Chem fundamentals (unit 1)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
1
New cards
Matter
Physical material; anything with mass that takes up space
2
New cards
Pure substances
Matter that has a definite composition, one that does not change, and has distinct properties. They can only be separated by chemical reactions.
3
New cards
Elements
Pure substances that cannot be decomposed into simpler substances.
4
New cards
Atoms
The smallest building block of matter. Each element is composed of 1 type of atom.
Ex: C
Ex: C
5
New cards
Molecules
2+ atoms, can be same or different.
ex: O2, H2O
ex: O2, H2O
6
New cards
Compounds
Pure substances composed of 2+ different elements. They can only be separated chemically.
Ex: H2O
Ex: H2O
7
New cards
Physical properties
Can be observed without changing the identity or composition of matter. They are the result of IMFAs between structures.
ex: melting point and color
ex: melting point and color
8
New cards
Intensive properties
Properties that are independent of quantity.
ex: boiling point, odor
ex: boiling point, odor
9
New cards
Extensive properties
Properties that are dependent on quantity.
Ex: mass, volume
Ex: mass, volume
10
New cards
Chemical properties
Observed by destroying substance, they result from chemical reactions.
11
New cards
Mixtures
A combo of 2+ pure substances. Each substance maintains its own properties. Mixtures can be separated into its pure substances.
12
New cards
Homogeneous mixtures
Mixtures that are uniform throughout. The components are evenly distributed. They look pure but they aren’t since they aren’t chemically combined
13
New cards
Solution
Homogeneous mixture with small particles that don't scatter light.
ex: brass, copper sulfate (aq)
ex: brass, copper sulfate (aq)
14
New cards
Colloid
Homogeneous mixture with large particles that scatter light.
ex: milk
ex: milk
15
New cards
Heterogeneous mixtures (suspensions)
Mixtures that aren't evenly distributed, you can see layers/each part
ex: wood, granite, rice pudding
ex: wood, granite, rice pudding
16
New cards
Physical change
Changes physical appearance, not composition.
ex: ice to water is a state change
ex: ice to water is a state change
17
New cards
Chemical change
Substance changes into a different substance.
ex: heat of combustion, flammability
ex: heat of combustion, flammability
18
New cards
Distillation
Process that depends on the boiling points to separate mixtures.
ex: boiling NaCl and water. Water evaporates, leaving NaCl behind
ex: boiling NaCl and water. Water evaporates, leaving NaCl behind
19
New cards
Chromatography
Process that depends on the differing size and polarity of substances to separate mixtures.
20
New cards
Filtration
Process of pouring a mix of solids and liquid through filter paper to separate them. The liquid passes through, solid stays behind
ex: coffee
ex: coffee
21
New cards
Dalton’s atomic theory:
1. Each element is composed of extremely small particles (atoms)
2. All atoms of a given element are identical to each other
1. All O2 atoms are the same, all N2 atoms are the same
3. Atoms of 1 element can’t be changed into atoms of different elements by chemical reactions.
1. O2 can’t turn into N2
4. Compounds are formed when atoms of more than 1 element chemically combine.
1. O + N (elements)→NO (compound)
22
New cards
Law of conservation of mass:
matter isn’t created or destroyed, just rearranged
23
New cards
Law of constant composition/definite proportion:
given compounds always have same elements in the same proportion. The ratios are fixed
ex: water is always H2O, a 2:1 ratio of H to O
ex: water is always H2O, a 2:1 ratio of H to O
24
New cards
Law of multiple proportions:
compounds with different ratios of the same atoms are different
ex: H2O2 is different from H2O
ex: H2O2 is different from H2O
25
New cards
Democritus:
made first atomic model in 400 BC
proposed that all matter is made up of atoms (small, solid, indivisible particles)
Model: ball
proposed that all matter is made up of atoms (small, solid, indivisible particles)
Model: ball

26
New cards
Dalton:
determined that each element is made up of atoms, created atomic theory
model: ball
model: ball
27
New cards
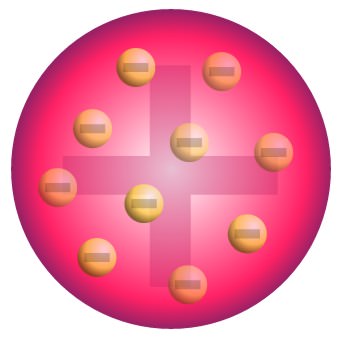
Thomson:
through cathode ray tube experiments, determined that there are negatively charged electrons
because electrons contribute a small fractions of atom’s mass, they are small
model: plum pudding
because electrons contribute a small fractions of atom’s mass, they are small
model: plum pudding
28
New cards
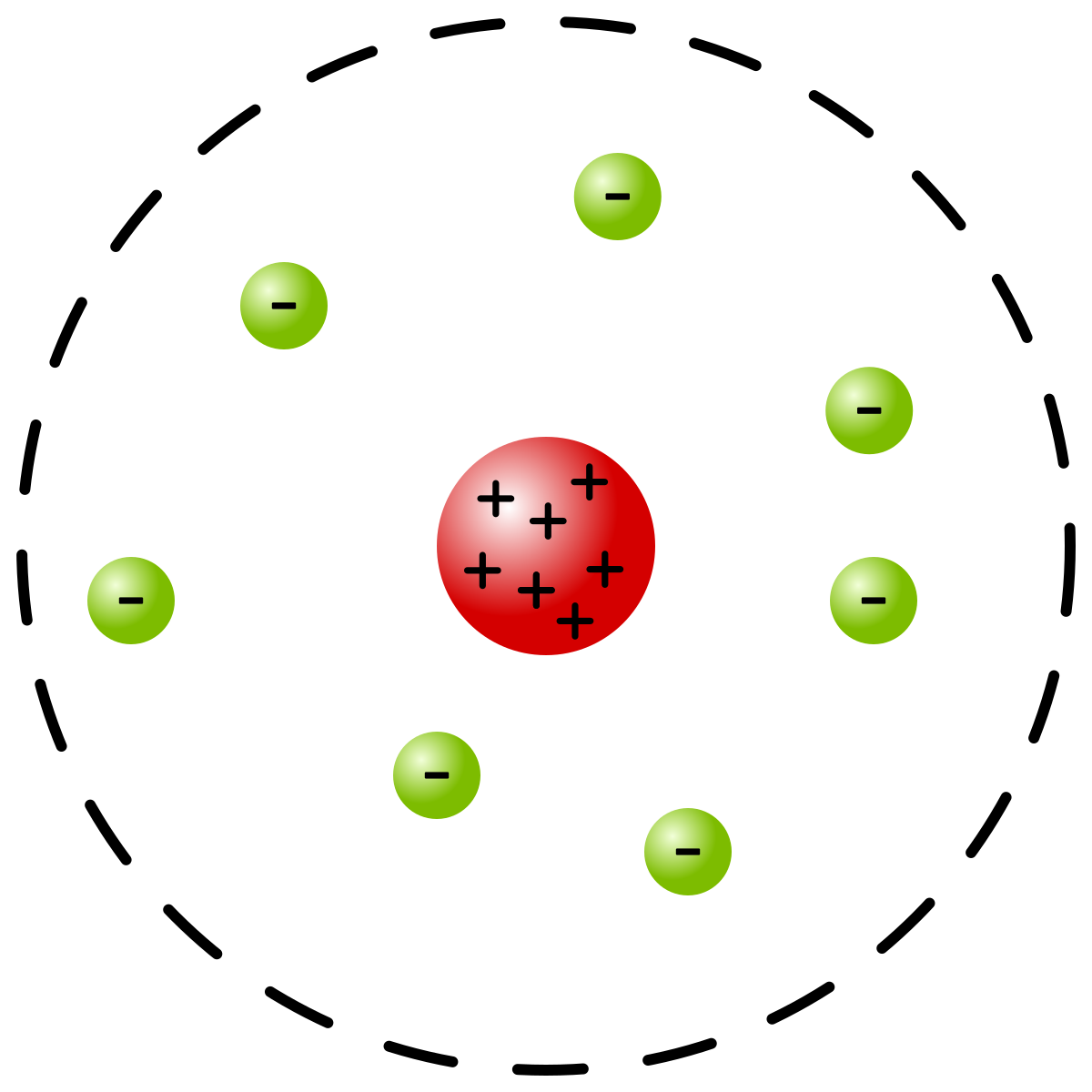
Rutherford:
discovered protons and nucleus
Most of the atom’s mass comes from dense + nucleus and most of the volume is empty space (electron cloud)
model: nuclear
Most of the atom’s mass comes from dense + nucleus and most of the volume is empty space (electron cloud)
model: nuclear
29
New cards
Chadwick:
through nuclear bombardment, he found the neutron
30
New cards
Beta radiation
high speed electrons with charge -1
31
New cards
Alpha radiation
charge: +2
32
New cards
Gamma radiation
high energy, no mass, no charge
33
New cards
Nucleus:
contains protons and neutrons with an overall + charge.
very small and dense (1x10^-15 m)
very small and dense (1x10^-15 m)
34
New cards
Electron cloud:
contains negatively charged electrons
almost no mass but most of atom volume (1-5 x10^-10 m)
almost no mass but most of atom volume (1-5 x10^-10 m)
35
New cards
Angstrom:
1x10^-10m=100pm
36
New cards
Atomic mass unit (amu)= __g
1\.66054x10^-24 g
37
New cards
Proton:
1\.0073amu (1amu)
\+1
\+1
38
New cards
Electron:
5\.486x10^-4amu (0amu)
\-1,
\-1,
39
New cards
Neutron:
1\.0087amu (1amu)
0
0
40
New cards
Isotopic Notation
A= mass #
Z=atomic #
q=charge
Z=atomic #
q=charge
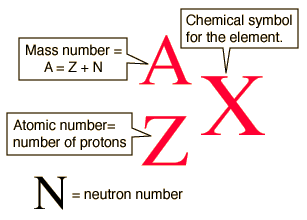
41
New cards
mass number
protons+neutrons
42
New cards
Isotopes:
same # protons but different # neutrons, differing mass numbers
43
New cards
atomic number
just protons, used to identify element
44
New cards
Charge in isotope notation
\#protons vs electrons
45
New cards
1amu=____g
1\.66054x10^-24 g
46
New cards
1g=____amu
6\.02x10^23 amu
47
New cards
How to calculate atomic mass
the number from the periodic table is dependent on isotopic abundance
Σ (isotope mass)(isotope abundance)
Ex: 9/16 atoms have a mass of 70, 6/16 have a mass of 72, 1/16 have mass of 74
AM=70(9/16)+72(6/16)+74(1/16)=71amu
Σ (isotope mass)(isotope abundance)
Ex: 9/16 atoms have a mass of 70, 6/16 have a mass of 72, 1/16 have mass of 74
AM=70(9/16)+72(6/16)+74(1/16)=71amu
48
New cards
Spectrometer
1. Get atoms into gas phase and convert them into ions (cations)
2. When gas phase cations made, they’re accelerated towards negative grid
3. Only a narrow beam of ions can pass
4. Beam passes through magnet poles that deflect ions
5. Ions separated into their masses (isotopes)
49
New cards
Mass spectroscopy:
uses spectrometer to determine the mass of an element/molecule
Provides mass of ions and relative abundance, allows us to calculate atomic mass
Provides mass of ions and relative abundance, allows us to calculate atomic mass
50
New cards
Periods:
the rows
51
New cards
Groups:
the columns
52
New cards
Molecular vs empirical formula
molecule is the actual # of atoms in a molecule while empirical is the smallest ratio
Molecular: H2O2
Empirical: HO
Molecular: H2O2
Empirical: HO
53
New cards
Formula weight
the sum of each atomic weight in a substance
FW of H2O: 2(1.008)+1(16)=18.016 g
FW of H2O: 2(1.008)+1(16)=18.016 g
54
New cards
% composition
the mass contributed by each element
% comp= #atoms of element (atomic weight) /formula weight x100
% comp= #atoms of element (atomic weight) /formula weight x100
55
New cards
How to get the empirical formula from % of each element
Base the calculation on 100.g of compound. It’s easier
Determine # moles of each element for 100.g of compound
Divide each mole value by the smallest mole value to get the ratio
Multiply by the integer to get a whole number formula
Determine # moles of each element for 100.g of compound
Divide each mole value by the smallest mole value to get the ratio
Multiply by the integer to get a whole number formula
56
New cards
How to get molecular formula from empirical
whole # multiple=molecular weight/empirical formula weight
Then multiply empirical formula by that multiple
Then multiply empirical formula by that multiple
57
New cards
Combustion analysis to get empirical formula
1. Use mass of CO2 to find the amount of C in organic substance
2. Use mass of H2O to find amount of H in organic substance
3. If there’s oxygen in the organic, subtract Cmass and Hmass to get Omass by itself
4. Once you have masses of each element, proceed like before, get mole substance ratios
58
New cards
Coefficients:
the relative # of molecules in a reaction
* Ex: 2H2 +O2 →2H2O shows 2 molecules of H2 reacting with 1 molecule of O2 to form 2 molecules H2O
* Ex: 2H2 +O2 →2H2O shows 2 molecules of H2 reacting with 1 molecule of O2 to form 2 molecules H2O
59
New cards
Limiting Reactant
Reactant that limits how much product is formed. Once LR runs out, the reaction stops
60
New cards
Theoretical yield:
quantity of product calculated to form (100% completion, no error)
61
New cards
Experimental yield
Quantity of product that actually formed in lab
62
New cards
Percent yield
How much product you got compared to the true amount
experimental/theoretical x100 = ___%
experimental/theoretical x100 = ___%
63
New cards
Percent error
How far off you were from the theoretical value
exp-theo/theo x 100 = ± ___%
exp-theo/theo x 100 = ± ___%
64
New cards
Molarity
Concentration of moles/L
65
New cards
Dilution
Adding water to make a concentration lower
C₁V₁=C₂V₂
C₁V₁=C₂V₂
66
New cards
Titration
combining solution with unknown concentration w reagent of known concentration
67
New cards
Equivalence point:
where stoich equivalent quantities are brought together
68
New cards
Indicator
dye that changes color as passing equivalence point