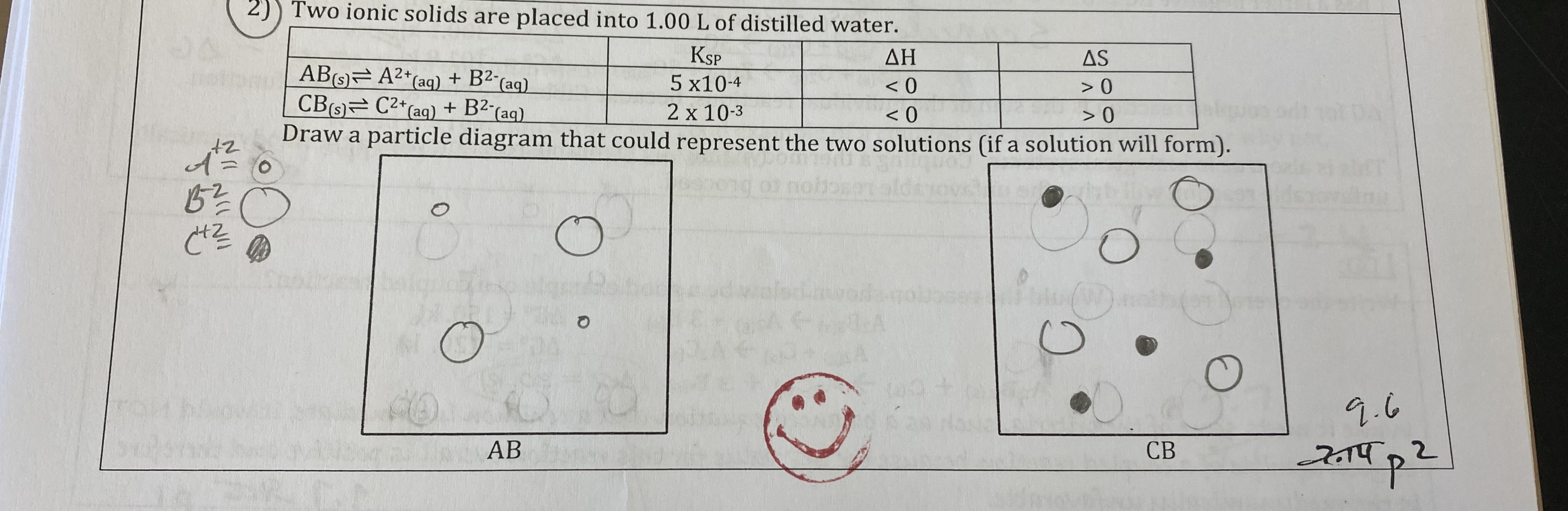



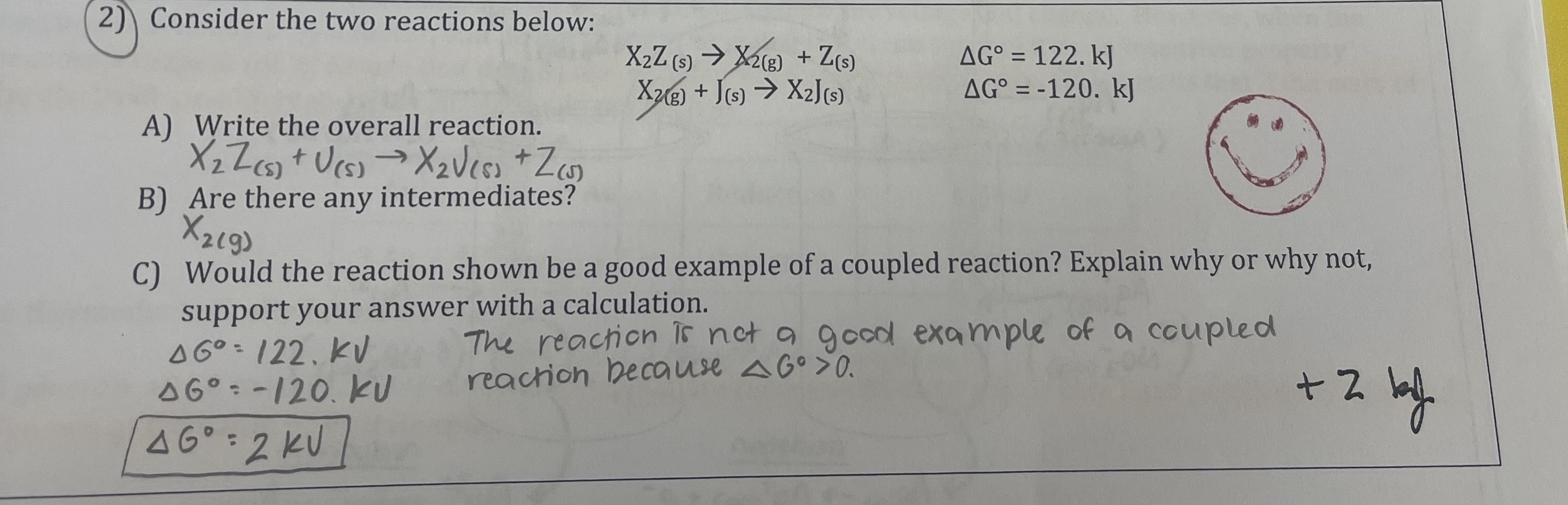

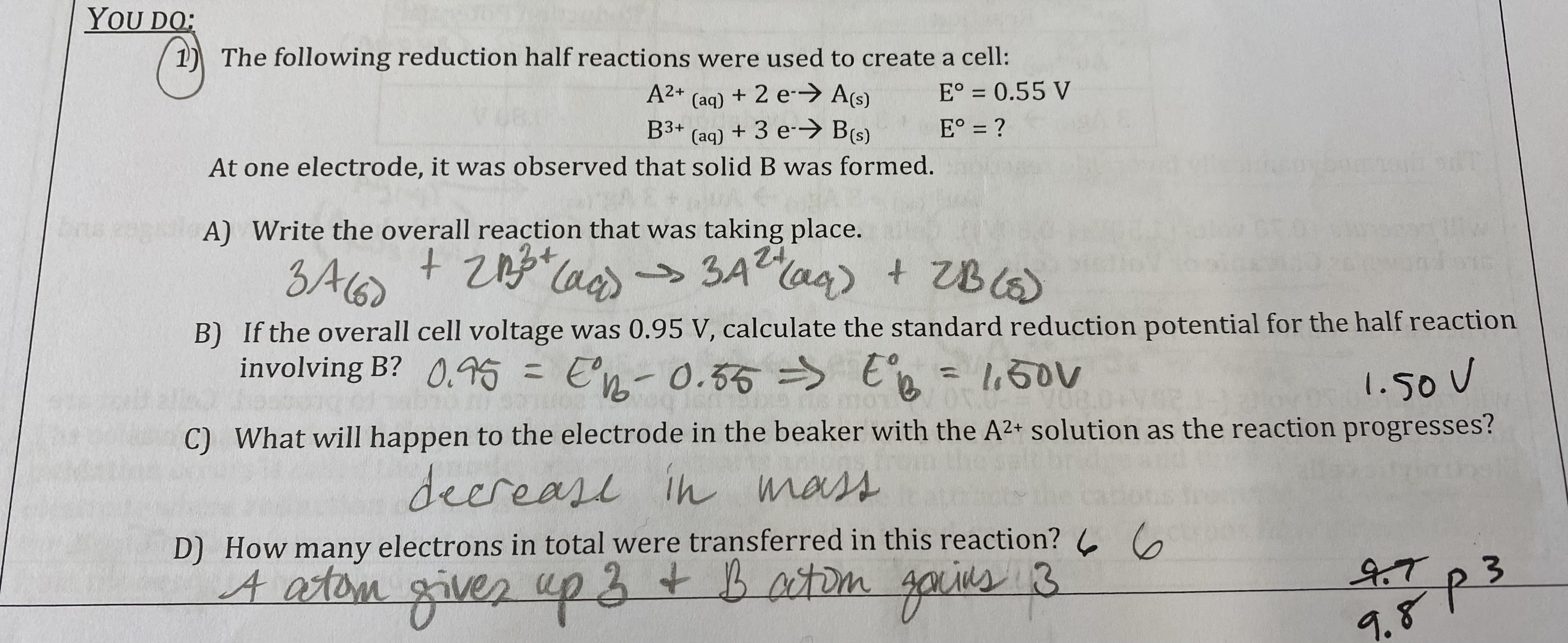

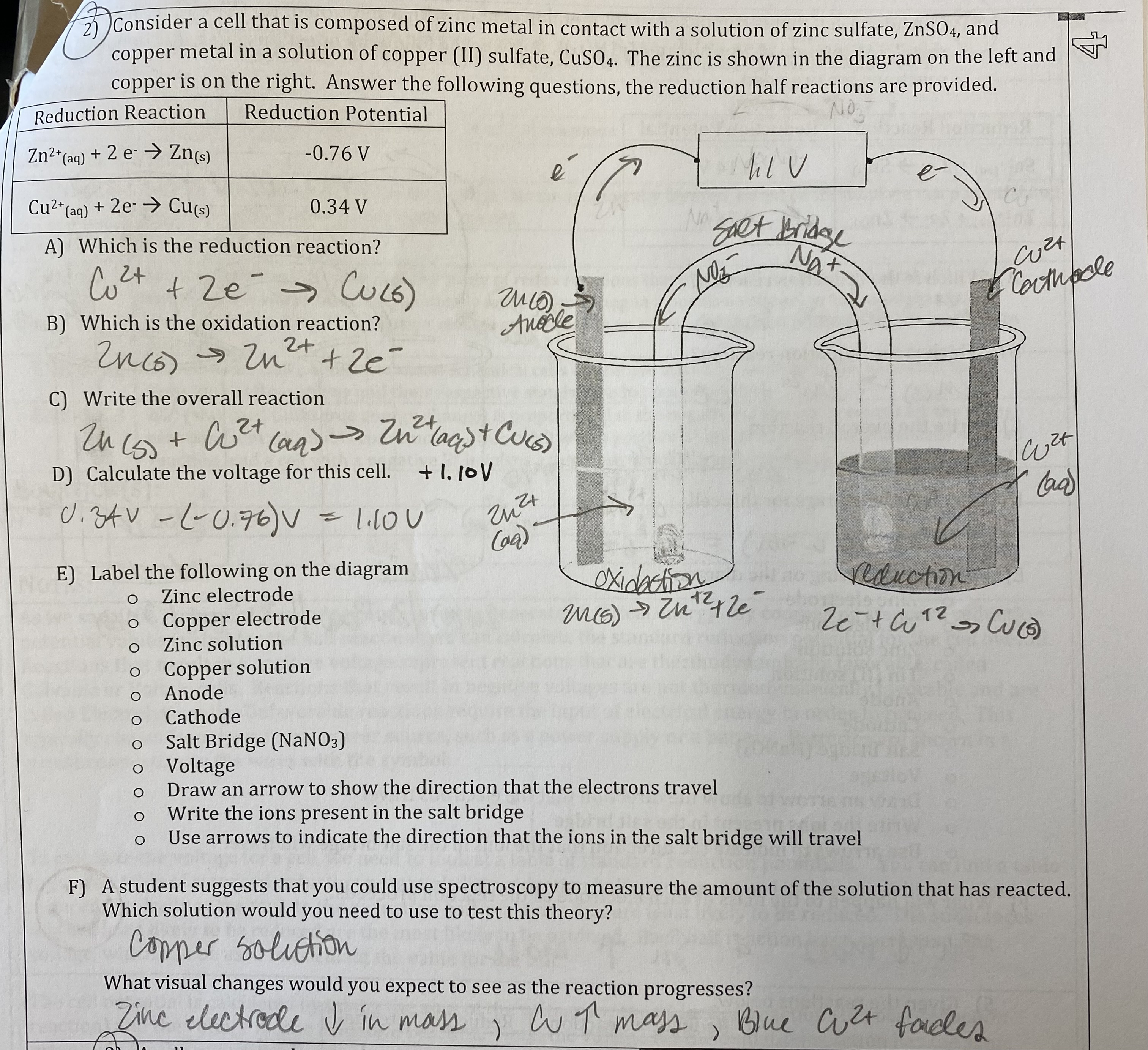



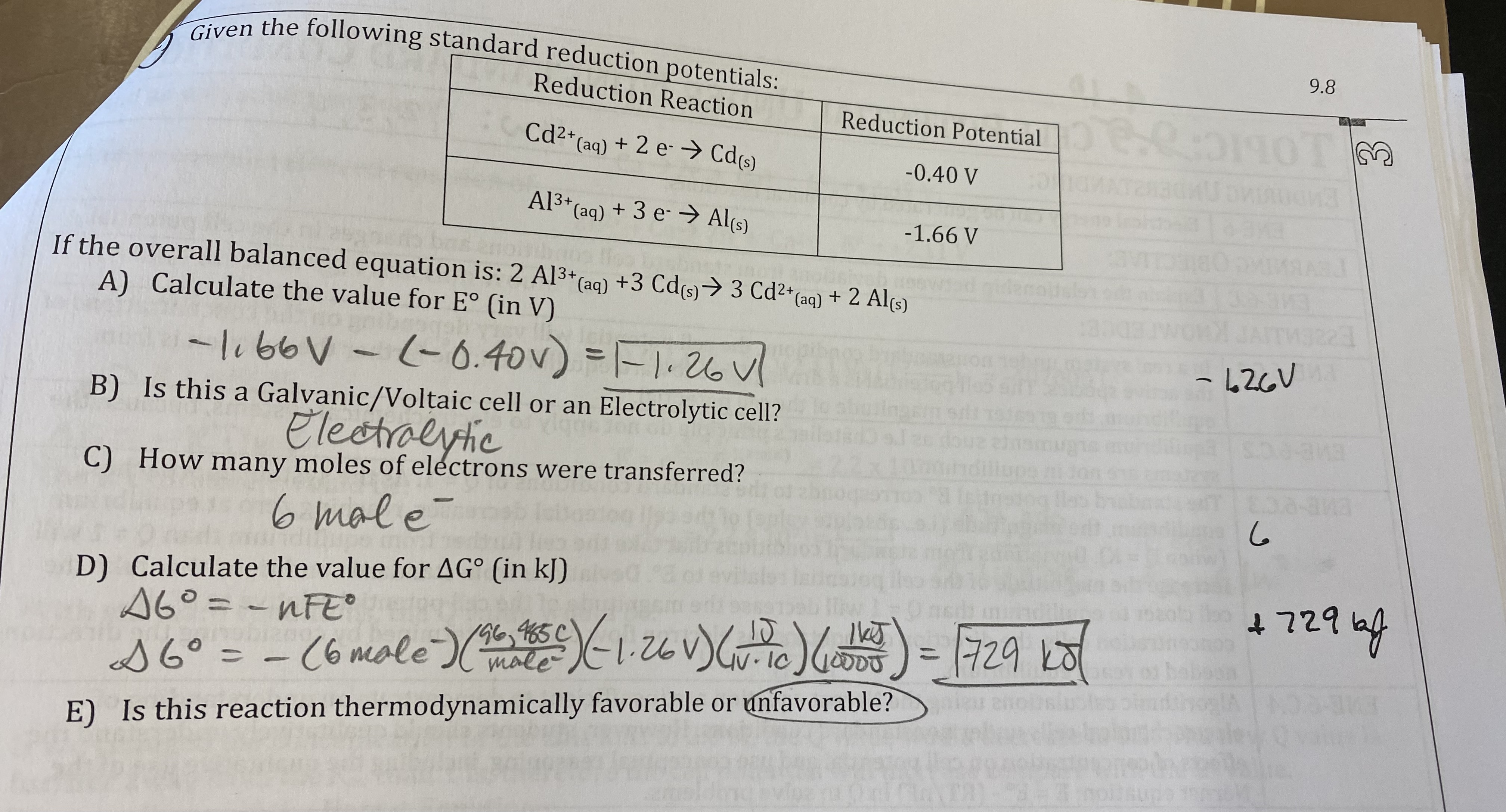
What will happen to the voltage of the cell in the “we do” question if the cell is allowed to run? Justify your selection.
Stays the same
Decreases
Increases
It decreases because the concentration of the reactant decreases and the concentration of the product increases, so cell potential decreases.
A student tried to make a thermodynamically spontaneous cell at 298 K composed of 100. ml of 1.00 M Mg^2+ (aq) in one beaker with a magnesium electrode and 100. mL of 1.00 M Al^3+(aq) in another beaker with an aluminum electrode. The beakers are connected with a porous disc and the electrodes are connected with a wire connected to a voltmeter:
Al^3+(aq) + Mg(s) —> Mg^2+(aq) + Al(s)
E = +0.71 V
The student ran out of magnesium nitrate and could only make 100. mL of a Mg^2+ solution with a concentration of 0.75 M. What effect, if any, will this have on their cell potential? Explain.
It will increase due to decrease in the concentration of Mg^2+. The reaction proceeds right to reestablish equilibrium.
Stoichiometry: 2 + 3 —> 3 + 2
How long in minutes would it take to completely consume an electrode composed of 2.50 grams of magnesium, Mg, if the current for the cell was 0.750 amps?
(2.50 g/1)(1 mol/24.31 g)(2 mol e-/1 mol)(96,485 C/1 mol e-)(1 sec/0.750 C)(1 min/60 sec) = 441 min